🎓Lecture 3: Biodiversity
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what are the rules for binomial nomencleasure
Specices names are always in italics.
Unless you are writing by hand - in which you underline
Genus always stats with a capital e.g Canis
Species is Always lower case: famiiares
rank the most organims in our wordl
THe prodomient is Plants due to accumilated carbon and form most terrestrial habbitat.
Then in bacteria
then fungis
then us.
Animals are only making .5 percent of the whole biomass.
specifically for animals
Looking specifically at the Animals we mostly have livestock (things we like to eat)then humans have the 2nd to least then wild mammals are the last (elephents ex).
why is understanding biodiversity important
to understand if species are being extinct or not.
What is Biodiveristy
The veriaty of microbe, plant in the world and in the habitat.
what type of scientific word do we use when trying to figure out the biodiversity of a habitat.
contrain
what is contraining our subjects mean when looking at a biodiversity
so we CONTRAIN our sealves. we look specifically at CORALS and the biodiversity specicifcally to understand the measure to the coral reefs
what are the 3 ways new species arrive in nz
Descended from those species that where present.
Arrive recently without human assistance.
Native where here for several million years.
why is biodiversity important
Interstic Value
what does Intestic Value mean
Ecosystem an bioversity as a whole have value because they exist.
what are the 3 types of diversity.
Genertic diveristy
species diveristy
Ecosystem diveristy
what does Genetic diveristy mean
Genetic variation amoung indidivuals within a population to addapt.
species diveristy
the number of species within an area (no of species and some form of relative abundance)
Ecosystem diveristy
diversity amount different Areas. (dependent on what question we are asking).
what is important for ecologica thinking
Space and Time is importatn for ecologcal thinking
an example of time
If this was once a forested area then cut by setler was there an decrease or increase in biodiversity if there is a recovery of biodiverisy.
How do we measure species
we just count species and if we can identify which species they belong to.
example
Look at several lakes and record how many birds there are including kids, what’s there sex, there age, there diet and help predict there presence and abundance of a species.
What must we not do
DO NOT GO TO ONE LAKE. it is not representive and look at more than one to help understand the temporal (time) representation of birth diversity spatial over an area or time.
How Do we Measure Species and BioDiversity.
Species Diversity
Identify and Count Species= Richness
COund the Number of individuals = Abundance.
Can use videos rather than counting in person.
Diversity is a value that represent richness and abundance.
Key metric we use is the Shannon Weiner/ Simpsons index.
Indices are influenced by eveness and dominance of the community
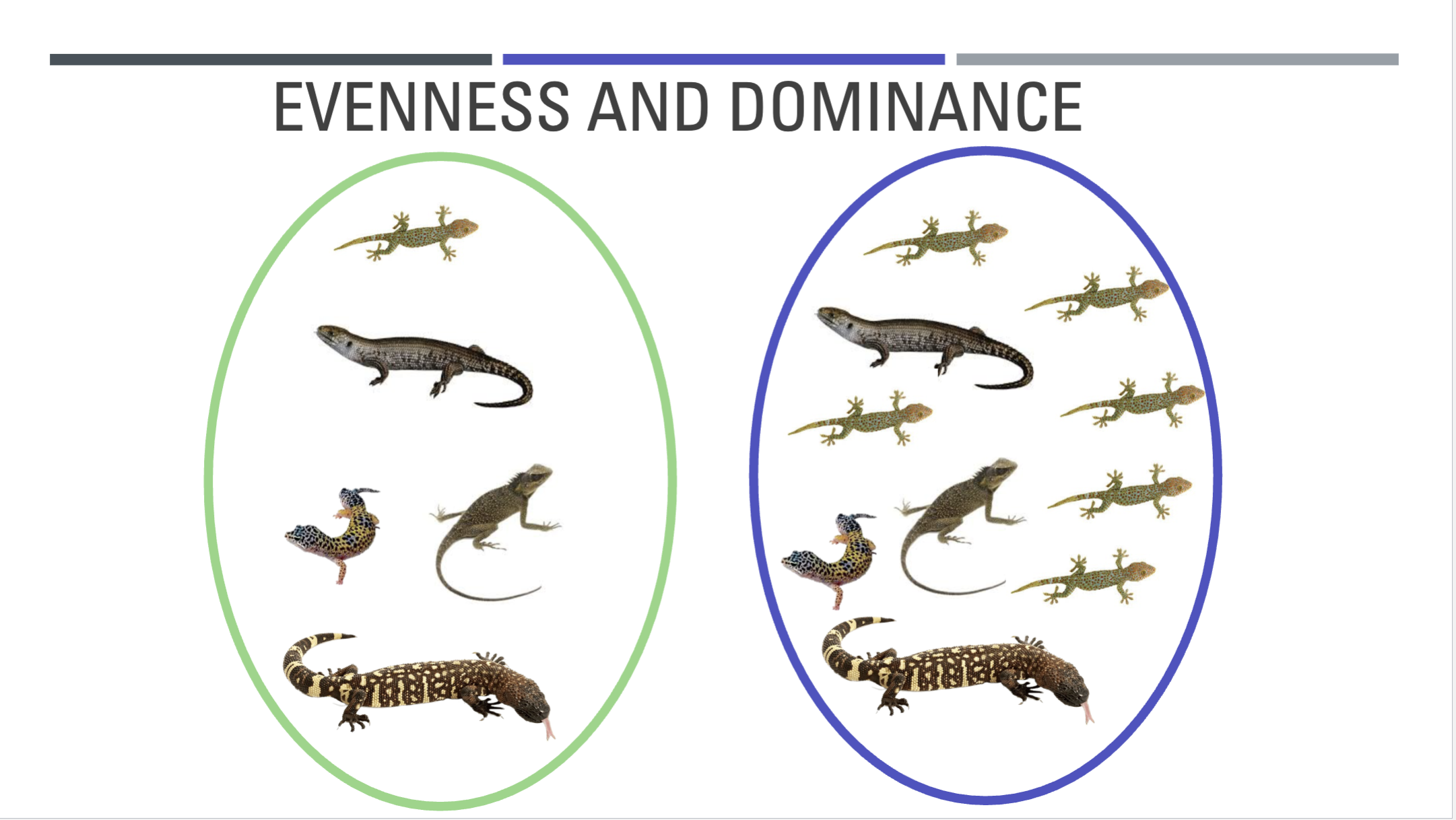

EVENESS AND DOMINANCE
we can see that the comunity in the left is even because there is an even amount of species in them while in the right there is a dominant species numerically meaning there is more species of on than the other.
How to quantify biodiversity
Alpha
Gamma
Beta
alpha
ALpha = interested in a specific habitat. such as a section coarl reefs.
beta
Beta= we tend to use this more. difference in diversity between two specific locations at the great barrier reef. representation ration Loacal:alpha:and sepcies diveristy.
Gamma
Gamma = interested in a species diveristy over a whole landscape we you gamma diversity. (the whole coral reefs) take more time.
Diverisity
How many species and their relitive abundance (how many indidivuals/species are ther)
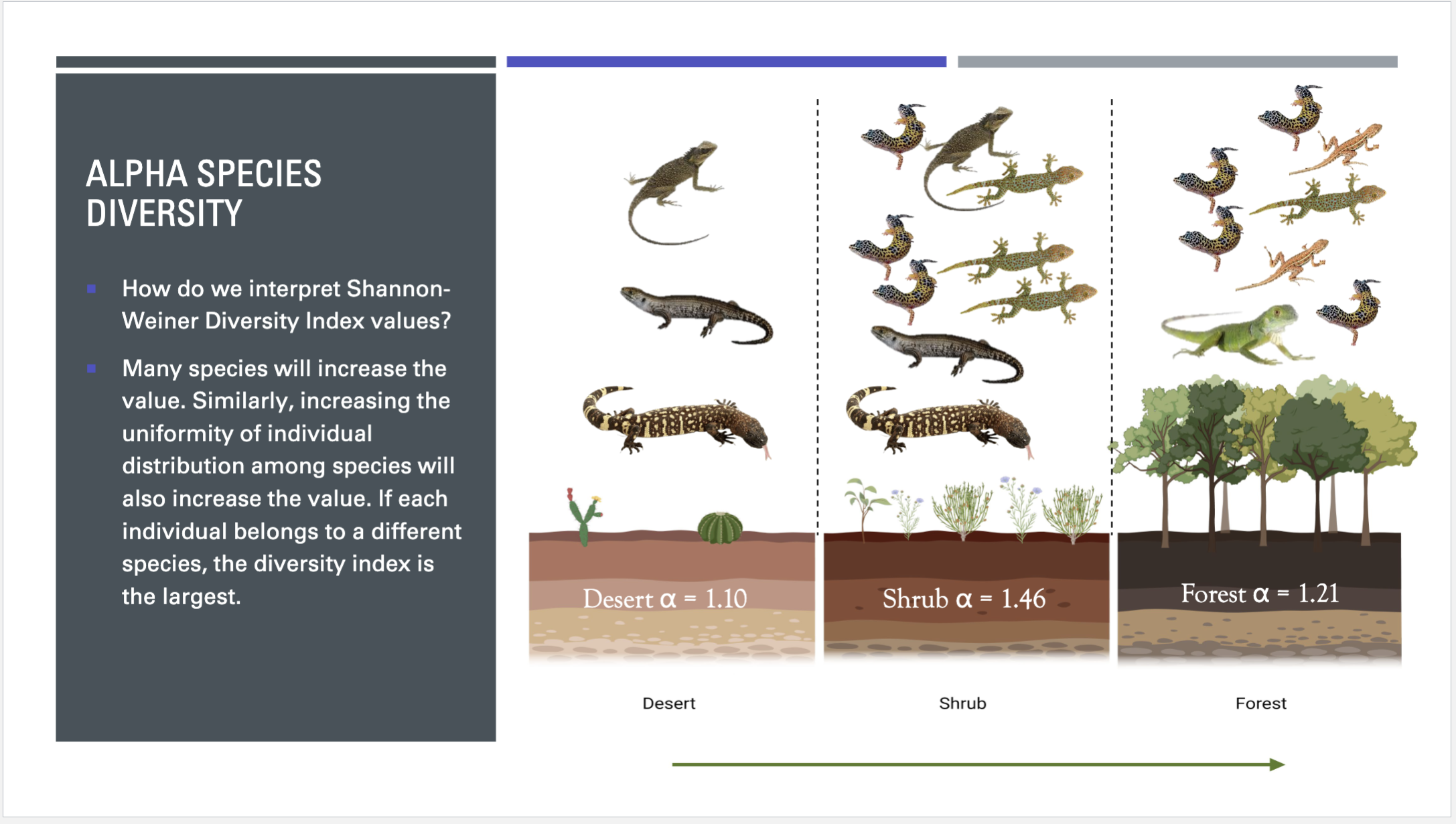
explain this
The species richness is the same, still 7 species but the abundance thus the diversity is different.
why does shrub hav emost biodiveristy
The shrub has the most biodiveristy even though people think forest might but it is drived by the species richness and their is more abundance so it drives species diveristy.
explain how the biodiveristy can fluctuate.
Many species will increase the value. Similarly, increasing the uniformity of individual distribution among species will also increase the value. If each individual belongs to a different species, the diversity index is the largest.
How does calculating beta diversity look like
if we want to calculate beta diversity and landscape and we look at it like a ratio between a local and regional diversity (alpha and gamma).