5. Community Ecology (Biodiversity - measuring, causes, consequences)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
3 levels of biodiversity
genetic diversity
species diversity
ecosystem/landscape diversity
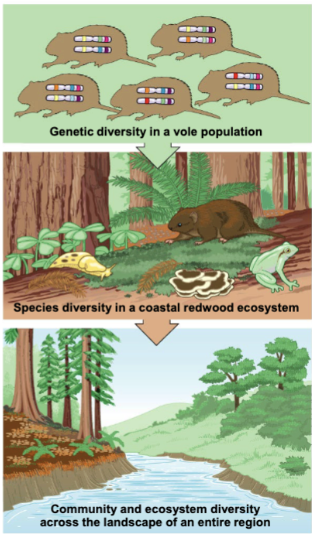
species diversity of a community
is the variety of organisms that make up the community
two components of species diversity
species richness
relative abundance
species richness
the total number of different species in the community
relative abundance
is the proportion each species represents of the total individuals in the community
S is:
the number of species
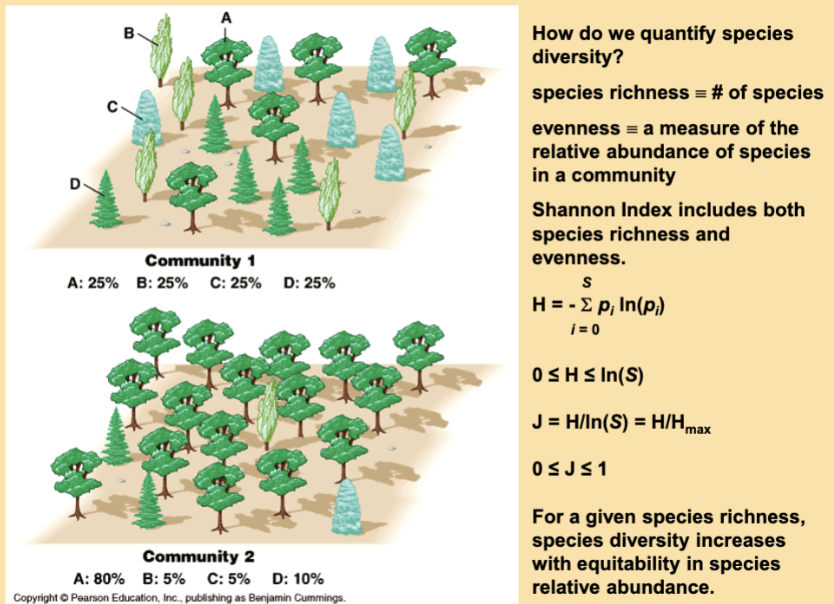
(pic)
solve
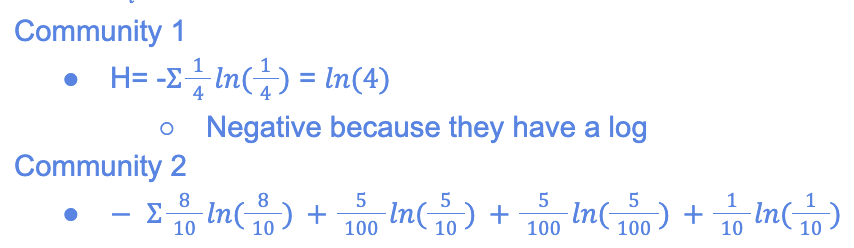
whats is disturbance?
is an event that changes a community, removes organisms from it, and alters resource availability
ex. fire
intermediate disturbance hypothesis suggest that":
moderate levels of disturbance can foster higher diversity than low levels of disturbance

human disturbance
most widespread agents of disturbance
usually reduces species diversity
also prevent some naturally occurring disturbances, which can be important to community structure
ecological succession is the:
sequence of community and ecosystem changes after a disturbance
primary succession
occurs when no soil exists when succession begins
secondary succession
begins in an area soil remains after the disturbance
xerarch succession
low water
hydrarch succession
saturates soil
two factors correlated with a communities species diversity
geographic locations
size
two key factors in equatorial-polar gradients of species richness are probably
evolutionary history
climate
rate of evapotranspiration
is evaporation of water from soi plus transpiration of water from plants
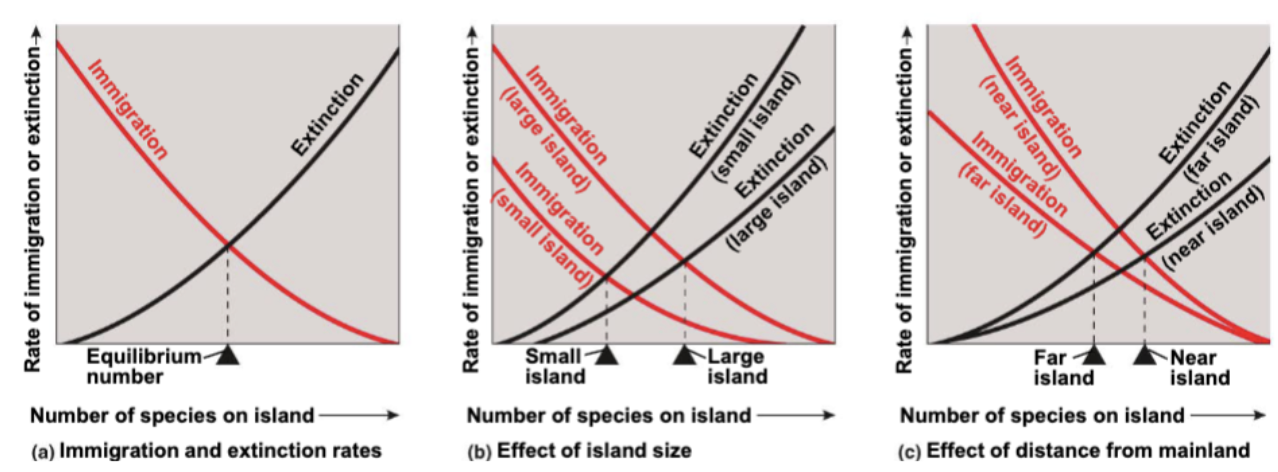
ecologists observed:
islands contain fewer species than does a nearby mainland
small islands contain fewer species than do larger islands
islands closer to the mainland contain more species that do similar size islands located at a greater distance from the mainland
island equilibrium model
species richness on islands depends on island size, distance from the mainland, immigration, and extinction
four major threats to biodiversity
habitat destruction
introduced species
overexploitation
disruption of “interaction networks“
habitat destruction
human alterations
threat to biodiversity
natural landscapes have been broken up, fragmenting into small patches
introduced species
those humans move from native locations to new geogrpahic regions
gain footholds in a new habitat, and usually disrupt their adopted community
humans have deliberately introduced some species with good intentions but disastrous effects
overexploitation
poaching
fishing
deforestation
pet trade
disruption of interaction networks
extermination of keystone species by humans can lad to major changes in community structure