B6: PPC/OMM Exam THE BIG ONE
1/518
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
519 Terms
gynecologic history
What encompasses all components of Hx (medical, surgical, social, family, immunizations) and:
-RFs for STI, domestic violence, unintended pregnancy
-menstrual Hx (age of onset, regularity, bleeding issues)
-menopause (onset, severity of Sx, Tx)
-Sexual Hx (M/F/both, contraceptive use, partners both new and duration of relationship, Hx of abuse/violence)
-pregnancy (total #, outcome of each, complications, post-partum conditions and follow-up)
-infertility (evals and Tx)
-hormonal therapies
-cancer screenings (PAP + HPV Hx, mammograms, colonoscopies)
menstrual Hx
What history includes:
-Menarche (age of onset, initial character, change over time) -- note: 1st 2 years not predictable and no discomfort present
-frequency of bleeding (days or weeks apart, regular v. irregular -- predictable is more important!)
-Duration of bleeding - total days
-Amount of Bleeding - try to quantitate w/ pads, tampons, how frequent changing, soaking bedclothes/extra protection overnight, clot size
-change over time
-Tx in past
amenorrhea
What is no menses for previous 6 mos?
oligomenorrhea
What is bleeding frequency >35 days?
menorrhagia
what is too much bleeding?
metrorrhagia
What is too long of bleeding?
menometrorrhagia
What is too much bleeding and too long of bleeding?
polymenorrhea
What is bleeding too often?
dysmenorrhea
What is painful menses?
sexual Hx
Components of a(n) ________ include:
-menstrual and pregnancy Hx
-STI Hx
-contraceptive usage (current + previous)
-sexual orientation
-difficulty with sexual functions
-lifetime # of partners and gender
-abuse/violence
contraceptive Hx
Components of a(n) ________ include:
-use or need
-types used previously
-any rxns (adverse bleeding, thrombolic event)
-failures (pregnancy w/ normal use)
-non-compliance issues)
-coercion from partner
obstetric Hx
Components of a(n) ________ include:
-gravida = total # of pregnancies
-para = # of pregnancies achieved potential viability (>20 weeks) -- includes TPAL
T = term (>37 weeks)
P = pre-term (20-37 weeks)
A = abortions (loss before 20 weeks)
L = living children
Delivery outcome (obstetrical conditions, complications, post-partum issues)
Abortions (spontaneous (miscarriage) and induced) which should include gestation, maternal or fetal conditions, methods (meds/surg), complications
preventative visit
Objectives of ________ include:
1. Determine risks (unintended pregnancy, STIs and disease, domestic violence)
2. provide guidance on risk reduction
3. cancer screening and prevention counseling
4. ID and address pt concerns and gaps in knowledge
unintended pregnancy
Pts at risk for _________ include:
-poor
-uninsured
-young
-uneducated
intended
(intended/unintended) pregnancy:
-desired at time it occurred or later
unintended
(intended/unintended) pregnancy:
-mistimed or unwanted
-41% of pregnancies
-inc. cost of care
-poorer pregnancy outcomes
STIs
RFs for _______:
-Hx of multiple sex partners
-sexual partner with multiple sexual contacts
-sexual contact with individuals with culture-proved STI
-Hx of repeated STI
-attendance at clinics for STIs
questions to ask: multiple concurrent sex partners, serial monogamy, new sex relationships, partner's sex hx
HIV
Screening for which STI involves:
Test: ELISA (blood, saliva, urine)
Age: 15-64 at least once
Frequency: annually if RFs (IV drug use, sex partners with IVDU, sex partners with bisexual men since last HIV test, sex partners with +HIV, exchange sex for drugs or money)
**recommended for all persons seeking evaluation for sexually transmitted infections where HIV status is unknown
chlamydia
Screening for which STI involves:
Test: NAAT swab
Age: <25 or >25 if at risk
Frequency: annually
gonorrhea
Screening for which STI involves:
Test: culture, NAAT
Age: <25, >25 if at risk
Frequency: annually
syphilis
Screening for which STI involves:
Test: VDRL or RPR
Frequency: annually if at risk
HIV
Prophylaxis for _______ includes combination tenovofir and emtricitabine HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors
domestic violence
RFs for __________ include:
-Female
-age 18-36
-lower household income
-educational attainment of < high school grad
-drug and alcohol abuse
domestic violence
Prevention strategies for _________ include:
-ID discrepancy in goals or values and present behavior
-avoid confrontation
F- Feedback- compare risk behavior with non-risk behavior
R-Responsibility- stress patient’s responsibility to make change
A- Advice- give direct advice to change behavior
M- Menu- Identify risky situations and offer options for avoiding that
E –Empathy- Understanding and involved interaction
S- Self-sufficiency- develop strategies, commit to implement
q3 years
What is the ACOG guidelines for PAP smear in ages 21-29?
co-test with PAP and HPV q5 yrs
What is the ACOG guidelines for PAP smear in ages 30+?
A
What is the USPSTF guideline for screening for cervical cancer every 4 years with cervical cytology alone in F aged 21-29 years, screening every 3 year with cervical cytology alone or every 5 years with HPV testing alone, or 5 years with HPV testing in combo with cytology in women 30-65?
mammogram
USPSTF recommendation for _________ screening is to begin at 40 years of age and screen q2 yrs between 40-74
10 years earlier than pt's age of diagnosis
How many years in advance should pts at risk (e.g., 1st degree family member with breast cancer) begin mammogram screening?
50
What age is the recommendation to begin colon cancer screening?
osteoporosis
Recommendation for _________ screening involves:
-bone measurement testing at 65
-screening intended to prevent fracture, not prevent development of disease
-in absence of new risk factors, screening no more frequently than every 2 years
Early Screening: Family Hx of osteoporotic fracture, high risk meds, smoker
transgender
___________ care involves:
-All patients should receive routine preventive health care
-Screen all patients for intimate partner violence, depression, substance use, cancer and STIs including HIV
-Contraceptive discussion with transgender male patients
-Extent of exam is dependent upon stage of transitioning
-Preventive care should evaluate for adverse effects of hormonal therapy
-Lipid and liver function testing
-Cancer screening should be consistent with guidelines based upon anatomy and age:
-Pap smear samples have 10-fold higher unsatisfactory rate
-Patient collected HPV test may be preferred, although not FDA approved
-A transfeminine patient with a neovagina does not require cytologic screening and prostate cancer screening should follow recommendations for cisgender men
gynecologic exam
The preparation for _________ involves:
-pt properly covered (gown open in front)
-bladder empty
-chaperone present
-look at pts face for any cues
breast exam
The _________ involves:
3 positions
1. upright with hands on hips or above the head
2. leaning forward to move the breast off the chest wall
3. supine with hands behind head
Inspect:
-individually: skin changes, lesions
-BL: symmetry, developmental stage
-lean forward to see any skin retraction fixed to chest wall
Palpate:
-all 4 quadrants of breast and axillary tail
-adenopathy
-express nipple discharge
breast implants
In pts with ___________ the breast exam should be as follows:
Inspection: symmetry and position
Leaning forward: should move away from chest wall
Palpation: smooth contour, fullness uniform, + fluid wave
It is considered abnormal when: tense or too squishy, consolidation
breast exam
Documentation of a(n) _________ involves:
Inspection:
-developmental stage for peds pt
-symmetry
-skin lesions (character, location)
-nipple (inversion and if it can/cannot evert, discharge including character of the fluid such as color, turbidity, viscosity, amount)
Palpation:
-normal (no masses BL)
-tenderness (BL or UL, limited to quadrant)
-fibrous (dense fibrous bands, fibrocystic changes)
-implants if present
-masses (location by quadrant and character such as solid/cystic, moble/fixed)
-LN (axilla, supraclavicular)
dorsal lithotomy
Which pt position for pelvic exam:
-supine
-buttocks at table edge
-hips abducted ~30 degrees and flexed ~75 degrees
-either knees or feet supported
stretcher position or frog legged
Which pt position for pelvic exam:
-supine
-hips abducted and slightly flexed
-soles of feet together
M-shaped position
Which pt position for pelvic exam:
-supine
-hips abducted and flexed
-soles of feet on table, at the table's corners
seated
Which physician position during pelvic exam:
-best for speculum exam
-height and distance adjusted to comfortable working level
-do NOT lean in! move stool back to bend down
-light source positioning (dependent on the light source)
standing
Which physician position during pelvic exam:
-used for obstetrical cervical exam
-bimanual exam
mons pubis
What part of the external female genitalia:
-the hair-covered fatty eminence at the anterior margin of the UG triangle
-may provide some protection to the underlying pubic symphysis
labia majora
What part of the external female genitalia:
-two prominent folds of skin covered with hair and consisting primarily of fatty tissue (they are homologous to the skin of the scrotum)—provide some protection to the clitoris, and urethral and vaginal openings
labia minora
What part of the external female genitalia:
-hairless folds of fat-free skin that lie between the labia majora—surround and close over the vestibule of the vagina (which contains both urethral and vaginal openings)
-Anteriorly, each bifurcates, with one layer contributing to formation of the prepuce of the clitoris, and the other, to the frenulum of the clitoris
-homologous to the skin of the penis
hymen
Within the vestibule the ________ is a fold of mucosa covered CT that is fragmented into segments with sexual activity and childbearing
external genitalia
Examination of the __________ involves:
1. Speak
2. Touch thigh
3. Touch Perineal body - space between vagina and anus
4.Exam clitoris- retract labia major superiorly and cephalad
5. Spread the labial fold (between labia major and labia minora) to visualize the lateral aspect of labia minora
6. Open the vestibule- spread the labia minora to view the:
• Urethral meatus
• Periurethral gland openings
• Hymen
• Prolapse of vaginal walls
7. Palpate inguinal nodes (part of abdominal exam)
speculum
Insertion of the ________ should be as follows:
1. OBLIQUE! (pronate wrist 15-30 degrees)
2. depress posterior forchette with non-dominant hand and slide speculum over fingers
3. rotate speculum (wrist supinates) so blades are horizontal
4. continue inserting slightly posterior with blade (stop when feel resistance)
5. open blades by pushing thumb level (posterior blade in posterior vaginal fornix, anterior blade in anterior vaginal fornix)
6. adjust to visualize cervix
nulliparous
(nulliparous/parous) cervix:
-no parturition
-no deliveries
-rounded
parous
(nulliparous/parous) cervix:
-delivered previously
-elongated
conventional
Which PAP smear:
-Q-tip into canal for endocervical cells
-spatula scrapes surface for ectocervical cells
-brush both onto dry slide
-apply fixative
-wrap in cardboard envelope and send to lab
-CANNOT do HPV testing
liquid based
Which PAP smear:
-swirl cytobrush to obtain cells from canal and transition zone simultaneously
-swirl brush into liquid medium
-send to lab
-HPV TESTING AVAILABLE
vagina
Speculum exam of the _________ involves:
-follows inspection of cervix
-rotate speculum to visualize vaginal fornixes
-unlock blades before retracting speculum
-rotate speculum as withdraw from vagina, visualizing lateral walls
-close blades before removing speculum through vestibule
version
What description of the uterine position relates to the position in the coronal plane?
bimanual exam
What portion of the gynecologic exam:
-insert 2 fingers of dominant hand into vagina (palm up)
-palpate the cervix (note its character -- soft, firm, thick, length, tenderness)
-move to lateral fornix (move cervix noting any resistance or tenderness) to assess the broad ligament
-place other hand on abdomen (typically non-dominant) at the midline suprapubic region and depress the abdominal wall to feel uterine fundus between hands moving towards the pubis to palpate anterior uterine wall --> note the size of uterus, texture, position, mobility, and tenderness
-vaginal hand in the posterior fornix to extend vagina (lifting superiorly) to palpate posterior uterine wall -- note if any resistance or mass in uterovaginal space
-while vaginal hand in lateral fornix, abdominal hand moves laterally and sweeps down on diagonal to pubic symphysis to feel the ovaries (note size, texture, tenderness, mobility) and compare BL
flexion
What description of the uterine position relates to curvature of the endometrial canal (axis within uterus body)?
true
T/F: uterus may also be rotated along the midline (R/L deviation)
gynecoid
which pelvic shape:
-round
platypelloid
which pelvic shape:
-oval
android
which pelvic shape:
-wedge
anthropoid
which pelvic shape:
-oval long
rectovaginal exam
The __________ exam involves:
-inserting lubricated finger in vagina and rectum simultaneously
-vaginal finger palpates cervix and then posterior fornix
-rectal finger palpates rectouterine pouch, rectovaginal septum, and rectal mucosa
-abdominal hand palpates uterine fundus
Note any rectal mucosal masses, posterior cul de sac masses, nodularity of rectovaginal septum, restriction of tissue, or significant discomfort
hemoccult test
What test allows you to smear finger from the rectum onto slide, send to lab for processing, and note any gross blood?
blood from vagina, external hemorrhoids
What can cause false positives of a hemoccult test?
endocrine
The general exam as part of the ______ exam involves looking at the eyes and eyebrows, skin changes, hands and nails, hair
primary hypercholesterolemia
What disorder:
-changes are subtle but can be seen on exam
-eye changes usually most significant
-fundoscopic eye exam changes can be significant
-xanthomas are common findings (irregular yellow patch/nodule on skin caused by deposition of lipids)
-secondary hyperlipidemias can also present with similar findings (hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome, pancreatitis)
cholesterol emboli
ID
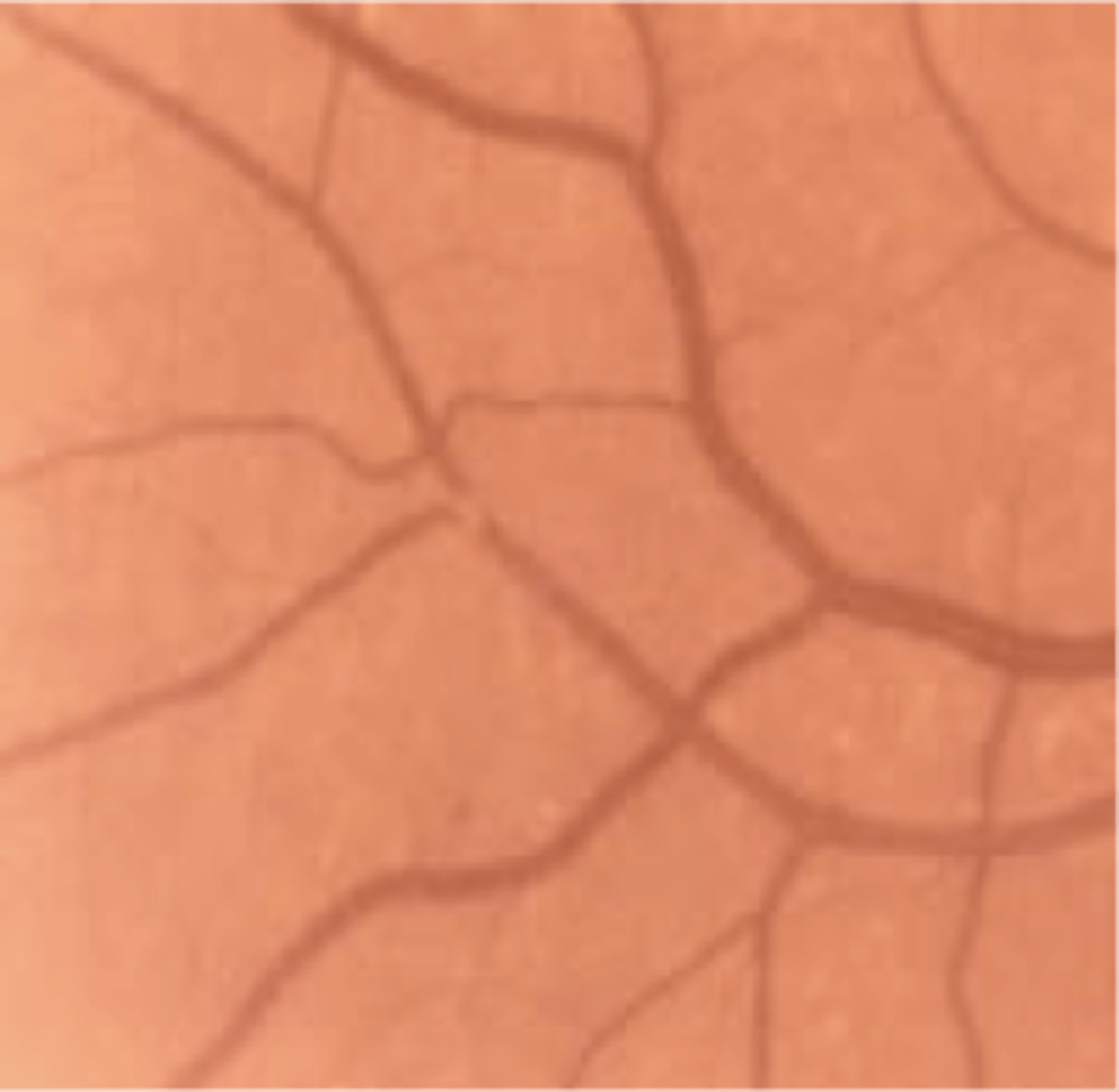
copper wiring
ID - usually found in conjunction with HTN but may be present with hyper cholesterolemia with infiltration of lipids into the vessel in the elderly

diabetes
What disorder:
-Sx and PE related to poor control of blood sugar
-goal to keep HbA1C at acceptable level
-multiple changes can be seen in skin and eyes of diabetics
-screening should include exams for peripheral neuropathy (reflects advancement of disease)
-Hx of Sx is key in diagnosing problems (paresthesias, blurred vision)
diabetes
Possible PE findings in a pt with ________ include:
Obesity: central
HTN
Eye: hemorrhages, exudates, neovascularization
Skin: acanthosis nigricans, candida infections, dermopathy
Neurologic: dec. or absent light touch, temp sensation, and proprioception, loss of DTRs in ankles
Feet: dry, muscle atrophy, claw toes, ulcers
diabetes
Fundoscopic changes in _________ include:
Non-proliferative (early) = mild visual changes, capillary leaks, microaneurysms, macular edema, nerve infarcts (cotton wool spots)
diabetes
Fundoscopic changes in _________ include:
Proliferative (diabetic retinopathy) = advanced disease, profound visual loss, neovascularization, fragile vessels bleed, retinal detachment, can be treated with laser
foot exam
The diabetic ________ should include:
1. monofilament testing for pts who have lost sensation b/c they are at increased risk for ulcers, infection, and later amputation (Use Semmes-Weinstein monofilament 5.07, applying 10g force)
2. vibratory testing
tuning fork
Which component of the diabetic foot exam:
-more accurate in detecting diabetic neuropathy b/c picks up an earlier disease
Studies show:
-detection <8s had normal monofilament
-detection <4s had some normal monofilament
thyroid exam
The __________ exam:
-largest endocrine gland and only one accessible to palpation
-butterfly-shaped each lobe 5cm long, 3cm wide, 2cm thick
-normal consistency = meaty/rubbery
-lobes curve posteriorly and are covered largely by SCM
-connecting central isthmus found below cricoid cartilage
Normal: not visible or palpable
Inspection: normal neck position, extended, then extended while swallowing (should rise), shine light from inferior border to observe trachea for deviation
Palpation: A/P, pull muscles aside for lateral, flex neck forward to relax SCM, push and pull trachea to one side to palpate CL, tilt head or rotate to side and palpate
Auscultation: carotids for bruits
hyperthyroidism
Which thyroid condition can cause systolic or continuous carotid bruit?
enlargement
Which thyroid condition can cause bruits from impingement on the carotid aa.?
Graves' disease
The following consistency of the thyroid corresponds to which disease process:
-soft
Hashimoto's, malignancy, nodules
The following consistency of the thyroid corresponds to which disease process:
-firm
thyroiditis
The following consistency of the thyroid corresponds to which disease process:
-tender
pregnancy
The following consistency of the thyroid corresponds to which disease process:
-enlarged
hypothyroidism
What disorder:
-lack of thyroid hormone
-metabolism decreases
-body systems react the same
S/Sx: weight gain, fatigue, constipation, dry skin, thinning hair, cold intolerance, infertility, myxedema, depression, muscle pains, hearing difficulty, thick fingernails, dry/rough/thick skin covered with fine superficial scales especially over the elbows/knees/heels, pale/waxy/cool skin sometimes with a yellow tinge due to interstitial edema from inc. tissue osmotic pressure from mucopolysaccharide deposits or from vasoconstriction/anemia/defect conversion of beta-carotine into vitA, periorbital edema (mucopolysaccharide deposition with increase osmotic effect and fluid accumulation, coarse/brittle/dull hair, alopecia involving the scalp, lateral 1/3 eyebrows, or generalized, brittle nails with transverse striations, lack of sweating
hyperthyroidism
What disorder:
-excess thyroid production
-most common cause = Graves' disease (autoimmune)
S/Sx: nervousness/anxiety, weight loss, tremor (fine trembling in hands and fingers), heat intolerance, tachy, palpitations, dysrhythmia, inc. appetite, sweating, skin thinning, difficult sleeping, fatigue/muscle weakness, elevated AM temp, hyperreflexia, fine/brittle hair, non-pitting pre-tibial myxedema, changes in bowels and menstruation
graves disease
What disorder:
-Goiter: diffuse, soft to slightly firm, non-nodular, bruit + thrill, mobile, non-tender, NO prominent adenopathy
-hyperthyroidism
-exophthalmos
-localized myxedema
-thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins
-Thyroid acropachy: an uncommon condition associated with autoimmune dysfunction of the thyroid gland that is marked especially by swelling and clubbing of fingers and toes and periostitis of the hands and feet + soft tissue swelling (pigmented, hyperkeratotic)
exophthalmos
clinical characteristics of _______ include:
Proptosis: abnormal protrusion or displacement of eye
Corneal damage
Periorbital edema
Chemosis: swelling of conjunctiva due to exudation from abnormally permeable capillaries, non-specific eye irritation, eyes may become difficult or impossible to fully close
Conjunctival injection
Extraocular muscle impairment
Optic neuropathy
localized myxedema
clinical characteristics of _______ include:
-raised surface
-thick, leathery consistency
-nodularity (maybe)
-sharply demarcated margins
-prominent hair follicles
-usually pre-tibial
-non-tender
pheochromocytoma
What disorder:
-excess catecholamine production
-Spells or paroxysms of headache, severe hypertension with paradoxical responses to antihypertensives, severe unexplained orthostatic hypotension, palpitations, and diaphoresis
conn's syndrome
What disorder:
-autonomous aldosterone secretion (usually aldosteronoma but can be idiopathic adrenal hyperplasia or carcinoma)
-hypernatremia with hypokalemia
-HTN with rare edema
-weakness, abdominal distension, ileus from hypokalemia
-primary aldosteronism
cushing syndrome
What disorder:
-excess endogenous or exogenous glucocorticoids
-weight gain and Sx big problem
-80% pituitary tumors
S/Sx: obesity (esp. central), plethoric face, HTN, hirsutism, muscle weakness, menstrual disorders, acne, mental disorders, bruising, osteoporosis, striae, moon facies
hirsutism
What disorder:
-abnormal hair growth from excess androgens (T)
addison's disease
What disorder:
-chronic adrenal insufficiency
-complain of fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain (severe cases can cause hypotension and coma)
-some have marked cravings of salt due to urinary loss
-hyperpigmentation
-hyperkalemia, hyponatremia (N:K ratio <30:1)
-ACTH elevated
acromegaly
What disorder:
-pituitary excess production of GH usually from adenoma
-Sx related to excessive bone growth, prognathism, macroglossia, coarse facial features
Metabolic: DM, heart disease, hyperhydrosis
Bitemporal Hemianopsia: BL loss of temporal vision due to pressure at optic chiasma
Hats/rings no longer fit
hypoparathyroidism
What disorder:
-hypocalcemia
-usually occurs after thyroidectomy
-increased neuromuscular irritability (hyperreflexia)
-carpopedal spasm
-hypotension and irregular heart rhythm
-dry skin
-ridged brittle nails
-seizures, tetany, facial spasms, cramping, paresthesias
-hyperactive bowel sounds, bronchospasm, laryngospasm
-depression, slowed responses
chvostek's sign
What clinical finding:
-medical sign observed in pts with low calcium
-increased neuromuscular irritability
-taping on cheek causes facial twitching
trousseau sign
What clinical finding:
-medical sign observed in pts with low calcium
-increased neuromuscular irritability
-may be (+) before other manifestations of hypocalcemia (e.g., hyperreflix and tetany)
-more sensitive
-inflate cuff for 3 min above SBP
-fingers extend and thumb adducts
-checks for latent tetany
hypercalcemia
What disorder:
-HTN and bradycardia
-abdominal pain
-muscle weakness (esp. proximal)
-longstanding bony tenderness
-hyporeflexia
-tongue fasciculations
-severe lethargy and stupor
-band keratopathy
hyper
(hyper-/hypo-) thyroidism:
-hyperreflexia (Brisk) with rapid relaxation phase
hypo
(hyper-/hypo-) thyroidism:
-hyporeflexia (depressed reflexes) with possible hypotonia of muscles if severe
hyper
(hyper-/hypo-) parathyroid:
-hyporeflexia
hypo
(hyper-/hypo-) parathyroid:
-hyperreflexia
informed consent
What is the permission granted in the knowledge of the possible consequences which is given by a patient to a doctor for treatment with full knowledge of possible risks and benefits?