CH 9.1 and 2 (psychopharm)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Recreational drug
Psychoactive substances consumed voluntarily: has the potential to be used problematic way
Illegal drug use
Most common is marijuana
Most prevalent among young adults
Legal drugs
Alcohol and tobacco
The paradox of addiction
Continued use of drugs despite aversive consequences
Alcohol temperance
Advocated for reduced consumption of alcohol
Movement that culminated in prohibition (complete ban of alcohol) equated drug use with criminal behavior
ended in 1933
Advances in chemistry
Events led to current drug use: Led to a more concentrated form of drugs, these were more addictive
ex: morphine was purified from opium & cocaine from coca
Hypodermic syringes
Events led to current drug use: Development of this allowed injection into the bloodstream & faster route of administration
No drug control laws
Events led to current drug use: Cocaine and heroin were used in tonics and cough syrups
heroin synthesized by Baylor and marketed as non addictive alternative to codeine
Medicalization of drug addiction
Events led to current drug use: now thought that addiction was a disease and addicts should be treated by medical establishment
alcoholism was declared a disease by the WHO
In the second half of 20th century
Disease model of addiction: promoted by self help organizations
Harrison Act
1914: regulated opiates and cocaine, prohibiting nonmedical use; addicts turned to street dealers
Goal: not to abolish but to control use of narcotics and revenue for federal government
Pure Food and Drug Act of 1906
Accurate labeling of food and drugs; increasingly controlled the commercialization of drugs
Goal: not to abolish but control use of narcotics, and revenue for federal government
Alcohol prohibition (18th amendment)
In 1920: spawned organized crime movement of basement alcohol
ended in 1933
Marijuana tax act of 1937
This drug was banned for non medical use. Levied a tax on importers, sellers, and dispensers
Controlled substances Act
Established five schedules of controlled substances and created the Drug enforcement Agency
Clinics/Physicans treating addicts
Began providing maintenance doses to addicts, but then addicts were cut off from this source. This avenue of treatment was largely ineffective.
Physical Dependence
Abstinence leads to highly unpleasant withdrawal symptoms that motivate the person to return to drug use
some drug only produce minor ________
Compulsive drug seeking
Highly motivated to seek; the addict is driven by a craving a strong urge to take the drug
Remissions
Individuals cease drug use for periods
Relapses
Individuals begin to take drugs again
Chronically relapsing disorder
Characterized by compulsion to seek and take the drug, loss of control in limiting intake, and emergence of a negative emotional state when access to the drug is prevented
DSM5 SUD drugs
Activate the neural circuitry that mediates the rewards commonly experienced as a drug induced high
alcohol
Caffeine
Cannabis
Hallucinogens
Sedative Hypnotics and anxiolytic drugs
Inhalants
Opioids
Stimulants
Tobacco
Etc
Substance use disorders
A cluster of cognitive, behavioral, and physiological symptoms indicating that the individual continues using the substance despite significant substance related problems
Substance induced disorders
Development of a reversible substance specific syndrome due to recent ingestion of a substance
eg. substance induced psychotic disorder
Eg substance induced depressive disorder
Behavioral addictions
(Non substance related disorders)
gambling, eating disorders, compulsive sexual behaviors, etc
Gambling
is the only one in the dsm5 that meets several of the criteria for substance abuse disorder
shows similar neurobiological and cognitive dysfunctions
Gateway theory
Young people often progress from legal substances like alcohol or tobacco or marijuana; a few go on to try cocaine, heroin, or illegally obtained prescription drugs
Non problematic or recreational use
Progression of drug use from nonproblematic to problematic: First stage
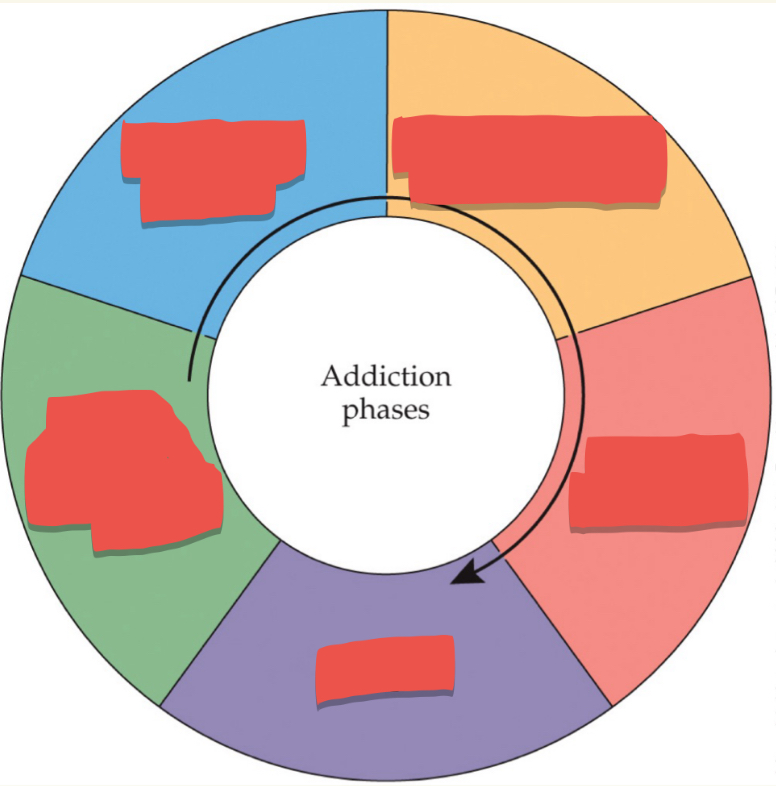
Escalation of drug use
Progression of drug use from nonproblematic to problematic: Second Stage
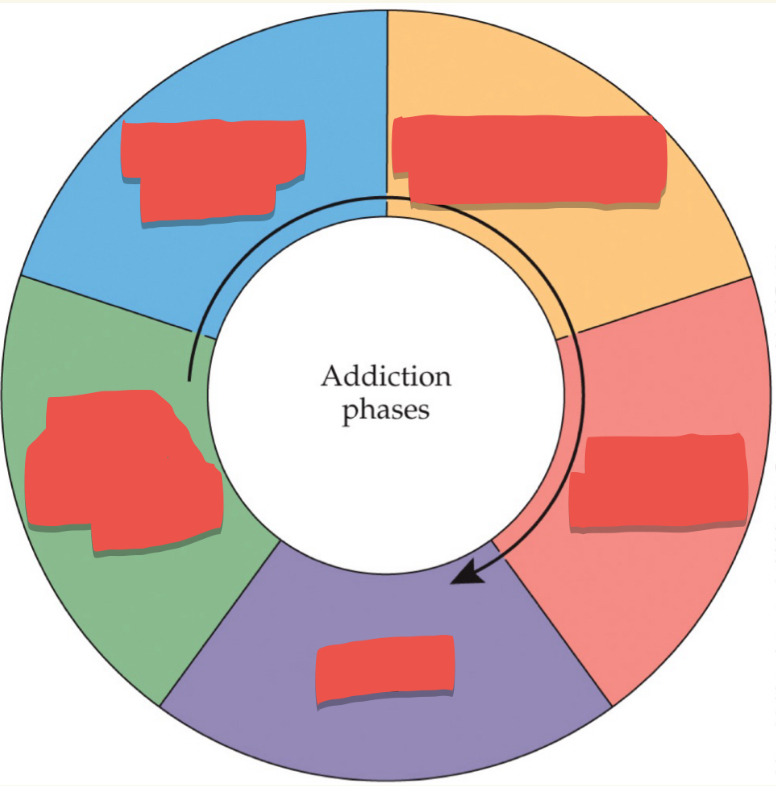
Compulsive or problematic use
Progression of drug use from nonproblematic to problematic: Third Stage
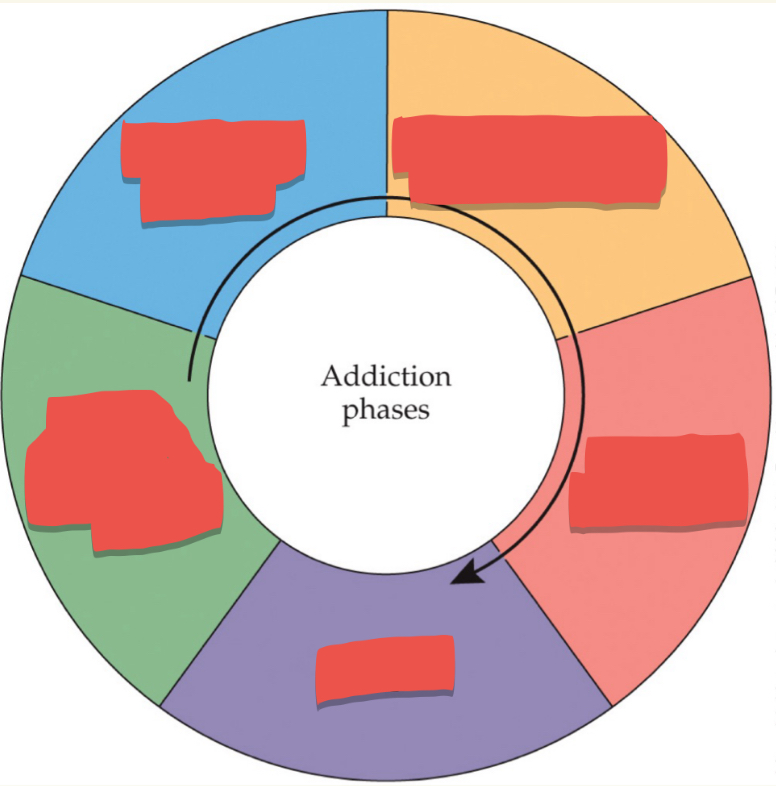
Abstinence (withdrawal)
Progression of drug use from nonproblematic to problematic: Fourth Stage
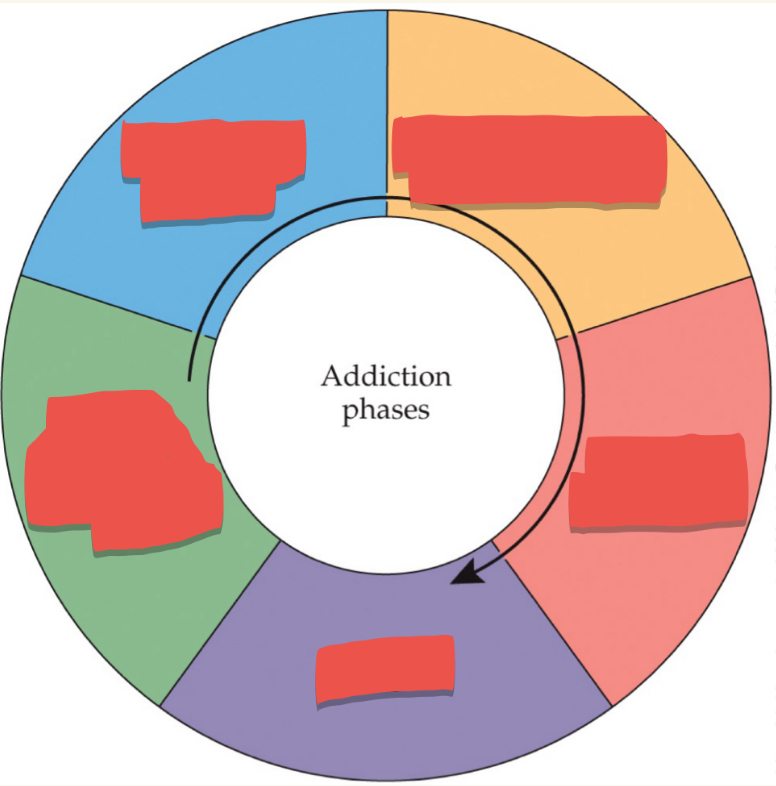
Relapse
Progression of drug use from nonproblematic to problematic: Last stage
Schedule of controlled substances
5 classes of potentially addictive drugs; based on degree of potential misuse and medicinal value
Schedule 1 drugs
No medicinal value and can only be obtained for research use
heroin, LSD, Mescaline, Marijuana, THC, MDMA
Schedule II drugs
Substances have a high abuse potential with severe psychic or physical dependence liability
opium, morphine, codeine, meperidine, cocaine, amphetamine, methylphenidate, PCP, pentobarbital
Schedule III drugs
Substances that have an abuse potential less than other, including compounds containing limited quantities of certain narcotics and nonnarcotic drugs
paregoric, barbiturates other than those listed in other schedule
Schedule IV drugs
Substances that have an abuse potential less than prior
phenobarbital, chloral hydrate, diazepam, alprazolam
Schedule V drugs
Have a low abuse potential and mild dependence