ACS CHEM FINAL
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
For Hawthorn projections, how do you differ wedges and hashes on hexane drawings?
wedges = up and Dashes = Down.
For molecular orbitals, how would you draw all the arrows?
You have to draw them in opposing directions, first you put all arrows UP, then you draw them DOWN, but make you make sure the lower orbitals are fi
Write out the hubridization for all bonds?
Triple bonds = sp
Double bonds = sp2
Single bonds = sp3
How is radical stability ranked?
primary (least stable) < secondary < tertiary (most)
Resonance does not ___________.
change the atoms!!! an O is an O
Lowest to highest boiling points:
Just alkane groups < OH < CA acid
What is most soluable in water
propanol
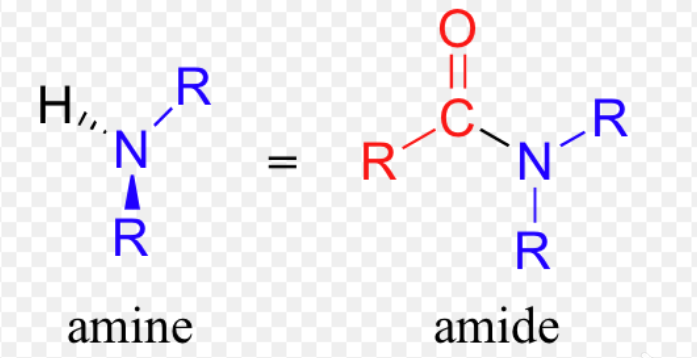
Amide vs amine
Define Hydrogen Bonding
A special, stronger type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom — specifically fluorine (F), oxygen (O), or nitrogen (N) — and is attracted to another electronegative atom nearby.
What is an example of hydrogen bonding?
Water (H₂O) — hydrogen bonds form between the hydrogen atom of one molecule and the oxygen atom of another.
What is Dipole-Dipole Interactions?
Give an example of dipole-dipole ineraction
HCl — the partial positive hydrogen is attracted to the partial negative chlorine of a neighboring molecule.
S vs R steochemistry
R (right - clockwise) and S (left - counterclockwise)
Rank the priority groups for S vs R stereochemistry
Higher atomic number = higher priority
(Iodine> Bromine > Clorine > Oxygen > Carbon > hydrogen) iodine has the highest atomic number (53) is the highest.
Rank the following priority groups for R and S:
I, H, CH3, CHO, NH2, OH, Cl, SH, Br
highest: I > Br > Cl > SH > OH > NH2 > COOH > CHO > CH3 > H (always lowest/lower)
For Newmann projections, the front carbon is represented by a _____________, and the back carbon is represented as a _________.
dot, and circle
What makes a compound optically active ?
The molecule must have at least one chiral center — a carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
E vs Z sterochemistry
Z (together) = the higher priority groups on each double-bonded carbon are on the same side
E (opposite) = the higher-priority are on opposite sides
Constitutional isomers vs enantiomers vs conformational isomers vs diastereomers
Constitutional isomers = same molecular formula, but atoms are connected differently
Conformational Isomers (conformers) = same molecules, but differ by rotation around single (sigma) bonds
Enantiomers = non-superimposable mirror images
Diastereomers = stereoisomers that are NOT mirror images
Bronsted acid =
H+ donor
Bronsted base =
proton acceptor
Lewis acid =
molecular capable of accepting a lone pair of electorns
Lewis base =
electron pair donor
Nucleophile
electron rich and capable of donating an electron pair
Electrophile
accepts an electron pair forming a bond
Weakest to strongest acid =
organize the following = H3C-OH, H3C-NH2, H3C-NH3+, H3C-OH2+
H3C-NH2 < H3C-OH < H3C-NH3+ < H3C-OH2+
Base strength based on hybridized orbitals:
sp < sp2 < sp3
K>1 vs. K < 1 for the reactants vs products thing
K>1 = the acid on the product side is stronger than the reactant
K<1 = the acid on the reactant side is stronger than the reactant
what does K =
K=[reactants] / [products]
Nucleophiles rated slowest to fastest:
rank the following, CH3O-, CH3OH, and CH3NH2
CH3OH < CH3NH2<CH3O-
What is the Alkyl halide expected to undergo an SN1 reaction most rapidly…
HI is the strongest conjugate acid to the halides
SN1 vs. SN2. How many steps is each?
SN1 = 2 steps: leaving group leaves first, forms carbocation, nucleophile then attacks carbocation to form the product.
SN2 = 1 step: nuc attacks electrophilic carbon (w/leaving group) simutaneously as the LG leaves
SN1 works best with ____________, and SN2 works best with _______________.
SN1 = tertiary carbocations
SN2 = Works best with methyl or primary carbons
For __________, the configuration does __________.
For SN2 reactions, the wedge will invert to the hash.
After doing Subsiution (ex: Br on a wedge is treated with NaI in acetone) = inversion of chemistry happens so the Br leaves and the I is now on a hash!! This is due to ____________.
The reaction being SN2. SN1 can have inversion, but its not garenteed.
E1 and E2 both ______________.
result in the formation of a double bond (alkene)
What are the differences between E1 and E2?
E1 = 2 steps = Leaving group leaves → forms a carbocation. (carbocation present).
E2 = 1 step = The base removes a β-hydrogen at the same time the leaving group leaves (no carbocation)
What is the product of dehydrohalogenation by KOH?
typically an alkenee!!!!!!!!
Which Hydrogen i preferably abstracted by dehyrohalogenation with KOH?
Yes — the preferred hydrogen abstracted during dehydrohalogenation with KOH is the β-hydrogen.The most substituted (more stable) alkene is typically favored, so the β-hydrogen removed is usually the one that leads to the more substituted double bond.
What does H₂O / H⁺ do?
Markovnikov addition of –OH (OH to more substituted carbon).
What does BH₃/THF → H₂O₂/OH⁻ do?
Hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes.
Anti-Markovnikov addition of OH.
Hg(OAc)₂/H₂O → NaBH₄/OH⁻
Markovnikov hydration.
B₂H₆/H₂O₂, NaOH
Anti-Markovnikov addition of OH.
What does H₂O / H₂SO₄, HgSO₄ do?
Markovnikov addition → forms ketone via enol intermediate.
HOEt, H⁺
–OH replaced with –OEt.
Reduction of triple bond but not double
Li, EtNH2, -78 C followed by NH4Cl wash
What does DIBAL do?
used to reduce carboxylic acids and derivatives to aldehydes
What does LiAlH4/THF followed by H+ do?
reduces ketones, carboxylic acids, and derivatives to alcohols
Primary OH can be oxidized to ______________.
aldehydes or carboxlyic acids
PCC does what
PCC oxidizes a primary OH to an aldehyde and a secondary OH to a ketone
NaBH4/EtOH followed by H+ does what
selectively reduces ketones to OH
CrO3/H2SO4pr chromic acid oxidizes a primary OH to ? and a second OH to a __________.
Primary = CA
secondary = ketone
KMnO4 and Primary OH to what?
carboxlyic acid
O₃ (ozone) + H₂O₂ or oxidative workup + alkene
carboxxlyic acids /ketones
O₃ + Zn / DMS (reductive workup) + alkene =
aldehyde/ketone
MCPBA + alkeene =
epoxide
OsO₄ / H₂O₂ + alkene =
vicinal diols (syn)
LiAlH₄ (LAH) reduces esters/CA acids =
primary OH
LiAlH₄ (LAH) reduces aldehydes=
primary OH
LiAlH₄ (LAH) reduces ketones =
secondary OH
LiAlH₄ (LAH) reduces amides to
amines
NaBH4 reduces aldehydes to =
primary OH
NaBH4 reduces ketones =
secondary OH
H₂ / Pd, Pt, or Ni does what?
reduces everything
H2/Lindlars reduces alkynes to ___.
alkenes
Na / NH₃ (liq) reduces alkynes to _______
alkenes
DIBAL reduces esters to _____
aldehydes