IB Design Technology - Topic 3 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:34 PM on 5/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
Aesthetic models
A model developed to look and feel like the final product.
2
New cards
Animation
The ability to link graphic screens together in such a way as to simulate motion or a process.
3
New cards
Assembly drawings
A diagram that shows how components fit together to make a whole. Typically presented in an exploded view.
4
New cards
Bottom-up modelling
A designer creates part geometry independent of the assembly or any other component. Although there are often some design criteria established before modelling the part, this information is not shared between models. Once all parts are completed, they are brought together for the first time in the assembly.
5
New cards
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
The use of computers to aid the design process.
6
New cards
Conceptual modelling
A model that exists in the mind used to help us know and understand ideas.
7
New cards
Data modelling
A model that determines the structure of data.
8
New cards
Digital human
Computer simulation of a variety of mechanical and biological aspects of the human body
9
New cards
Fidelity
The degree to which a prototype is exactly like the final product.
10
New cards
Finite element analysis
The calculation and simulation of unknown factors in products using CAD systems. For example, simulating the stresses within a welded car part.
11
New cards
Formal drawing techniques
A type of drawing technique that has fixed rules, the most widely used being isometric projection and perspective drawing.
12
New cards
Fuse deposition modelling
A 3D printing technique that places melted layers of material on a bed to build up a 3D model.
13
New cards
Graphical models
A visualization of an idea, often created on paper or through software, in two or three dimensions.
14
New cards
Haptic technology
An emerging technology that interfaces the user via the sense of touch.
15
New cards
Instrumented models
Prototypes that are equipped with the ability to take measurements to provide accurate quantitative feedback for analysis.
16
New cards
Laminated object manufacturing (LOM)
A system that virtually slices a 3D CAD model into thin layers, then cuts out each layer from a roll of material using a laser or plotter cutter. The layers can then be glued in the correct order to create a 3D model.
17
New cards
Mock-ups
A scale or full-size representation of a product used to gain feedback from users.
18
New cards
Motion capture
The recording of human and animal movement by any means, for example, by video, magnetic or electro-mechanical devices.
19
New cards
Parts drawings
Orthographic drawings of the components of an assembly containing details just about that component.
20
New cards
Perspective drawings
A set of formal drawing techniques that depicts an object as getting smaller and closer together the further away they are. The techniques drawings are one-point perspective, two-point perspective, and three-point perspective.
21
New cards
Physical modelling
The creation of a smaller or larger tangible version of an object that can be physically interacted with.
22
New cards
Projection drawings
Systems of drawings that are accurately drawn, the two main types are isometric projection (formal drawing technique) and orthographic projection (working drawing technique).
23
New cards
Prototypes
A sample or model built to test a concept or process, or to act as an object to be replicated or learned from. Prototypes can be developed at a range of fidelity and for different contexts.
24
New cards
Scale drawings
Drawings that are bigger or smaller than the real product, but exactly in proportion with product.
25
New cards
Scale models
A model that is either a smaller or larger physical copy of an object.
26
New cards
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
An additive manufacturing technique that uses a laser to fuse small particles of material into a mass that has a desired 3D shape.
27
New cards
Sketches
Rough drawings of ideas used to convey or refine the idea.
28
New cards
Solid modelling
Solid models are clear representations of the final part. They provide a complete set of data for the product to be realized.
29
New cards
Stereolithography
A modelling technique that creates 3D models layer-by-layer by hardening molecules of a liquid polymer using a laser beam.
30
New cards
Surface modelling
A realistic picture of the final model, offering some machining data. Surface models contain no data about the interior of the part.
31
New cards
Top-down modelling
This type of design is a product development process obtained through 3D, parametric and associative CAD systems. The main feature of this new method is that the design originates as a concept and gradually evolves into a complete product consisting of components and sub-assemblies.
32
New cards
Virtual prototyping
Photorealistic CAD-based interactive models that use surface and solid modelling. They can be considered 'digital mock-ups'.
33
New cards
Virtual reality
The ability to simulate a real situation on the screen and interact with it in a near-natural way.
34
New cards
Working drawings
Drawings that are used to guide the production of a product, most commonly orthographical projection, section drawings, part drawings, assembly drawings and plan drawings
35
New cards
Orthographic Projection
projection of a single view of an object (such as a view of the front) onto a drawing surface in which the lines of projection are perpendicular to the drawing surface
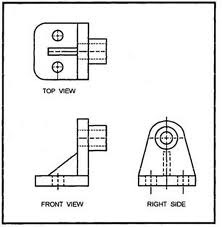
36
New cards
2 pt perspective drawing
2 vanishing points are used and the object is diagonal to viewer
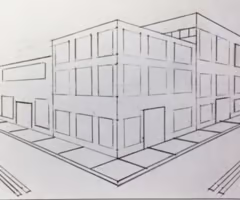
37
New cards
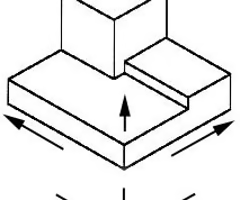
Oblique Drawing
A type of drawing involving a combination of a flat, orthographic front with depth lines receding at a selected angle, usually 45 degrees.
38
New cards
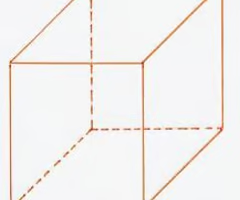
Isometric drawing
The drawing of a 3d object that shows a corner view of a figure. it is not drawn in perspective and the distances are not distorted.
39
New cards
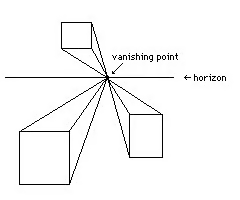
1 point perspective drawing
Illusion of forms drawn back to one vanishing point on the horizon lin
Explore top notes
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)
Personality 210 Psychology Notes (Part 3) Continuing Traits and Trait Traditions
Updated 1335d ago0.0(0)