IB Bio SL B1.1+B1.2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Organic Compound
A compound that contains carbon and hydrogen and is found in living things
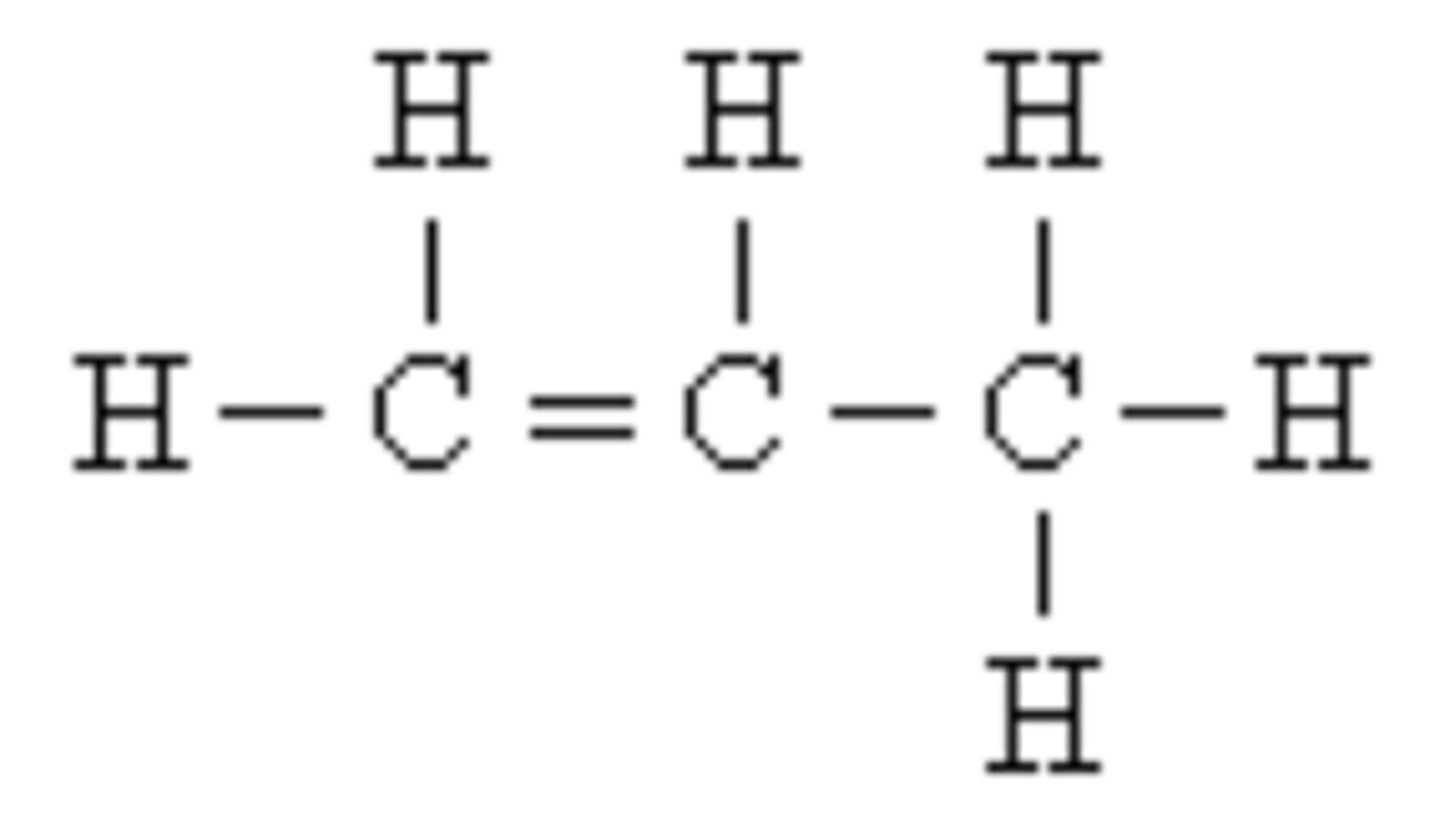
What does carbon form?
Carbon forms four covalent bonds and therefore is the basis of all organic compounds
Variety of structures
Branched or unbranched chains and single or multiple rings
Types of carbon compounds
Carbs, Fatty Acid, Protein, Nucleic Acid
Organic compounds are typically polymers made up of subunits called
Monomers
Monomer of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Monomer of Nucleic acids
Nucleotide
Proteins consist of linked chains of
Amino Acids
Polymers are formed by
Condensation reactions
What type of energy is required to build larger molecules
ATP energy
Polymers are broken down into monomers by
Hydrolysis Reaction
A type of molecule is split and added in this process
Water molecule
The monosaccharide that makes up the polysaccharides cellulose, glycogen and starch
Glucose
unbranched and its monomer is beta-glucose
Cellulose
Starch and glycogen consist of
Alpha-Glucose
Unbranched molecules form
1'-4' linkages
Branched molecules form
1'-4' and 1'-6' linkages
Monosaccharides have
3-7 carbon atoms
Pentoses have
5 carbon atoms
Hexoses have
6 carbon atoms
Both pentoses and hexoses can exist as
straight chains and strings
Glucose is
Soluble, relatively small, easily transported, circulates in blood, dissolved in blood + in plasma
Glucoses function
Chemically stable, food storage, cannot be stored in large amounts because it is osmotically active, so it is stored in the form of starch or glycogen
Glucose releases
Energy when it is broken down (oxidized) in cell respiration
What part of blood does glucose travel in
Plasma
Why can it travel in the blood
Glucose is hydrophilic (dissolvable)
What happens when your blood sugar is low?
Low energy
What happens when your blood sugar is high
Increased risk of heart attack and other medical complications
Both starch (in plants) and glycogen (in animals) are used for
energy storage
Both starch and glycogen consist of
Alpha-Glucose molecules
Amylose (starch)
Unbranched, 1'-4' bonds, because of the bond angle the chain is helical
Amylopectin (starch)
Branched, 1'-4' and 1'-6' glycosidic bonds, it branche at about one in every 20 glucose molecules
Glycogen, similar to amylopectin is also
Branched (1'-4' and 1'-6' glycosidic bonds), branches every 10 glucose molecules
Cellulose
Consists of beta-glucose, unbranched (1'-4' glycosidic bonds), makes up the cell wall
Glycoproteins
Made up of proteins with short carb chains attached (oligosaccharides), Trans-membrane, face outwards
Lipids
Diverse group of substances which encompass fats, oils, waxes and steroids. Hydrophobic as they dissolve in non-polar substances for example oil
Biological "consequences" of the hydrophobic properties of lipids
Waxes prevent water loss from leaves, bird feathers are coated with oil which in turn makes them waterproof, phospholipids from membranes and thus different compartments
Triglycerides
Consist of three fatty acid chains linked to a single glycerol molecule
In phospholipids
One of the fatty acid chains is replaced by a polar phosphate group
Main classes of lipids
Simple lipids
Compound lipids
Derived lipids
Simple lipids
Esters of fatty acids and alohols (waxes and triglycerides)
Compound lipids
Esters of fatty acids and alcohol and additional groups (phospholipids and glycolipids)
Derived lipids
Produced from the hydrolysis of the other compounds (steroids)
Fatty acids consist of
A chain of hydrocarbons (14-20 Carbons long)
Variable parts of a fatty acid
The length, the number and the location of the double bonds
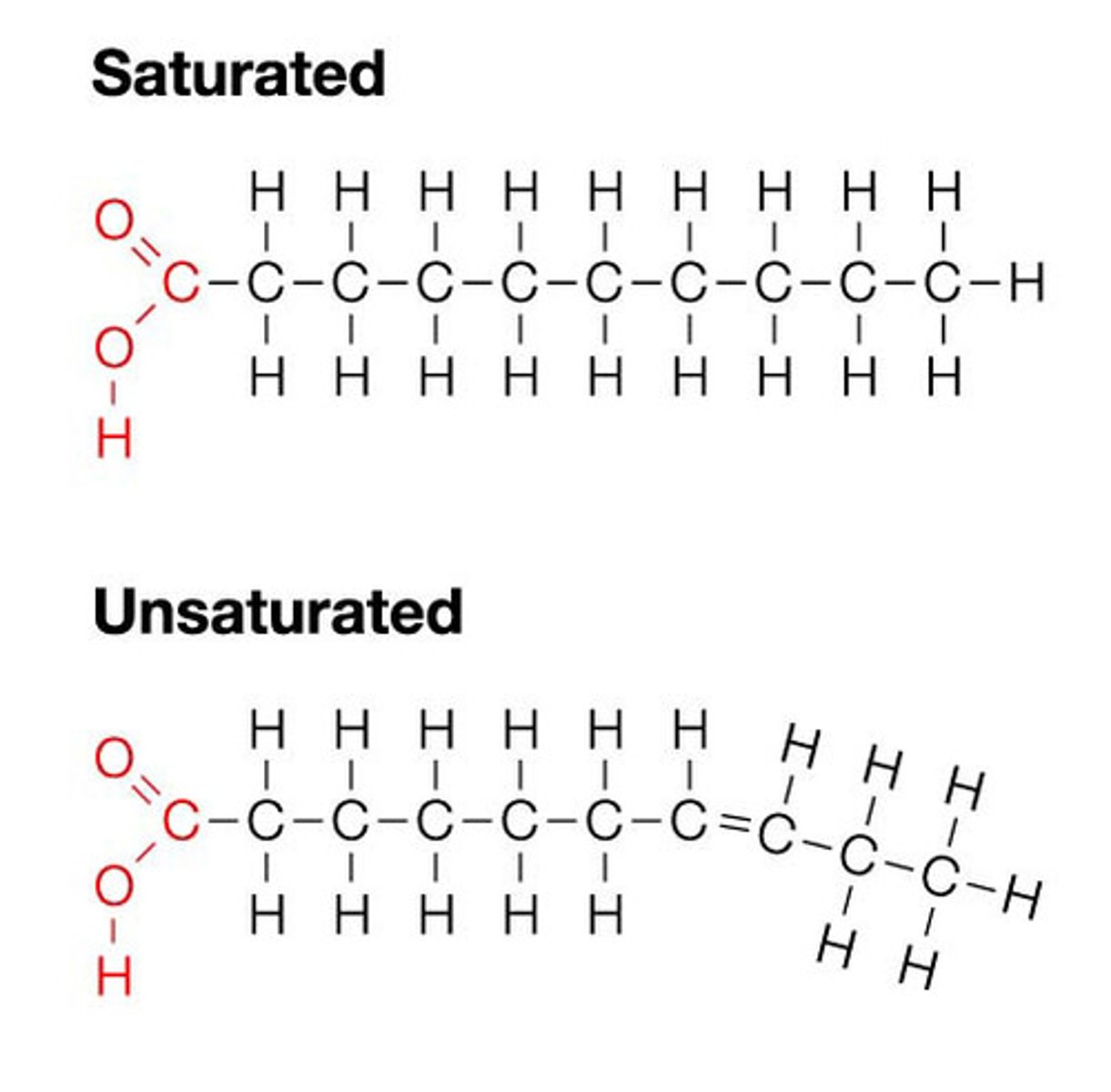
Saturated fatty acids
Straight fatty acids with NO double bonds
Unsaturated fatty acids
Contain double bonds (Monounsaturated = 1 double bond ; Polyunsaturated = More than one double bond) (can be cis or trans)
Cis-unsaturated fatty acids
When the hydrogen atoms on the double bonds are on the same side
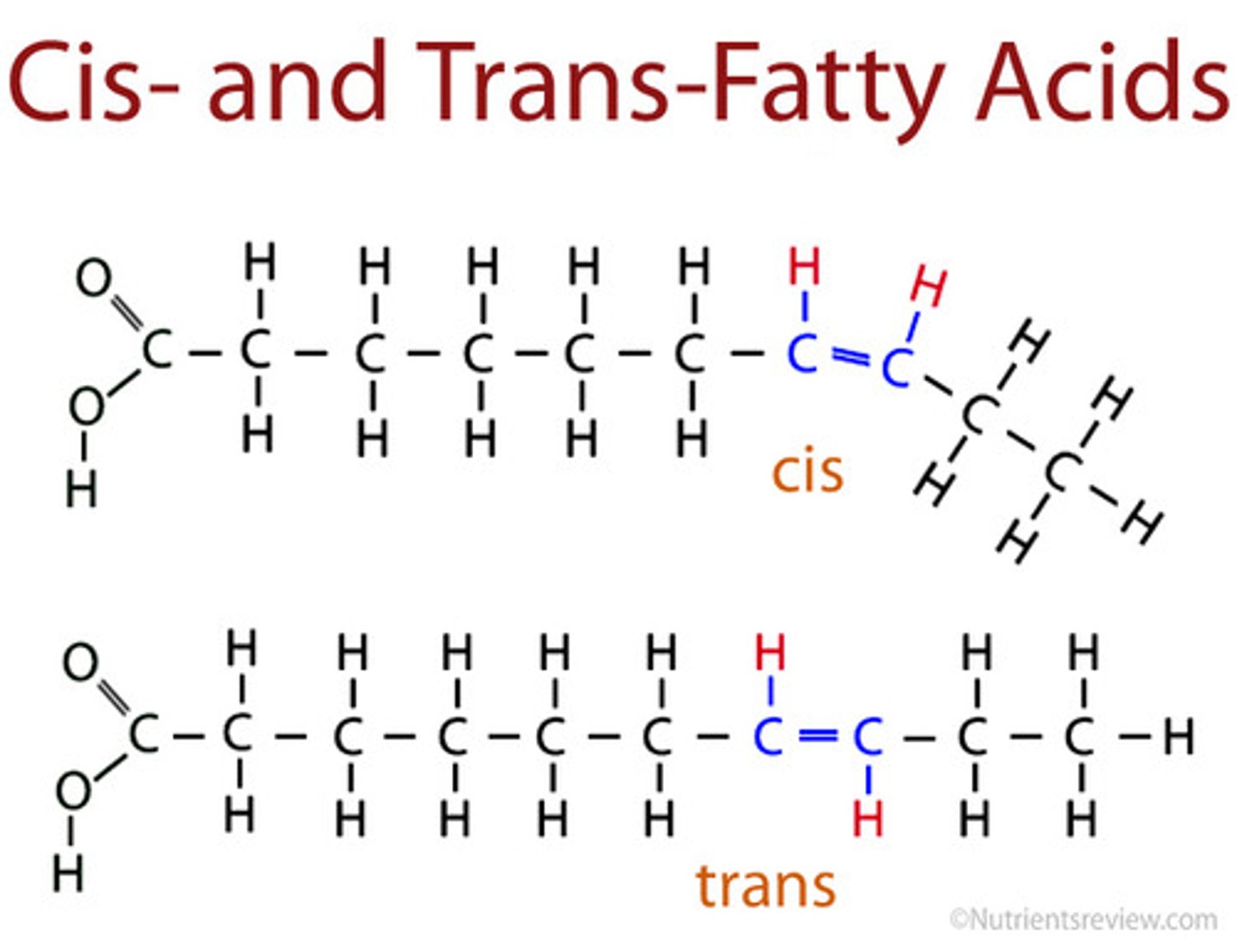
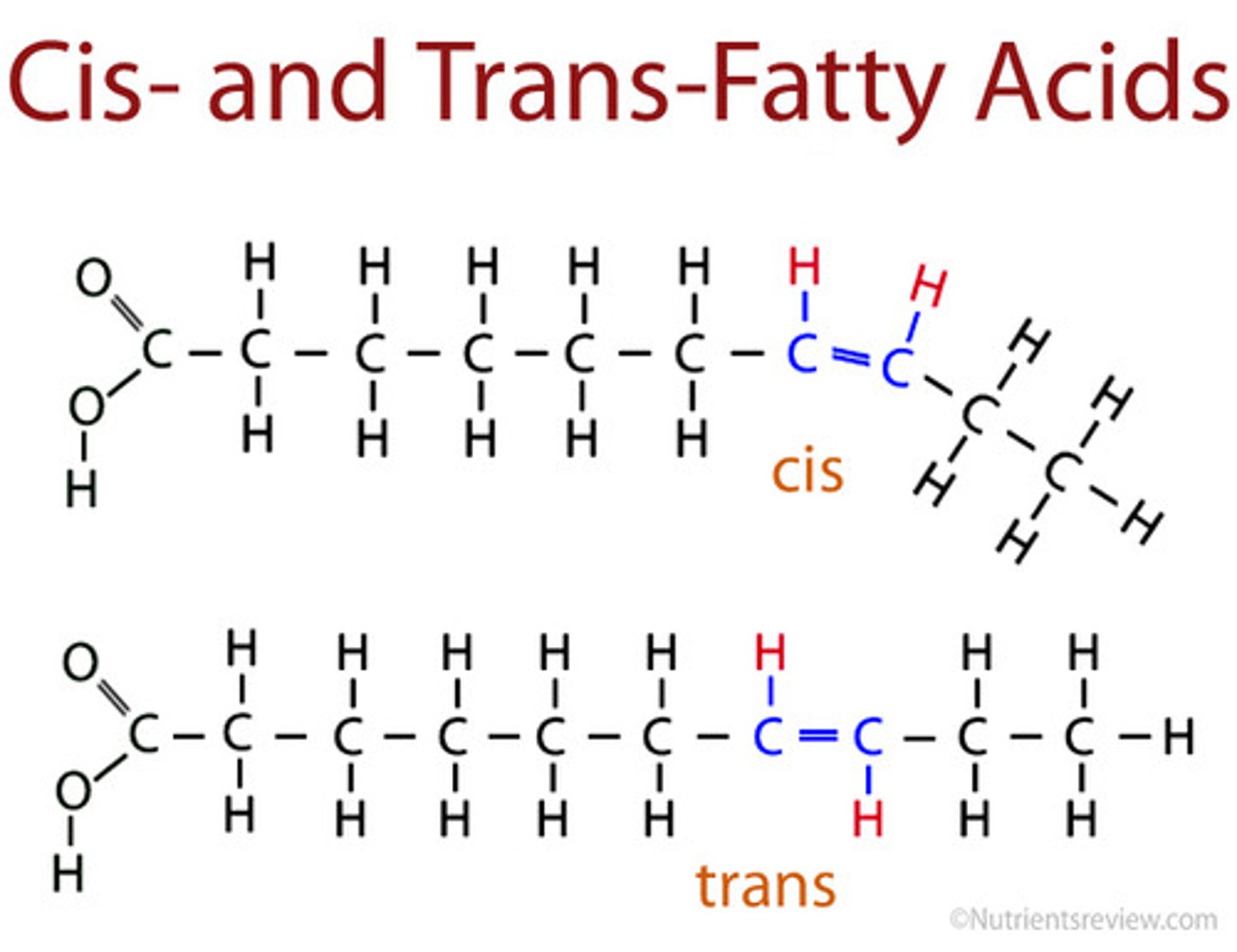
Trans-unsaturated fatty acids
When the hydrogen atoms on the double bonds are on opposite sides
Lipid storage
Organisms need fatty acids to stay liquid at their body temperature, but they also want them to be packed as tightly as possible for energy storage
Triglycerides in energy storage and thermal insulation
They are stable so no energy is lost over time
They are hydrophobic so they can be stored without having an osmotic effect on the cell
Contain twice more energy per gram than carbs or proteins
Phospholipids are
Amphipathic, they have both hydrophilic (phosphate group) and hydrophobic (fatty acids) parts
When phospholipids are added to water they
Spontaneously assemble into bilayers with the phosphate head pointing to the watery solutions inside and outside the fatty acids pointing away from the water
Structure of steroids
4 fused carbon rings that are non-polar and lipophilic (fat-loving), they are also hydrophobic
Function of steroids
Steroid hormones function as a signaling molecule in the body
They freely diffuse across the phospholipid bilayer and bind to receptors in the target cell
Steroids are hydrophobic and cannot be freely transported within the bloodstream and must be bound to a carrier protein (ex: albumin)
examples of steroids are estrogen or testosterone