BIOL 1202 Exam 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
1
New cards
Protists are ____.
eukaryotes
2
New cards
Are eukaryotic organelles more or less complex than prokaryotic cell?
more complex
3
New cards
What is the organism that is in most eukaryotic lineages?
protists (unicellular)
4
New cards
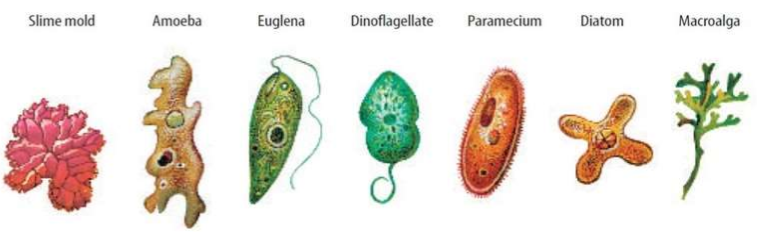
Name these protists from left to right.
Slime mold, amoeba, euglena, dinoflagellate, paramecium, diatom, macroalga
5
New cards
Photoautotroups
contain chloroplasts
6
New cards
Heterotrophs
absorb organic molecules or ingest food
7
New cards
Mixotrophs
combine photosynthesis and heterotrophism
8
New cards
How do protists reproduce?
sexually and asexually
9
New cards
What four groups are all eukaryotes (including) protists separated into?
excavata, SAR (stramenopiles, alveolates, and rhizarians), archaeplastida, unikonta
10
New cards
Endosymbiosis
a relationship between two species in which one organism lives inside the cell or cells of the other organism (the host)
11
New cards
What is derived from prokaryotes and how?
mitochondria and plastids, prokaryotes were engulfed by ancestors of early eukaryotic cells
12
New cards
What specifically did mitochondria evolve from?
endosymbiosis of an alpha proteobacterium
13
New cards
What specifically did plastids evolve from?
endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic cyanobacteria
14
New cards
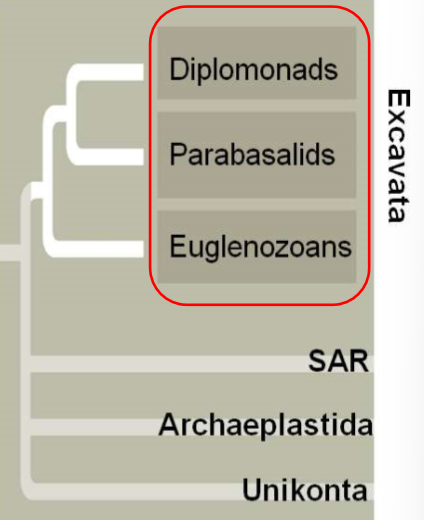
Excavata
diplomonads, parabasalids, euglenozoans
15
New cards
Why was this group given the name excavata?
some members have an “excavated” feeding grove on one side of the body
16
New cards
What is unique about diplomonads and parabasalids?
they lack plastids and have modified mitochondria; most live in aerobic environments
17
New cards
Diplomonads
mitochondria called mitosomes, derive energy from anaerobic biochemical pathways, are often parasites
18
New cards
Parabasalids
have a reduced mitochondria called hydrogenosomes, generate some energy anaerobically
19
New cards
Trichomonas vaginalis
a sexually transmitted parasite
20
New cards
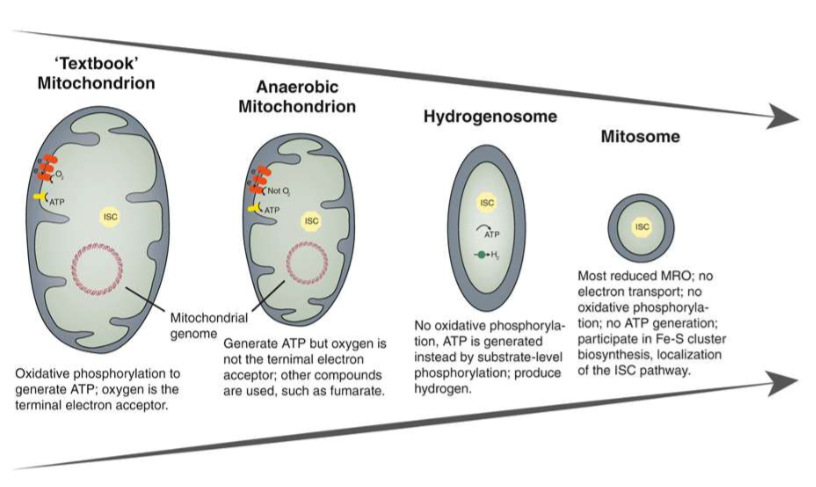
Name these from left to right.
“textbook” mitochondrion, anaerobic mitochondrion, hydrogenosome, mitosome
21
New cards
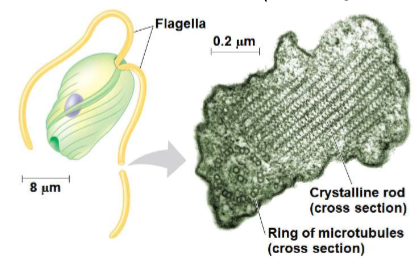
What is unique about euglenozoans?
they have a spiral or crystalline rode inside their flagella
22
New cards
Euglenozoans
predatory heterotrophs, photosynthetic autotrophs, mixotrophs, and parasites
23
New cards
What is unique about kinetoplastids?
have a single mitochondrion with an organized mass of DNA called kintoplast
24
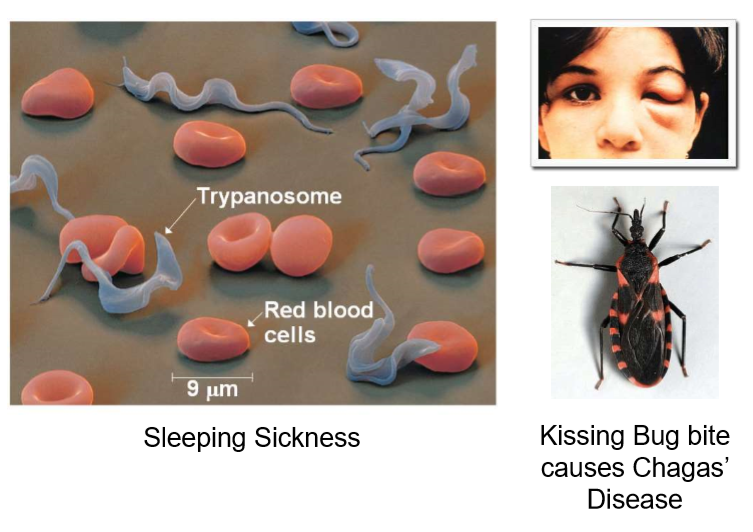
New cards
Trypanosomes
evade host immune responses by producing cell-surface proteins with different molecular structures in each generation
25
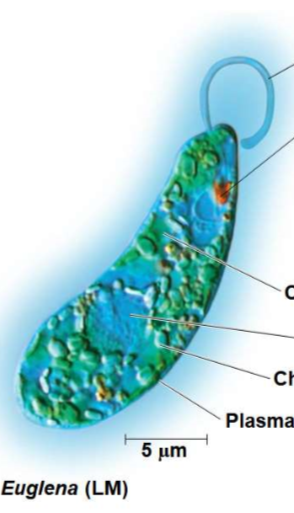
New cards
Euglenids
can be autotrophic or heterotrophic
26
New cards
SAR
stramenopiles, alveolates, rhizarians
27
New cards
Stramenopiles
photosynthetic organisms, examples are diatoms, golden algae, and brown algae
28
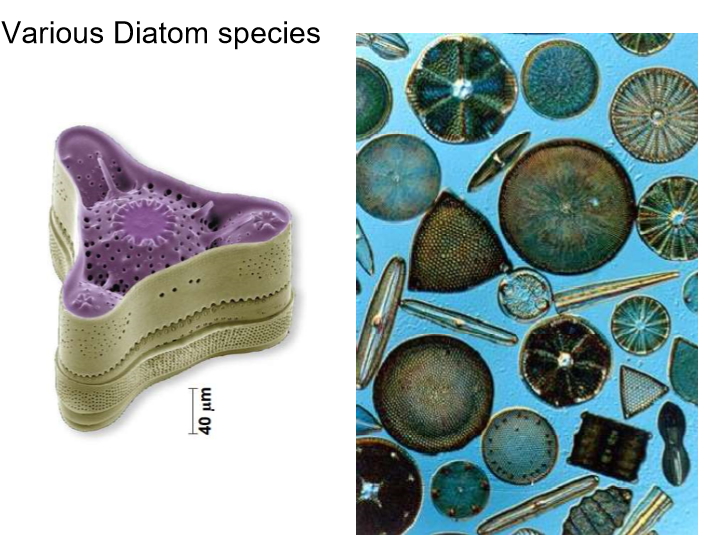
New cards
Diatoms
unicellular algae
29
New cards
Brown algae
largest and most complex algae; multicellular and often marine (seaweed)
30
New cards
Alveolates
dinoflagellates, apicomplexans, ciliates
31
New cards
Dinoflagellates
aquatic phototrophs, mixotrophs, and heterotrophs (“red tides”)
32
New cards
Apicomplexans
parasites of animals, spread as sporozoites (Plasmodium causes malaria)
33
New cards
Ciliates
a large varied group of protists
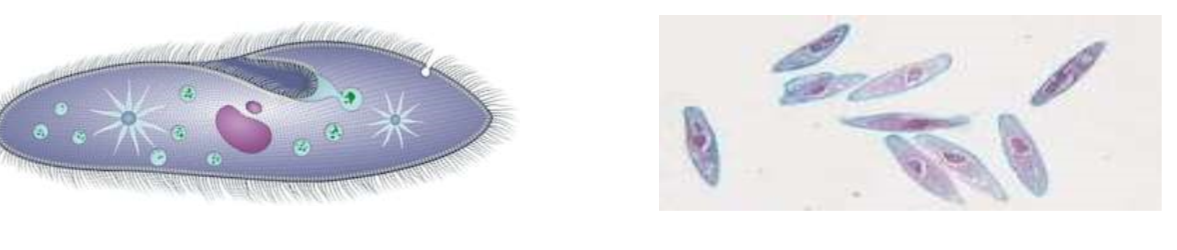
34
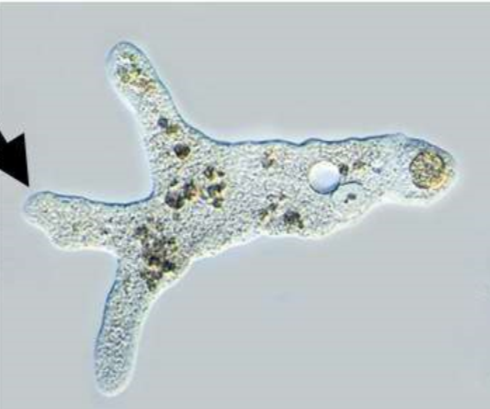
New cards
Rhizarians
many are amoebas, protists
35
New cards
What do rhizarians consist of?
radiolarians, forams, cerrozoans
36
New cards
Radiolarians
mostly marine protists
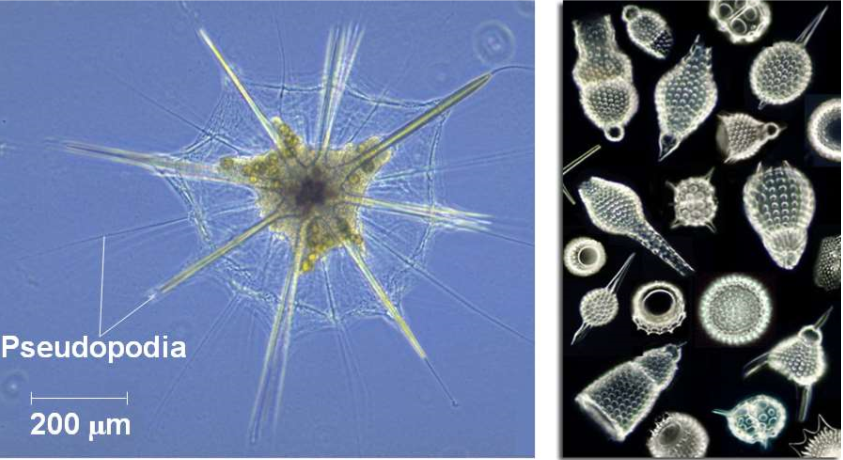
37
New cards
Forams
named for their porous shells called “tests”, made of calcium carbonate (seashells)
38
New cards
Archaeplastida
red algae, green algae, and plants
39
New cards
Unikonta
animals, fungi, and some protists; includes two clades (amoebozoans and opisthokonts)
40
New cards
Amoebozoans
lobe or tube-shaped amoebas (slime molds, tubulinids, and entamoebas)

41
New cards

Slime mold A
Plasmodial slime molds (unicellular)
42
New cards

Slime mold B
Cellular slime molds (motile)
43
New cards
Tubulinids
unicellular protists, heterotrophic
44
New cards
Entamoebas
parasites of vertebrates and some invertebrates
45
New cards
Symbiotic protists
some benefit their host and some are parasitic
46
New cards
Photosynthetic producer protists
convert CO2 to organic compounds
47
New cards
When did cyanobacteria and protists likely exist on land?
1\.2 million years ago
48
New cards
When did small plants, fungi, and animals emerge on Earth?
within the last 500 years
49
New cards
Where does Earth’s oxygen come from?
marine microbes, land plants, and macro algae (kelp)
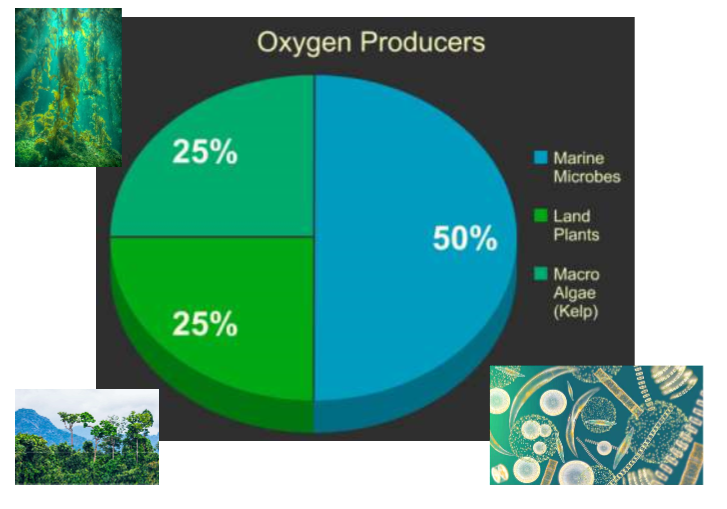
50
New cards
Which plant species produces the most oxygen?
snake plant
51
New cards
What are the closest relatives to plants?
green algae (charophytes); rings of cellulose synthesizing proteins, structure of flagellated sperm, and formation of a phragmoplast
52
New cards
Sporopollenin
a durable polymer layer that prevents zygotes from drying out
53
New cards
What are the benefits for charophytes moving to land?
unfiltered sunlight, more plentiful CO2, and nutrient rich soil
54
New cards
What were the challenges for charophytes moving to land?
scarcity of water and lack of structural support against algae
55
New cards
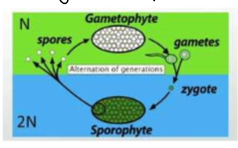
Alteration of Generations
gametophyte generation (haploid and produces haploid gametes by mitosis) and fusion (diploid sporophyte which produces haploid spores by meiosis)
56
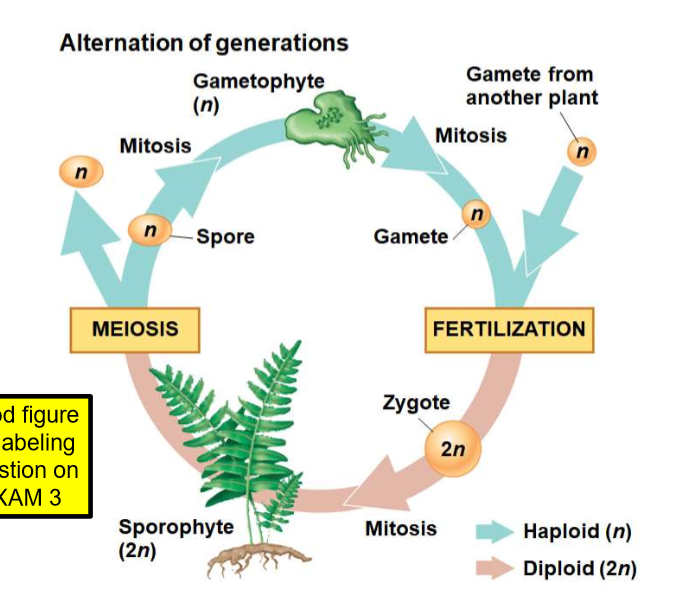
New cards
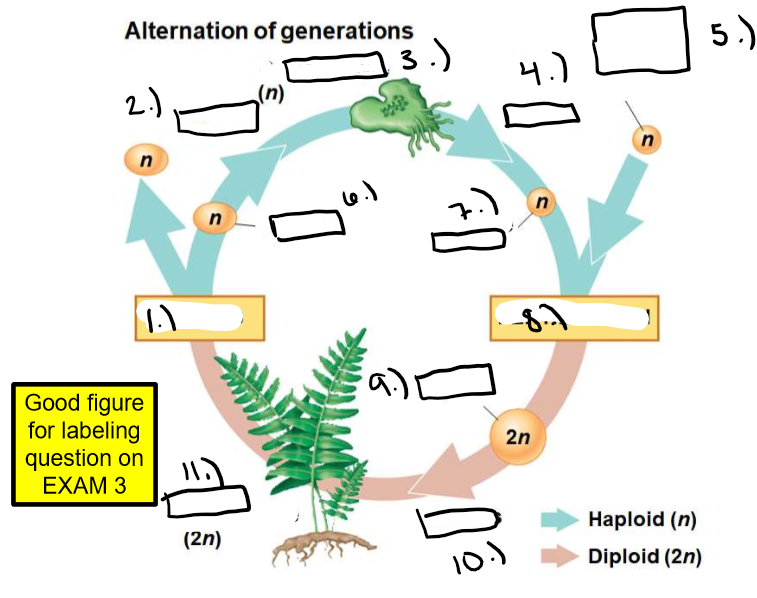
Label this picture
meiosis, fertilization, spore, gametophyte, mitosis, gamete from another plant, spore, gamete, fertilization, zygote, mitosis, sporophyte
57
New cards
How are nutrients transferred from parent to embryo?
placental transfer cells
58
New cards
Why are plants called embryophytes?
because of the dependency of the embryo on the parent
59
New cards
Spoeocytes
diploid cells that undergo meiosis to generate haploid spores
60
New cards
Archegonia
female gametangia, produce a single non-motile egg
61
New cards
Antheridia
male gametangia, produce and release sperm
62
New cards
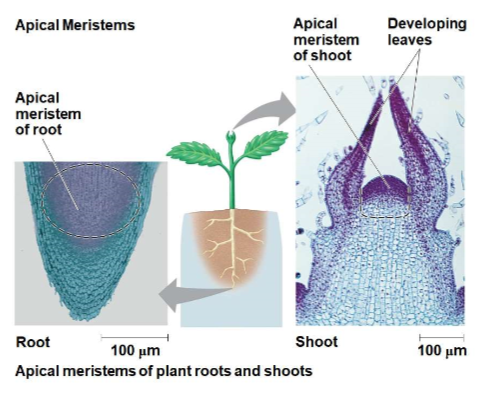
Apical Meristems
within this plants sustain continual growth in length by repeated cell division
63
New cards
Cuticle
a waxy covering of the epidermis
64
New cards
Stomata and Guard cells
specialized cells that allow for gas exchange between the outside air and the plant
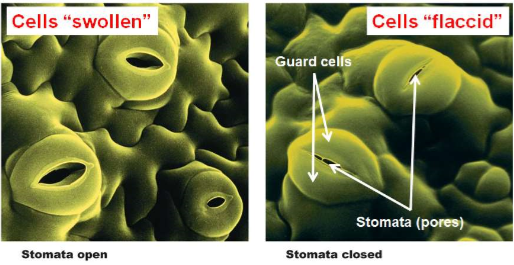
65
New cards
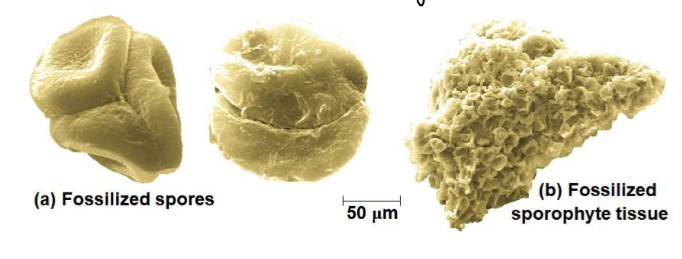
What do the appearance of plant spores in the fossil record indicate?
that plants colonized land at least 470 million years ago
66
New cards
Vascular tissue
cells joined into tubes for the transport of water and nutrients
67
New cards
Bryophytes
nonvascular plants
68
New cards
Seedless vascular plants
lycophytes (club mosses and their relatives) and monilophytes (ferns and their relatives)
69
New cards
Seed
an embryo and nutrients surrounded by a protective coat
70
New cards
Seeded vascular plants
gymnosperms ('“naked seeds, not in chambers) and angiosperms (“enclosed seeds”, develop inside chambers)
71
New cards
Bryophytes
liverworts, mosses, and hornworts
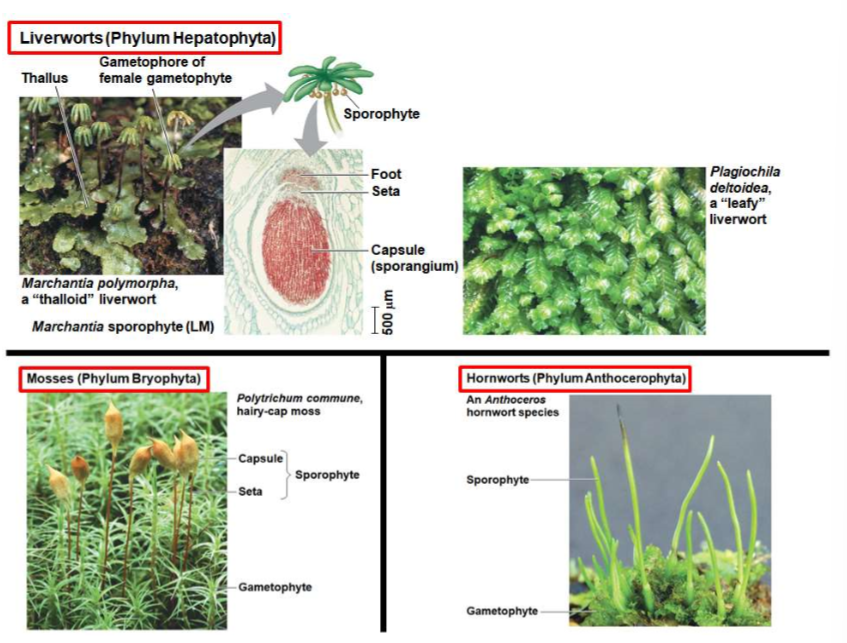
72
New cards

73
New cards
Rhizoids
anchor gametophytes to substrate
74
New cards
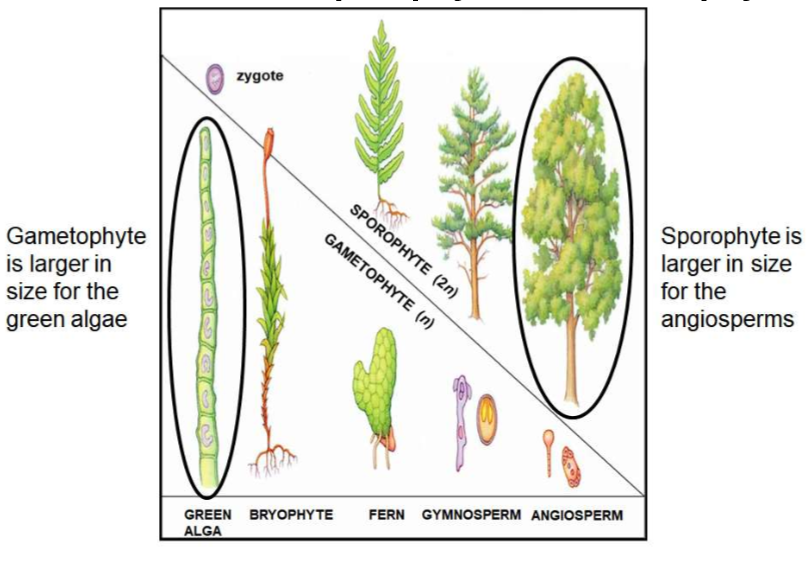
Sporophyte vs. Gametophyte
75
New cards
What does a sporophyte consist of?
a foot, a seta (stalk), and a sporangium (capsule)
76
New cards
What were the prominent types of vegetation during the first 100 million years of plant evolution
bryophytes
77
New cards
What do the earliest fossils of vascular plants date to?
425 million years ago
78
New cards
Xylem
conducts most of the water and minerals and includes tube-shaped cells called tracheids
79
New cards
Lignin
strengthens water conducting cells and provides structural support
80
New cards
Phloem
has cells arranged into tubes that distribute sugars, amino acids, and other organic compounds
81
New cards
Roots
organs that anchor vascular plants, absorb water and nutrients from soil
82
New cards
Leaves
organs that increase the surface area of vascular plants, maximizing photosynthesis
83
New cards
Microphylls
small leaves with a single vein
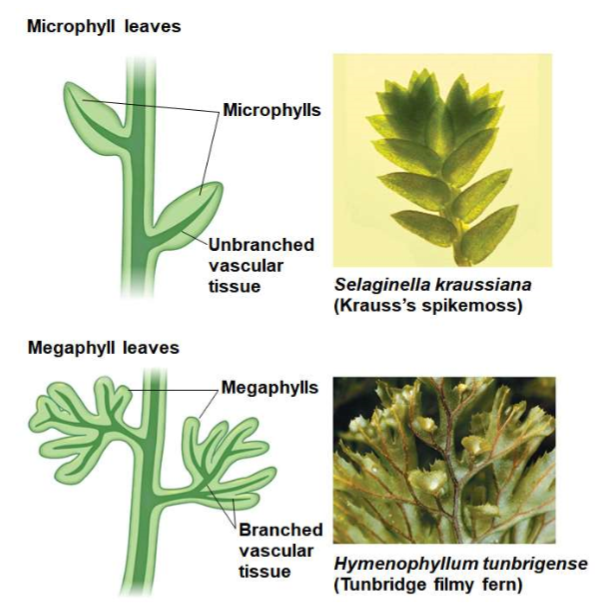
84
New cards
Megaphylls
larger leaves with a highly branched vascular system
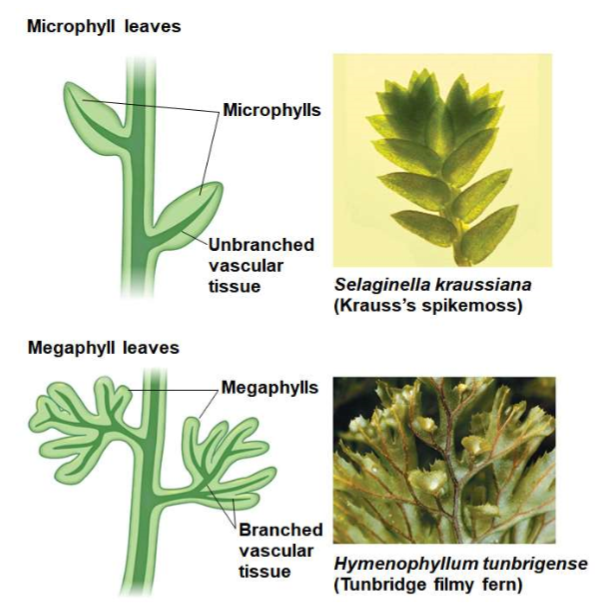
85
New cards
Sporophylls
modified leaves with sporangia
86
New cards
Sori
sporangia clusters on sporophyll undersides
87
New cards
Strobili
cone-like structures formed from groups of sporophylls
88
New cards
Homosporous
producing one type of spore that develops into bisexual gametophyte
89
New cards
Megaspores
produced by heterosporous species, give rise to female gametophytes
90
New cards
Microspores
give rise to male gametophytes
91
New cards
Lycophyta
club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworms
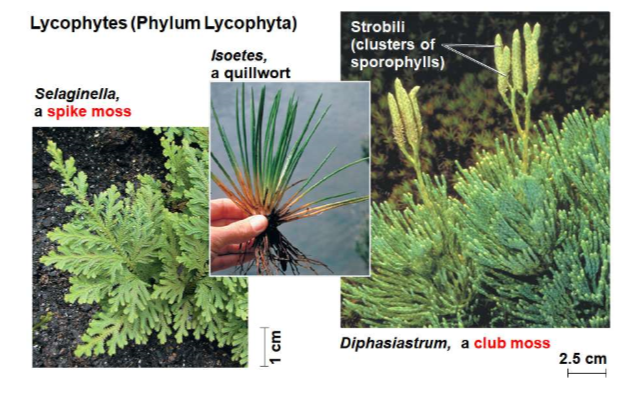
92
New cards
Monilophyta
ferns, horsetails, and whisk ferns and their relatives
93
New cards
When did seed plants originate?
360 million years ago
94
New cards
Reduced gametophytes
develop within the walls of spores that are retained with tissues of the parent sporophyte, protects the developing gametophyte
95
New cards
Ovule
consists of megasporangium, megaspore, and one or more protective integuments
96
New cards
How many integuments do gymnosperm megasporangia and angiosperm megasporangia usually have
gymnosperm megasporangia have 1 and angiosperm megasporangia have 2
97
New cards
Pollen grain
what a microspore develops into, consists of a male gametophyte enclosed within the pollen wall
98
New cards
Pollination
the transfer of pollen to the part of a seed plant containing the ovules
99
New cards
Pollen tube
discharges sperm into the female gametophyte within the ovule
100
New cards
What does gymnosperm mean?
“naked seed”