bio principles test 3
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Prokaryotic genome
A single DNA macromolecule, a closed circle
Genome
The total genetic information of a cell or organism
Eukaryotic genome
Several DNA macromolecules, humans have 23 different chromosomes
Most of our cells are _____ and some cells/organisms are _____
Diploid and haploid
Diploid
A cell, nucleus, or organism containing two sets of chromosomes (2n)
Haploid
A cell, nucleus, or organism containing one set of chromosomes (n)
DNA double helix is wound around _____ proteins to for many _____, which are collectively called ______
Histone, nucleosomes, chromatin
Chromosomes are
Linear
What is prokaryotic cell division called?
Binary fission
Step 1 of binary fission
DNA replication
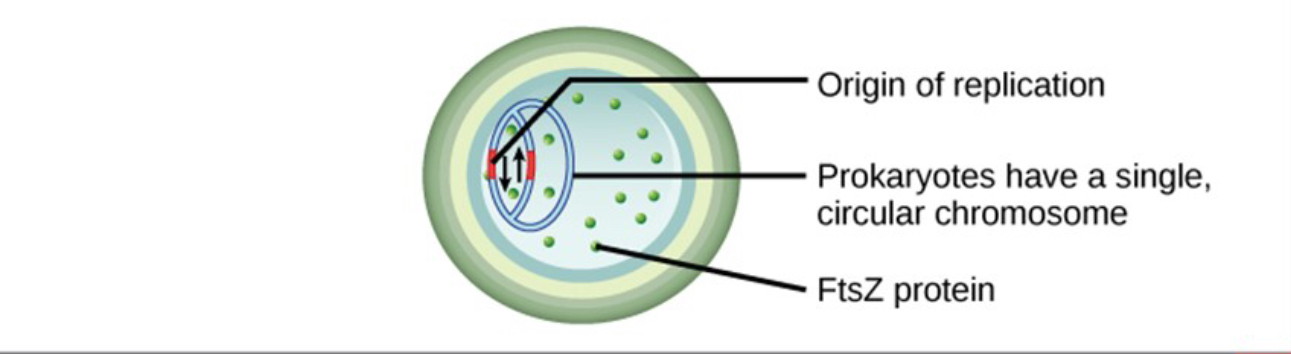
Step 2 of binary fission
Cell elongation, FtsZ protein moves to center of cell
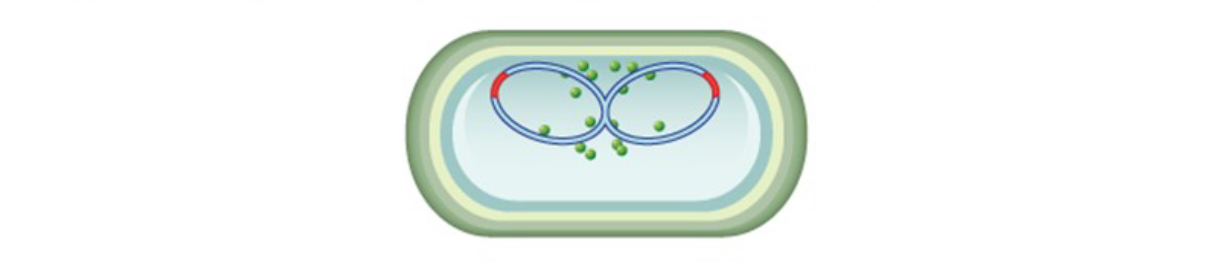
Step 3 of binary fission
Chromosomes moved to opposite sides of cells, FtsZ forms a ring
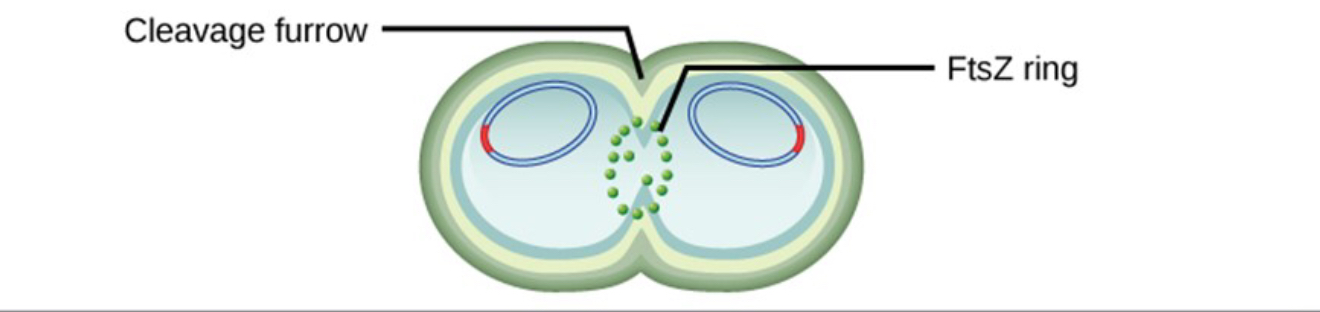
Step 4 of binary fission
FtsZ directs formation of septum (dividing cell wall) in cell center
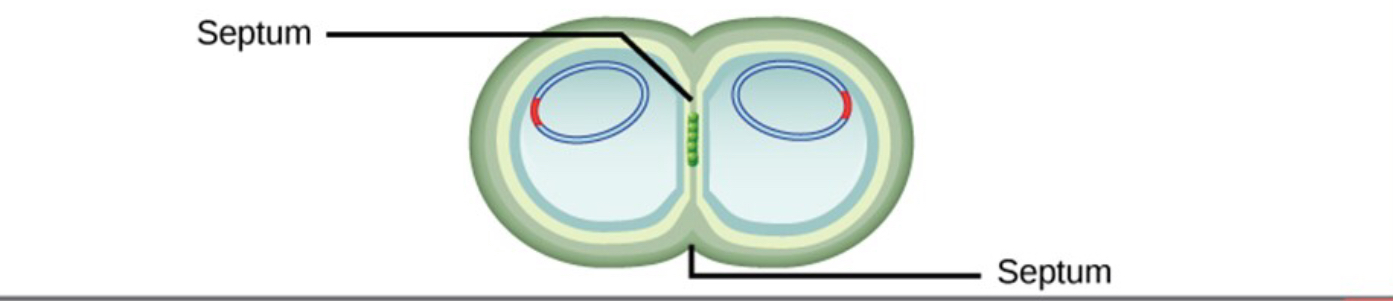
Step 5 of binary fission
Cell pinches in two, forming two identical daughter cells
Gap Phase 1
Growth, accumulation of resources, longest stage
Synthesis (building something)
DNA replication, in animals replication of centrosome (contains centrioles, contain microtubules)
Gap Phase 2
Replication of some organelles, further growth and accumulation of resources
Mitosis
Several steps, PPMAT
Prophase
Nucleus, golgi, and ER break down, chromosomes condense become visible distinct, spindle apparatus forms
Prometaphase
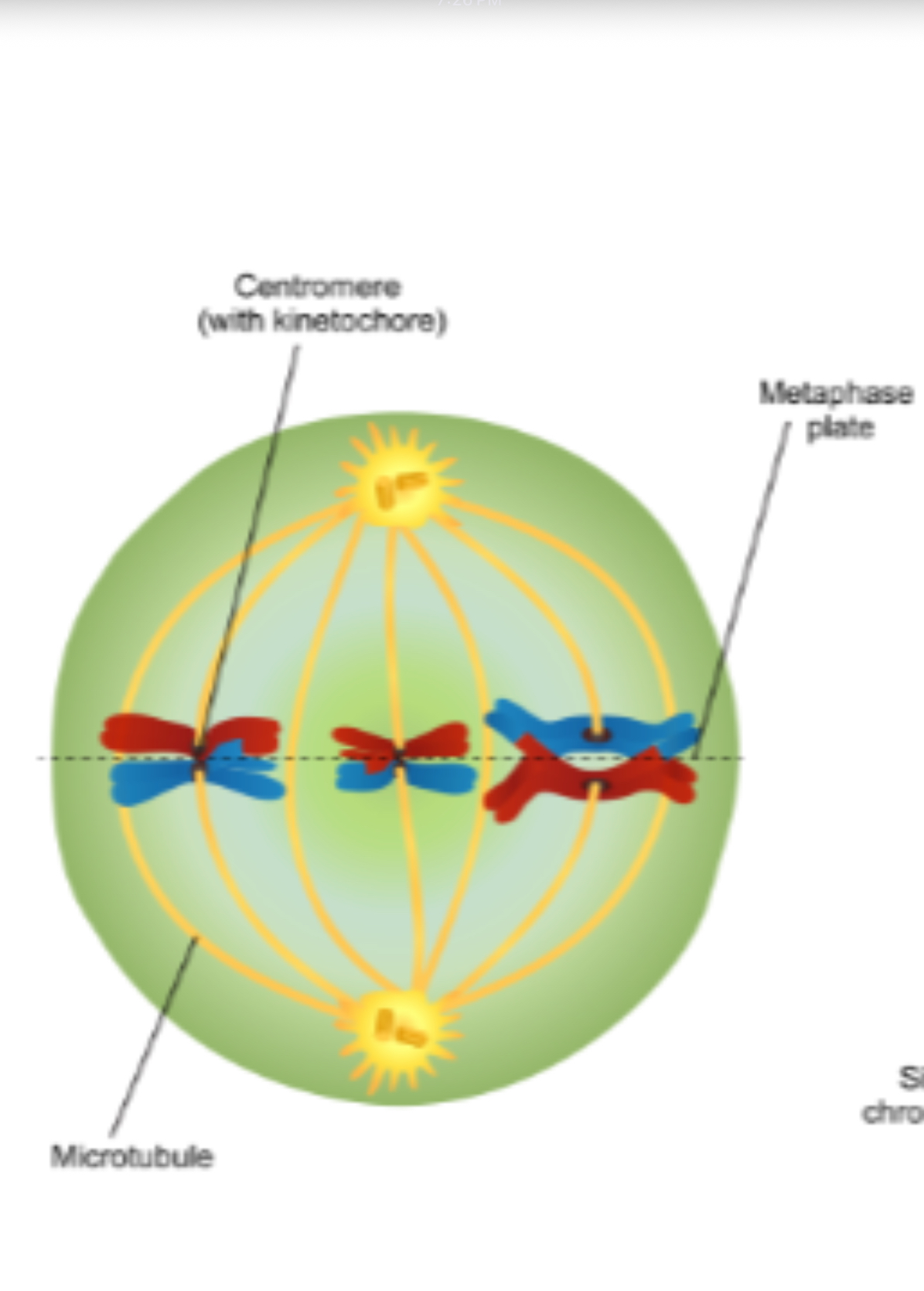
Microtubules (part of spindle apparatus) attach to sister chromatids at points called kinetochores
Sister chromatids
Two connected identical copies of a chromosome
Metaphase
Sister chromatids align at center of cell, positioned to move to opposite sides of the cell
Anaphase
Sister chromatids split, spindle apparatus pulls the, to opposite sides of cell
Telophase
Chromosomes de-condense, nucleus, golgi, and ER reform x2
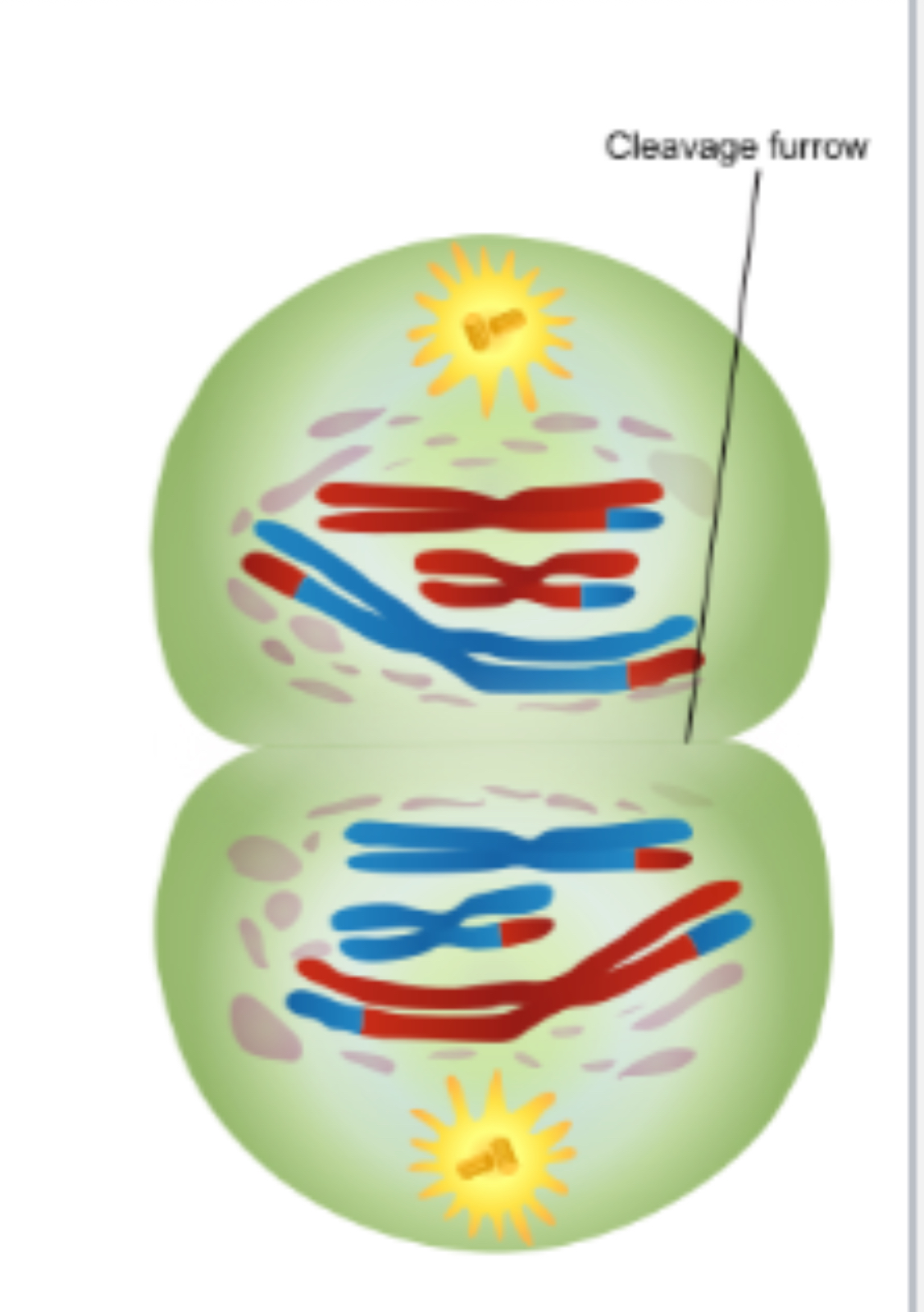
Cytokinesis
Cleavage furrow (animal) or cell plate (plant) separates cell in two identical daughter cells
G0 (resting phase)
Not part of cell cycle, offshoot- after cytokinesis, before G1, cells in G0 are not actively dividing they are fulfilling their normal functions
Where are most cells?
In G0
G1 checkpoint
Checks for energy and resources for DNA replication and damage to DNA
G2 checkpoint
Checks for damage to DNA
M (metaphase) checkpoint
Checks that all sister chromatids are connected to spindle apparatus
Cells need …
Permission from surrounding cells to divide, this maintains normal cell number/density
There are many ____ involved in regulating cell cycle
Proteins
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell growth, which causes harm, caused by faulty cell cycle control proteins, caused by mutations in the DNA sequence, caused by un-repaired DNA damage
Proto-oncogene
A normal gene involved in the cell cycle that, when mutated, becomes an oncogene
Example of tumor suppressor gene/protein
p53
p53
Locates damage to DNA and brings in DNA repair proteins, if repair is successful, cell cycle proceeds, if damage is too severe, causes apoptosis
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
If p5 is mutated
No longer encodes a functional protein, allows cell with damaged DNA to divide, leads to more mutations, more oncogenes
Virtual all eukaryotic cells are
Capable of sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction results in
More diverse offspring than asexual reproduction
High diversity among offspring
Increases likelihood of survival
Meiosis is done by
Special germ cells
Meiosis I
PPMAT I
Prophase I
Nucleus, golgi, and ER break down, chromosomes condense, synapsis, allows for crossover
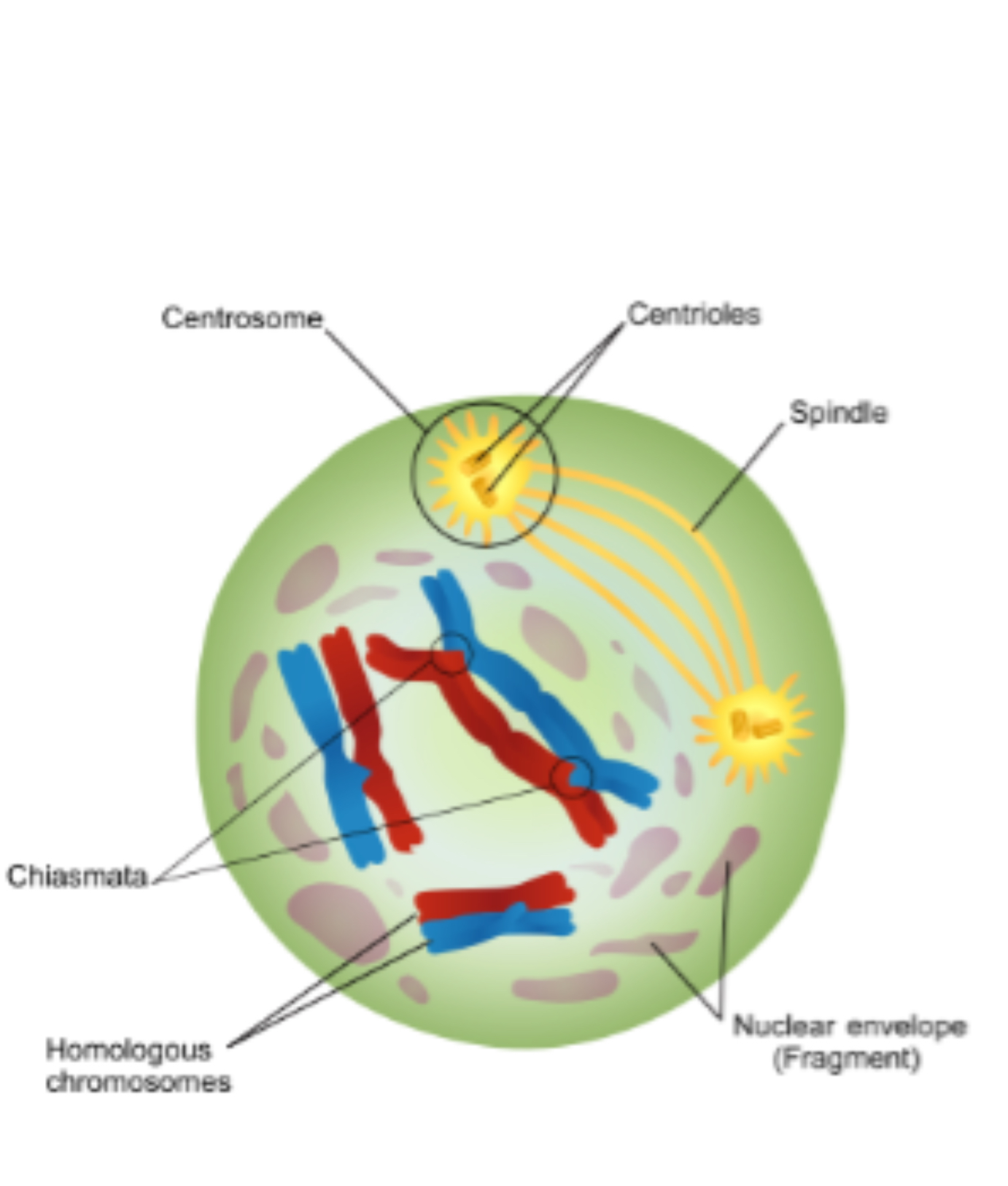
Synapsis
Formation of tetrads
Oncogene
A mutated version of a normal gene involved in the cell cycle- can lead to cancer
Tetrad
Two duplicated homologous chromosomes (four chromatids) bound together during prophase I
Homologous chromosomes have
The same genes, but the exact sequences are different
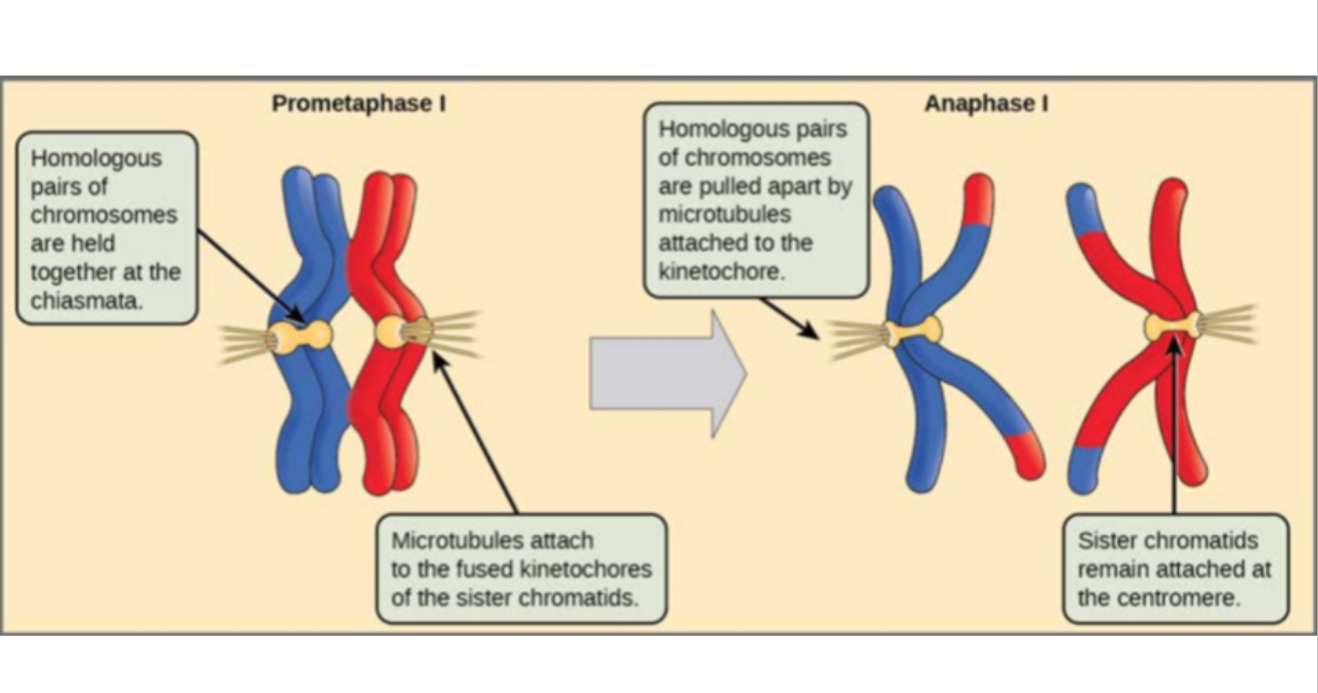
Prometaphase I
Microtubules attach to tetrads
Crossover
The exchange of genetic material between homologous (non-sister) chromatids, resulting in chromosomes that incorporate genes from both parents of the organism
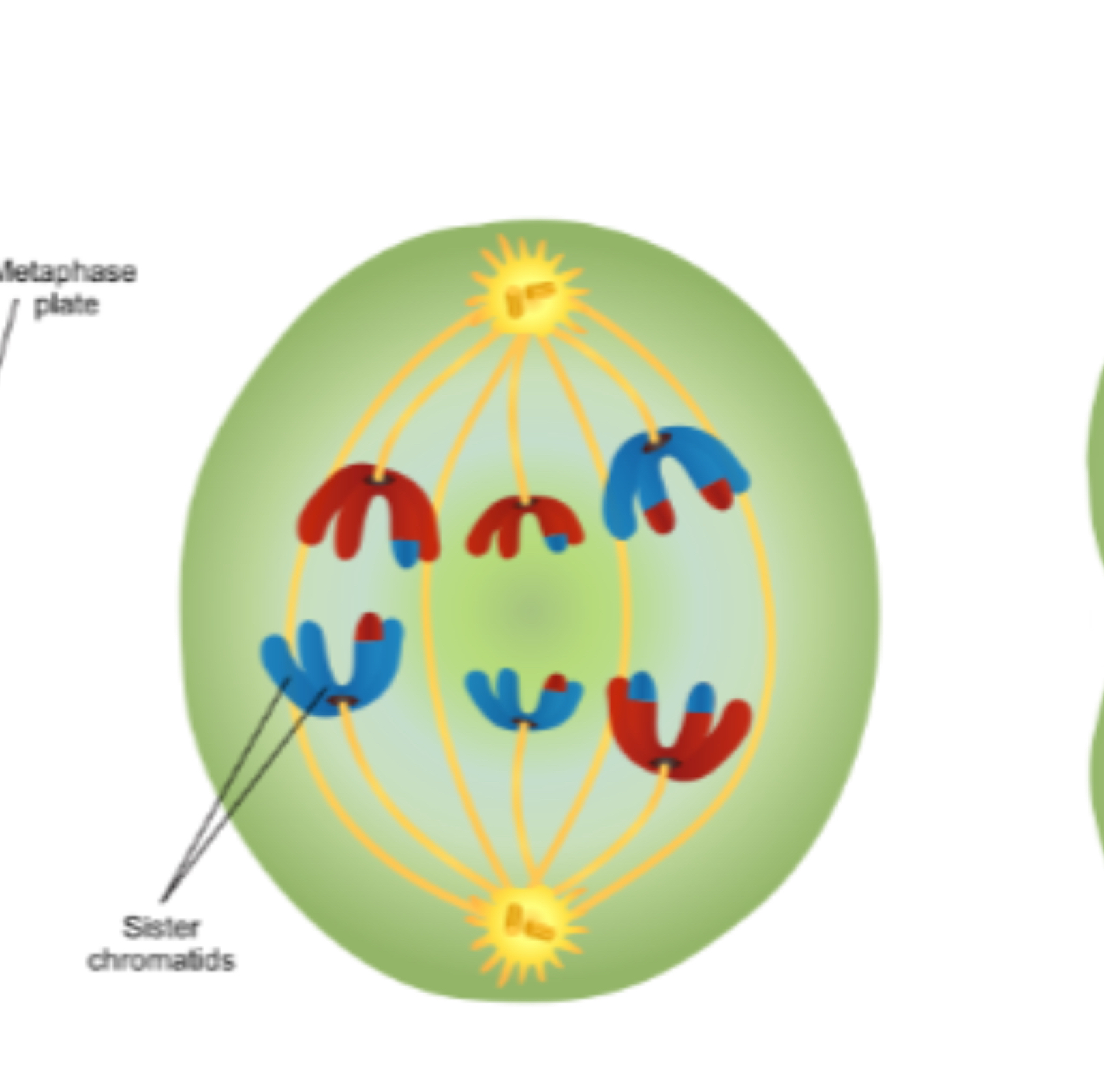
Metaphase I
Tetrads align at center of cell, their orientation is random- different daughter cells will receive different homologous
Anaphase I
Tetrads pulled apart, sister chromatids go to same side
Telophase I
Chromosomes de-condense, nucleus, Golgi, and ER reform x2
Cytokinesis (after telophase)
Result 2 “haploid with replicated DNA” cells
Where is there no interphase?
Between meiosis I and meiosis II
Meiosis II
PPMAT II, just like mitosis
Cytokinesis (after meiosis II)
Result: four haploid cells
Chromosomes contain
genes
Genotype
the underlying genetic makeup of an organism (can’t see)
Phenotype
the observable traits expressed by an organism (you can see)
What do most genes encode?
proteins
Genotype leads to
phenotype
A given gene can have different versions/variations called
alleles
Diploid organisms have two copies of each chromosome, which means
two copies of each gene
Homozygous
two of the same allele
What phenotype will homozygous have?
the allele version they have
Heterozygous
two different alleles
For any given gene
one allele is dominant and the other is recessive
What phenotype will heterozygous have?
the dominant allele
What are the 3 possible genotypes?
homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive, and heterozygous
Parents are both diploid but
only pass on one of each chromosome to offspring
How is the version of each chromosome put into egg/sperm chosen?
randomly
Punnett square
used to predict possible genetic outcomes of offspring, usually one gene at a time
What does each box of the Punnett square represent?
25% probability of possible offspring
What do many human traits/diseases follow?
Mendelian Inheritance patterns
Polygenic inheritance
phenotype is the result of two or more genes
What does polygenic inheritance lead to?
continuous variation
Continuous variation
an inheritance pattern in which a trait/phenotype shows a range of values
Incomplete dominance
heterozygotes are intermediate in appearance between the two homozygous
Codominance
the complete and simultaneous expression of both alleles in a heterozygote
Example of multiple alleles
ABO blood types in humans
Recessive lethal
an allele that’s only lethal when homozygous
Recessive lethal in heterozygote
may or may not have an effect on phenotype
What system do most mammals use for biological sex determination?
X/Y
X and Y chromosomes are
two versions of the sex chromosome
All other chromosomes are called
autosomes
Autosomes are
not directly involved in sexual development
X chromosomes
have many genes required for life, directs development to female sex
Y chromosome
no genes required for life, alters x-directed development, leading to male sex
We are diploid so we have
two copies of the sex chromosome
How can sex be determined in other animals?
through different mechanisms
X-linked traits
gene located on X chromosome
XY individuals are most likely to have a trait because
they have only one copy of the gene
Epistasis
an antagonistic interaction between genes such that one gene masks or interferes with the expression of another
Example of epistasis
coat color of mice
What is DNA made of?
nucleotides
5’ phosphate of one nucleotide is connected to what?
3’ OH of the next
Two strands of DNA form
a double helix
What is a double helix held together by?
H bonds between bases
Two strands of DNA in the double helix run
antiparallel to one another