Chemistry - Acid/Base Equilibria
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Bronsted-Lowry theory
theory that states that any compound that can transfer a proton to any other compound is an acid, and the compound that accepts the proton is a base
conjugate pair
a pair of substances that only differ through a single proton that are formed in a reversible reaction between a Bronsted-Lowry acid and a Bronsted-Lowry base, where a pair consists of one of the reactants and one of the products
conjugate acid
a compound formed when a Bronsted-Lowry base accepts a proton in a reversible acid-base reaction
conjugate base
a compound formed when a Bronsted-Lowry acid donates a proton in a reversible acid-base reaction
strong acid
an acid which has a high tendency to donate its proton and fully ionizes in solution
weak acid
an acid that has a lower tendency to donate its proton and partially ionizes in solution
strong base
base that has a high tendency to accept a proton and fully ionizes in solution
weak base
that which has a lower tendency to accept a proton and partially ionizes in solution
p notation (2)
a logarithmic scale used to express chemical values simply and draw comparisons rooted in concentration
-log[number]
pH (2)
a scale that measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a substance and is generally used to scale acidity
-log[H⁺]
pOH (2)
a scale that measures the concentration of hydroxide ions in a substance and can be used to scale acidity but rarely as hydroxide ions less evidently/relevantly relate to changes in acidity
-log[OH⁻]
Describe the pH and pOH scales (2)
pH typically follows a scale of 0-14, where lower values are more acidic and higher values are more basic
pOH typically follows a scale of 0-14, where lower values are more basic and higher values are more acidic
Kᵥᵥ (3)
an equilibrium constant that expresses the concentration of water’s ion relative to neutral water at equilibrium
[H⁺][OH⁻]
@25⁰C = 1×10⁻¹⁴
Define Kᵥᵥ in terms of pH and pOH
pKᵥᵥ = pH + pOH = 14 @25⁰C
Kₐ (2)
an equilibrium constant that expresses the equilibrium ratio of an acid’s disassociated ions to its associated form
For the reaction, HA ↔ H⁺ + A⁻, Kₐ = [H⁺][A⁻]/[HA] or [H⁺]²/[HA]
Describe how Kₐ and pKₐ scale acidity (2)
In Kₐ larger values means the acid ionizes more and is stronger
In pKₐ lower values means the acid is stronger
K₆ (2)
an equilibrium constant that expresses the equilibrium ratio of a base’s disassociated ions to its associated form
B + H₂O ↔ BH⁺ + OH⁻, Kₐ = [BH⁺][OH⁻]/[B] or [OH⁻]²/[B]
Describe how K₆ and pK₆ scale acidity (2)
Higher values of K₆ means the base ionizes more and is stronger
Lower values of pK₆ means the base is stronger
Describe Kᵥᵥ in terms of Kₐ and K₆
pKₐ + pK₆ = pKᵥᵥ
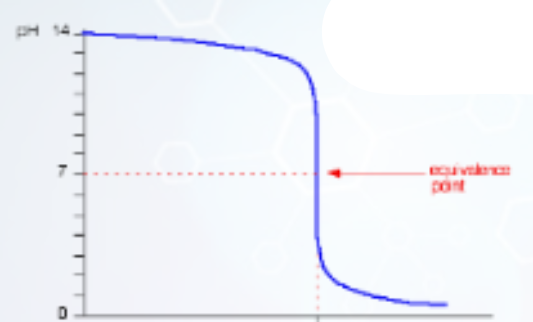
Describe this graph
pH titration curve for a strong acid being added to a strong base
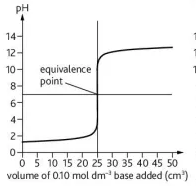
Describe this graph
pH titration curve for a strong base being added to a strong acid
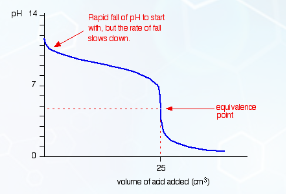
Describe this curve
pH titration curve for a strong acid being added to a weak base
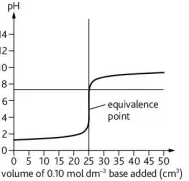
Describe this curve
pH titration curve for a weak base being added to a strong acid
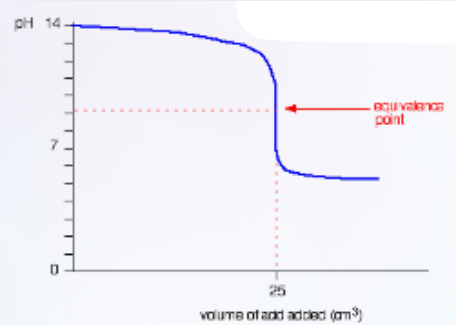
Describe this curve
pH titration curve for a weak acid being added to a strong base
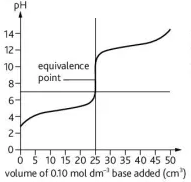
Describe this curve
pH titration curve for a strong base being added to a weak acid
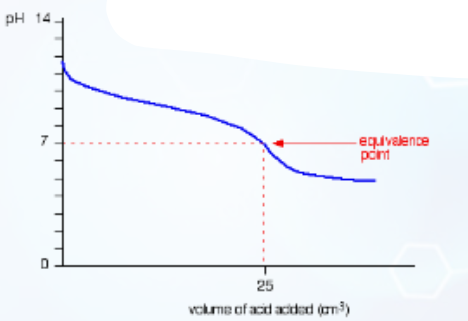
Describe this curve
pH titration curve for a weak acid being added to a weak base
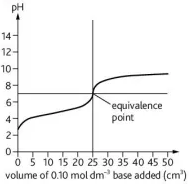
Describe the curve
pH titration curve of a weak base being added to a weak acid
indicator
a substance which changes colour when the pH changes within a certain range of pH values
pH range of an indicator
the intermediate point between two pH values at which the indicator changes colour
Denote the pH ranges and colour changes of methyl orange, screened methyl orange, bromophenol blue, litmus and phenolphtalein
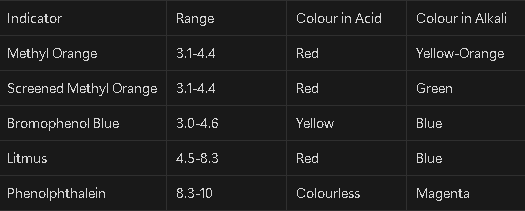
How do you choose a suitable indicator for a reaction?
The indicator must fall between the range in which the most rapid pH change occurs in the reaction
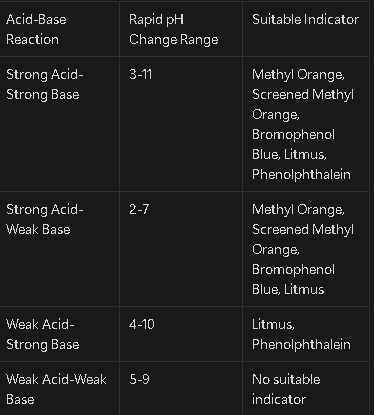
Denote the ranges of the various acid-base reactions and the suitable indicators for each (1/5/1/4/1/2/1/1)