Chapter 1 - Terminology, Positioning, and Imaging Principles
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Distinguish the difference between “projection” and “position”.
Projection refers to the path or direction of the central ray, projecting an image onto an IR.
Position refers to the patient’s general physical position (supine, recumbent, prone, erect, etc.)
_________ refers to the back half of the patient, or the part of the body seen when the person is viewed from the back.
posterior (or dorsal)
__________ refers to the front half of the patient, or the part seen when viewed from the front.
anterior (or ventral)
What projection involves the central ray entering the anterior side and exiting the posterior side of the body?
anteroposterior (AP)
What projection involves the central ray entering the posterior side and exiting the anterior side of the body?
posteroanterior (PA)
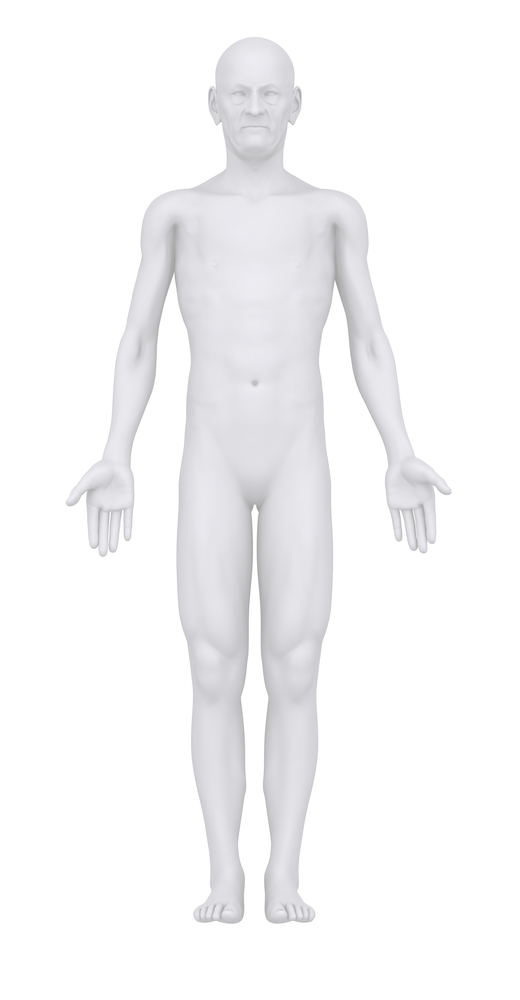
The following image describes the body in __________________.
anatomical position
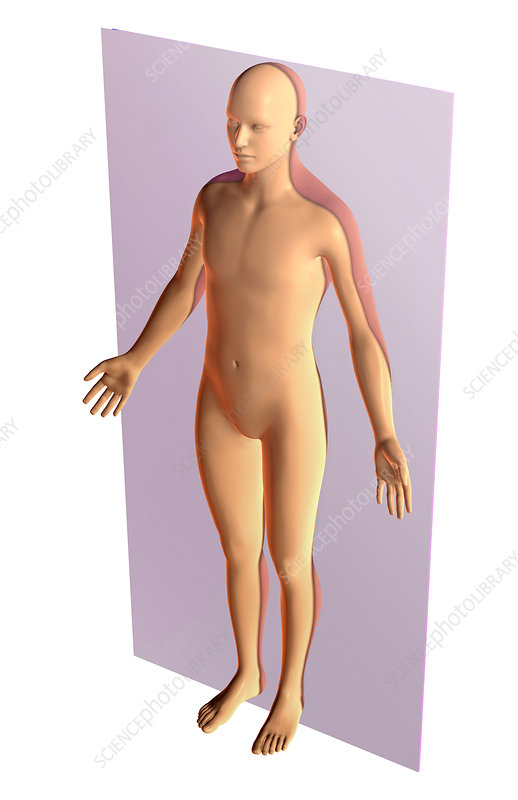

The plane in the following image is the _______________.
coronal plane
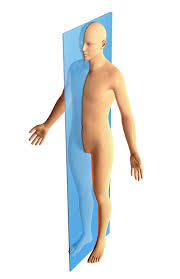
The plane in the following image is the ________________.
sagittal plane
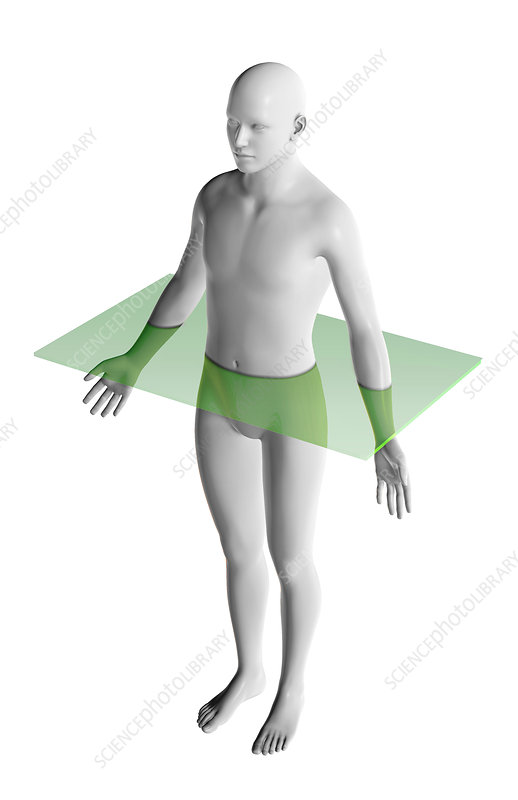

The plane in the following image is the ________________.
horizontal/transverse plane (or axial)
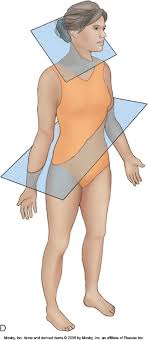
The plane(s) in the following image is the ________________.
oblique plane
The _______ angle in radiographic imaging is when the X-ray tube is angled toward the patient’s head.
cephalic angle
The _______ angle in radiographic imaging is when the X-ray tube is angled toward the patient’s feet.
caudad/caudal angle
What are the 8 general body positions used in radiographic imaging?
Supine - lying on back
Prone - lying on abdomen
Erect - an upright position (standing or sitting upright)
Recumbent - lying down in any position
Trendelenburg - recumbent position with the body tilted, head higher than the feet
Reverse Trendelenburg - recumbent position with the body tilted, feet higher than the head
Left lateral recumbent or Modified Sim’s Position - (for enema tip insertion)
Lithotomy - a recumbent position with knees and hip flexed and thighs abducted and rotated externally, supported by ankle supports (mainly used for urinary studies)
When a patient is in a dorsal decubitus position, the patient is lying on their ______.
back
What position is described when a patient is lying down and the central ray is horizontal?
decubitus
Decubitus positions are primarily for checking what?
checking air-fluid levels or free air in a body cavity, such as the chest or abdomen
When the body is divided into unequal right and left halves, which plane is being used?
sagittal plane
What term describes the movement of an extremity towards the midline of the body?
adduction
What term is used when the hand is turned over with the palm facing downward?
pronation
When the body is divided into equal anterior and posterior portions, which plane is being used?
mid-coronal plane
During a radiographic examination, a patient is asked to rotate their leg towards the midline of their body. What is the proper term for this movement?
medial rotation
Which plane divides the body into a superior portion and inferior portion?
transverse plane
In a 45-degree left anterior oblique (LAO) position, which side of the body is closest to the image receptor (IR)?
left anterior side
The midsagittal plane divides the body into…
equal right and left halves
A radiographic technologist positions a patient’s arm so that it is moving away from the midline of the body. Which term best describes this movement?
abduction
What is the term used to describe rolling a patient’s extremity away from the midline of the body?
lateral rotation
In the anatomical position, are the hands considered supinated or pronated?
supinated
How many bones are there in the adult axial skeleton?
80
How many individual body systems comprise the human body?
10 total systems
Skeletal
Circulatory
Digestive
Respiratory
Urinary
Reproductive
Nervous
Muscular
Endocrine
Integumentary
How many separate bones are found in the adult human body?
206
Movement in the form of a circle is the definition of __________.
circumduction
The position in which the head is lower than the feet is the ___________ position.
Trendelenburg
Define ipsilateral.
“on the same side of the body or part”
What is the term that describes lying down in any position"?
recumbent
What are the two divisions of the skeletal system?
Axial skeleton - includes the skull, vertebral column, ribs, and sternum (80 total bones for adults)
Appendicular skeleton - consists of all the bones in the upper and lower limbs/extremities, including the shoulder and pelvic girdles (126 total bones for adults)
The ______ refers to the sole or posterior surface of the foot.
plantar
_______ refers to the top or anterior surface of the foot.
dorsal
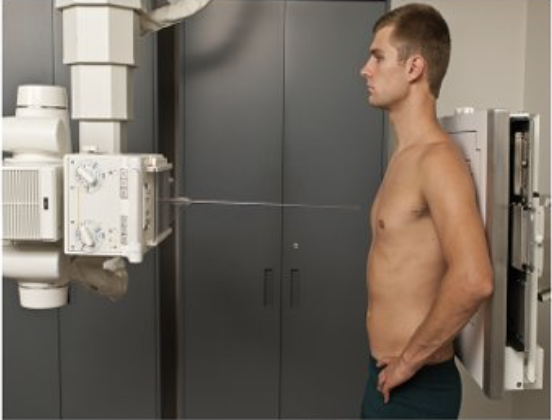
Describe this projection.
anteroposterior (AP)
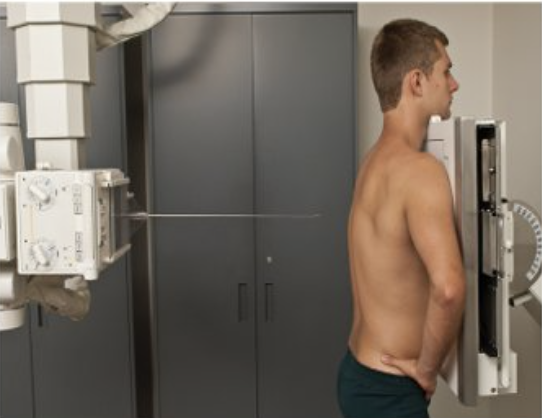
Describe this projection.
posteroanterior (PA)
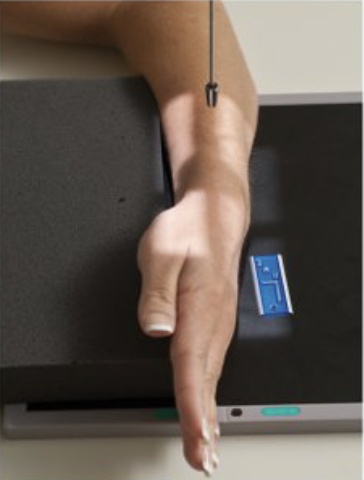
Describe this projection.
lateromedial projection (wrist)
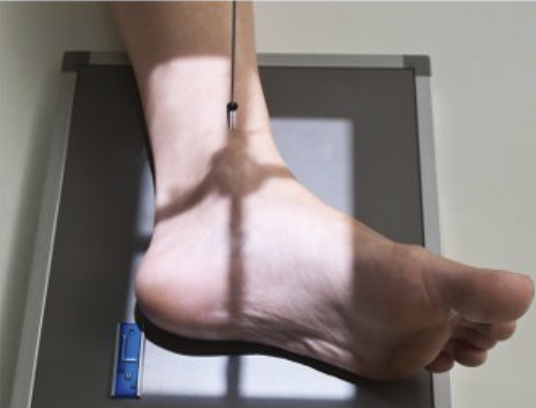
Describe this projection.
mediolateral projection (ankle)
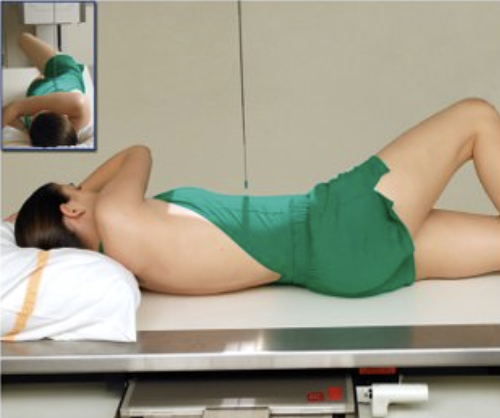
Describe this position.
recumbent left posterior oblique (LPO)
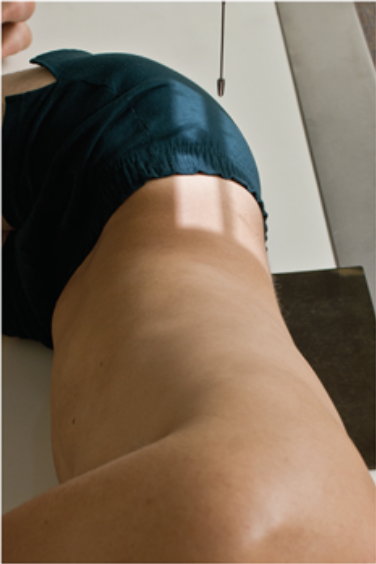
Describe this position.
recumbent left lateral position

Describe this position.
erect right lateral position
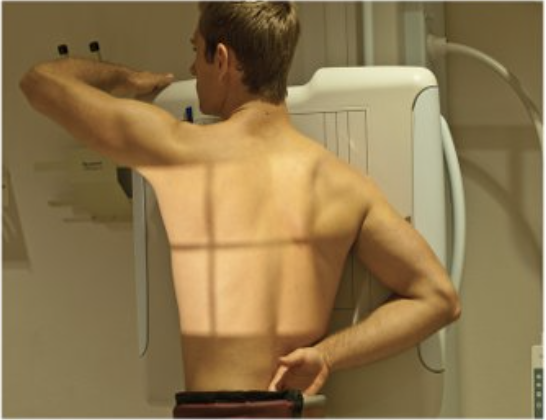
Describe this position.
erect right anterior oblique position
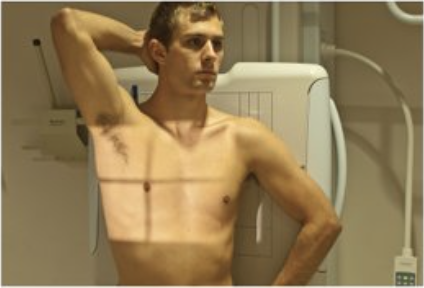
Describe this position.
erect left posterior oblique position
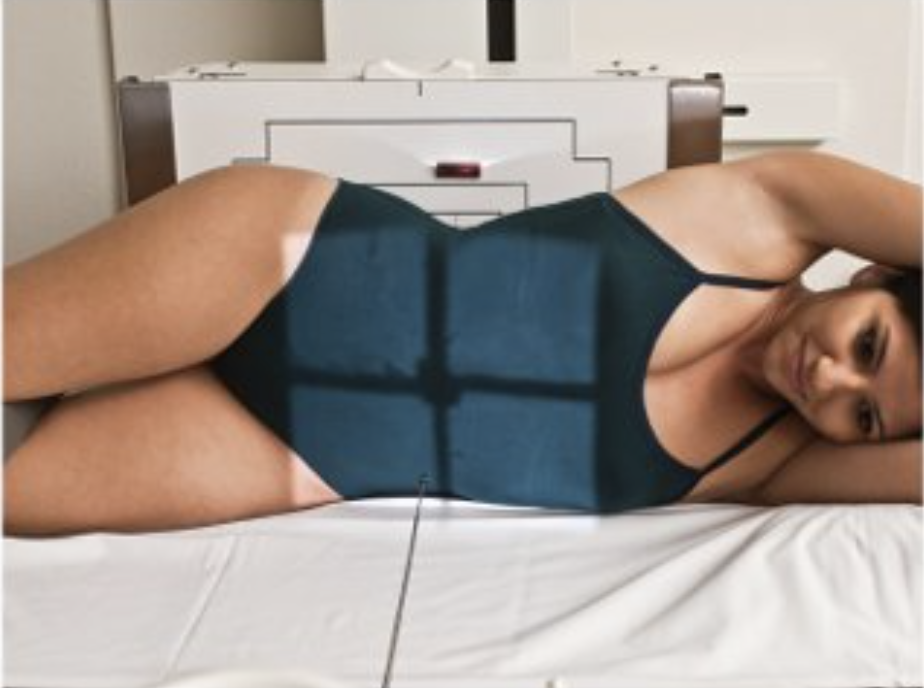

Describe this position.
left lateral decubitus position
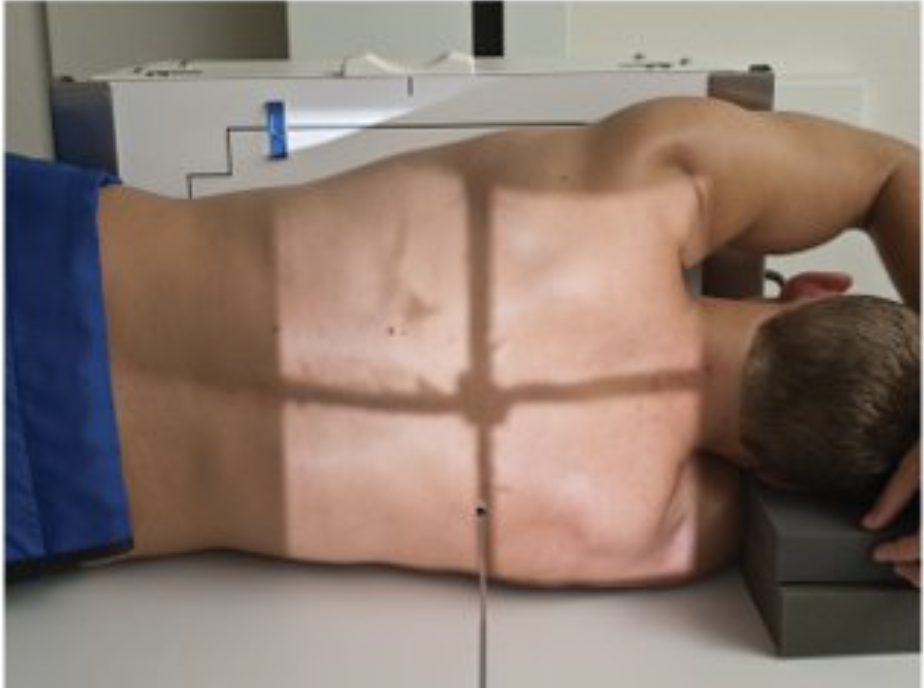
Describe this position.
right lateral decubitus position
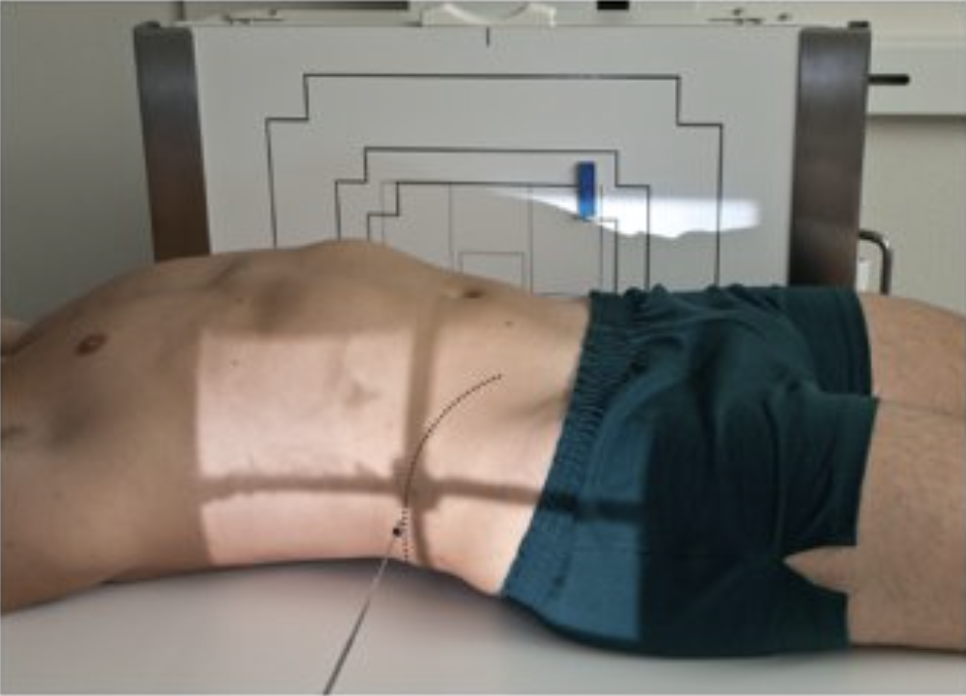
Describe this position.
dorsal decubitus position
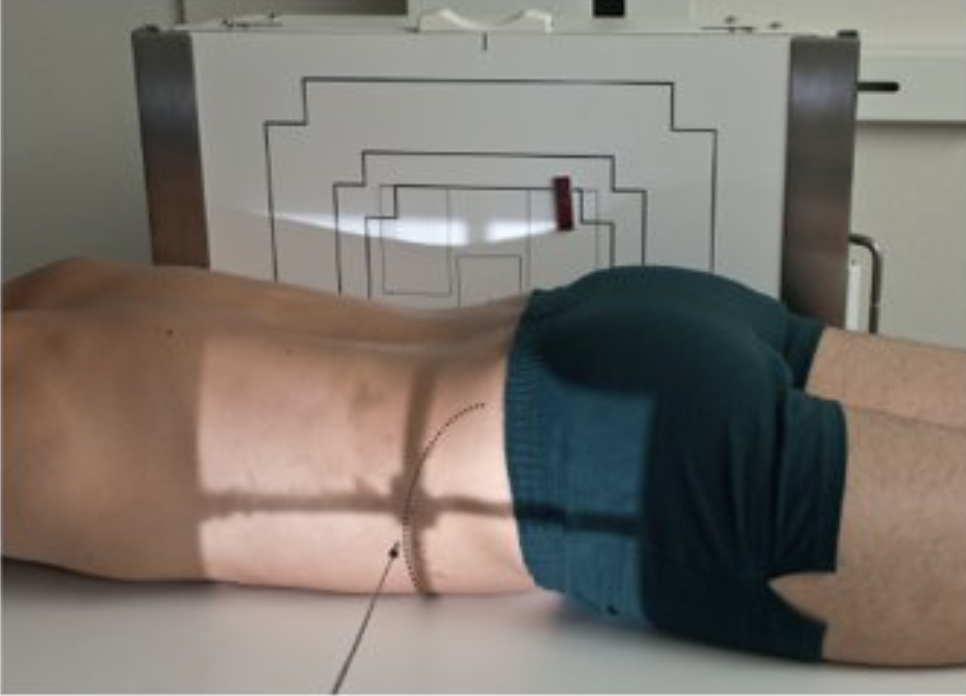
Describe this position.
ventral decubitus position
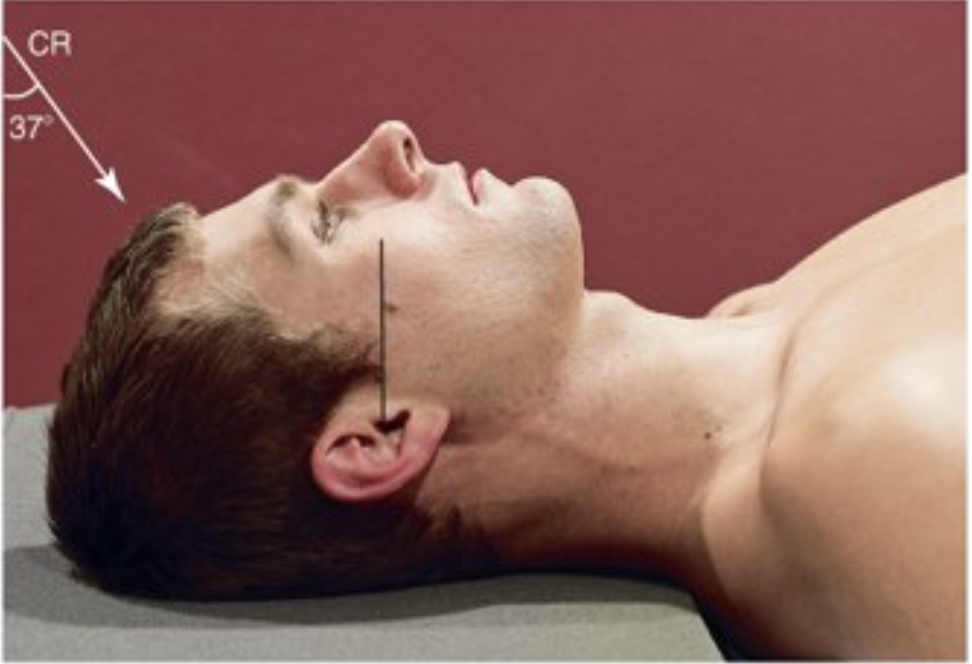
Describe this special projection.
AP axial (semi-axial) projection
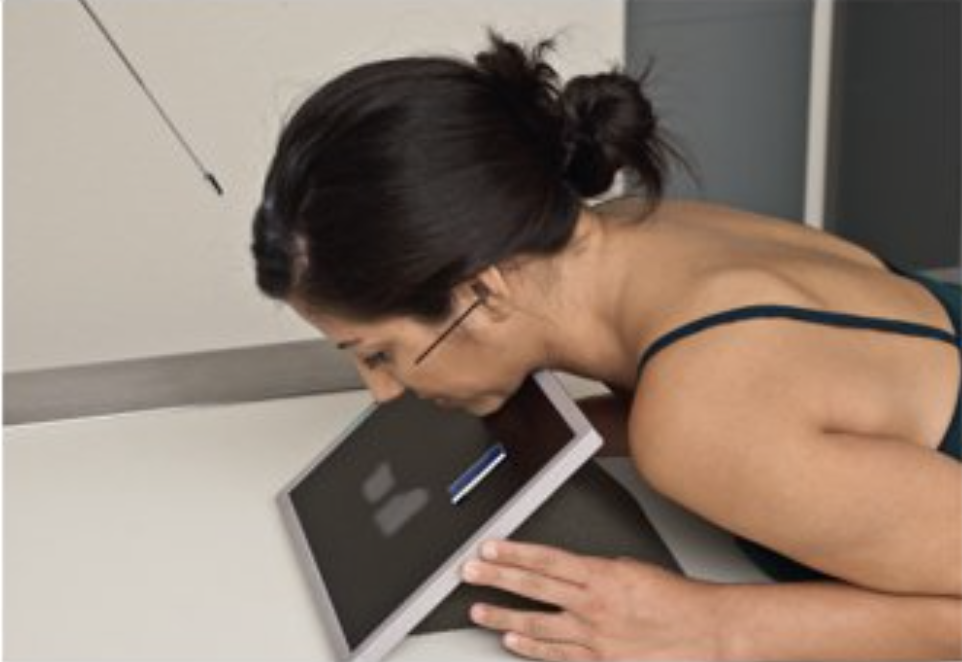

Describe this special projection.
superoinferior axial projection
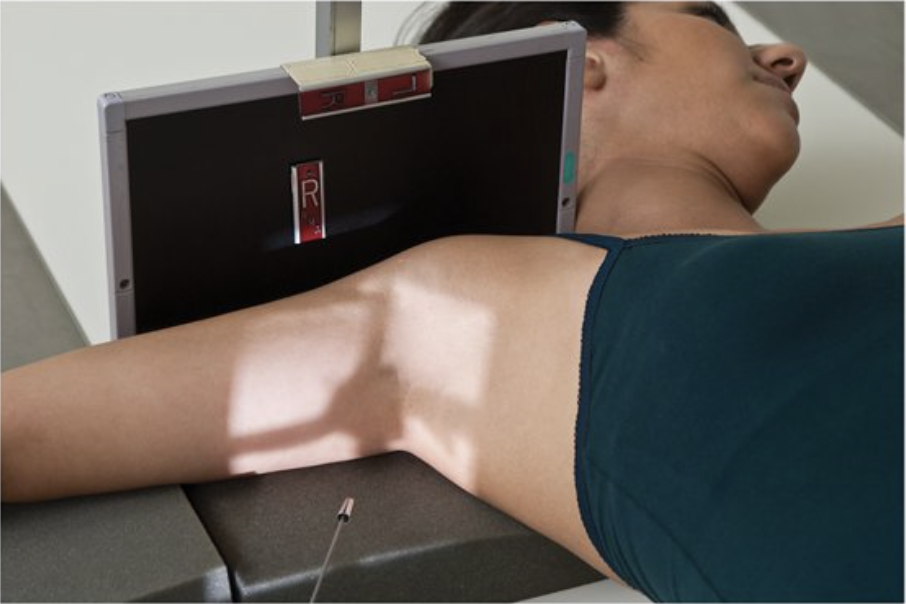
Describe this special projection.
inferosuperior axial projection
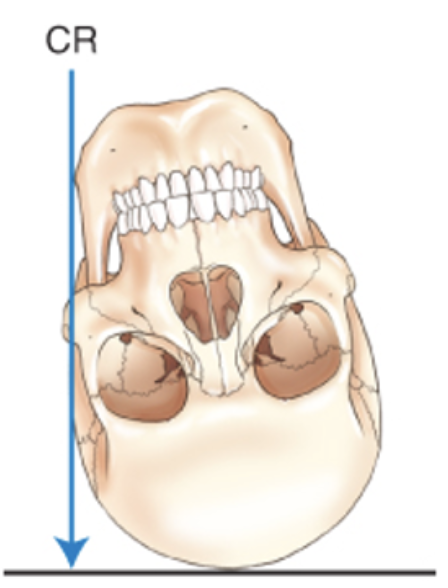
Describe this special projection.
tangential projection
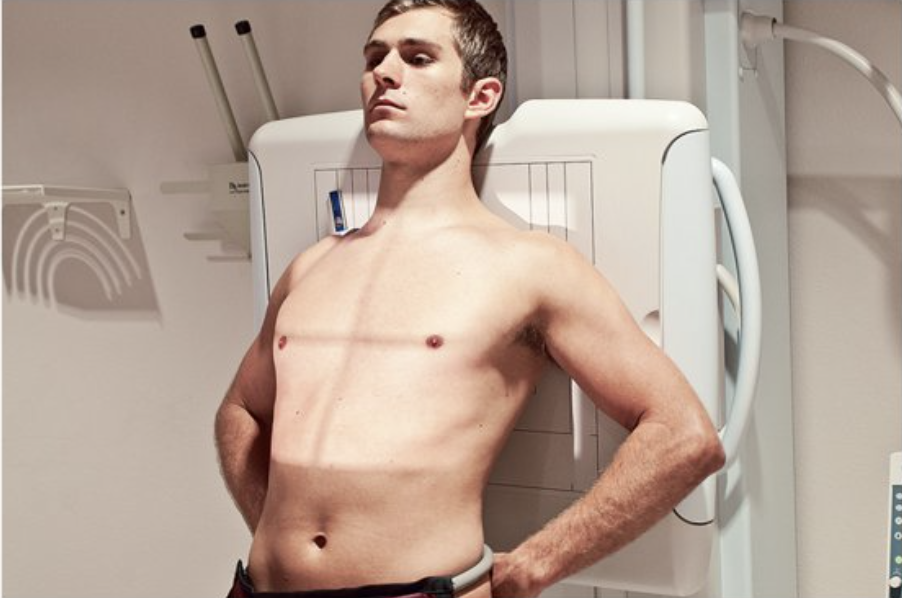
Describe this position.
AP lordotic chest position
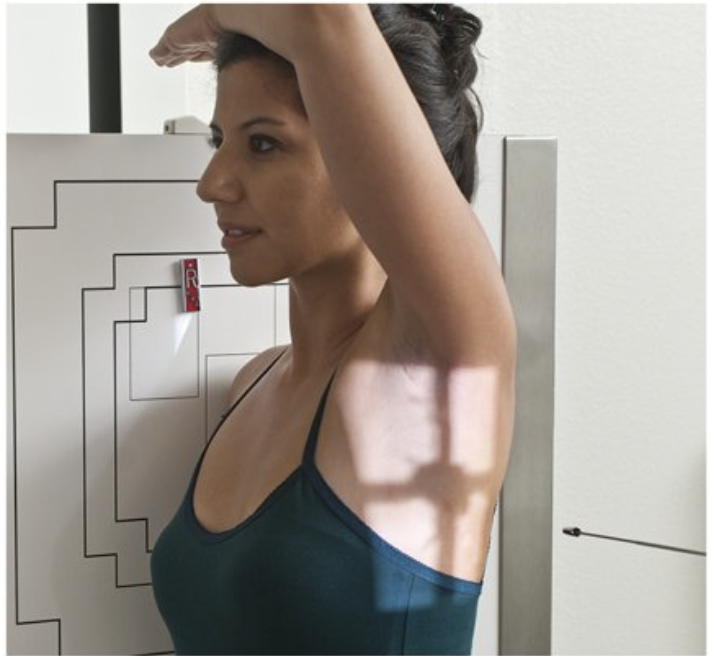

Describe this projection and position.
transthoracic lateral shoulder projection (right lateral shoulder position)
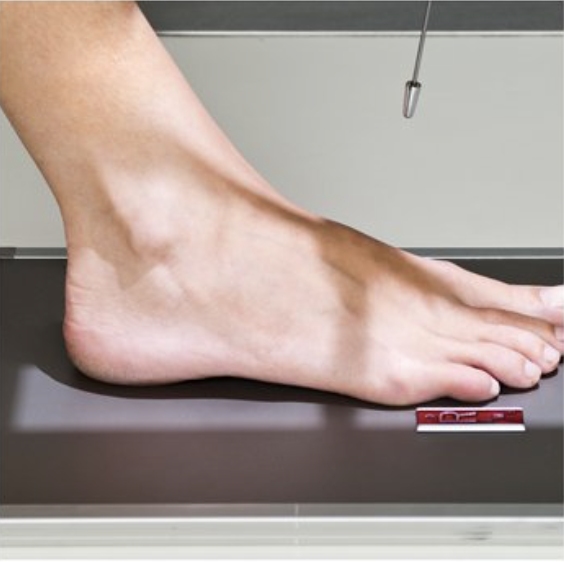
Describe this projection.
AP or dorsoplantar (DP) projection of foot
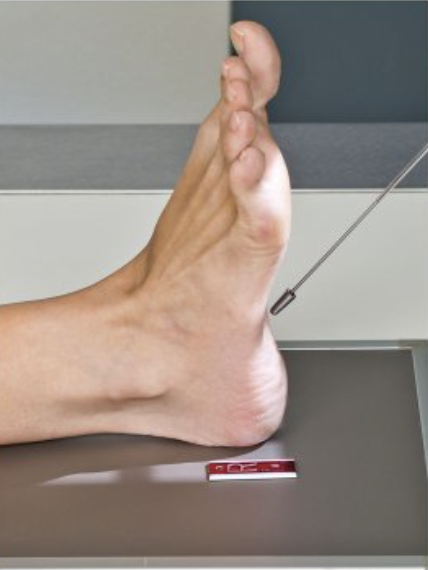
Describe this projection.
axial plantodorsal (PD) projection of calcaneus
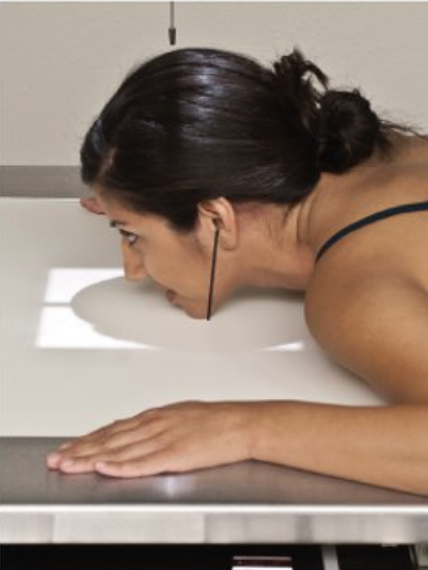

Describe this unique projection.
parietocanthial projection (PA Waters position)
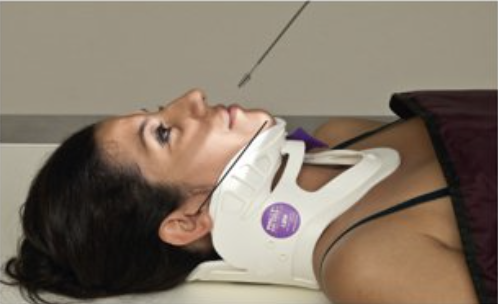
Describe this unique projection
acanthioparietal projection
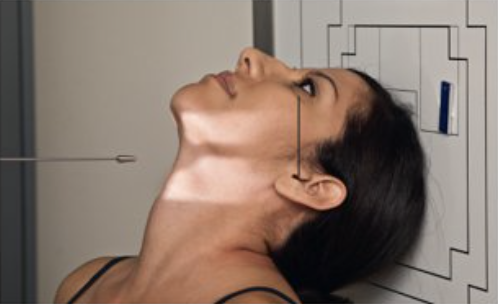
Describe this unique projection.
submentovertical (SMV) projection
________ refers to near the source or beginning, and ________ is away from.
proximal, distal
________ describes an abnormal position in which a part or limb is forced outward from the midline of the body.
valgus
________ describes an abnormal position in which a part or limb is forced inward toward the midline of the body.
varus
_______________ is extending a joint beyond the straight or neutral position.
hyperextension
________ decreases the angle of the joint.
flexion
_________ increases the angle as the body part moves from a flexed to a straightened position.
extension
____________ is to turn or bend the hand and wrist from the natural position toward the ulnar side of the wrist.
ulnar deviation
____________ is to turn or bend the hand and wrist from the natural position toward the radial side of the wrist.
radial deviation
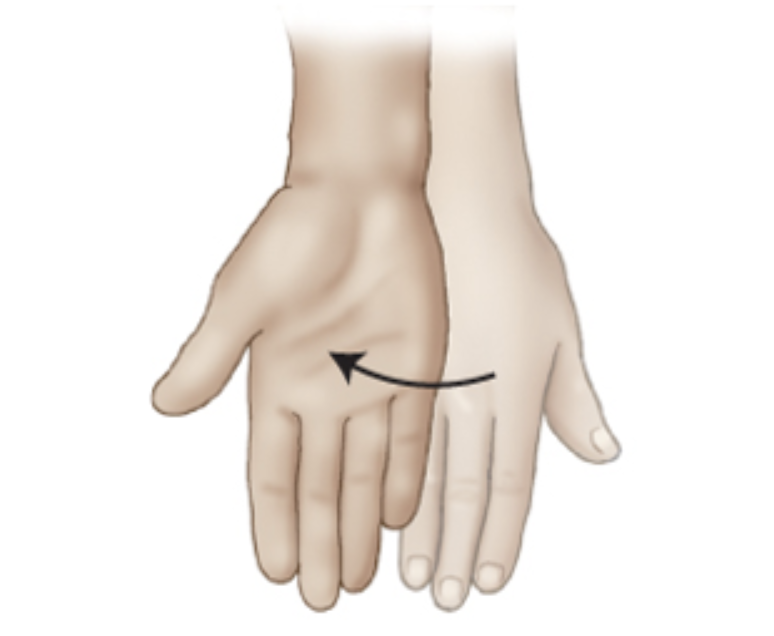
___________ is a rotational movement of the hand into the anatomic position.
supination
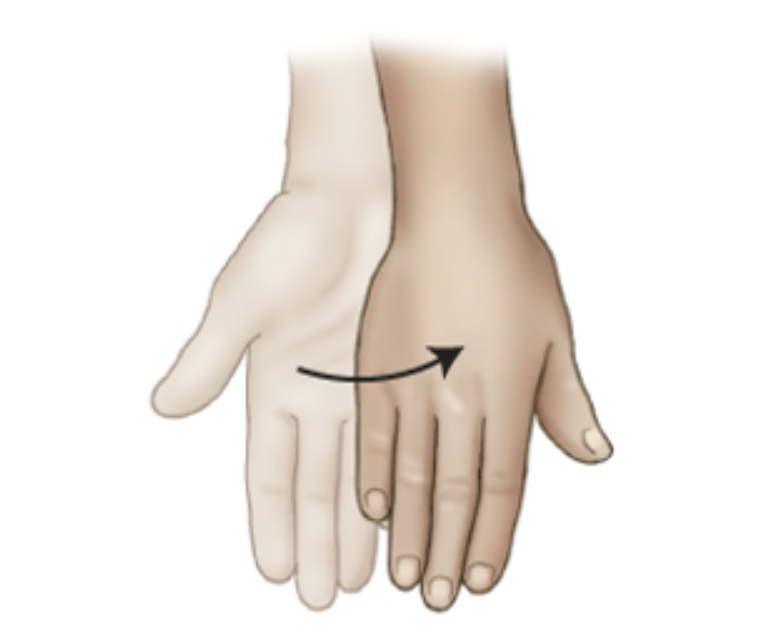
__________ is a rotation of the hand into the opposite of the anatomic position.
pronation
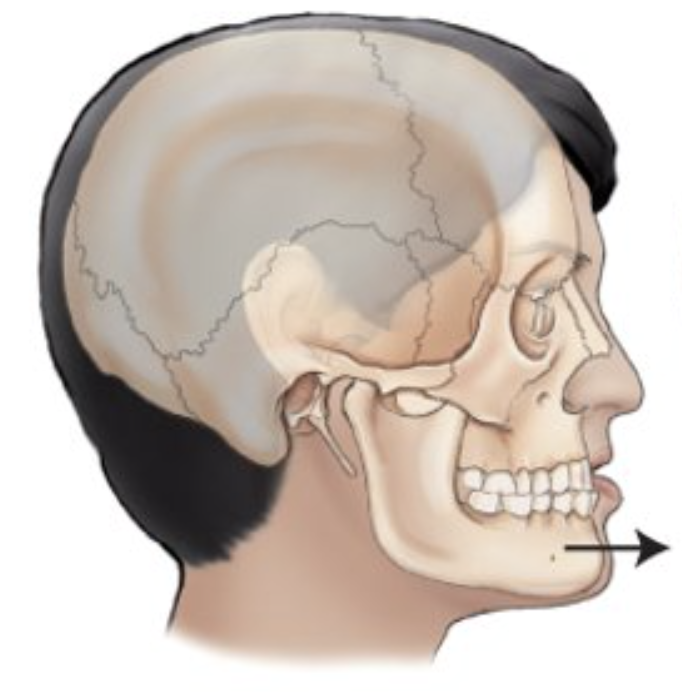
___________ is a movement forward from a normal position.
protraction
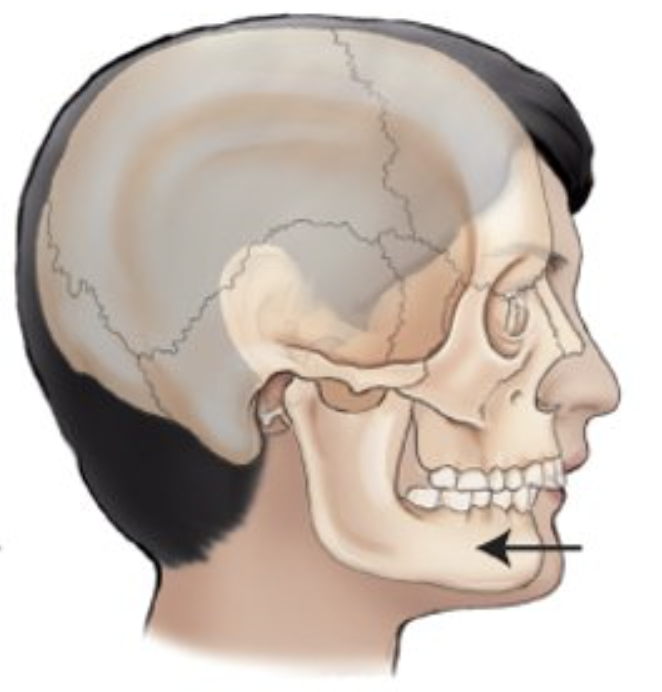
__________ is movement backward or condition of being drawn back.
retraction
True or False: Anatomic side markers are legally required in all radiographic images.
True
What is the minimum number of projections that should be taken for most radiographic procedures?
2 projections minimum
What is the minimum number of projections that should be taken when joints are of interest?
3 projections minimum
Define palpation.
the process of applying light pressure with the fingertips directly on the patient to locate positioning landmarks
_____________ is nearer the skin surface, _______ is farther away.
superficial, deep
What are the 3 types of functional joints?
Synarthrosis (immovable joint)
Amphiarthrosis (joint with limited movement)
Diarthrosis (freely movable joint)
What are the 4 main classifications of bones?
Long bones
Short bones
Flat bones
Irregular bones
Sesamoid bones are not counted toward the axial or appendicular skeleton, except for the patellae.
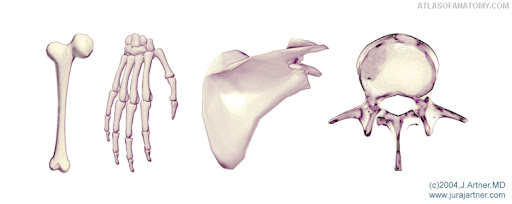
What are the 3 types of structural joints, along with their subclasses?
Fibrous joints
Syndesmosis
Suture
Gomphosis
Cartilaginous joints
Symphysis
Synchondrosis
Synovial joints
What are the 7 movement types of synovial joints?
Plane (gliding) joints
Ginglymus (hinge) joints
Pivot (trochoid) joints
Ellipsoid (condylar) joints
Saddle (sellar) joints
Ball and socket (spheroidal) joints
Bicondylar joints
What does the term dorsum manus refer to?
the posterior surface of the hand
What does the term dorsum pedis refer to?
the anterior surface of the foot
________ is a lifting, raising, or moving of a part superiorly.
elevation
__________ is a letting down, lowering, or moving of a part inferiorly.
depression
Body habitus is classified into what 4 general body styles?
Sthenic - considered to be average in shape and internal organ location. (50% of the population)
Hyposthenic - slenderer than the sthenic body habitus (35% of the population)
Hypersthenic - broader frame than that of the sthenic body habitus (5% of the population)
Asthenic - thin or slender with a long and narrow body build (10% of the population)
What are the 4 basic types of tissue?
Epithelial - tissues that cover internal and external surfaces of the body, including the lining of vessels and organs, such as the stomach and the intestines.
Connective - supportive tissues that bind together and support various structures.
Muscular - tissues that make up the substance of a muscle.
Nervous - tissues that make up the substance of nerves and nerve centers.
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a foot?
3 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a chest?
2 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for the hips?
2 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a forearm?
2 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for an elbow?
3 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a toe(s)?
3 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a hand?
3 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a femur?
2 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for the pelvis, assuming no injury is suspected?
1 projection (AP)
True or False: Post-reduction upper and lower limbs generally require only two projections for checking fracture alignment.
True
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a wrist?
3 projections
How many projections (minimum) should be taken for a tibia-fibula?
2 projections