Animal Science Exam 3
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Scientific Name for Cattle
Bos Taurus (European) Bos Taurus (South Asia)
Ancestors of Cattle
Auroch (Gaint wild ox)
Why did the domestication of Cattle have such an impact on society?
They were the first draft animals and changed trasportation, the market, and even how we tended to the land.
What type of industries seem to have the most milk production?
Less farms with more cows.
What is the average herd size?
115
74% of Dairy comes from…
more than 100 cows
85% of milk production comes from…
Less than 100 cow dairies
Where are traditional dairy states
Northwest or around the Great lakes
Where are the more modern dairy states
Southwest of the US
Name some traditional dairy states
Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, New York, Minnesota, and Ohio
Name some Modern dairy states
California, Texas, and Idaho
What are the biggest differences between Traditional and Modern dairy states?
Traditional- More Farms but are smaller and with less cows, older, slowly growing their tech, and are losing more farms and fast.
Modern- Less Farms but are much larger and with more cows, newer, have more tech, and are not losing as many farms.
where does 74% of milk production come from?
Modern dairy States (California most specifically)
Where does 80% if dairy farms come from?
Traditional dairy states (Wisconsin)
What is Colostrum and why is it important?
Orange liquid containing antibodies that calf should be given as soon as possible (with 24 hours of birth)
When does weaning happen for calves?
6-8 weeks
When does puberty happen for heifers?
9 months old
When are heifers first breed
14-15 months
How long is gestation for cows
285 days
How long does calving last?
23-24 months
How long is a cow’s lactation
305 days (average 336)
When in lactation is a cow breed again
80-90 days after lactation starts
How long is the dry off period for cows?
60 days (Average 57)
What are the 4 stages of lactation? cows
early lactation
Mid lactation
Late lactation
Dry period
What happens during early lactation and how long is it? cows
Milk production peaks, Cow stops eating as much dry matter (because calf is taking up space), Body weight lowers (Disease could occur) first 100 days (energy balance is negative)
What happens during Mid lactation and how long is it? cows
Milk (still high) starts to decline, Cows dry matter intakes and they begin growing there weight back to normal. (energy balance is neutral) 100 -200 day mark
What happens during Late lactation and how long is it? cows
Milk continues to decline, Dry matter intake goes back to normal, and body weight is positive. 200- 305 days mark
What happens during dry period and how long is it? cows
Body recovers. for 60 days and 45 days before next pregnancy.
How old is a cow before they have their first calf
2 years old (25 months)
How much milk does a cow produce per lactation?
23,000 pounds
If a cow does not get pregnant at 80-90 days, then when is the next time they can try and get pregnant, and why? What does this do to the lactation cycle?
21 days because that is how long the estrus cycle is. This extends the lactation cycle because now instead of at 80 the cow will be pregnant later into the lactation and will need to produce milk longer to go with the pregnancy.
How long do cows usually produce milk?
5 years
How old is a cow that has had 5 lactation cycles
7 years old
If a cow is 5 years old, then how many lactation cycles has it have?
3
How often is a calf born on average
every 13.1 months
What are reasons a cow may be culled
Reproductive failure, Udder breakdown, Low milk yield, Mastitis, Foot and leg problems.
Internal Udder Structure Lactation
{Parenchyma: Alveoli- Tiny sac- like structures where milk is synthesized. Lobules- Clusters of alveoli that group together.} Duct system- Network of tubes that transport milk from alveoli to storage. Gland Cistern- Storage chamber that collects milk before being released. {Teats- external structure that expels milk. Cistern- Hold milk before being released. Streak canal- Final Passage when milk Exits the teat. (barrier to infection and opens during milking)}
Alveolus
Where milk is synthesized, stored, and eventually ejected. It’s the core of the parenchyma. Contains: Epithelial cells- Milk synthesis and secretion, Lumen-Collect milk components and water, Myoepithelial Cells- Milk ejection (Muscle-like cells that surround the alveoli), and Capillary System- Supply milk components (supplies nutrients).
What is produced when milk is released?
Oxytocin (hormone)
Tandem dairy Parler
Animals enter and exit individually, Personnel is required to push animal through parlor, this type does not save space, you access the udder lateral, and person is required to do all steps individually to each cow.
Parallel dairy parlor
Animals enter and exit in groups, personnel is required to push animals through, it does save space, rear access to udder, and person is required to do all steps individually to each cow.
Herringbone dairy parlor
Animals enter and exit in groups, personnel is required to push animals through, it does save space, rear and side access to udder, and person is required to do all steps individually to each cow.
Rotarty
Animals enter and exit individually, Personnel is not required to move animals, but animals will need to be trained to move through parlor, this does not save space, access udder from rear, and once person can do a specific job to each cow.
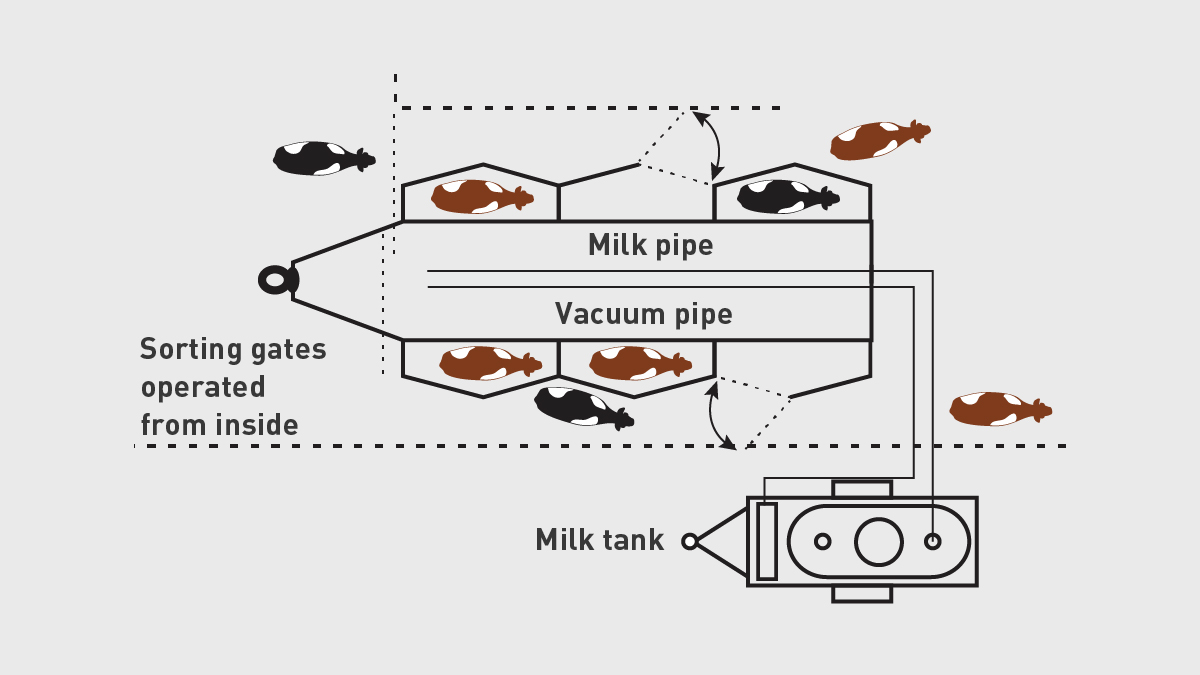
What type of parlor?
Tandem
What type of parlor?
Parallel
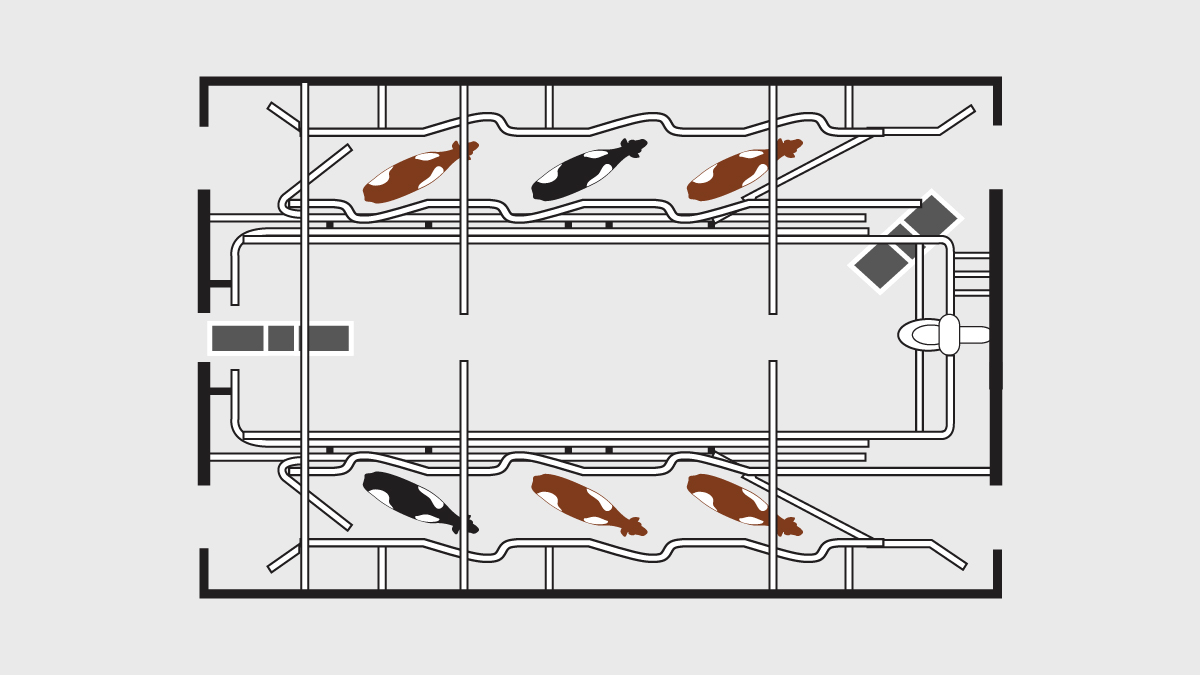
What type of parlor?
Herringbone
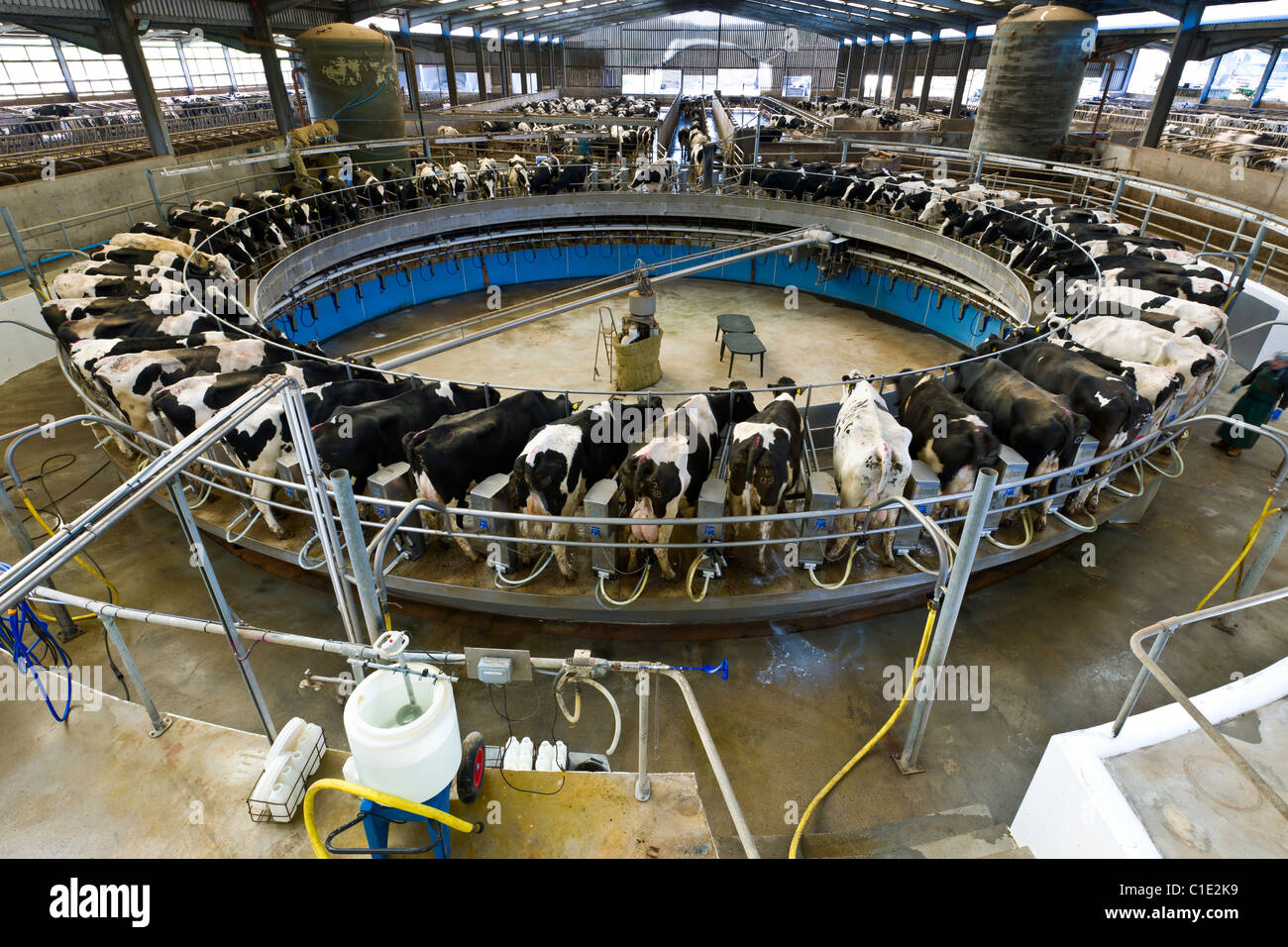

What type of parlor?
Rotary
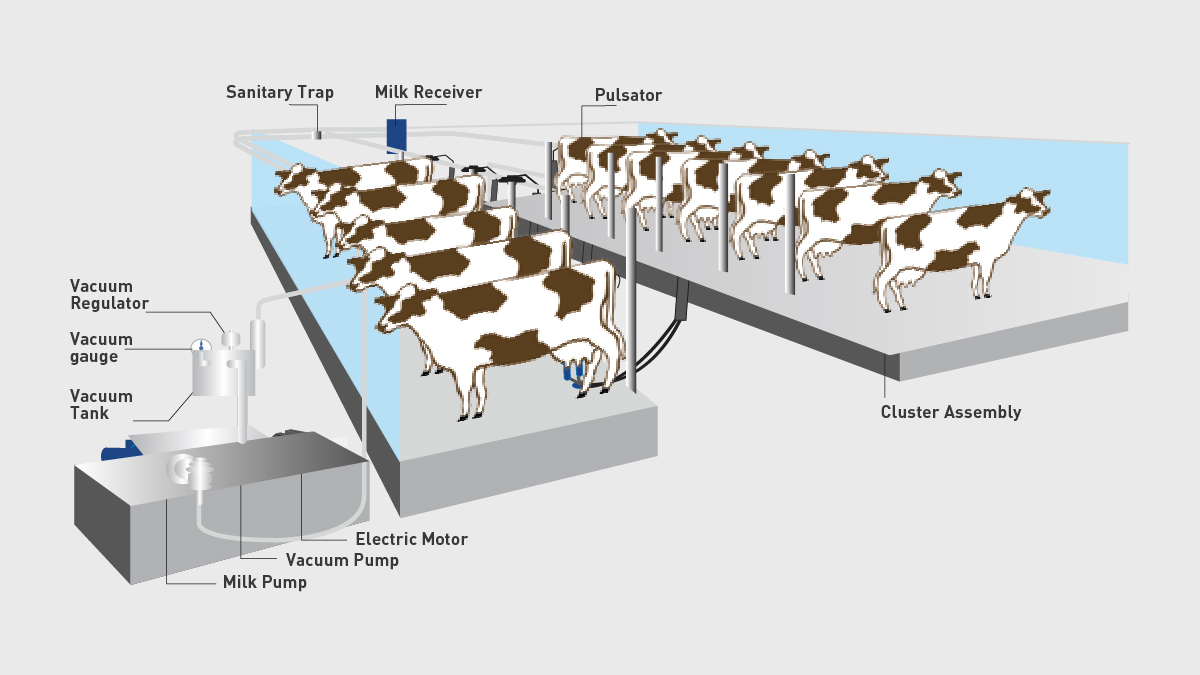
What is the milk process?
teat disinfectant
Strip milk into a strip cup
Wipe dry
Milk
Shut off the vacuum and remove the unit
What makes good milk quality?
Free of debris/sediments, off-flavors, color, odor, and chemicals. Low in bacterial count. Normal composition and acidity.
What happens to a cow’s milk is that they have to take medication.
It will show in milk and will not be good for market
What is milk mostly made of?
Water (87.7%)
What Protein is in milk?
Casein (80% of protein), Whey (20% of protein)
Somatic Cells
White blood cells that track infection and are usually present in small amounts unless there is an infection.
What is a normal number of somatic cells?
2,00,00 cells/mL or less
What is the difference and similarities between Grade A and Grade B Milk?
A can be sold as liquid or manufactured, while B can only be manufactured.
A cooled to 45 or less, while B cooled to 40 or less.
A tends to have 740,000 somatic cells/mL or less
Both have less than 100,000 cfu/mL and no positive drug residue.
What is cfu
colony-forming units (the number of living microorganisms)
What is the difference between Subclinical and Clinical?
Subclinical shows no signs and can only be shown through more than 200,000 somatic cells/mL.
Clinical cas visual signs and changes to health along with more than 200,000 somatic cells/mL. (Temp of udder, changes to milk)
What is mastitis?
An infection of the udder in the mammary gland
How does the California Mastitis Test work?
The reagent reacts with DNA in scc, Milk is collected from the first stream and combined with the reagent. Swirl and then read. THICK GEL=Mastitis
Pasteurization
Heat of milk to reduce microorganisms. Heat 161 for 15 seconds, then cool to 39 quickly
Homogenization
Nessel at high pressure and temp to blast fat globules so they won’t separate from milk and rise to the top.
Whole Milk
3.25% Fat
Low fat
1 or 2% fat
Skim
0.5% fat
Half and Half
10.5%+ fat
Wiping Cream
30% fat
Heavy Cream
36% fat
How is cheese made?
Milk + Rennet (enzyme) = Casein and Fat Globules
Butter
Separation of milkfat
Yogurt
Fermentation of milk. lactose + Bacteria = Lactic Acid
Ice cream
Freeze cream/milk
DHIA
Dairy Herd Improvement Association (Collects data, Compares, Selects best for future)
BCS
Body Condition Score
Best BCS for Cattle?
Round Hooks, Flat pins, not as visual Ribs
Has the Beef Industry gone up or down? And why?
Down because it’s expensive, not as healthy, takes longer to cook, and has e. coli
Where are most Beef Industry’s located?
Center of the U.S.
European Beef Cattle breeds
Hereford, Angus, Shorthorn
Continental Beef Cattle Breeds
Charolais, Simmental, Limousin
Zebu Beef Cattle Breeds
Brahman