Organic Acidemias- BioChem Genetics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Organic Acidemias Background
Primarily disorders of Amino Acid Catabolism: Mainly
Branch Chain Amino Acids (BCAA)
Lysine
Toxicity comes from accumulation of ORGNIC ACIDS not from an A.A. acid accumulating
Causes metabolic acidosis with increased “Anion Gap”: Decrease in main anion Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
Secondary toxic effects of acidosis
Mitochondria→ Lactic acidemia
Urea Cycle → Hyperammonemia
Bone marrow→ Bone marrow suppression
CNS function→ Encephalopathy/Mental retardation
Major Presentations: Neonatal encephalopathic acidosis, late chronic/intermediate
All autosomal recessive
Metabolic Acidosis
Blood pH low due to excess acid (H+) vs Base (HCO3-)
normal range pH 7.3-7.45 (measure via Atrial Blood Gas)
Normal HCo3- level: 22-26 mEq/L
Mutiple etiologies for Metabolic Acidosis
Lowered HCo3- : loss through GI (diahrria), Renal tubule acidosis, Medications
Elevated H+: creation of abnormal acids in blood due to starvation, diabetes; Lactic acidosis due to mitochondrial dysfunction, Organic Acidosis
Clinical Consequences
Neonatal: non-specfic, similar to UCDs presenations,
Lethargy, vomting, Tachypena, Hypotonia, Seizures, Coma, Death
Adult: Devleopmental Delay, Ataxia, Neurological Deficits, (then the neonatal presenations)
Organic Acidemias
Newborn Screening detects many Organic Acidemias
Organic Acidemias Treatment
Restrict Dietary Protein disease specific amino acid free formulas
Prevent Catabolism provide sufficient protein free calories
Reverse Acidosis ± Hyperammonemia
Hemodialysis
Ammonia and lactic acid scavengers
Sodium bicarbonate, sodium benzoate, phenylbutyrate
Cofactor therapy for specific Disorders
Propionic Acidemia Metabolism
Failure of Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
Step 11 of Isoleucine and Valine metabolism:
Propionyl-CoA → Methylmalonyl-CoA via Propionyl-CoA carboxylase activity
Propionic Acidemia
Also known as Ketonic hyperglycemia: high level of glycine and ketone bodies
Autosomal Recessive
Incidence 1:100,00 (higher in Saudia Arabia and Inuit)
Genetic Defect
Propinyl-CoA Carboxylase (PCC) alpha or beta subunit genes
some genotype/phenotype correlation (null alleles/deletions more severe)
Biotin cofactor for PCC
PA accumulation due to PA production from
MET/THR/VAL/ISO catabolism,
gut bacteria,
odd chain FAs
Untreated Propionic Acidemia
Classical Neonatal Encephalopathic Form
Normal at birth
Within a few days
Poor feeding, lethargy, vomiting hypotonia →encephalopathy, seizures, coma, death
Late-Onset Form
Developmental delays/regression
cyclic vomiting
protein intolerance
growth impairment
hypotonia
metabolic basal ganglia stroke
cardiomyopathy
Acute episode of toxic encephalopathy
Rare Cardiac Subtype isolated cardiomyopathy
Diagnosing Propionic Acidosis (PA)
Newborn Screening
Elevated Propinoyl Acylcarnitine and ratio to other carnatine species
other etiologies: Methylmolic Acidmia, Cobalamin Defects, Maternal B12 Deficiency, False +
Confirmatory Testing
Atrial Blood Gas: Elevated ammonia, low glucose, high acidosis, increased anion gap
Complete blood count: suppression of bone marrow→ less blood cells
Urine Organic Acid Analysis: High 3-OH-proprionate, mthylcitrate, tigly/proprionylglycine but NOT MMA
Plasma Amino Acid profile:
elevated glycine + glutamine, not homocysteine (seen with Cobalamin defects)
Acyl-Carnitine Profile: Elevated C3 acylcarnitine, not C4-DC unless SUCLA2 deficiency
PCC enzyme activity: can measure PC enzyme in leukocytes or fibroblasts
PCC Genotyping
Gene sequencing w del/dup analysis (99% detection rate)
Treating Propionic Acidosis
Acute Acidotic Encephalopathy
Remove acids and ammonia hemodialysis
severe hyperammonia: ammonia scavengers
Reduce PA production Protein restriction 24-25hr
Prevent catabolism: glucose and lipids IV
Enhance PA excretion: IV Carnitine
Decreased PA production in Gut: Antibiotics (Metronidzole
Biotin:
Chronic Treatment
protein restriction and MTVI-free metabolic formula
Oral Carantine, Biotin, and Antibiotics
Avoid decompensation
unresponsive to Tx → liver transplantation
Propionic Acidemia Deficiency Outcome
Treamtnet improves surivial, but invariable there is an affect to some degree
Neurodevleopmatl disabilty
metabolic basal ganglia stroke
seiures
pancreatisis
cardiomyopathy
gorwth impairment
nuetorpnia, AA defience
renal failure
premature ovarian fialure
hearing and vidual defecits (optic nerve atrphy)
Propionic Acidemia Deficiency Screening
Carrier Screening:
PRenatal Diaongis:
amontic fluid orgnaic acid measurment possible (some false negatives)
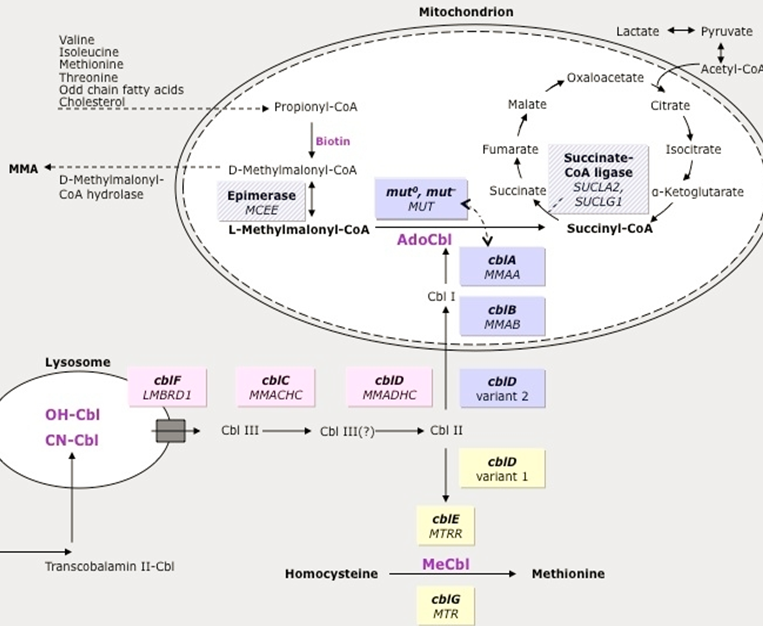
Methylmalonic Acidemia Pathway
Isoleucine and Valine
Methlymalonyl-CoA → Succinyl CoA via Methylmalonic-CoA mutase activity
Methlymalonyl-CoA accumulates
Methylmalonic Acidemia
Increased Methylmalonic Acid but not homocysteine (other forms of MMA have elevated homocysteine→ not primary MMA, but related to Adenosyl Cobalamin - A )
Genetic Defect: mutation of multiple genes cause similar phenotype
60% Methlymalonyl-Co mutase gene mutation (MUT)
37% Cobalamin A,B,D2 (MMAA, MMAB, MMADHC)→ the upstream vitamins that will be converted into Adenosyl Cobalamin→ leads to dysfunctional MM-Co mutase
Untreated Methylmolaynic Acdiemia
Infantile Subtype: Most common mut0, cblB mutations
Normal at Birth
Within days to weeks: poor feeding, lethargy, vomiting, hypotonia, encephalopathy→ progress to seizures, coma, death
Intermediate phenotype: mut-, cblA, cblD2
Normal for month to years: fialure to thrive, devleopmental delay, hypotonia, poriten aversion→ risk of carastrophic decompensations
Benign Adult form: typically asymptomatic, can decomapnste
Diagnosing Methylmolaynic Acdiemia
Newborn screening: Elevated Propinoyl Acylcarnitine (and ratios) → but non specific
Confirmatory testing
Atrial Blood Gas, Ammonia Levels, Completel blood ocunt:
Hi AG metabolic acidsosi
Elevated ammonia
Low gluclose
pancytopenia
Urine Organic Acid: High MMA
Plasma Amino Acid profile: high glycine + glutamine, no Homocystine (Hcy)
CblC/D/F - Hcf + MMA high ;
cblD2/E/G - Just hcf High
Enzyme activity: fibroblasts
Genotyping on genes = 95%
Treating MethylMonlic Acdicema
Treat acute acidotic encephalopathy
Remove acids+amonia: hemodialysis
Reduce MMA production: protein restriction
Prevent catabolism: IV glucose and lipids
Severe hyperammonemia: Amonia scavengers
Decrease gut bacteria: Antibotics
HYDOXYCOBALAMIN (B12) injects: cofactor
Chronic Treatment
protien restriciton and MTVI-free meatolibc fomumal
L-Carnitine + OH-B12
Avoid decompensation
Methylmalonic Acidemia Treatment outcome
Most patient will have some degree of mental impairment, long term affects
Methylmalonic Acidemia Diagnosis
Prenatal/Preimplantation:
Ammonitic organic acid fluid analysis possible
Enzyme activity of CVS and amniocentesis
Iso-valeric Acidemia
issues with the Isovaleryl-CoA dehygroenase enzyme
LEUCINE PATHWAY ONLY
Build up of Isovalryl-CoA (Isovaleric Acid)
Isovaleric Acidemia (IVA)
Disorder of Leucine metabolism
Genetic Defect
IsoValeryl-CoA Dehydrogenase (IVD) Gene Mutation
results in increased Isovaleric Acid
Sweaty feet odoer is prominent
Untreated Isovaleric Acidemia
Severe Neonatal Onset form
Normal at birth
Within day: poor feeding, lethargy, hypotonia, Sweaty feet order —> encephalophagy, seizure, coma, death
Mid/Late Onset Form
unexplained failure to thrive and developmental delay
Benign Adult Form : typically asymptomatic but can mildly decompensate
Diagnosing Isovaleric Acidemia
Newborn screening: elevated Isovaleryl Acylcarnitine → can also be increased in 2MBG+Antibitoic
Confirmatory testing
Blood tests:
High ammonia
Low glucose
High metabolic acidosis
Urine organic acid
High IVA
High isovaleryl glycine
Plasma AA levels:
High glycine
High glutamine
Enzyme activity: Fibroblast
Genotyping: exact genes unknown
Treating Isovaleric Acidemia
Treat Acute Acidotic encephalopathy
Remove acids and ammonia: hemodialysis
Reduce IVA production: protein restriction 24-26hrs
Prevent Catabolism: IV glucose and lipids
Enhance IVA excretion: IV carnitine
If hyper ammonia: ammonia scavengers
GLYCINE SUPPLMENTAITON-BINDS IVA
Chronic Treatment
Protein rection and LEUCINE-free metabolic formula
Oral L-Carnitine and L-Glycine
Avoid decompensation
Isovaleric Acdiemia Otucome
Outlook with Treatment is one of the best if treatment done early and effecetively enough
can be comepltely asymptomatic as long condition is monitored
Leucine tolerance gets better with age
Even if diaognsis is after neonatal period, and evne with major encaplapthic event in neonatal period—> longer term out look is vairable : CAN BE OK
Isovaleric Acidemia Prenatal Diagnosis
Ammniotic fluid can be checked for organic acids
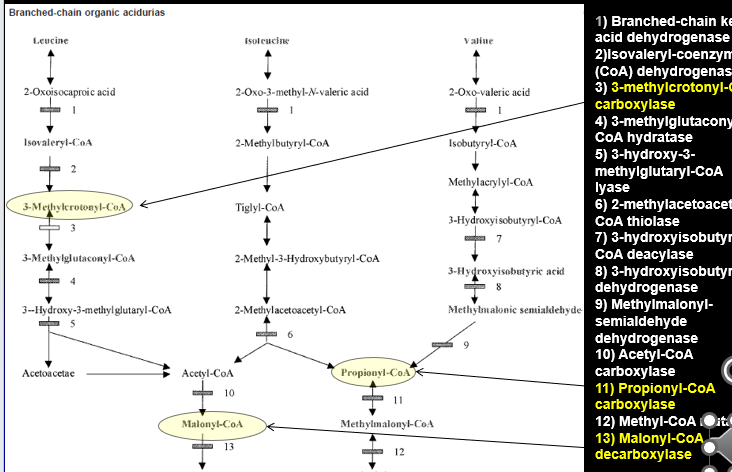
Biotinidase Deficiency Pathway
Biotin is a vital cofactor for of number of different enzymes:
ALL ARE CARBOXYLASES
3-Methylcrontoyl-CoA carboxylase (Leucine)
Propinoyl-CoA Carboxylase (Isoleucine and Valine)
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase
When there are mutations in the BIOTINADASE gene: Biotin is not properly recycled → these blocks develop
Biotinidase Deficiency (BTD)
Late multiple Carboxylase Deficiency
Slightly increased incidence in Hispanic and Middle Easter
Gene Defect: Biotinidase (BTD) gene
failure to recycle biotin = biotin deficiney
Biotin co-factor for the carboxylases: cannot combine and make function enzyme
Untreated Biotinidase Deficiency
Affect depends on the residual enzyamtic acitvity when biotin absent
Profound Defcieny (<10% enzyme)
Normal at birth
Symptoms devleop after few months
Developmental delay, seziures, hypotonia, ataxia, hearing loss, visual problems, ***alopecia***, ***eczema*** (uniquie to BTD)—>
Partial Defieciney (10-30% enzyme)
intermeinet symptoms with stress
Symptoms can be irreversible once present
Diagnosing Biotinadase
Newborn Screening: Elevated C5-OH Acylcarnitine, but not specfic to BTD
Confirmatory Testing
Blood:
High ammonia
High acidosis
Low gluclose
Urine Organic Acids: multiple organic acids b/c Bitonaisde affects multiple enzymes
( )
Elevated C5-OH Acylcarnitine
Enzyme activity: If Biotinadase activity is normal—> then issue is probably Holocarboxylase deficiency (presents the same way but is earlier)
Genotyping: sequencing 99% detection
Treating Biotinadase Deficeincy
Rarely severyl acidotic or hyperammonemic
may occasionally need sodium bi-cabonate (adress acidty)
may occasionally need amonia scavnerge (adress amonia levels)
Insitute Biotin therapy immediately
Chronic treatment
Biotin
No protien restction
Avoid raw egg whites (has protein that binds Biotin)
Biotinadase Deficiency outcome
Extremely great outlook for patients (one of the best for Organic Acidemias)
As long as treatment is implemented BEFORE the development of severe symptoms
If detected after symptoms, some are irreversible: optic atrophy, hearing loss, developmental delay can presist
Biotinadase Deficiency Prenatal diagonsis
Biotinadase enzyme activity can also be measuredin the amniocytes and the amniotic fluid
3-MethylCrotonyl-CoA (3-MCC) Carboxylase Deficiency
LEUCINE METABOLISM
Diagnosis:
Newborn screening: VERY COMMONLY FOUND High C5-OH
Mom can be asymptomatic
Urine Organic Acids: High 3-Methylcrotonyglycine, 3-OH-IVA
Cause: 3-MCCC Subunit 1 or 2 Genes : Biotin a cofactor → effected when bitoinadase
Symptoms
May be asymptomatic
Some episodic liver dysfunction, hypotonia, hypoglycemia
May cause development delay + sezures
Treatment
Restrict LEUCINE
Carnitine (to excert Leucine) and Biotin suppletion
3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl (3-HMG) CoA Lyase Deficiency
LEUCINE METABOLISM
Diagnosis
Newborn screening: High C5-OH
Urine Organic Acids: elevated 3-HMG, 3-methylglutacoant, 3-OH-IVA, 3-methylglutarate
Cause: HMGCL gene mutation
Symptoms
May be asymptomatic until decompaneaion
Liver dysfucntion
Treatment
Leucine restriction
Caritine supplementation (BUT NO NEED FOR BIOTIN)
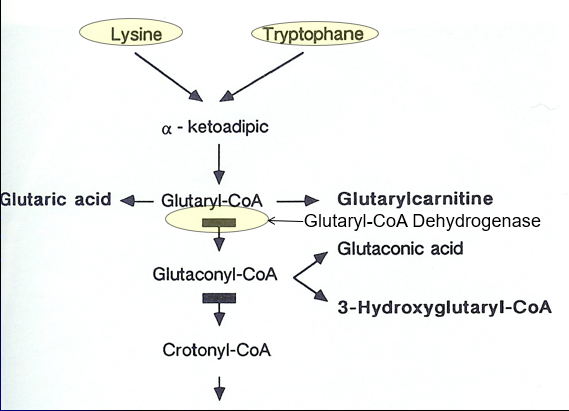
Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 (GA1) Metabolism
NOT a Branch Chain Amino Acid metabolism disorder
Breakdown of LYSINE and TRYPTOPHANE
Lysine + Tryptophane → Alpha ketoadipic→ Glutyrl-Coa
Glutyrl-Coa→ Glutaconyl-CoA (shunt to Glutaontic Acid) via Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase activity
Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 (GA1)
“Cerebral” Organic Acidemia: Often normal
Genetic Defect: Glutaryl-CoA Dehydrogenase (GCDH) gene mutation causing defective Lysine + Tyrptohan metabolism
Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 (GA1) Symptoms
Often normal at birth or only macrocephalic
symptoms often begin prior to 2 years of age
May start with a Sudden neurologic decompensation: 75% by 14months—> fever, illness, metabolic stress
Primary symptoms
Stress-induced encephalopathy
Ataxia
Epilepsy
Myoclonus
Storke-like episodes
Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 (GA1) Diagnosis
Newboarn screening: Elevated C5-DC (glutaryl) Acylcarnitine
many False negatives
Confirmatory Testing
Blood: elvated ammonia, low gluclose, Aciditiy
Plasma + Urine: C5-DC glutaryl acylcarnitine + glutaric acid
Enzyme activity: fibroblast
CT/MRI: Cerberallar atrophy, basal ganlia infact and hemorrhage
Genotyping
Glutaric Acidemia Type 1 (GA1) Treatment
Reverse/Prevent Catabolism When sick: protien free calroeis during metaoblic stress
Dietary Mdofication
Low LYSINE and TRYOPTHAN
MEdicaitons
B2 (Riboflavin) is a COFATOR
Carntine: Binds Glutaric acid and remvoes it
Avoid Valproate (Bind Carnitine)