OCEANOGRAPHY 1080 FINAL
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Iowa State 40% new, 60% whole course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
The time between two successive waves (i.e. the time it takes to complete one wave cycle) is called the
period
What is the definition of fetch with regards to wave generation?
the distance over which the wind blows in the same direction
A tsunami may result from:
tectonic activity on the seafloor
Which of the following is the best description of the path of a water molecule at location B as the wave moves through it (ignore Stokes Drift)?
the water molecule moves in a clockwise orbit
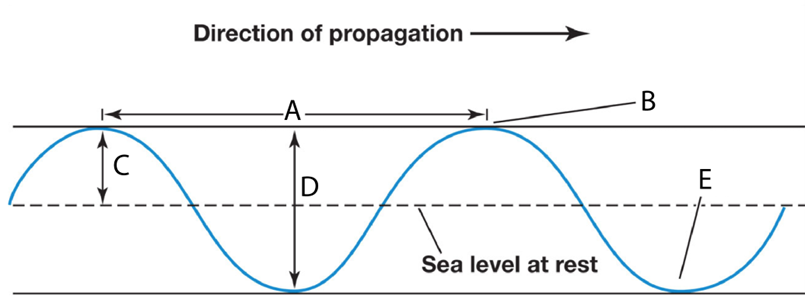
Match the letter with the appropriate term
wave crest: B
wave height: D
wavelength: A
trough: E
amplitude: C
As a wave approaches the shoreline, it eventually breaks because it:
reaches its critical steepness as friction causes waves to slow down and pile up
The duration of time it takes to reach a fully developed sea is influenced by:
both the distance of the fetch and the speed of the winds
Capillary waves:
have a restoring force that is primarily surface tension.
are also known as ripples
are the first waves to form when the wind starts to blow.
A region of the ocean is considered a fully developed sea when:
the energy imparted by the wind equals the energy dissipated by the breaking whitecaps
The differences between seas and swells include:
seas: wave conditions in areas where the wind is blowing (locally-generated) - have waves that have steep sides
swells: wave conditions in areas where the wind is not blowing (remotely-generated) - have symmetrically shaped waves.
Constructive interference results in larger waves while destructive interference results in:
smaller waves
What is Stokes Drift?
It describes the gradual net transport of material and water particles in the direction that the wave is moving.
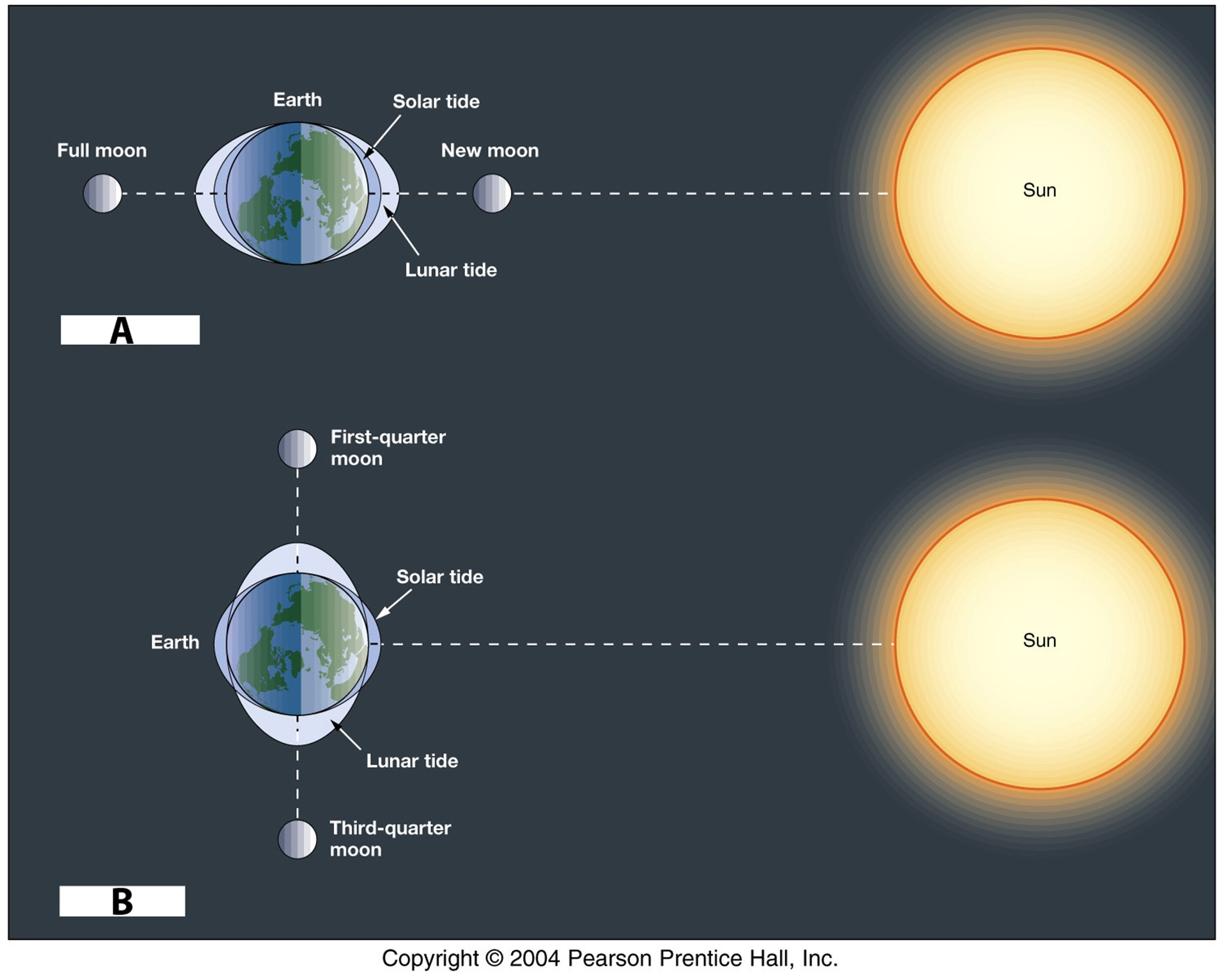
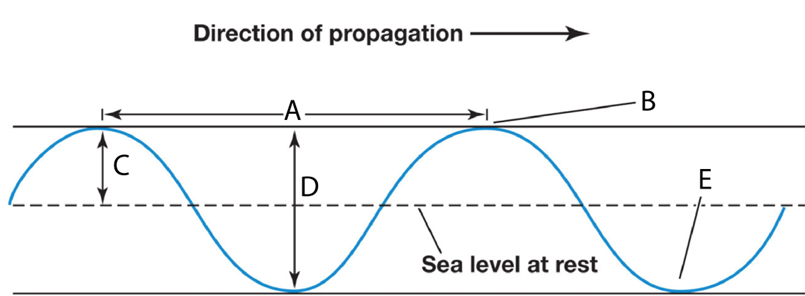
A neap tide would occur:
during the scenario represented in B
The gravitational attraction of ______ with the Earth results in the largest tide producing force on Earth.
the Moon
At amphidromic points:
the amplitude of the tidal wave is 0 (i.e. high and low tides do not influence sea level at these points)
What physical characteristics affect the magnitude of a gravitational attraction between two objects?
both the mass of the objects and the distance between the objects
A spring tide is characterized by:
very high high-tides and very low low-tides.
During full moons and new moons:
there are larger tidal ranges because the Earth, the Moon and the Sun are in line with each other
Which of the following descriptions is most accurate when describing the orbital relationship between the Earth and the Moon.
the Earth and the Moon rotate around each other with a center of gravity that is beneath the surface of the Earth
In one day, an area that experiences semidiurnal tides will have:
two high tides of nearly equal height and two low tides of nearly equal height
The two tidal bulges (two high tides and two low tides) on an idealized earth (without continents) occur because_________.
Moon’s gravity pulls water towards it on the near side creating a bulge. Inertia (centrifugal force) causes water on far side to lag behind, creating a second bulge
Which of the following statements is true with regards to respiration?
a phytoplankton cell can photosynthesize and respire at the same time
When does the spring phytoplankton bloom happen?
when the mixing depth is above the critical depth
The spring phytoplankton bloom (an increase in biomass) occurs because:
nutrients have been mixed to the surface during the winter so nutrient concentrations are high in surface waters during the spring.
light levels increase during in the spring.
the thermocline shoals (gets shallower) during the spring, allowing phytoplankton to live closer to the surface where there is more light for photosynthesis.
Where are rates of primary productivity higher (compared to the average ocean)?
along coastlines, the equator and higher latitudes
Why do dissolved nutrient concentrations (dissolved nitrate and phosphate) in ocean waters increase with depth in the ocean?
nutrients are incorporated into cells during biosynthesis at the surface and released by decomposition at depth.
because the water column is often stratified (i.e. a thermocline exists), it is difficult to get nutrients that are at depth back to the surface.
Why are rates of primary productivity higher (compared to the open ocean) along the coastlines?
Ekman upwelling and tidal mixing occurs along coastlines, bringing nutrients to the surface.
What answer best describes the role of the open ocean in primary productivity, compared to coastal and upwelling zones?
the open ocean has lower rates of primary productivity but a higher percentage of total ocean production.
Why are rates of primary productivity higher at higher latitudes?
there is more winter convective mixing at higher latitudes due to a deeper or absent thermocline during the winter months or, in some very high latitudes, throughout most of the year.
Why is nitrogen often the limiting nutrient in biological production?
phosphorous is released relatively quickly after organisms die and therefore it is more available in the surface waters.
according to the Redfield Ratio, phytoplankton cells need 16 nitrogen atoms for every 1 phosphorous atom.
What process releases nutrients (stored in cells) back into the ocean?
decomposition
An autotroph is an organism that:
makes its own food through photosynthesis (or chemosynthesis).
Explain what happens to the sea surface as the wind begins to blow, and as the wind continues to blow at a constant wind speed.
When wind begins to blow small ripples form known as capillary waves and the force that restores them is surface tension. When wind speed increases and continues blowing, the waves become larger and are surface waves with their restoring force being gravity. These waves will continue to grow in height, speed, length until they reach a max size for a wind speed duration and fetch and this is known as a fully developed sea. A wave will break when it's steepness exceeds it critical value. Whitecaps are the foamy crests of breaking waves that serve to limit further growth of the wave by dissipating excess energy from the wind into the water and atmosphere and precent the wave from becoming to steep and unstable.
Name a nutrient that is often limiting in the ocean.
What processes bring nutrients to coastal locations? Name at least two.
What process brings nutrients to equatorial regions?
What process brings nutrients to surface areas of the North Atlantic Ocean in the winter?
1. Nitrogen is often a limiting nutrient in the ocean
2. Upwelling and river runoff bring nutrients to coastal locations
3. Equatorial upwelling
4. Winter/vertical mixing
What is one of the controls on the efficiency of nutrient uptake by phytoplankton cells?
the cell’s surface area-to-volume ratio
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) result from:
blooms of phytoplankton species that produce biotoxins
The relationship between phytoplankton growth (as measured by density of biomass) and nutrient concentration can be described as:
the higher the concentration of nutrients, the more the phytoplankton grow.
The following are all primary producers in the oceans except:
whales
Meroplankton are:
zooplankton that spend only part of their lifecycles in the plankton
ex: barnacles, bivalves
All of the following statements about phytoplankton are true except:
They are very good swimmers (can move quickly through water under their own power).
All of the following are considered holoplankton except:
hippopotamuses
radiolarians
formanifera
copepod
pteropods
true jellyfishes
arrow worms
What happens to rates of photosynthesis by phytoplankton as light intensity increases?
rates of photosynthesis will increase up to a point (Pmax) after which they will decrease due to too high light intensity.
Which of the following statements is correct with regards to diatom reproduction?
diatoms can reproduce both sexually and asexually.
All of the following are true statements about cyanobacteria except:
All of these are true statements about cyanobacteria.
Cyanobacteria are bacteria.
Cyanobacteria are types of phytoplankton.
Some species of cyanobacteria create stromatolites.
Photosynthesis by cyanobacteria 2.4 billion years ago resulted in oxygen in earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
Why is there often a large buildup of organic matter in the sediment of salt marshes and mangrove forests?
the lack of oxygen in these sediments prevents decompositiont
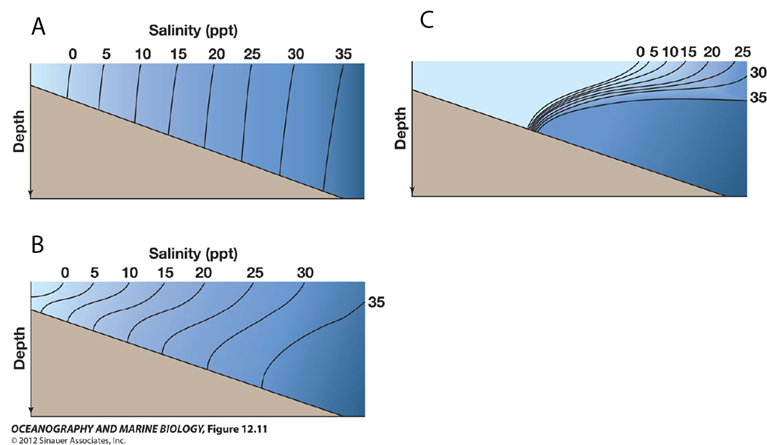
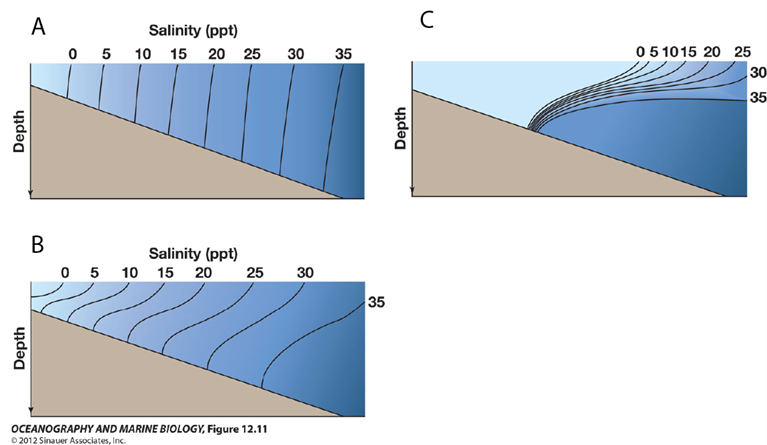
For diagram A (or any one of the diagrams), where is the head of the estuary (where the river flows into the estuary)?
to the left of the diagram
Which diagram represents an estuary with little to no tidal mixing?
C
Life in the rocky intertidal zone can be stressful for all of the following reasons except:
the tidal cycle is exactly 12 hours so organisms are always exposed during the same time of the day.
All of the following factors influence the distribution of marine organisms (i.e. are factors that influence where different types of species are found in the oceans) except:
All of these influence the distribution of marine organisms.
ocean currents.
depth.
latitude.
salinity.
Coral polyps get their food from:
zooxanthellae, stinging prey with their tentacles, AND filter feeding
What causes coral bleaching?
when zooxanthellae are stressed from high water temperatures or pollution, they leave the coral, making the coral white (the color of their calcium carbonate structures).
What is one major difference between salt marshes and mangrove forests?
salt marshes tend to be found at higher latitudes and mangrove forests tend to be found at lower latitudes.
For diagram B, what is the best description of water flow (estuarine circulation)?
flow is from left to right at the surface (top of the diagram) and right to left at depth, with some upward vertical mixing.
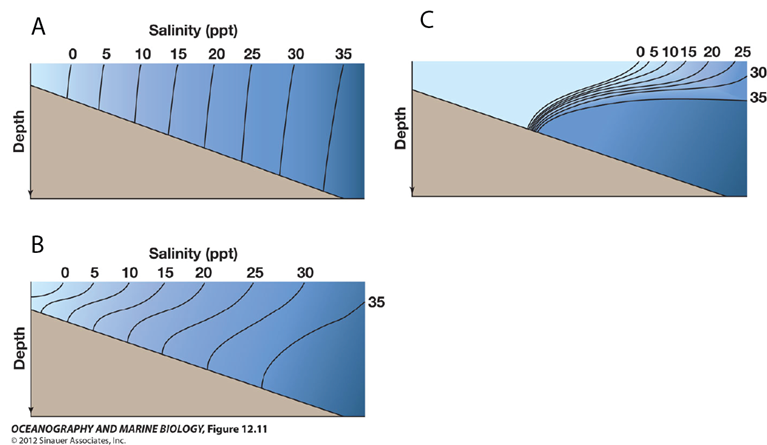
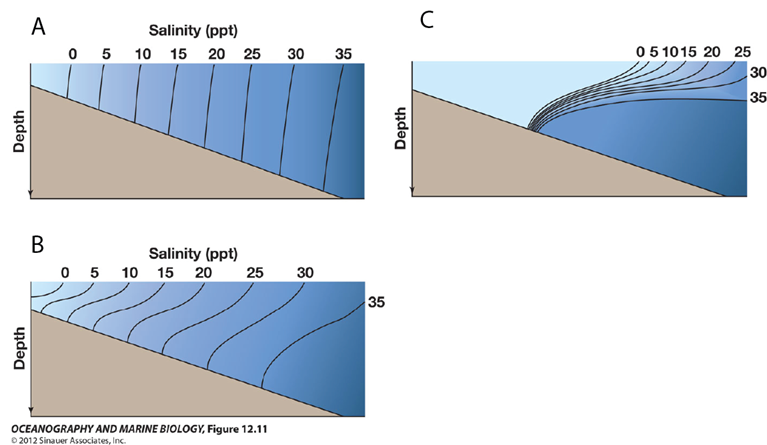
Which diagram represents a well-mixed estuary?
A
El Nino is ____.
also known as El Nino Southern Oscillation.
can be in a neutral state, La Nina or El Nino.
a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomena.
El Nino and La Nina can have substantial impacts on climate across the planet. During which of the following would we in Iowa expect warmer than average conditions?
El Nino
All of the following are true about El Niño events except:
upwelling off the coast of Peru increases during an El Niño event due to cold water in the eastern Pacific, resulting in very productive fisheries during these events.
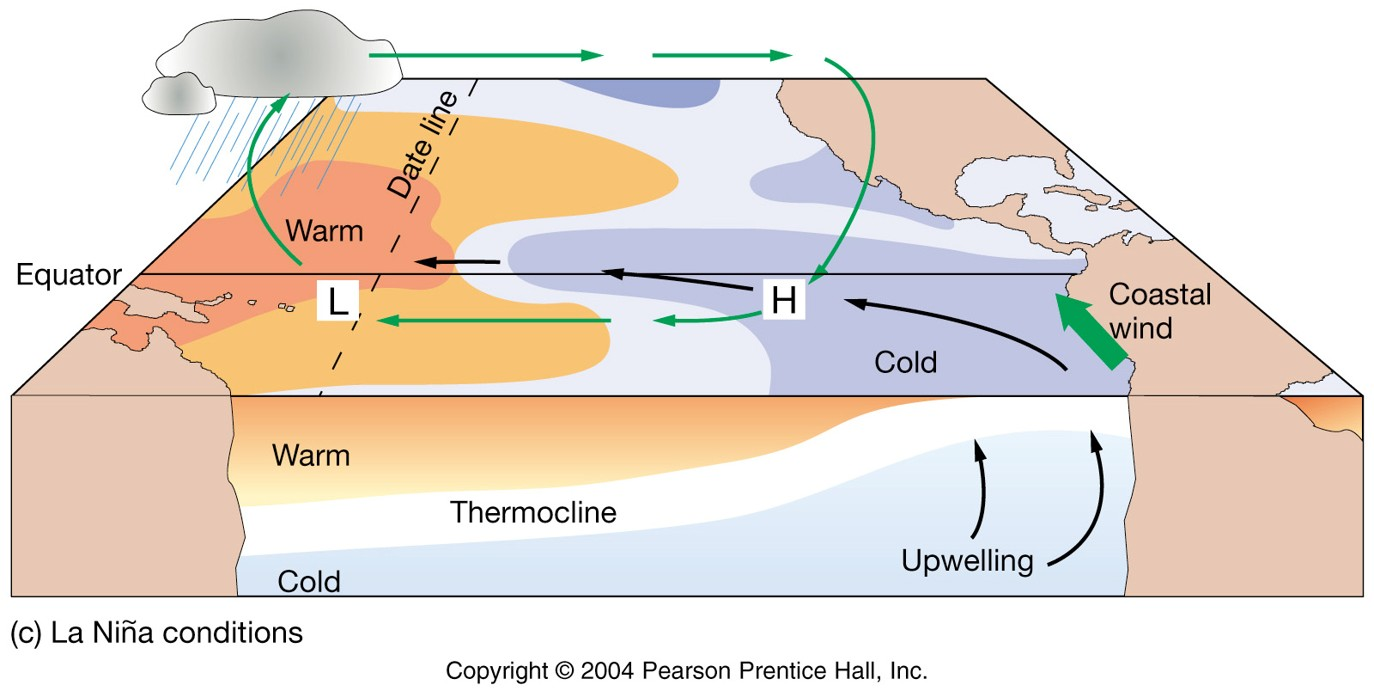
Which are true of La Nina conditions?
thermocline shoals (gets shallower) in easter Pacific
stronger trade winds
increased upwelling
more nutrient availability
What causes the "collapse" of the fisheries off the coasts of Peru and Ecuador during El Nino events?
anomalously warm and nutrient-poor waters
The atmospheric component of ENSO is called _____.
walker circulation
When the storm passed over the instruments from January 4 to January 6, was the relationship between barometric pressure and wind speed positive (e.g., both increasing or decreasing) or negative (one increasing and one decreasing)?
one increasing and one decreasing
A storm like this is referred to as a ‘bomb cyclone’ if the barometric pressure drops by at least 24 mbar in 24 hours. Does this storm fit the description of a bomb cyclone?
yes
There _________ relationship between wind speed and wave height.
a positive
Using the equation below, find the wavelength (L) in meters for the waves on January 5, 2018 at 0000 (remember, this was the time period of the largest wave height).
The wavelength (L) is calculated using: L = gT2/2π, where g=9.8 m/s2 and T is wave period in seconds
146.8
Higher chlorophyll concentrations ______ primary production.
are associated with higher primary production
Order the seasons from highest to lowest expected phytoplankton abundance. Assume the following seasons:
Winter = December, January, February
Spring = March, April, May
Summer = June, July, August
Fall = September, October, November
highest phytoplankton - spring
second highest phytoplankton - fall
third highest phytoplankton - summer
lowest phytoplankton - winter
Right whales feed on copepods (zooplankton), which in turn feed on phytoplankton.
1. Would the abundance of zooplankton in this area be expected to vary seasonally as well?
2. Would the abundance of zooplankton be highest and lowest in the same months as phytoplankton? why or why not?
yes the abundance of zooplankton would expect to vary seasonally as well because phytoplankton abundance varies seasonally due to things like sunlight and nutrient availability. Zooplankton feed on phytoplankton, so their food source is seasonal causing a fluctuation in population
no, the abundance would not be the highest and the lowest in the same months of phytoplankton
When there is an increase in phytoplankton population the zooplankton population has a delayed response since it takes time for them to reproduce and grow their population in relation to the increased food availability. When phytoplankton pop declines, zooplankton decline shortly after since food source is scarce.
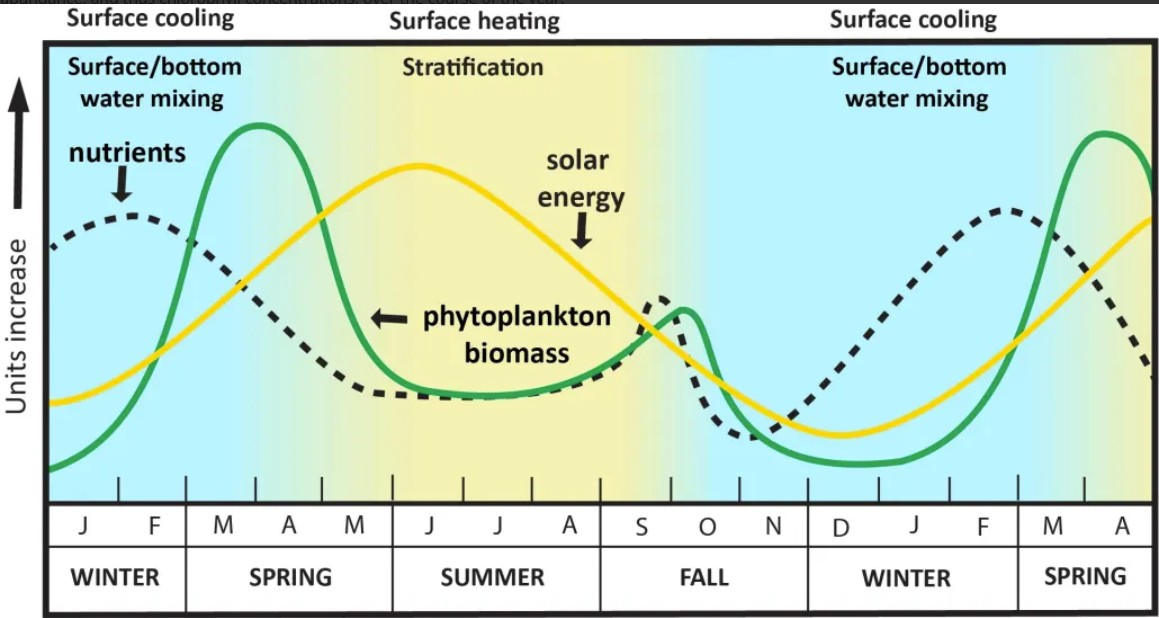
Use the following image to answer this question.
In the summer, solar energy is ____, nutrients are ____ and phytoplankton biomass is ______
high
low
low
In the summer, when surface temperature is ____, the large density difference between surface water and deep water results in a ____, which prevents nutrients from reaching the surface waters.
warm
density stratification
How would you describe the relationship between chlorophyll and temperature during fall months (Sep-Nov)?
when one increases the other decreases (a negative relationship)
Over the next few decades, surface water temperatures are predicted to increase potentially causing increased stratification, less nutrient availability and decreasing chlorophyll concentrations. Spring blooms may shift earlier and fall blooms may be delayed if the water remains stratified longer. How might these shifts in magnitude and timing of phytoplankton blooms affect the migration patterns of the North Atlantic right whale?
Select all that seem like logical impact(s) to migration of right whales.
Looking for alternative feeding grounds also exposes the whales to more risks from shipping traffic and fishing gear in new areas, where protective measures have not yet been instituted.
Whales might continue to migrate farther north if they arrive too late for the spring bloom and are unable to find sufficient food in the area near the OOI array.
Whales might migrate earlier if spring blooms occur earlier.
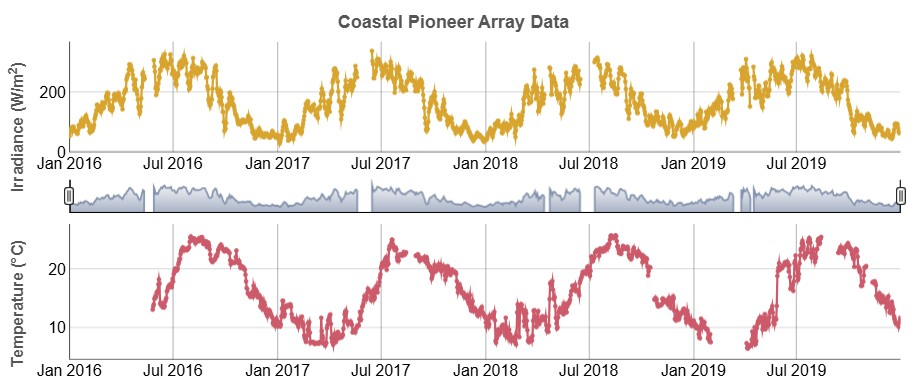
Use the irradiance and temperature data shown below to answer this question. What is the relationship between irradiance and temperature?
They follow the same pattern but the peaks and troughs in temperature are after the peaks and troughs in irradiance.
How and why do waves disperse?
As waves move away from the place they are generated they flatten, lengthen and move faster away from the wind.
Wave height decreases due to gravity so in order to create conservative energy, wavelength must increase.
Period (T) does not change so velocity increases because V= L/T. transition from sea to swell
At what depth are wave diameters 4% of what they are at the surface?
one half of the wavelength distance
Describe the process of surf formation (include critical steepness in your response). Where do waves break as they get closer to shore (i.e. surf) and why?
A deep water gravity wave approaches shore at a constant wavelength. When water depth shoals ½ the wavelength it transitions to intermediate water wave, wave velocity decreases and wavelength shortens, other waves behind begin to catch up with the leading waves, wavelengths shorten and wave height increases. Wavelength transitions to a shallow wave when depth is 1/20 the wavelength. Wave steepness becomes critical when the depth is about 1.3 x H, when wave will break as surf
Because approaching shallower water interaction with bottom creates friction
Newton’s Third Law
for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction
Gravitational Forces
F = G M1 x M2 / d^2
Tells us that gravity depends on 2 masses and distances meaning more mass equals more force but greater distance reduces it
Centrifugal Force
the apparent force, equal and opposite to the centripetal force (gravitational attraction) drawing a rotating body away from the center of rotation, caused by the inertia of the body
How are gravitational and centrifugal forces balanced along a plane that runs through the center of the Earth? How are they balanced at other locations on the Earth? What does this result in?
They are not really balanced but more so combined to create effective gravity. Gravity pulls inward while earth's rotation causes an outward centrifugal force strongest at the equator and zero at the poles
This results in equatorial bulge (earths shape) and weight differences where you feel lighter at the equator than the poles
What is tidal mixing? Describe its influence on coastal productivity
Process by which energy from ocean tides is converted into turbulence facilitating vertical and horizontal exchange of properties like heat, salt and nutrients within the water column
Makes them very biologically productive
What is photosynthesis? Know the chemical reaction (equation)?
plants and organisms use sunlight to make food from carbon dioxide. Use photosynthetic pigments (chlorophyll) to capture the sun's energy. Generates oxygen as byproduct
CO2 + H2O + light energy → CH2O + O2
CH2O is a carbohydrate (glucose, sugar i.e food) - energy from sun is stored in CH2O within the cells of primary producer
What is respiration? Know the chemical reaction
reverse reaction of photosynthesis. Done by primary products continuously; exclusively when there is no light. Burning of food, releases energy needed for other cellular processes such as growth
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy (heat)
What is biosynthesis?
substance (element) that provides nourishment essential for growth and the maintenance of life. Generally referring to minor elements (C, O, H not included)
What is decomposition? Know the chemical reaction
disassembling things back into their inorganic components and making nutrients available (same basic process as respiration). Often mediated by bacteria
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy (heat) + nutrients
What are the limiting factors of biological productivity?
The amount of biological production possible in a given time depends on the abundance of the least available necessary factor
Nutrients, temperature and light
Nutrients and light are often not limited in the same region because their availability often follows opposite gradients. Light most abundant at surface and decreases with depth, while nutrients are more concentrated in deeper waters
What is the Redfield Ratio?
In both phytoplankton and seawater, the ratio of carbon to nitrogen to phosphorus is almost always 106 carbon atoms to 16 nitrogen atoms to 1 phosphorus atom (106:16:1)
What is the critical depth? Why does it change with the seasons?
The depth on the ocean where the total production of phytoplankton from the surface down to the point exactly equals the total losses within the same layer. Balance between photosynthesis and respiration. Changes with seasons due to variations in sunlight and ocean mixing
What is the mixing depth? Why does it change with the season? How does it influence primary productivity?
Vertical distance from the Earth's surface to the top of the turbulent layer where air, pollutants, moisture and heat are thoroughly mixed by convection and wind. Changes with season due to heating/cooling and mechanical stirring (wind action)
Impacts primary production by controlling light and nutrient availability
Describe the relationship between the mixing and critical depth, and the occurrence of a phytoplankton bloom.
Phytoplankton blooms happen when surface mixing is shallow enough keeping cells in the sunlit zone above the critical depth, allowing net growth to outweigh losses especially as light and warmth inverse in spring creating a stable, nutrient rich layer for rapid multiplication. Deep winter mixing pushes cells too deep for light preventing blooms
Which taxonomic classes of organisms are present in this group (phytoplankton)?
Archaea - single cell, prokaryotes , cells do not have nucleus or membrane bound organelles
Bacteria - single cells, also prokaryotes
Eukarya - single celled or multicellular, have membrane bound organelles including nucleus
Where do phytoplankton want to be located in the water column? Why?
Too much sunlight right at top which inhibits photosynthesis, too deep they do not get enough light for photosynthesis
Want to be in the middle in sort of goldilocks area where they stay near the surface to catch light but also stay mixed to get nutrients (upwelling zones)
Are large or small cells better off in low nutrient environments? Why? What controls the efficiency of nutrient uptake in a cell.
Smaller cells generally better because they have a high surface area-to volume ratio which allows for more efficient nutrient absorption relative to their needs
What controls it is environmental factors, transport proteins, regulation of cell, etc
How do salinity concentrations change in relation to distance from shore? How does this influence the distribution of organisms? How have some organisms evolved to deal with salt?
Open ocean have higher more stable salinity, where areas closer to land have lower more variable salinity
Organisms less tolerant to salt are found upstream in estuaries, while those requiring high salinity are located closer to the ocean.
Evolved osmoregulation, behavioral adaptations
What is a rocky intertidal zone? What factors influence the characteristics of these zones? What are some challenges faced by organisms inhabiting these areas? How does zonation occur within these environments?
Harsh biodiverse area between high and low tide lines, solid rock where organisms must endure drastic shifts between submerged in sweater and exposed to air, sun and temp extremes
Tidal waves, wave action, temperature, salinity, moisture and substrate shape intertidal zones. Organisms face challenges from temperature extremes, dying, wave force, competition for space, predation, salinity shifts and human impacts like pollutants and habitat loss
Zonation creates horizontal bands of life from top (land) down (sea)
What is an estuary? How are they categorized? How are nutrients delivered to estuaries?
Partially enclosed coastal environments where freshwater (river) mixes with the salty seawater (ocean)
Categorized by geomorphology, salinity distributions
Riverine inputs, groundwater seepage, atmospheric deposition, direct discharge
What are coral reefs? What factors influence their location?
Underwater structures built by tiny animals (polyps) that secrete calcium bicarbonate structure forming complex, diverse ecosystems vital for marine life found mainly in warm, shallow, clear tropical waves
Location is influenced by warm temperatures, sunlight, clear water, normal salinity and suitable water flow
Why do coral reefs thrive in regions that are otherwise known as biological deserts? Why are these regions known as biological deserts?
Partnership with algae that provide food creating a self-sustaining highly efficient nutrient cycle, essentially acting as nutrient recyclers in otherwise barren areas while also getting food from zooplankton allowing them to flourish as hotspots of biodiversity
Describe the relationship between coral polyps and dinoflagellates known as zooxanthellae.
Vital mutualistic symbolic relationship. Algae lives inside the coral tissue using sunlight to produce food for the coral, while the coral provides shelter, carbon dioxide and other nutrients for the algae
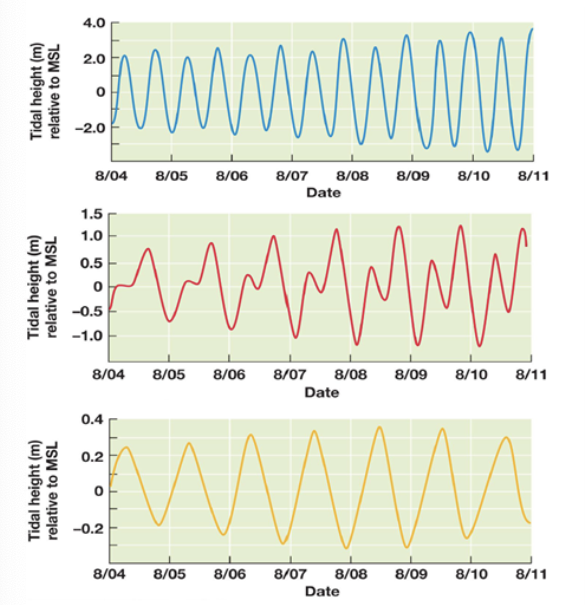
Match the following figures with the type of tide (Semidiurnal, Diurnal, Mixed)
Blue: semidiurnal tides (2 high tides and two low tides a day) - continents block them
Yellow: diurnal (one high tide a day) - gravitational attraction of the sun
Red: mixed (2 high tides and 2 low tides but one high tide is larger than the other)