APWH - Unit 1/2 - Chapter 2/3/4 - Period 1200-1450 - Test Rvw
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:28 PM on 11/13/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
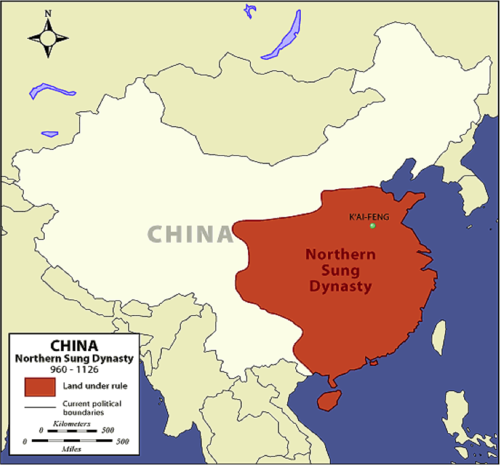
Song Dynasty (960-1279)
(Chinese dynasty)
Placed emphasis on administration, industry, education, and art. Characterized by advances in technology, medicine, astronomy, and mathematics. Ruled during the "Golden Age" of China.
Placed emphasis on administration, industry, education, and art. Characterized by advances in technology, medicine, astronomy, and mathematics. Ruled during the "Golden Age" of China.
2
New cards
The Grand Canal
Promoted trade between North and South China (because Chinese rivers flow west-east)
3
New cards
Civil service exam
exam based on Confucian teachings used to select people for government service jobs in the bureaucracy

4
New cards
Champa rice
tributary gift from Vietnam to China, fast ripening rice allowing for 2 crops per year, led to population increase

5
New cards
Song Dynasty Inventions
Porcelain, (agricultural tools, weaponry) gunpowder, refined printing, naval technology
6
New cards
Economy of Song China
better technology, urbanization, extensive infrastructure, produce for market, specialized crop sales (to then buy rice)
7
New cards
Flying cash
letters of credit (developed to deal with copper coin shortage)

8
New cards
Song Dynasty Patriarchy
emphasis on ancestor worship, foot binding, rapid commercialization of textile industries undercut local silk production by women, property rights expanded for women (could control dowries, inherit property), some argued women should be educated in order to educate their sons
9
New cards
Footbinding
(Male imposed) practice to mutilate women's feet (reduce size), produced pain, restricted movement, confined women to the household, seen as beautiful to the elite

10
New cards
Chan Buddhism
Buddhists adapt ideology to Chinese climate, (Dharma translated as dao, Nirvana translated as wuwei) Limited emphasis on textual study-meditation
11
New cards
Neo-Confucianism
Song didn't persecute Buddhists, but favors Confucians, influenced by Buddhist thought
12
New cards
Song Weaknesses
size of bureaucracy has heavy drain on economy, civil service leadership of military (lacked training, unable to contain nomadic attacks)
13
New cards
China is the dominant power of...
East Asia
14
New cards
Generally the .... (who adopted what?)
Elite adopted Chinese culture
15
New cards
China's influence on Korea
Tributary relationship, Korean elite culture influenced by China, filial piety began to erode elite Korean values (women lost rights), buddhism
16
New cards
China's influence on Vietnam
Tributary relationship, Vietnam closely copied Chinese political structures and systems (than Korea), women maintained more rights
17
New cards
China's influence on Japan
Chinese armies never invade (unlike it did to others), Chinese culture pervasive, Japan's isolation allowed for its freedom in borrowing Chinese culture (rather than forced?), women maintained more rights
18
New cards
Institution of the Shogun
Infighting between aristocratic lords and their clans using Samurai
19
New cards
Samurai
elite warriors (follow Bushido code), highly loyal to their aristocratic lords, honored
20
New cards
Tributary Relationship
one country gives gifts to another in exchange for protection
21
New cards
Aristocracy
power is in the hands of a hereditary ruling class or nobility
22
New cards
Centralization example
Building an interconnected system of roads and bridges
23
New cards
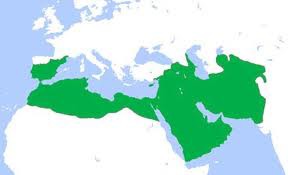
Abbasid Dynasty (750-1258)
Seizes control of Persia and Mesopotamia, defeats and replaces Umayyad army (750), slowly losing grasp of the region to independent Muslim rulers, swore formal allegiance to Caliph in Baghdad
24
New cards
Caliph
Successor to Muhammad as political and religious leader of the Muslims
25
New cards
Baghdad, Iraq
Abbasids built new capital here, center of trade
26
New cards
Seljuk Turkic Empire (11/12th centuries)
Turkic speaking pastoralists from Central Asia conquer much of Anatolia, Persia, Central Asia, converted to Islam, leader declares himself sultan, by 1200 controlled by regional sultanates
27
New cards
Ottoman Empire
Turkic warriors, conquer Anatolia to create a small sultanate (1300), sultanate rises in power to become prominent among Islamic world, Turks are dominant ethnic group of Islam, Ottoman sultan assumes title of caliph
28
New cards
Sultanate
Land ruled by a sultan (Muslim ruler)
29
New cards
Sunni Caliph belief
Anyone can be caliph
30
New cards
Shia Caliph belief
Caliph must be descendant of Muhammad
31
New cards
Devshirme
(Ottoman policy) system used to run the empire, Christian Balkan boys were recruited and forced into civil service, converted to Islam, given education, and produced high officials (governors, military commanders)

32
New cards
Janissaries
Elite infrantry soldiers recruited through devshirme, first modern standing army of Europe (served as Sultans bodyguards)

33
New cards
Islam in India (early 1000s)
Arabic trade with India predates Islam and continues, Mahmud of modern Afghanistan raids northern India (early 1000s), conquers region, destroys Hindu and Buddhist temples
34
New cards
Sultanate of Delhi
Major Turkic Muslim ruling in northern India from 1206-1526, weak administrative structure, reliance on cooperation of Hindu kings
35
New cards
Islam in India 1300-1500
Islam never able to claim more than a quarter of Indian population, Muslims live apart from Hindus as a minority, strong Hindu Kingdom of Vijayanagar ruling, Islamic merchants influence Southern India
36
New cards
Al-Andalus (Islamic Spain)
Muslim Berber conquerors from North Africa, refused to recognize the Abbasid dynasty, a center of learning, Christians, Muslims, and Jews live in harmony until replaced by intolerance
37
New cards
Dar al-Islam
"house of Islam", refers to lands under Islamic rule, uniformity of Islamic law throughout this promotes trade
38
New cards
Status of Women in Islam
Quran improves status of women, male dominance preserved
39
New cards
Sufism
Sufi missionaries, asceticism, mysticism
40
New cards
Ibn Battuta (1304-1369)
Muslim Berber scholar and explorer who traveled the medieval world, visited most of the Islamic world and many non-Muslim lands, completed Hajj
41
New cards
Byzantine Empire
Eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived (the fall of the Western half)
42
New cards
Capital of the Byzantine Empire
Constantinople (named after Emperor Constantine)
43
New cards
The Later Roman Empire and Byzantium
Challenges from strong Persian empire, invasions of Germanic peoples, roman infrastructure
44
New cards
Caesaropapism
Political and religious power centralized in the emperor, claims divine authority (cannot claim divinity), authority even over church, empire and church unity
45
New cards
Religious Schism
Tensions between Eastern Orthodox and Roman Catholic Church, Patriarch of Constantinople and Pope of Rome excommunicate each other, Western Europe and Roman church conquer Constantinople during fourth crusade
46
New cards
Challenges from the East
As the Europeans expanded into the Byzantine empire, Muslim Seljuks invade Anatolia, defeat Byzantine army in 1071, period of steady decline until Ottoman Turks capture Constantinople (1453), renamed Istanbul
47
New cards
Kievan Rus
First civilization in Russia that was greatly influenced by the byzantine
48
New cards
Feudalism Political System
-decentralized, local government
-Lord and his vassals administered justice and were the highest authority in their land
-Lord and his vassals administered justice and were the highest authority in their land
49
New cards
Lords and Retainers
formation of small private armies, incentives such as land grants, income from mills, cash, formation of hereditary class of military
50
New cards
Serfdom
Slaves, free peasants in both Roman and Germanic societies, appeals to lords (midway between slave and free peasant)
51
New cards
Serf's rights and obligations
pass on land to heirs, obligation to provide labor/income, payments in kind to lord, unable to move from land, fees charged for marrying serfs of another lord
52
New cards
Order of the feudal system
King, Nobles, Knights, Peasants
53
New cards
Competing Powers
Church (Roman Catholic), Monarchies (Kings/Queens), Nobility (Wealthy landowners), fought for supremacy, checks and balances gave merchants autonomy
54
New cards
Charlemagne
Centralized imperial rule, major military achievements
55
New cards
Charlemagne's Administration
Re-establishes centralized rule, counts run on local government, imperial officials, hesitated to challenge Byzantines by taking title of emperor, crowned as emperor in 800 (challenges Byzantium)
56
New cards
The Vikings
Invaders of Europe from Scandinavia, capable of river travel against wind, attacked villages, sacked constantinople three times
57
New cards
Holy Roman Empire
Military forays into eastern Europe, enters Italy twice to aid Roman Catholic church
58
New cards
Henry IV
Holy Roman Emperor, opposed the pope, excommunicated and ends up begging the pope for forgiveness
59
New cards
Increase in food supply leads to...
Urbanization, increase in trade, developments
60
New cards
Hanseatic League
Hansa association of trading cities, trade in Baltic and North seas, used Danube, Rhine, to connect to Mediterranean trade networks
61
New cards
Improved business techniques
Banking, letters of credit - freed merchants from having to deal in bullion or currency
62
New cards
Chivalry
Code of conduct for nobles, established ethics and morality into society, sponsored by Church to minimize fighting among Christians
63
New cards
Guilds
Organizations of merchants, workers, artisans, created social support networks
64
New cards
High Middle Ages
1000-1300 CE; Western Europe making a comeback; time of revival and progress; huge increase in population and growth of cities, increasing wealth makes education possible
65
New cards
Universities
Academic guilds (12th century) transformed cathedral schools into universities, higher standards of education
66
New cards
Influence of Aristotle
Latin translations of Byzantine Greek texts circulate Europe, Jewish and Muslim scholars provide other translations from Arabic translations
67
New cards
Beginning of the Crusades
1095 CE, Pope Urban calls for liberation of Jerusalem from Muslims, foundation of Anti-Muslim and Anti-Semitism
68
New cards
Fourth Crusade
1202-1204, destroys Constantinople, weakens Byzantine empires, Europe encounters new trade goods: sugar and coffee, provide contact with Muslim ideologies, trade increase, growth of power of kings, feudalism declines
69
New cards
The Mexica
Aztecs, became nomadic, settled in Tenochtitlan 1375 CE, grew chinampas (up to 7 crops per year)
70
New cards
Mexica Society
Hierarchical social structure, high stature for soldiers, mainly drawn from aristocratic class, land grants, food privileges
71
New cards
Mexica Women
Patriarchal structure, emphasis on childbearing, mothers of warriors especially honored
72
New cards
Mexico Cultivators and Slaves
Communal groups - calpulli, kin based, managed communal lands, work obligations on aristocratic lands, slave class - debtors, children sold into slavery
73
New cards
Mexica religion
Influenced by Olmec traditions, polytheistic, nature, based gods; ritual sacrifice to please gods (especially sun god Huitzilopochtil)
74
New cards
Mexica Ritual Bloodletting
Emphasis on human sacrifice, victim fingertips torn off before death, ritual wounds, victims: Mexica criminals, captured enemy soldiers, personal rituals
75
New cards
Cahokia
900-1250 CE, mound-building peoples, ceremonial platforms, homes, burial grounds, severe collapse
76
New cards
Inca Administration
Incas ruled by holding hostages, colonization, no writing systems; rather system of cords and knots called quipu
77
New cards
Inca Roads
Massive road building system, paved/shaded/wide roads, courier and messenger services, limited long-distance trade
78
New cards
Incan Society and Religion
Social elites dominated by infallible king, worship of ancestors
79
New cards
Inca Religion
Polytheistic, Inti sun god, Viracocha creator god, temples as pilgrimage sites, peasant sacrifices - usually produce, animals (not humans), sin understood as disruption of divine order
80
New cards
Gender Relations (Aztec / Inca)
Parallelism, two separate but equal systems
Inca men patrilineal, women matrilineal (relationship to dad/mom)
Aztec: Children belonged to mother/father equally
Separate cults with male and female priests
Inca: Parallel hierarchies of government officials
Aztec: Female officials exercised local authority
Inca men patrilineal, women matrilineal (relationship to dad/mom)
Aztec: Children belonged to mother/father equally
Separate cults with male and female priests
Inca: Parallel hierarchies of government officials
Aztec: Female officials exercised local authority
81
New cards
Development of trade networks
Maintenance of roads, bridges, discovery of Monsoon wind patterns, increased tariff revenues used to maintain open routes
82
New cards
Trade in Hellenistic World
Spices/pepper/gems/pearls - India
Grain - Persia/Egypt
Wine/Oil - Mediterranean
Development of professional merchant class
Grain - Persia/Egypt
Wine/Oil - Mediterranean
Development of professional merchant class
83
New cards
Silk Roads
Land-based trade routes that linked Eurasia, named after principal commodity from China (Silk!), dependent on imperial stability
84
New cards
Major transfers on trade routes
Physical trade goods (silk, gold, salt, spices), Culture (religions), Technology (paper, iron plow, horse collar), Disease (bubonic plague)
85
New cards
The Organization of Long-Distance Trade
Divided into small segments, tariffs and tolls finance local supervision, tax income incentives
86
New cards
Arabian Camel
A domesticated animal that was widely used in the Sand Roads due to its ability to hold water in it's humps for extended periods of time. These animals only need water every 10 days.
87
New cards
Cultural Trade - Buddhism and Hinduism
Merchants carry religious ideas along silk routes, Buddhism becomes dominant faith of silk roads 200-700 CE
88
New cards
Monasteries
Shelter traveling merchants

89
New cards
Religious Interactions Summary
Buddhism east to China, SE Asia
Hinduism to SE Asia
Christianity to SW Asia, Africa, Europe
Development of Zoroastrianism in Persia
Hinduism to SE Asia
Christianity to SW Asia, Africa, Europe
Development of Zoroastrianism in Persia
90
New cards
Arab Dhow - Maritime technology
More navigable ship, better (triangular) sails

91
New cards
Lateen triangular sails - Maritime technology
Allows ships to sail against the wind, decreases the time needed to trade
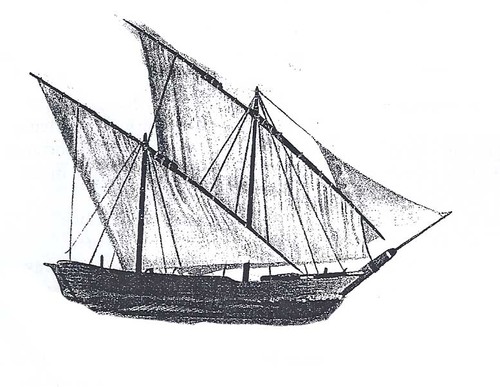
92
New cards
Srivijaya (State Building - SE Asia)
Locals begin to compete for Malay sailors to stop on their trade missions, choke points, gold, spices, taxes on passing ships, many convert to Buddhism
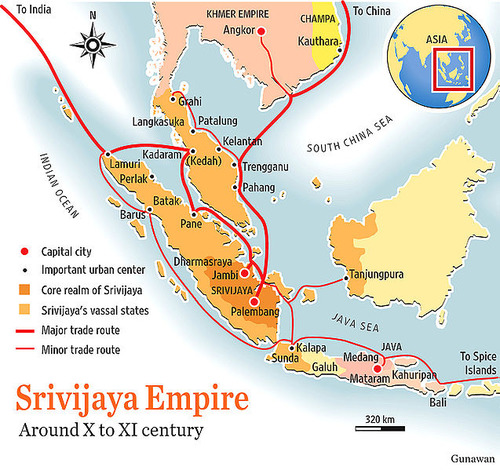
93
New cards
Choke point
a strategic, narrow waterway between two larger bodies of water
94
New cards
City of Malacca
transformed from a small fishing village to a major port city that became the capital of Malay Muslim Sultante; showcased Islam growth and commerce/state building of the Indian Ocean
95
New cards
State Building - East Africa
Swahili Coast ~ Mogadishu, Mombasa, Kilwa
Indian Ocean Trade Routes brought wealth, goods from interior would be brought to these cities then loaded onto ships
Indian Ocean Trade Routes brought wealth, goods from interior would be brought to these cities then loaded onto ships
96
New cards
Kilwa
City-state on east African coast, fishing, turns to agriculture, increased trade in pottery and stoneware
Major trading center by 1300
Major trading center by 1300
97
New cards
Early Christianity in North Africa
Popular in Egypt, initially weak in sub-Saharan Africa, Christian Kingdom of Axum, merchants then kings convert, bible translated into Ethiopian
98
New cards
Aksumite Empire
Converts to Christianity, Aksum became isolated from other Christian communities

99
New cards
State Building in Sub-Saharan Africa
Trading through Sahara Desert allows powerful empires to grow, Middle men (protect trade routes), influenced by Islam
100
New cards
Kingdom of Ghana
Protection against camel driving raiders, center of African gold trade, sold ivory and slaves