Antihypertensive Agents (Medicinal Chemistry)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
thiazides
warning for sulfonamide hypersensitivity reactions (nausea, allergy, hematopoietic disease
benzothiadizine
Thiazides derived from ___________ which are bicyclic heterocyclic benzenes.
lipophilicity and duration of action
What do the alkyl groups on position 2 on thiazides increase?
increase potency
What does the lipophilic groups on the position 3 of the thiazides do?
increases activity 10 fold
What does the lipophilic groups on the position 3-4 of the thiazides do?
chlorine
What is the electron withdrawing group on the position 6 of thiazides?
sulfonamide
The _________ on position 7 adds activity (hyper-sensitivity) to thiazides.
Chlorothiazide
-Representative thiazide diuretic.
-It was patented in 1956 and approved for medical use in 1958.
-Warning: sulfonamide sensitivity!
Hydrochlorothiazide
-Widely used thiazide diuretic.
-Prototypical thiazide.• 3-4 bond saturated => more active than chlorothiazide.
-Called HCTZ.
-Warning: sulfonamide sensitivity!
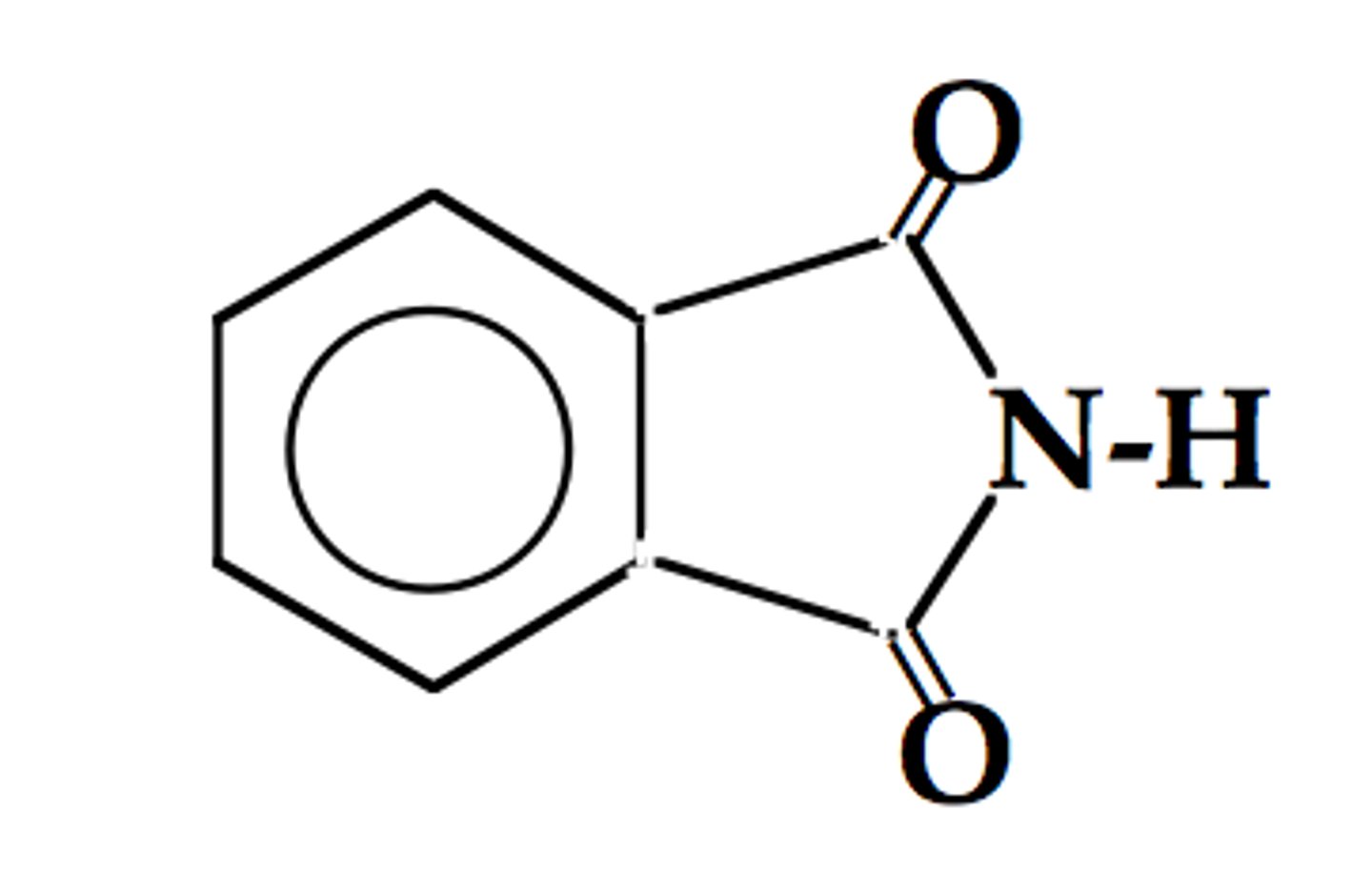
phthalimide ring
Chlorthalidone has a structural modification which is the __________
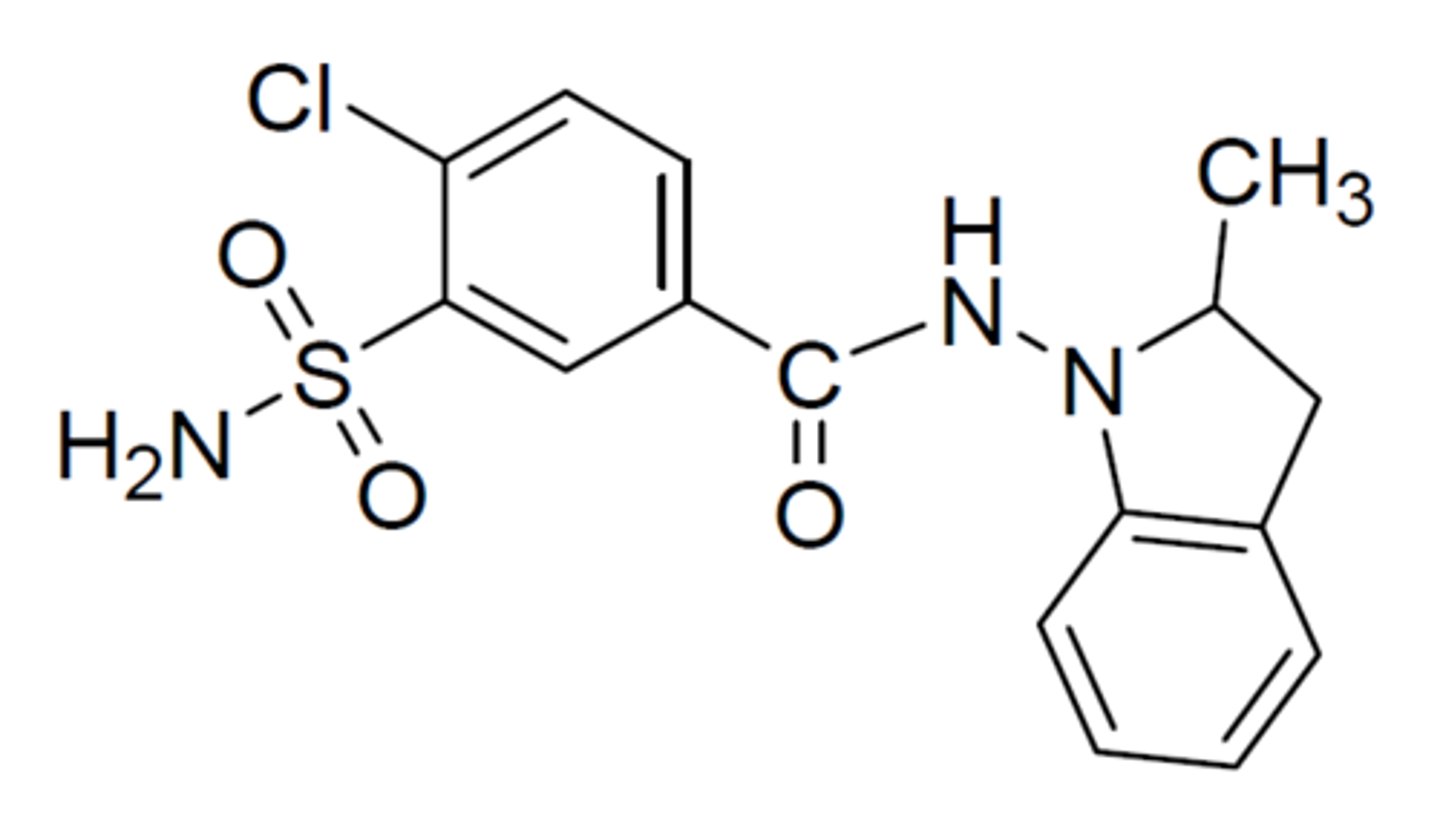
Indapamide
-Structure: 1-(4-chloro-3-sulfamoylbenzamido)-2-methylindoline.
-Displays a chlorobenzenesulfonamide.
-No benzothiadiazine scaffold.
-Longer activity and inhibits carbonic anhydrase.
-Warning: sulfonamide sensitivity!
"sulfa" allergy
-3-6% of the population
-sulfonilamide (sulfone + amide)
sulfonamide
is a synthetic derivative of p-aminobenzenesulfonamide,which is sulfonilamide in antibiotics like sulfamethoxazole (SMX)
potassium-sparing diuretics
-Reduce urinary excretion of K+.
-May cause hyperkalemia at different levels.
-Combination with the other diuretics to maintain the [K+] balance.
-May not have a clinically significant effect on BP
Spironolactone
-Cyclized (lactone) aldosterone (steroid hormone) derivative
-Competitive antagonist against aldosterone
-Selective aldosterone receptor blocker
-Old and widely used drug
Eplerenone
-Cyclized aldosterone (steroid hormone) derivative
-Structurally similar to Spironolactone (small chemical modifications)
-Competitive antagonist against aldosterone
-Selective aldosterone receptor blocker
-Widely used potassium-sparing diuretic
triamterene
-Sodium channel blocker
-Three highly aminated aromatic rings
-Bicyclic ring (pyrimidine and pyrazine)
-Weak potency
Amiloride
-Sodium channel blocker
-Open-ring analog of triamterene (chlorination instead of phenyl)
-100-fold more potent than triamterene
propranolol
s a racemic mixture of 2 enantiomers where the S(-)-enantiomer has approximately 100 times the binding affinity for beta adrenergic receptors
Metoprolol
-Selective blocker of the β1-adrenergic receptors in the heart.
-Chemically similar to propranolol, but with a hydroxyethyl group attached to the C4 carbon of a phenol group instead of a naphthalene(1-naphthol)
Verapamil
As a phenylbutylamine, this compound
contains a phenylbutylamine moiety,
which consists of a phenyl group
substituted at the fourth carbon by a
butan-1-amine
Dilitiazem
As a benzothiazepine, it contains a benzene fused to a thiazepine ring (a seven-membered ring with a nitrogen atom and a sulfur atom replacing two carbon atoms)
Nifedipine
As a dihydropyridinecarboxylic acid, it contains a
dihydropyridine moiety bearing
carboxylic acid groups
ACEis
Inhibit, directly or indirectly, the converting enzyme peptidyl dipeptidase that hydrolyzes angiotensin I to angiotensin II,
consequently decreasing inactivation of bradykinin (a potent
vasodilator)
Captopril
-Competitive inhibitor of ACE.
-Sulfhydryl-containing analog of proline.
-Sulfhydryl moiety enables ACE inhibition
Enalapril
-Prodrug which is converted by hydrolysisof the ethyl ester to enalaprilat, the activeACE inhibitor form with carboxylic acid.
- (S)-(-)-1-[N-(1-Ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)-L-alanyl]-L-proline. Modifieddipeptide containing Ala and Pro
prodrug
Enalapril
active form
Enalaprilat
Perindopril
-ACE inhibitor
-As a prodrug, its ester group is cleaved in the liver and converted into its carboxylic acidactive form Perindoprilat
-Non-sulfhydryl proline-containing dipeptide
prodrug
Perindopril
active form
Perindoprilat
Ramipril
-ACE inhibitor.
-As a prodrug, its ester group is cleaved in the liver, and to a lesser extent in the kidneys,
and converted into its carboxylic acid active form Ramiprilat.
-Non-sulfhydryl proline-containing dipeptide
prodrug
Ramipril
active form
Ramiprilat
Trandolapril
-ACE inhibitor.
-As a prodrug, its ester group is modified in the liver, to its biomedically active its carboxylic
acid active form, Trandolaprilat.
-Non-sulfhydryl Proline-containing dipeptide
prodrug
Trandolapril
active form
Trandolaprilat
Fosinopril
-ACE inhibitor.
-Phospho ester-containing prodrug that is rapidly
hydrolyzed in the gastrointestinal mucosa and liver to
Fosinoprilat (phosphonic acid active form).
-Analog of proline
prodrug
Fosinopril
active form
fosinoprilat
benazepril
-ACE inhibitor.
-As a prodrug, its ester group is cleaved in the
liver and converted into its carboxylic acid
active form Benazeprilat.
-Non-sulfhydryl and benzazepine
prodrug
benazepril hydrochloride
active form
benaeprilat
quinapril
-ACE inhibitor.
-As a prodrug, its ester group is cleaved in the liver and converted into its carboxylic acid
active form Quinaprilat.
-Non-sulfhydryl and quinolone
prodrug
quinapril
active form
quinaprilat
moexipril
-ACE inhibitor.
-Ester-containing prodrug that is rapidly hydrolyzed in the gastrointestinal mucosa and liver
to Moexiprilat (carboxylic acid active form).
-Non-sulfhydryl and di-O-methyl quinolone
prodrug
Moexipril
active form
Moexiprilat
sulfhydryl
can cause taste disturbances and maybe skin rashes
captopril
is preferable in patients with underlying liver issues
Dicarboxylic
_______ ACEis are more potent than captopril
no
Does captopril have activation?
benzazepine
What is the scaffold of benazepril?
quinolone
What is the scaffold of quinapril?
methylated quinolone
What is the scaffold of moexipril?
sulfhydryl + carboxylic
What are the functional groups of captopril?
phosphonic + carboxylic
What are the functional groups of fosinopril?
ARBs
-sartan
-Bind and block angiotensin II receptor
-similar benefits of ACEis, but with no action on bradykinin metabolism and are more selective blockers of angiotensin effects that ACEis
losartan
-As a biphenyl, this organic compound contains benzene rings linked together by a C-C bond.
-was granted FDA approval on 14 April 1995
-First marketed blocker of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1)