Biological Sciences - Exam 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Atomic Number
Number of protons in an atom, always the same for each element
Atomic Mass
Teh combined weight of the protons and neutrons in an atom
Isotopes
Different forms of the same element (same number of protons, different number of neutrons)
Which types of atoms form covalent bonds with one another?
nonmetal
What makes a covalent bond polar
Unequal sharing of electrons (difference in electronegativity)
Which types of atoms form ionic bonds with eachother?
Metals and nonmetals
Hydrogen bonds
formed when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded in one molecule bonds to an O, N, or F atom in a DIFFERENT MOLECULE
Why do hydrogen bonds form between water atoms
hydrogen (partial positive charge) in one water molecule attracts to oxygen (partial negative charge) in another water molecule
How are hydrogen bonds responsible for water’s resistance to change in temp.?
It requires a lot of energy to break hydrogen bonds, meaning it requires a lot of energy to change the temp. of water
How do hydrogen bonds in water store/ release heat energy?
Because hydrogen bonds are so hard to break, water absorbs a lot of energy before changing temp. This also means that water can release a lot of energy with minimal temp. changes.
Polarized molecules relation to water
hydrophilic, can dissolve
Non-polar molecules relation to water
Hydrophobic, can’t dissolve
What is the measurement for concentration of solute molecules?
Molarity (mol/L)
When an acid is dissolved in water, what ions does it release?
H+
When a base is dissolved in water, what ions does it release?
OH-
A solution is considered alkaline if…
There are more OH- ions than H+ ions
A solution is consdiered a
What pH values are considered acidic?
Lower than 7
What pH values are consider basic?
above 7
pH=
-log(H+)
Why is carbon the perfect basis for large, complex biological molecules
Because it has four valence electrons (potential to form four covalent bonds)
What are Hydrocarbons?
Organic compounds that are ONLY made of Hydrogen and Carbon
Why don’t hydrocarbons absorb in water?
They are nonpolar (hydrophobic) in nature
What are the 7 functional groups that are most important in the chemistry of life?
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Sulfhydryl, Phosphate, Amino, Methyl
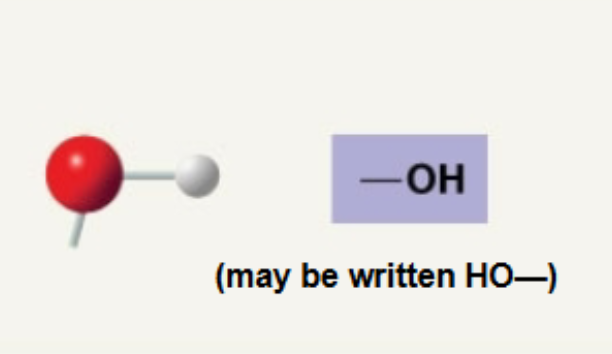
Hydroxyl
Adds polarity to molecules
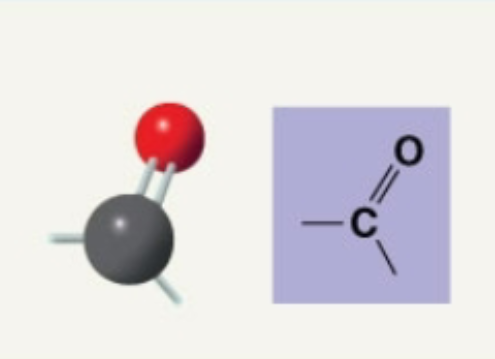
Carbonyl
Adds polarity to molecules
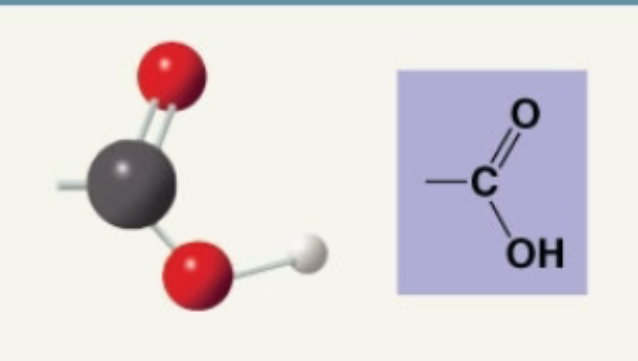
Carboxyl
Acidic: donates H+ ion
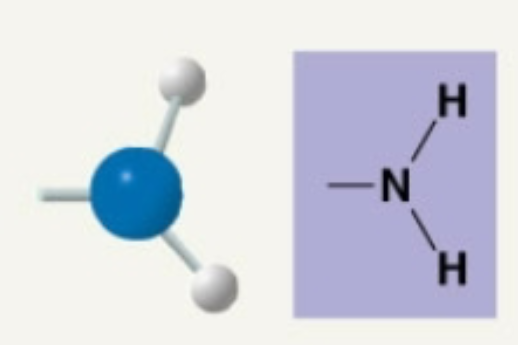
Amino
Basic in aqueous solutions: takes H+ out of solution. Becomes Nh3+
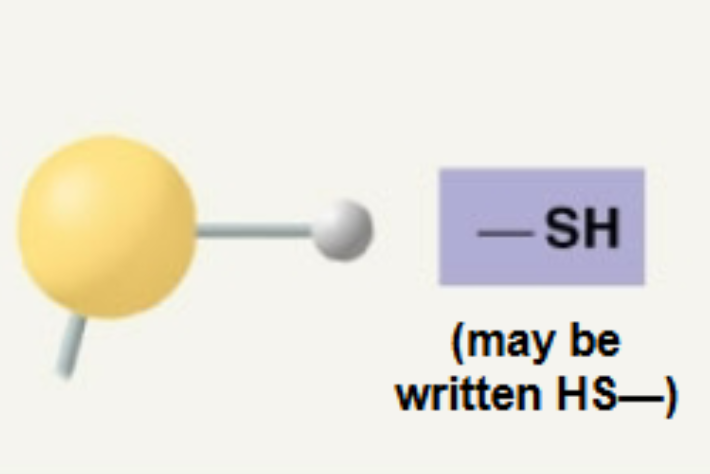
Sulfhydryl
Adds polarity; Contribute to stability of proteins,
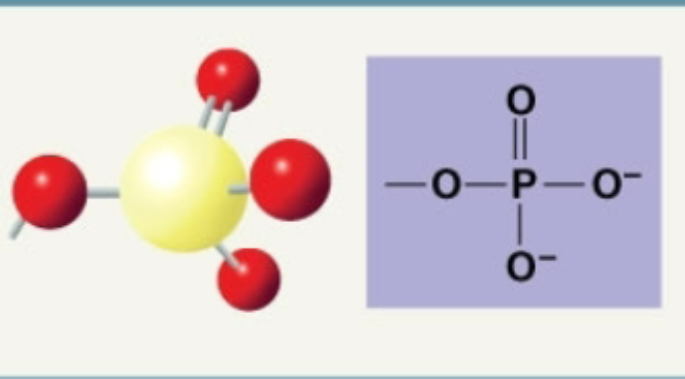
Phosphate
Facilitates energy transfer, massive polarity allows it to interact with water and other polar moelcules
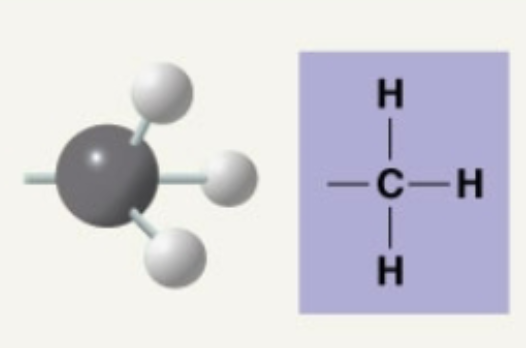
Methyl
Only non-polar common functional group
What makes two molecules isomers of each other?
Same molecular formula but different arrangement or atoms
What are the four major biological macromolecules?
Lipids, polysaccharides, proteins, Nucleic Acids
Which biological macromolecule(s) are/ is NOT A POLYMER
Lipids
Which biological macromolecule(s) are/ is a POLYMER
Polysaccharides, proteins, nucleic acids
What is a dehydration reaction?
A chemical process where monomers combine to form polymers by removing a water molecule.
What is hydrolysis?
A chemical process that breaks down polymers into monomers by adding a water molecule to break down covalent bonds.
Prokaryotic cells example(s)
bacteria
Eukaryotic cells example(s)
plants, animals, fungi, protists
What are the cellular components required in all cells?
plasma membrane, cytosol/ cytoplasm, chromosomes, ribosomes
Chromosomes function in cells
carry genes
Ribosomes function in cells
make proteins
What do eukaryotic cells have that prokaryotic cells lack?
nucleus and internal membrane-bound organelles
What are cellular membranes made out of?
phospholipids in a liposome shape
What is a liposome?
Polar heads and nonpolar tails of lipids associate with one another in a bilayer
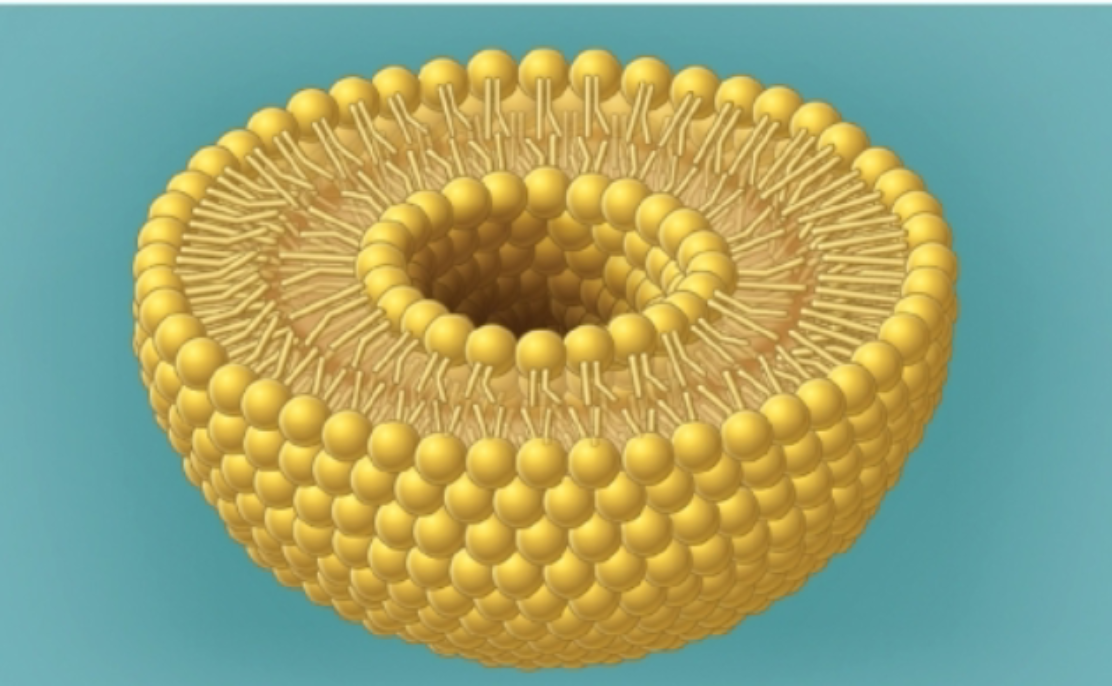
What is the importance of a selectively permeable membrane?
Allows for only certain substances to pass through while blocking others.
What molecules can pass right through the cellular membrane?
hydrophobic (nonpolar) ones
What molecules can pass through with the help of membrane proteins but without the expenditure of energy?
small polar ones
What molecules require the expenditure of energy to cross the membrane?
Large polar ones
How do hydrophobic (polar) molecules pass through the membrane?
easily, through simple diffusion.
The phospholipid bilayer’s hydrophobic tails ______ water-soluble and charged substances from passing freely
prevent
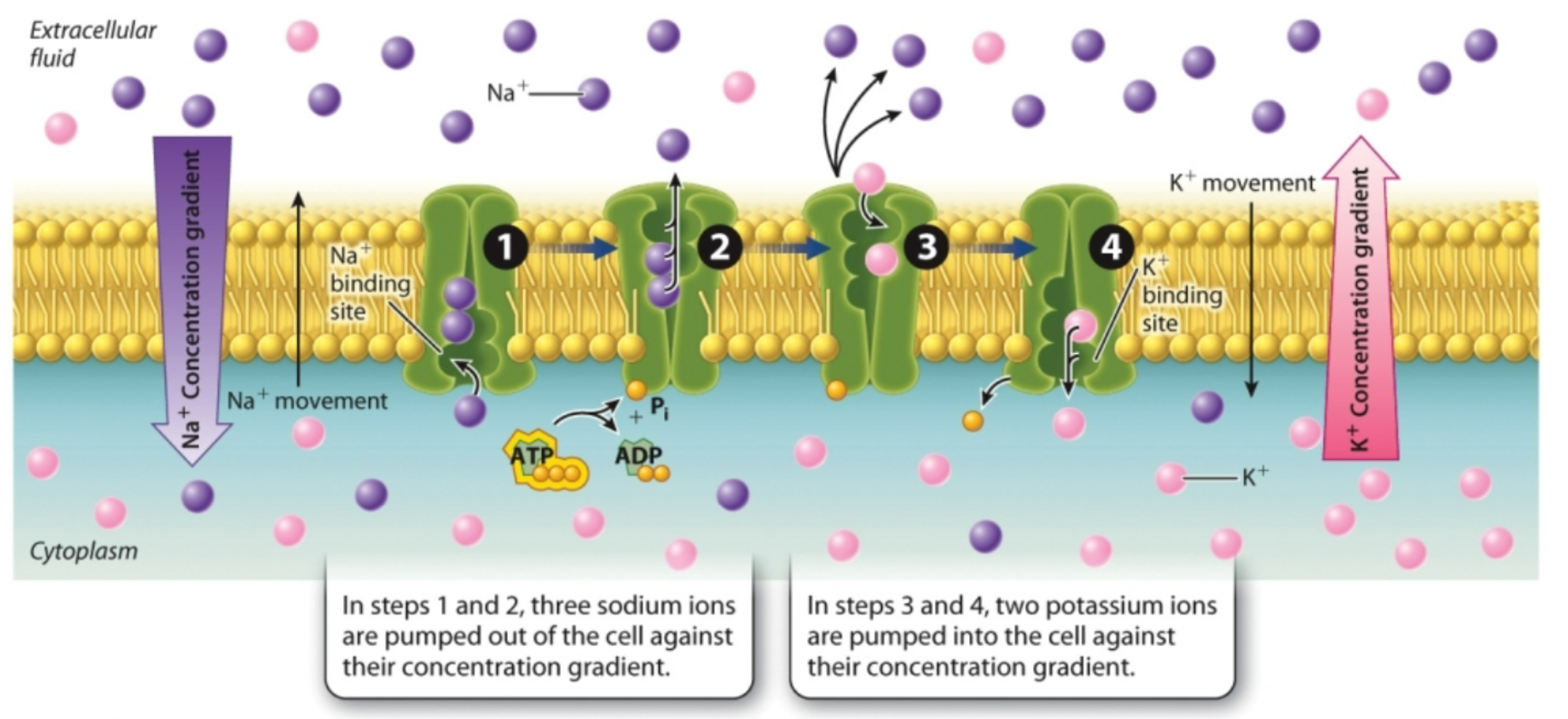
What is active transport?
Moves substances against their concentration gradients, requires ATP, performed by specific proteins embedded in the membrane (pumps)
What is passive transport?
molecules move across the cell membrane without expending energy, driven by the concentration gradient (high to low concentration)
Passive transport examples
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
transport proteins speed the passive movement of molecules across the plasma membrane
Tonicity
The ratio of solute concentration inside the cell vs outside the cell
Isotonic Solution
Solute concentration is the same as that inside the cell; no net movement across the membrane
Hypotonic Solution
Solute concentration is less than inside the cell; cell gains water
Hypertonic Solution
Solute concentration is greater than that inside the cell; cell looses water
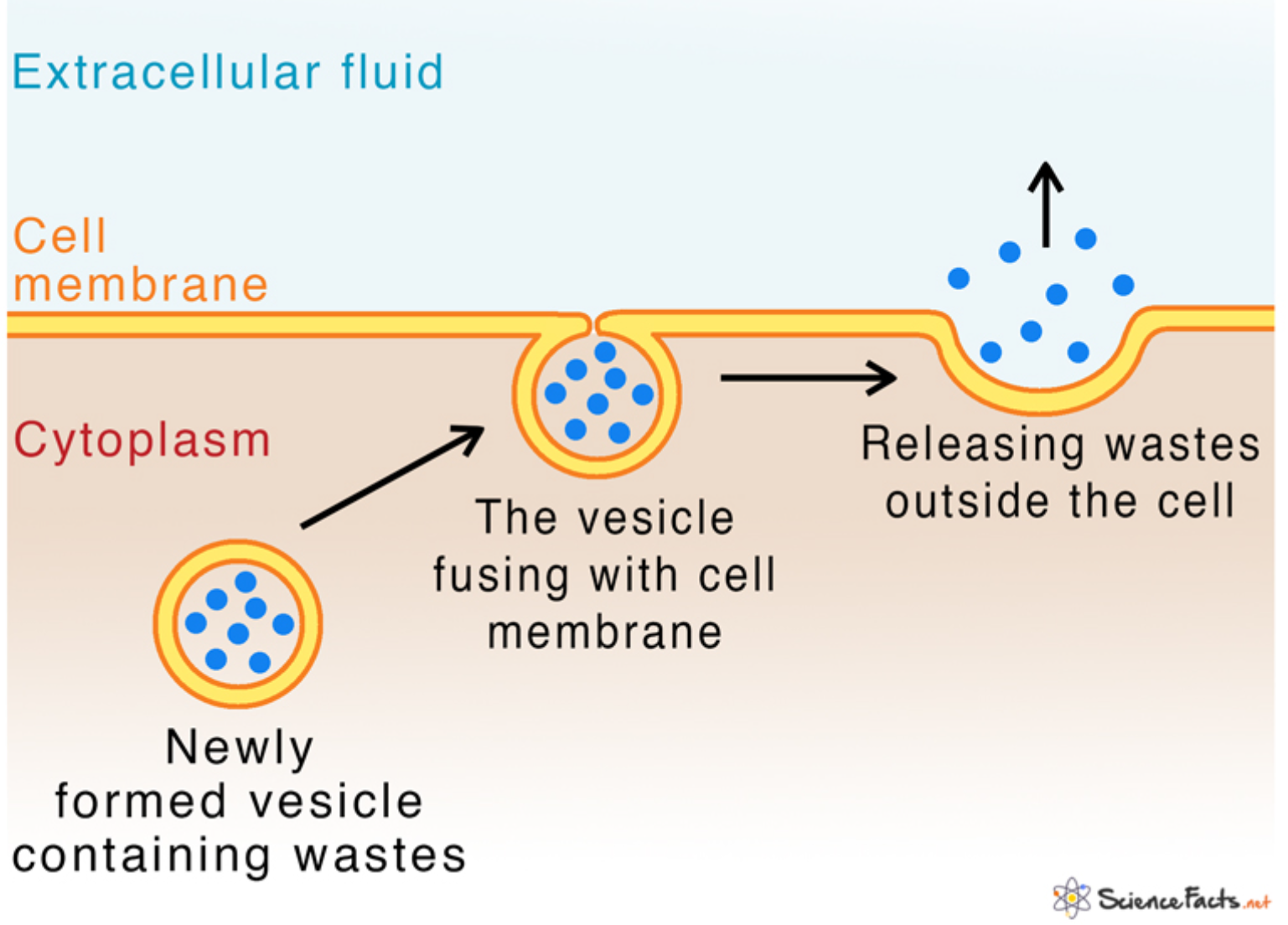
Exocytosis
transport vesicles migrate to the membrane, fuse with it, and release their contents
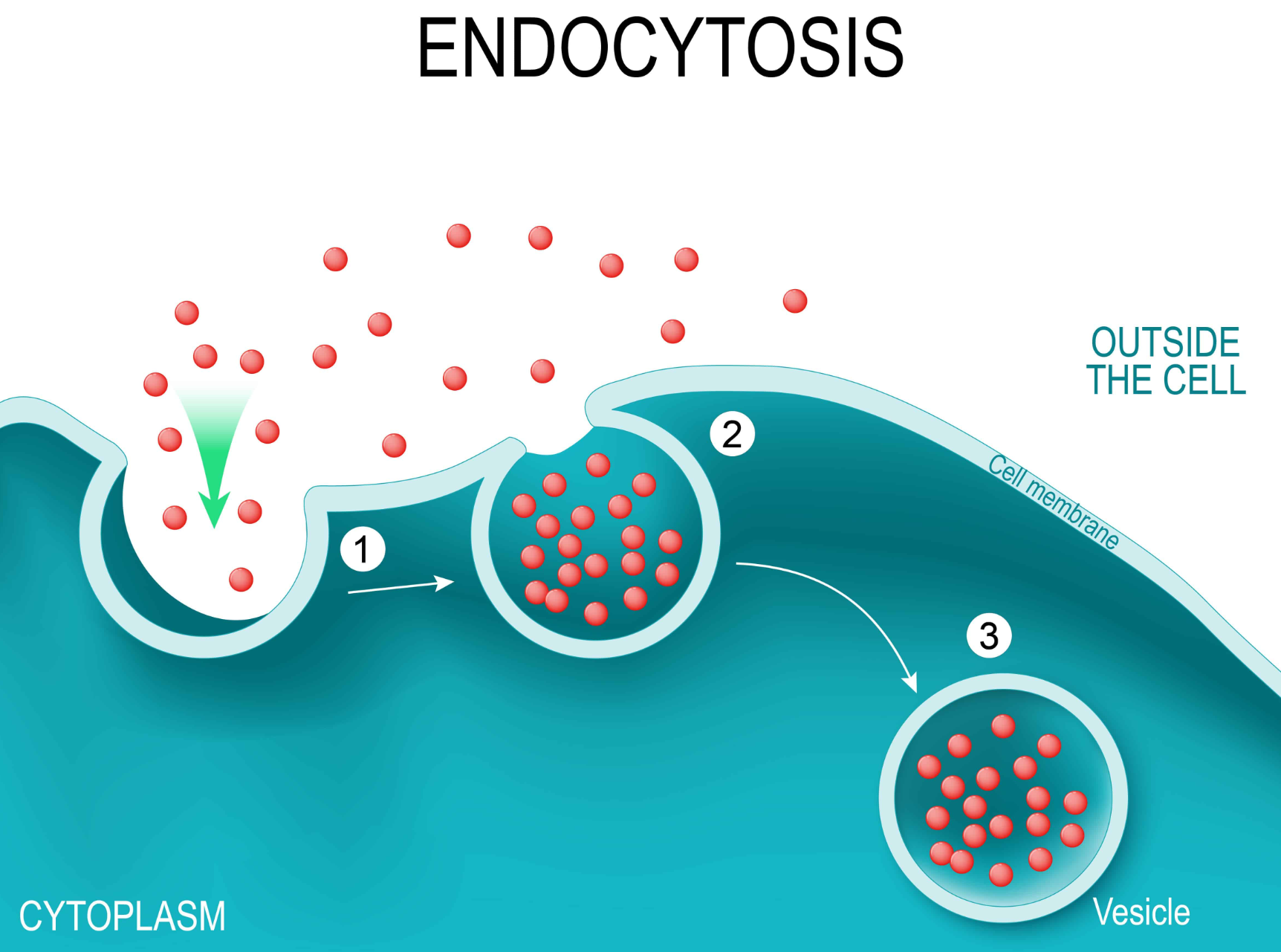
Endocytosis
The cell takes in macromolecules by forming vesicles from the plasma membrane
Bulk Transport
Endocytosis, exocytosis, requires energy
Endomembrane system
has separate cell structures that allow specific functions to take place within defined places in the cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Associated with ribosomes, which help with protein synthesis and modification
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Lacks ribosomes, primary sight of lipid synthesis
Golgi Apparatus
cisternae carry proteins or modified sugars to the membrane or organelles, enzymes chemically modify proteins and lipids
Lysosomes
vesicles derived from Golgi, degrade damaged or unneeded macromolecules, maintain a pH of 5, contain hydrolytic enzymes that break down molecules
What do mitochondria and chloroplasts have in common?
not included in endomembrane system, grow and multiply independently from rest of the cell, contain their own DNA in circular genomes
Mitochondria
convert chemical potential energy from organic molecules (sugar, fat) into ATP
Chloroplasts
Capture energy from sunlight to convert CO2 gas into larger organic molecules