Micro: Midterms
1/349
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
350 Terms
Bergey's Manual
bacteria were grouped by morphology (rod, coccus), staining reactions, presence of endospores, and other obvious features. Pratical but not logical
Bacteria
microscopic, unicellular, prokaryotic organisms.
Prokaryota
They do not have membrane-bound cell organelles and lack a true nucleus, hence are grouped under the domain
Backerion
• Bacteria, a singular bacterium, is derived from the Ancient Greek word
Bacilli
First bacteria
Bacteriology
A branch of microbiology that is called the study of bacteria
Ubiquitious
Bacteria are evolved to adapt and survive in any kind of ecological niches; from normal to extreme environments.
Psychrophiles
extreme cold
Thermophiles
extremely hot
Acidophiles
acidic pH
Alkaliphiles
basic pH
Barophiles
extreme pressure
Anaerobic
anoxic environments
Coccus
Spherical Shaped Bacteria
Cocci
Meaning berries
Bacillus
Rod-shaped bacteria
Bacilli
Little staffs
Coccus

Bacillus

Curved Rods

Pleomorphic

Cocci
usually round but can be oval, elongated, or flattened on one side
Cocci
divide to reproduce, the cells can remain attached to one another
Diplococci
Cocci that remain in pairs after dividing
Streptococci
those that divide and remain attached in chain like pattern
Tetrads
Those that divide in two planes and remain groups of four
Sarcinae
Those that divide in three planes and remain attached in cubelike groups of eight are
Staphylococci
Grapelike dusters or broad sheets
Diplococci

Streptococci

Tetrad

Sarcinae

Staphylococci

Bacillus
Rod shaped bacteria
Coccobacillus
in between bacilli and coccus
Bacillus

Diplobacillus

Streptobacillus
Coccobacillus

Bacillus
Streptobacilli
Coccobacillus

Spiral
bacteria have one or more twists; they are never straight
Vibrio
curved rods
Spirilia
helical shape, like a corkscrew, and fairly rigid bodies
Flagella
Spirillia uses this mechanism for motility
Spirochetes
helical and flexible move by means of axial filaments, which resemble flagella but are contained within a flexible external sheath.
Vibrio

Vibrio
Spirillia

Spirochetes

Spirochetes

monomorphic
Most bacteria maintain a single shape
Rhizobium, Corynebacterium
genetically pleomorphic. which means they can have many shapes, not just one
Unicellular
Cells of bacteria
Bacteria
They are prokaryotes and their cells are different from animal and plant cells
Flagella, Pili/Fimbriae
External Structure of Bacteria
Flagella
-long hair-like filamentous structures of about 4 – 5 μm long and 0.01 – 0.03 μm in diameter
Flagella
They confer motility to the bacteria.
Filament, Hook, Basal Body
Flagella are divided into three parts;
filament
threadlike part extending outside the cell wall. It is made up of flagellin protein.
Flagellin
Protein in the filament of a flagella
Basal Body
Anchors the plasma membrane and cell wall
Hook
short curved structure that joins filament with the basal body
Hook
produces repulsion like the propeller during the revolving of flagella.
basal body
set of rings embedded in the cell wall and plasma membrane.
Gram-negative bacteria
Contains two pairs of rings in basal body
Gram-positive bacteria
Contains one pair of rings in basal body
Basal body
It synthesizes polymers of the flagellum, produces energy for revolution, and regulates movements of the flagellum
Taxis
Particular stimulus
Motility, Chemotaxis, Pathenogenicity
Functions of flagella
Axial filament/endoflagella
bundles of fibrils that arise at the ends of the cell beneath an outer sheath and spiral around the cell
Axial filament/endoflagella
Movement of spirochetes
Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum
Axial filament/endoflagella
Axial filaments
which are anchored at one end of the spirochete
rotation of the filaments
produces a movement of the outer sheath that propels the spirochetes in a spiral motion movemen
Gliding motility
provides a means for microbes to travel in environments with a low water content, such as biofilms and soil.
Atrichous
w/o projections
peritrichous
distributed over the entire cell
peritrichous

Monotrichous
- a single flagellum at one pole
Monotrichous
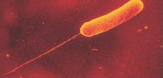
lophotrichous
a tuft of flagella coming from one pole
lophotrichous
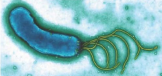
amphitrichous
flagella at both poles of the cell;
amphitrichous

Fimbriae
have a tendency to adhere to each other and to surfaces biofilm production
Fimbriae of E. coli 0157
enable this bacterium to adhere to the lining of the small intestine, where it causes a severe watery diarrhea
Pili
usually longer than fimbriae and number only one or two per cell.
Pili
Involved in motility and DNA transfer
Twitching motility
a pilus extends by the addition of subunits of pilin, makes con tact with a surface or another cell, and then retracts (powerstroke) as the pilin subunits are disassembled
Pili/Fimbriae
They are the short, hollow, non-helical filamentous structure of about 0.5 μm in length and 0.01 μm in diameter
Pili/Fimbriae
They are exclusively found in Gram-Negative bacteria.
Pilin
Protein found in Pili
Pili
They are composed of protein ‘pilin’ arranged non-helically
Pili
They are short, numerous, and straight than flagella.
Sex pili
a special kind of pili that take part in bacterial conjugation.
Sex pili
They are larger than usual pili; 10-20 μm in length. They are few in number, just 1-4 in number.
F-pili, I-pili
Two classifications of Sex Pili
Adherence to host cells, Bacterial DNA transfer
Functions of Pili/Fimbriae