Bis 2A
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Last updated 3:38 AM on 6/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
1
New cards
How does electronegativity predict bonds
* if electronegitivity below .4 it is = non polar covalen
* Bean .5 and 2 = polar covalent
* Above 2= ionic
* Bean .5 and 2 = polar covalent
* Above 2= ionic
2
New cards
Condensation
Water is released ‘
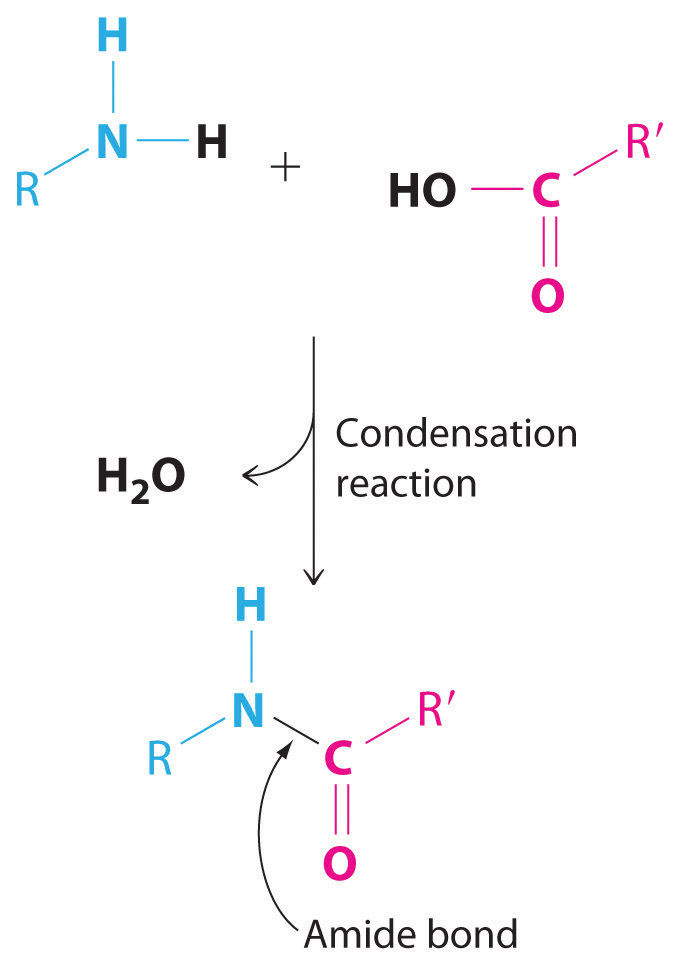
3
New cards
Protein
Series of amino acids (amino group and carbonyl groups)
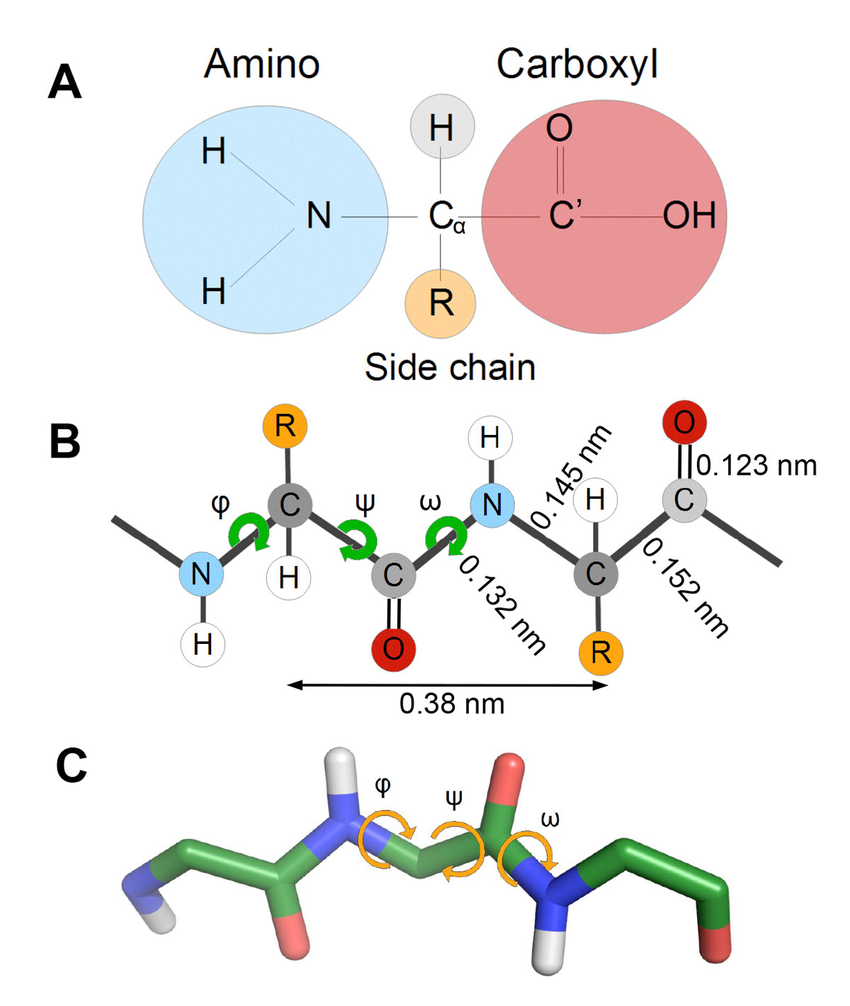
4
New cards
Carbonyardes
C -h2-c
* long chain of Monomers-and polymers
* long chain of Monomers-and polymers
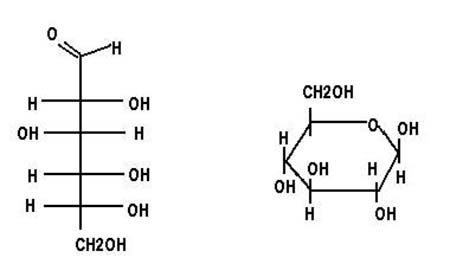
5
New cards
Nucleic acids
Phosphate group WTH nitrogen and Pentose sugar (deoxiribose)
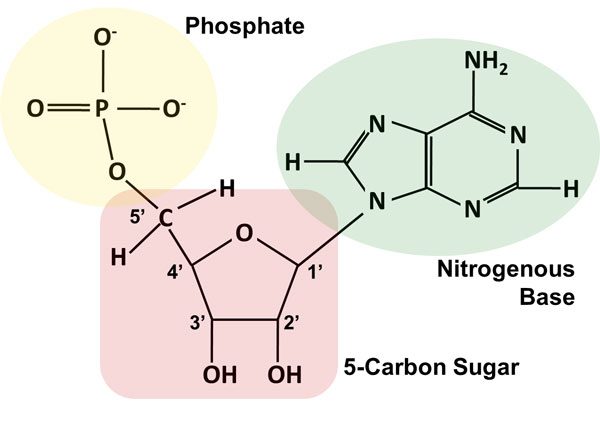
6
New cards
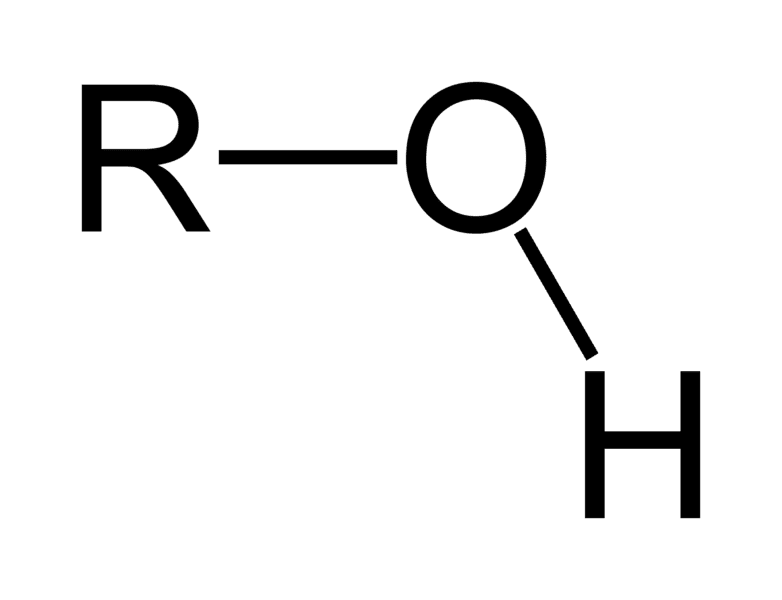
Hydroxyl functional group
OH
7
New cards
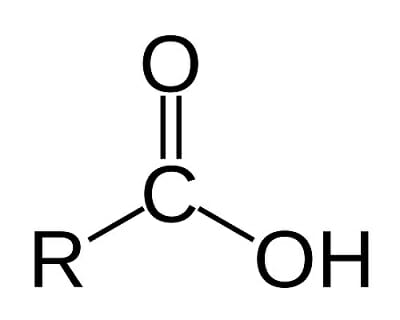
Carboxyl functional group
O= C - OH
8
New cards
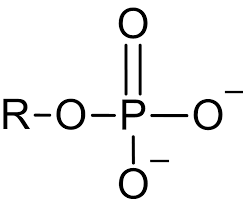
Phosphate functional
P and 4 O
9
New cards
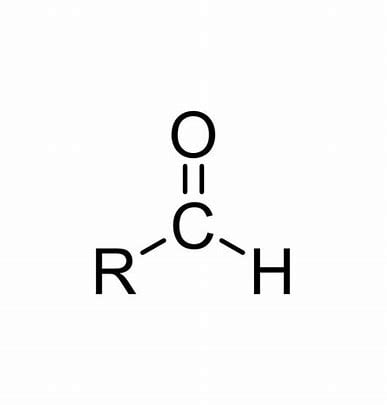
Aldehyde functional group
O=c-h
10
New cards
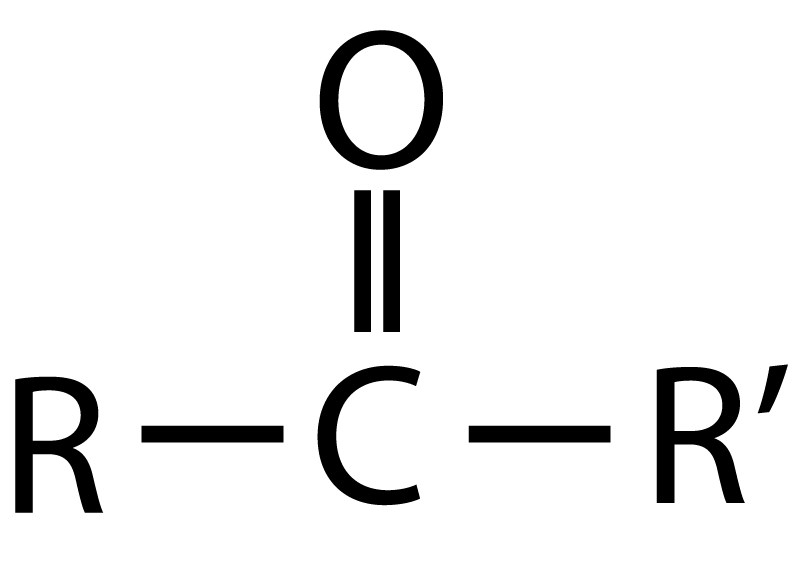
Ketone functional group
0=c with two carbons
11
New cards
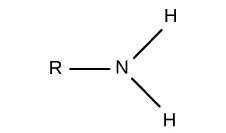
Amino functional group
N-2H
12
New cards
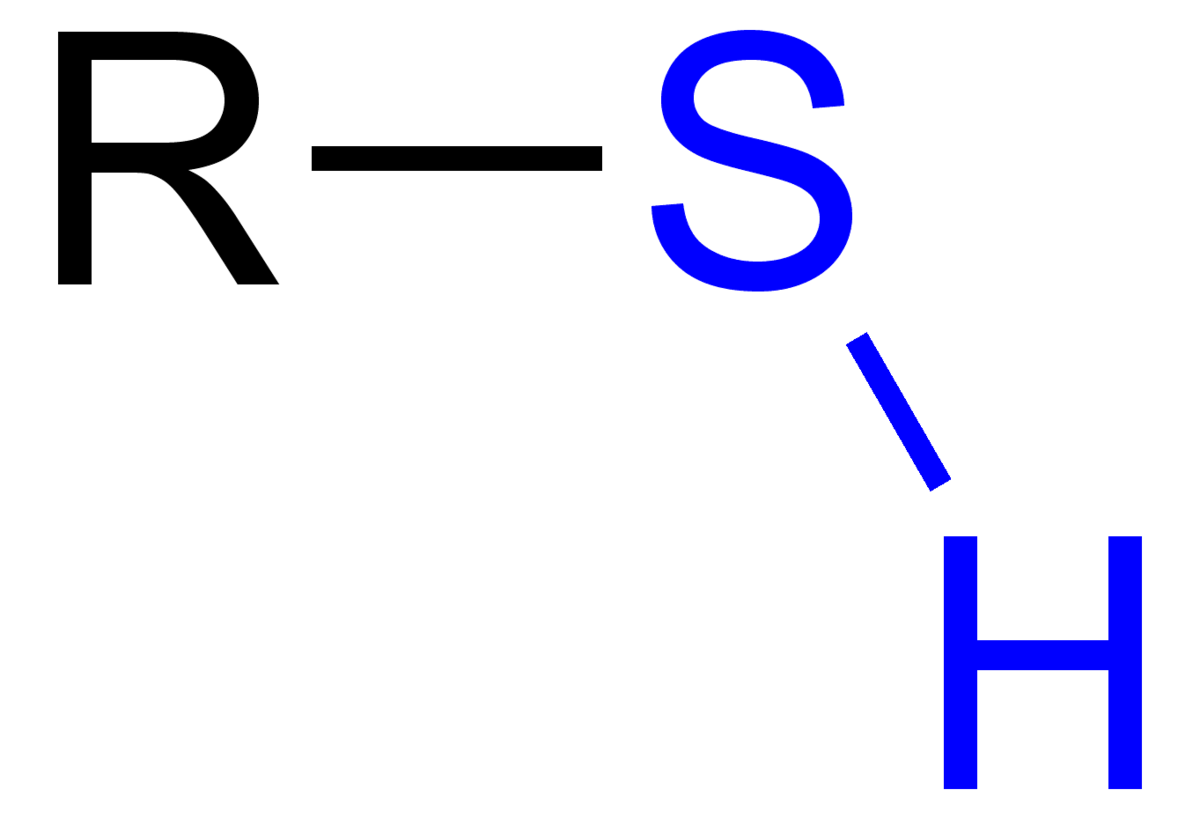
Sylfhydral functional group
S-H
13
New cards
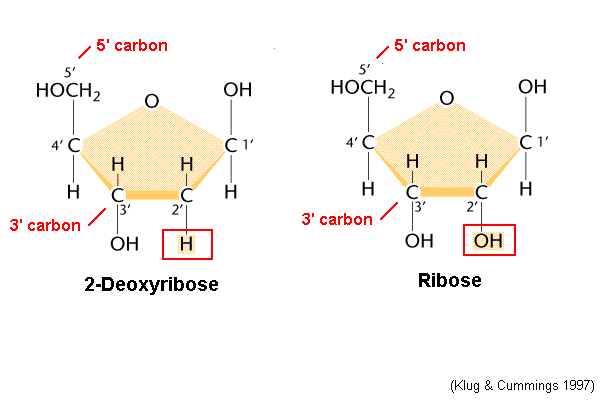
Deoxiribose vs ribose
* C2-H = deoxiribose
* C2-OH= ribose
Count where carbonyl starts
* C2-OH= ribose
Count where carbonyl starts
14
New cards
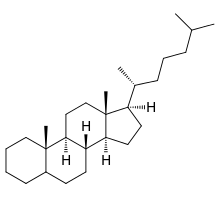
Steroids
* ring structure
* 4 linked carbon
* Tail
* Lipids
* Some have OH (STEROLS ALCOHOL CLASSIFICATION)
* 4 linked carbon
* Tail
* Lipids
* Some have OH (STEROLS ALCOHOL CLASSIFICATION)
15
New cards
Unsaturated
\-Double bonds present
\-kinks
\-Liquid and not lightly packed
\-kinks
\-Liquid and not lightly packed

16
New cards
Saturated
* long chain of singlebonds
* No kinks
* Stacked
* \
* No kinks
* Stacked
* \

17
New cards
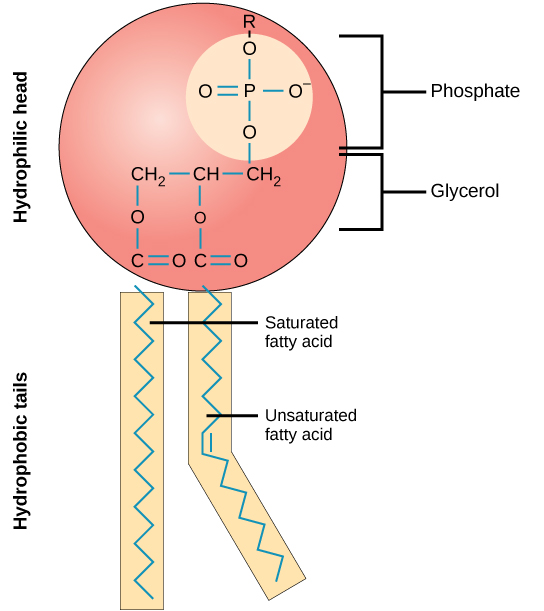
Explain structure of phospholipid
* Phosphate group polar
* Glycerol
* Two non polar fatty acid l
* Make Micelle structure
* Glycerol
* Two non polar fatty acid l
* Make Micelle structure
18
New cards
Define pKa
The quantative measure of how readily acid donates H+
( when ph increases the more the acid will become depronated)
( when ph increases the more the acid will become depronated)
19
New cards
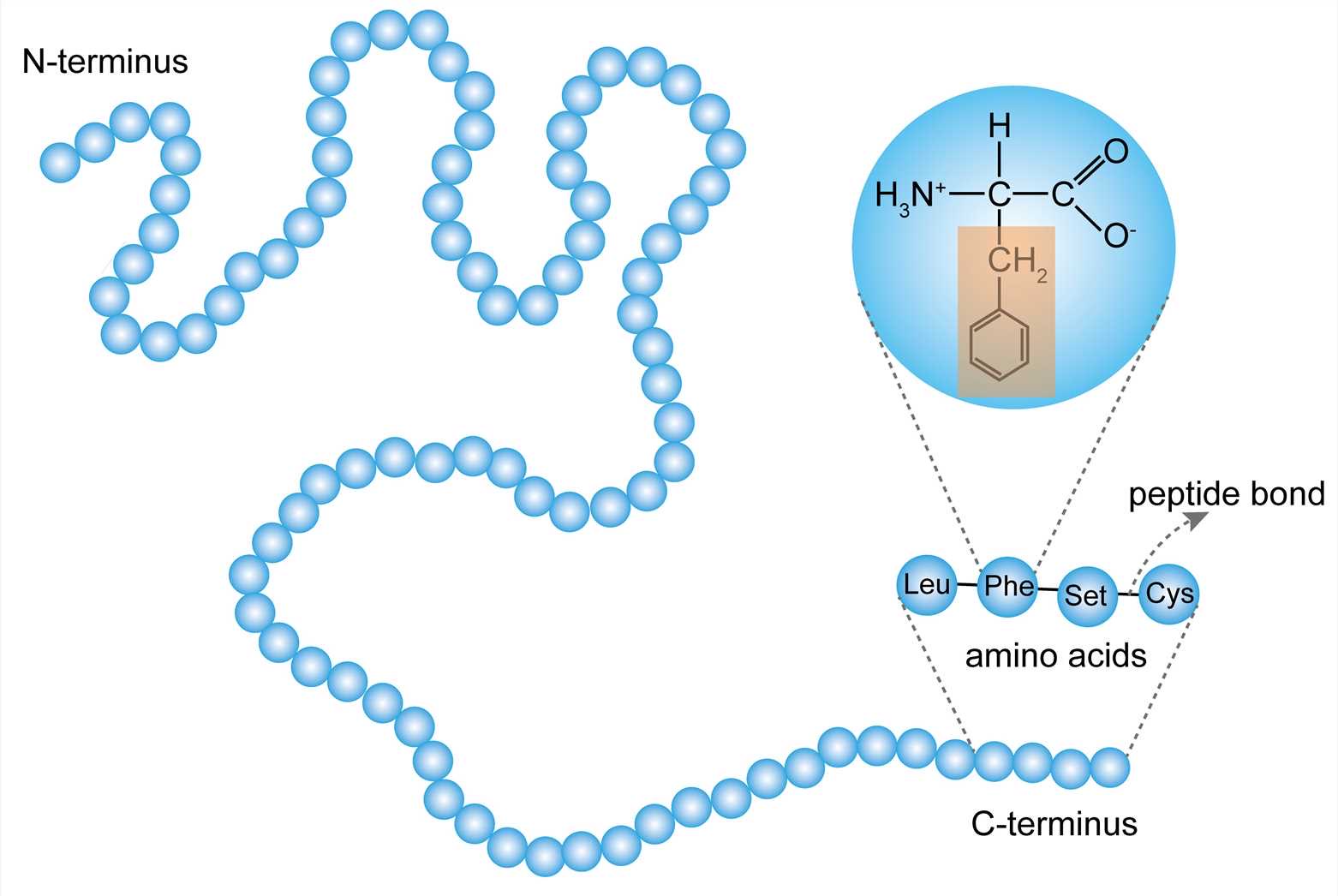
Primary structure protein
Series of amino. Acids. Held by peptide Bonds
\
\
20
New cards
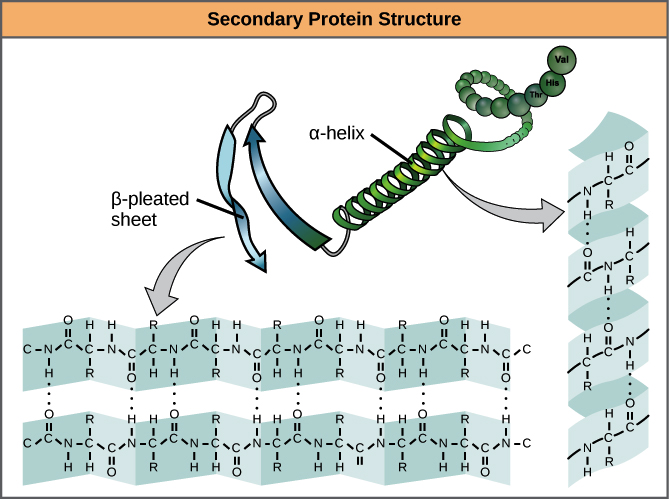
Secondary structure protein
* localized structure within primary Structure (intra)
* Held by hydrogen Bonds ( btwn carbonyl O and H of two amino acid)
* Folding bc hydrogen bonds
* Held by hydrogen Bonds ( btwn carbonyl O and H of two amino acid)
* Folding bc hydrogen bonds
21
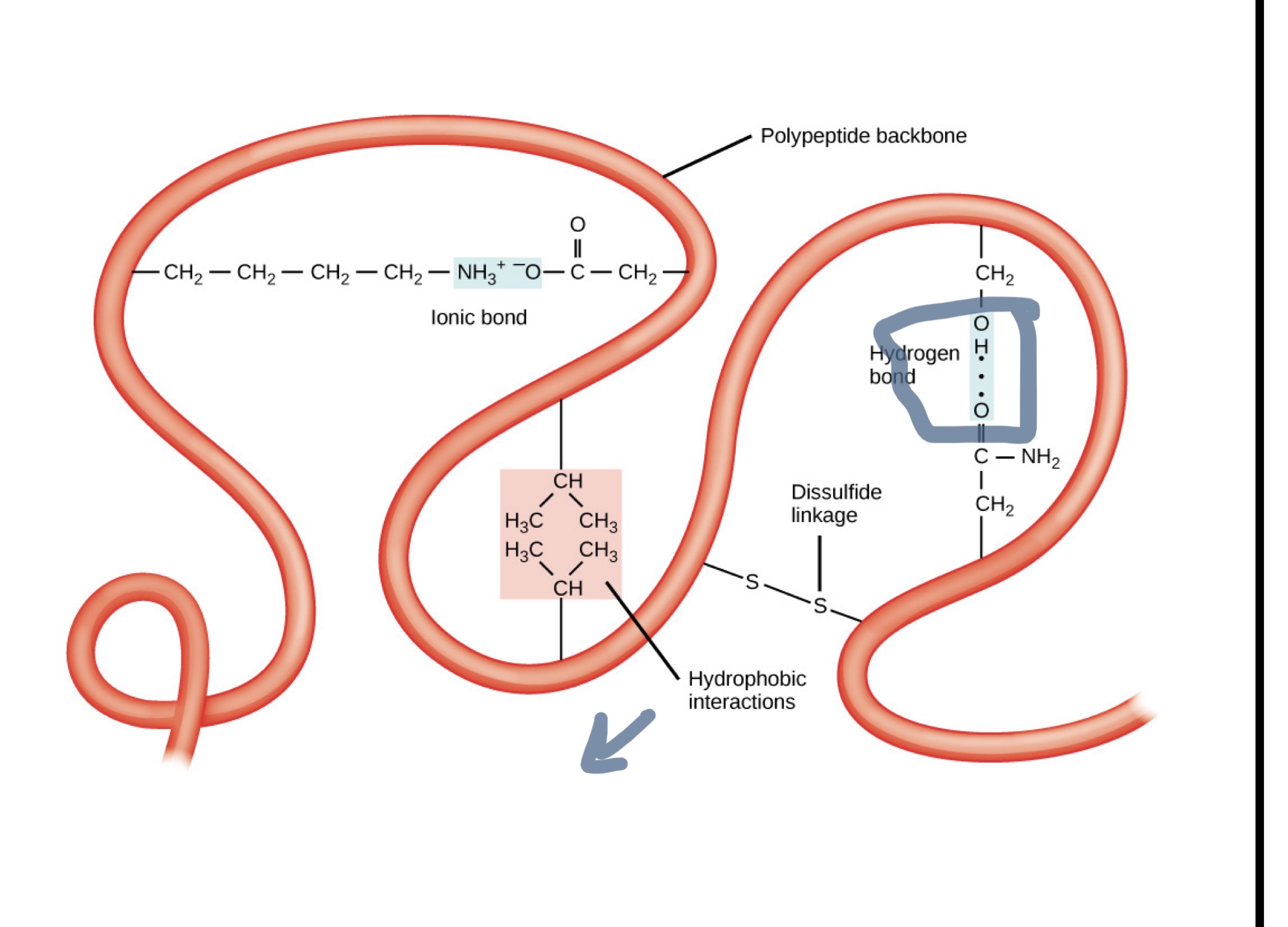
New cards
Tertiary structure
* held together by everything But non covalent bonds
* Shaped bcc of side chain interactions
* Shaped bcc of side chain interactions
22
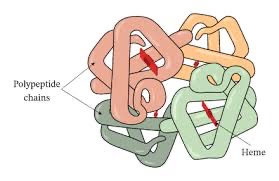
New cards
Quaternary structure
Peptide bonds
* protein-consists of more than one amino acid
* protein-consists of more than one amino acid
23
New cards
Describe interaction between amino acids during protein folding of 1,2,3,4)
Drives the folding and intramdecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain
24
New cards
How do differences in lipid composition affect the fluidity of different membranes?
Lipids that can pack more tightly make membranes more rigid and stronger but less fluid
25
New cards
Cell membrane
Protects cell from surrounding
26
New cards
Nucleus
Control Center of cell
27
New cards
Endoplesmic rectum
* folding of protein molecules
* Transport of proteins to Golgi apparatus
* Transport of proteins to Golgi apparatus
28
New cards
Golgi apparatus
* modifying and sorting of proteins
* Transport lipids
* Creation of lysosomes
* Transport lipids
* Creation of lysosomes
29
New cards
Lysosomes
* contain digestive enzymes
* Engulf viruses or bacteria
* Engulf viruses or bacteria
30
New cards
Vacuole =
Maintains proper pressure
* provide structure and support for growing plants
* provide structure and support for growing plants
31
New cards
Chloroplasts
Convert light into sugars
32
New cards
Explain how water moves in and out of cell
Osmosis
* low to high
* low to high
33
New cards
Passive transport
High to low
\-down concentration gradient
\-down concentration gradient
34
New cards
Facilitated transport
* move molecules WTH membrane proteins
* \
* \
35
New cards
Active transport
* move molecules against concentration gradient
* Use ATP
* Use ATP
36
New cards
First law of thermodynamics
* energy is conserved
* Neither destroyed or created
* Neither destroyed or created
37
New cards
Second law of thermodynamics
After energy transformation some energy is no longer usable
38
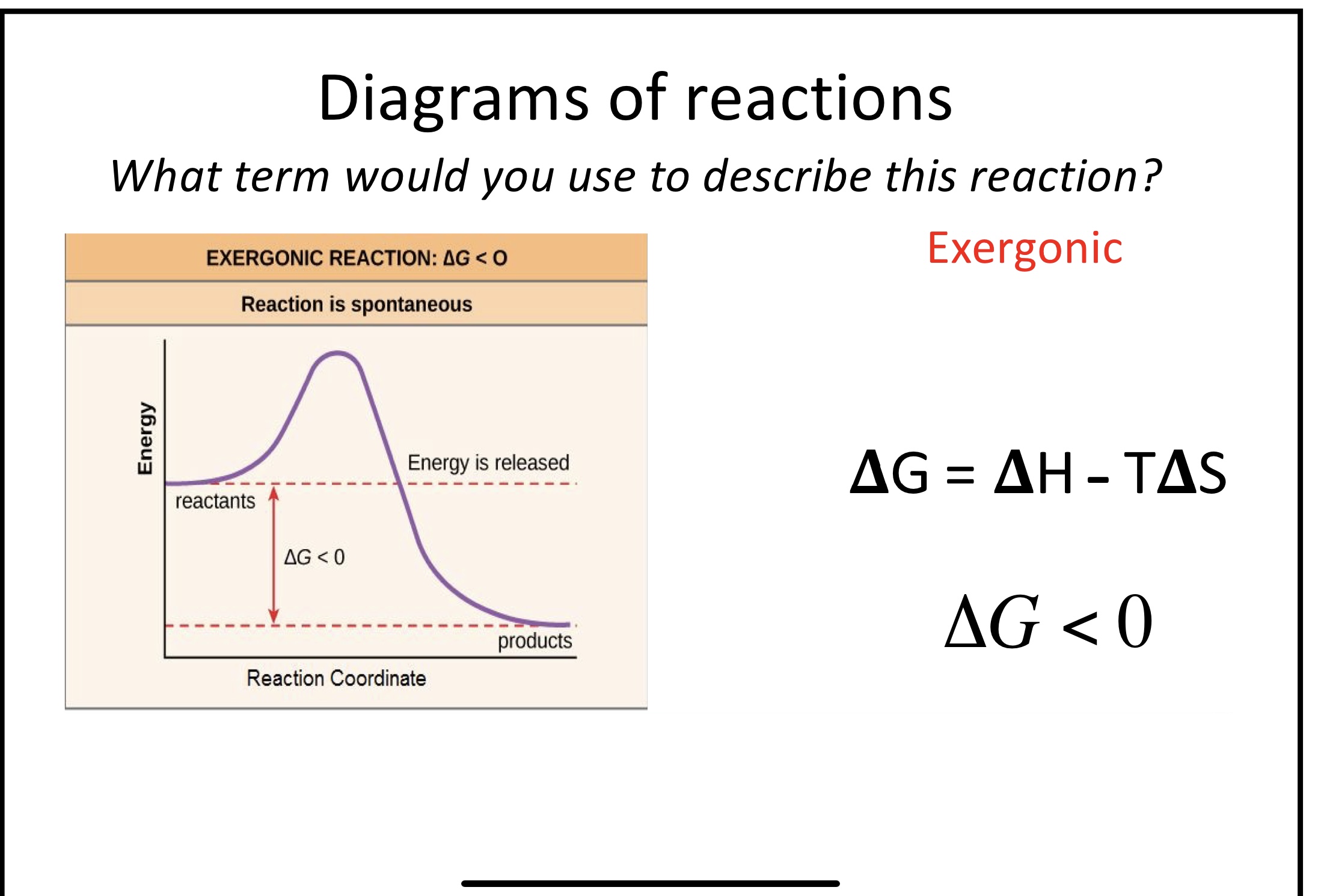
New cards
What makes a reaction spontaneous
delta G
39
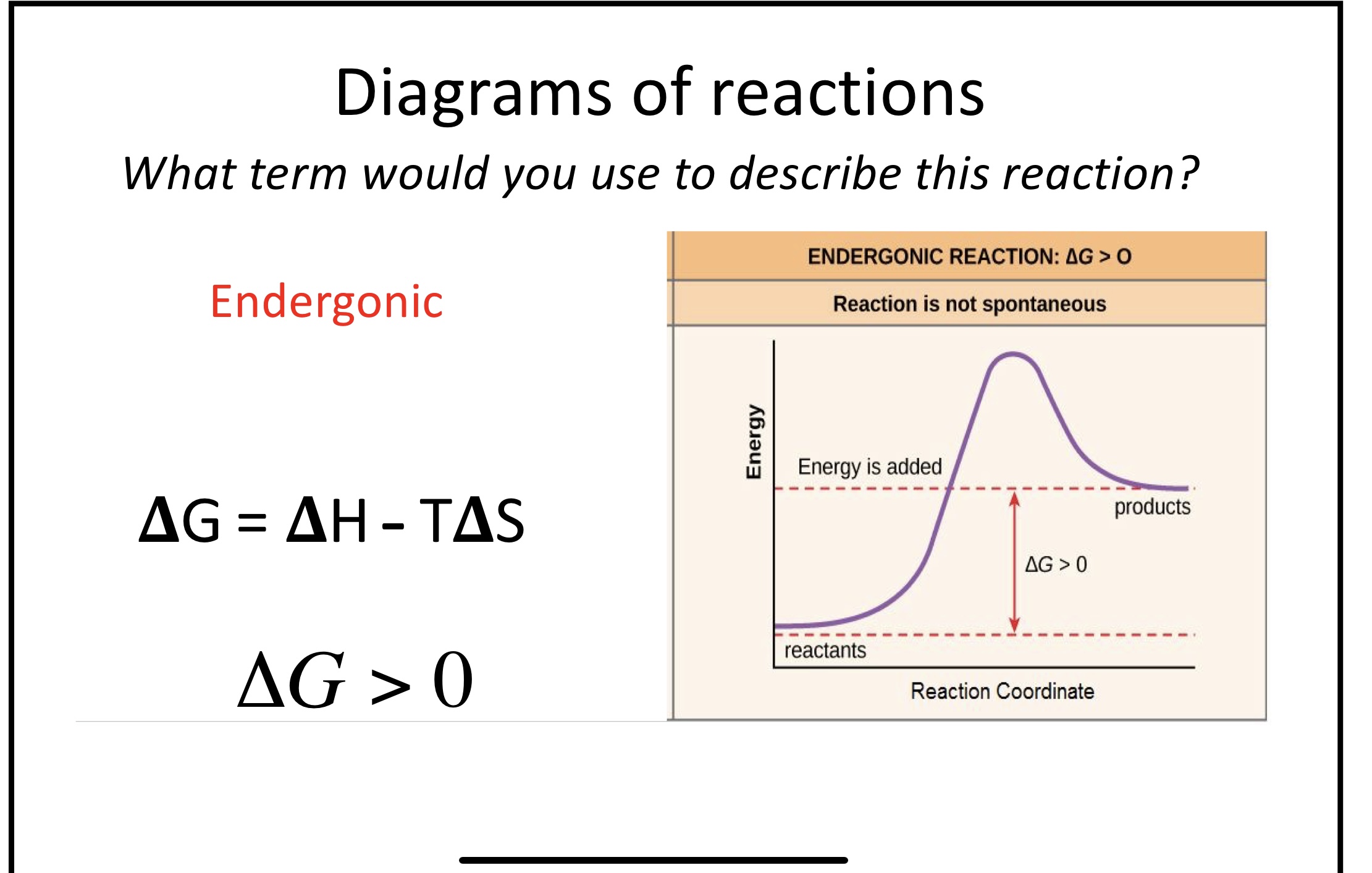
New cards
What makes a reaction nonspontancus
Delta G >0
Endorganic
Endorganic
40
New cards
Now ATP hydrolysis can be coupled to endorgenic beatin
ATP drives endorganic reactions bY phosphorylation
* transferring a phosphate group
* transferring a phosphate group
41
New cards
What happens during glycolysis
Glucose broken down into pyruvate and energy
* 2 ATPDerived
* Cytoplasm
* Catabolic
* Exorgenic
\
* 2 ATPDerived
* Cytoplasm
* Catabolic
* Exorgenic
\
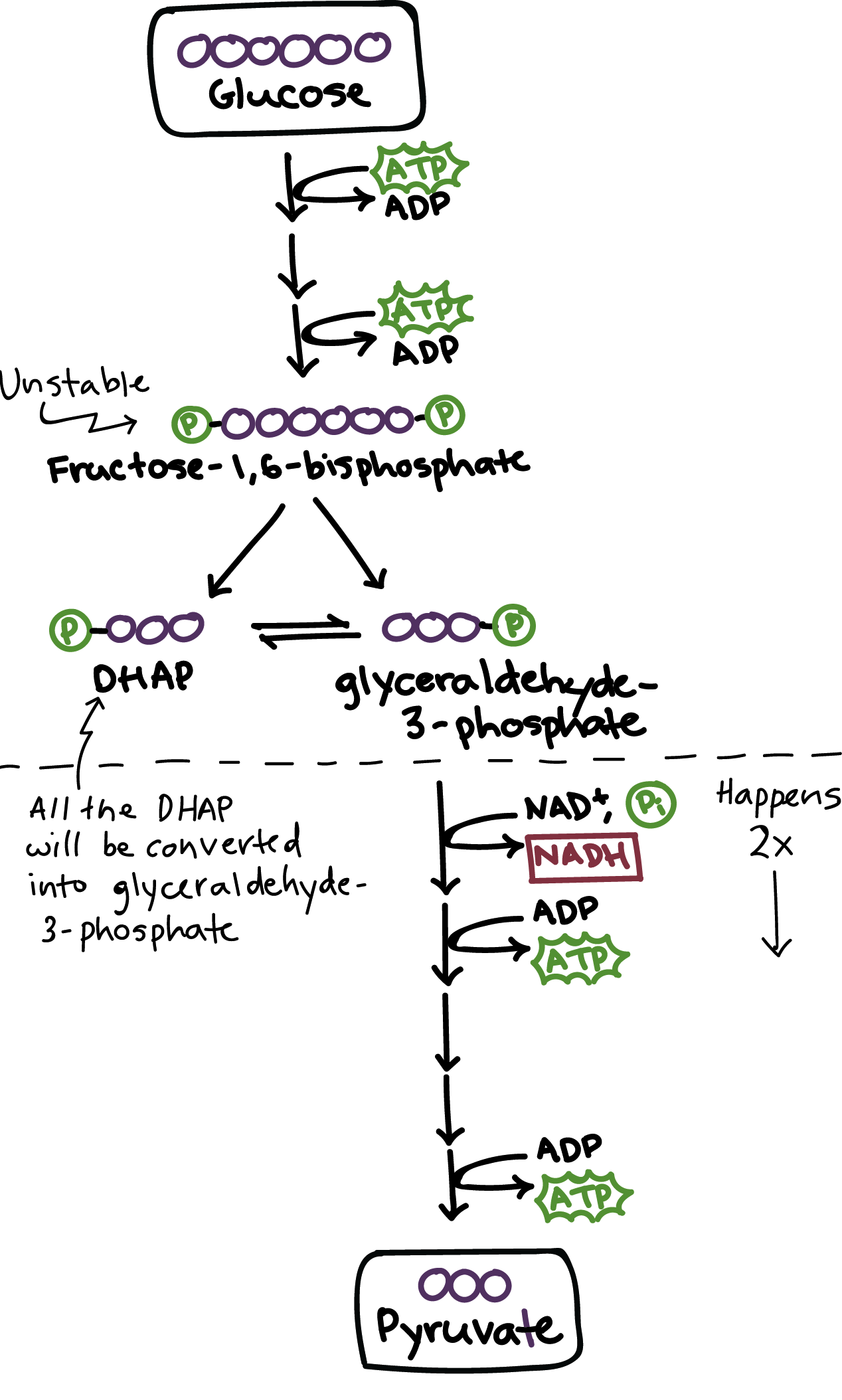
42
New cards
Substrate level of phosphorylation
* phosphoryl group transferred from substrate to ADP
* Forms ATP which releases energy
* Forms ATP which releases energy
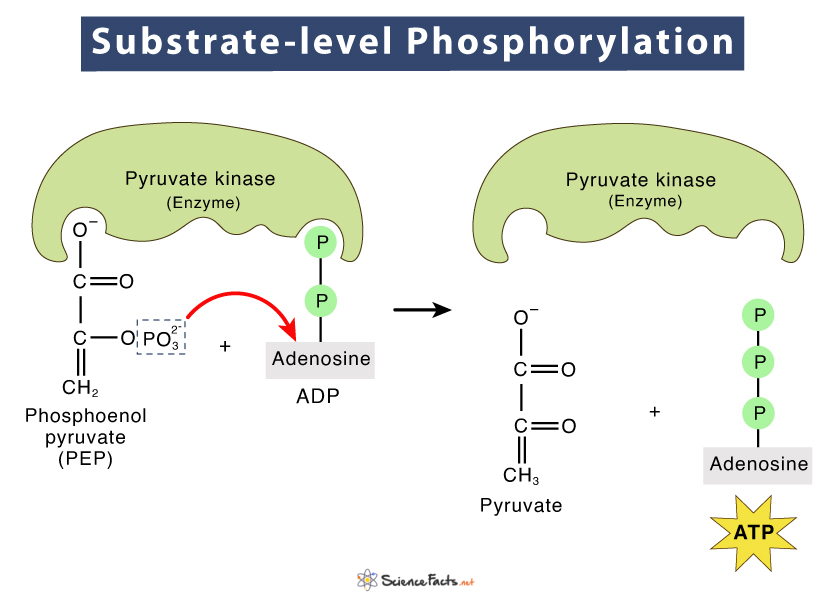
43
New cards
Fermentation explain
Anaerobic pathway breaking down glucose
* glycolysis is the only energy extraction
* Absent oxygen
* glycolysis is the only energy extraction
* Absent oxygen
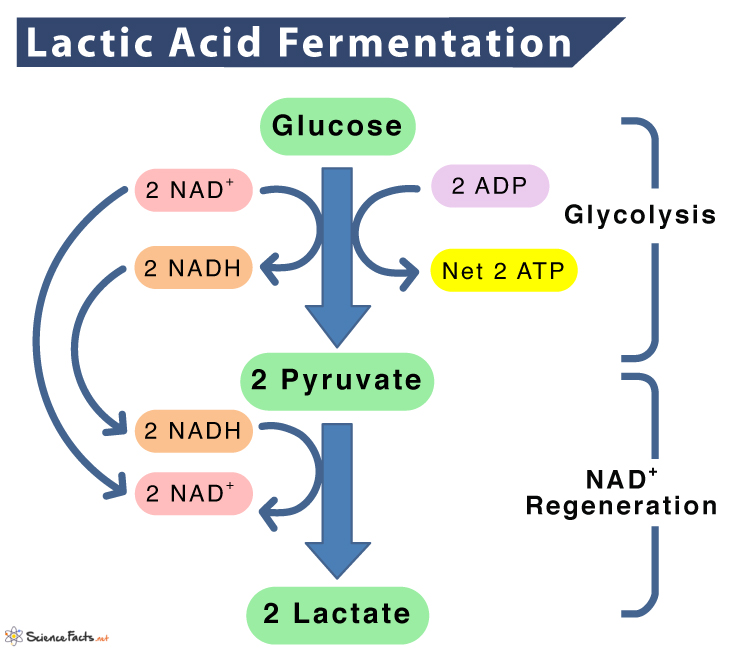
44
New cards
Oxidative phosPhoralyation VS fermentation
\
fermentation
* produces little ATP
* Does not need O2 l ‘‘
* Evolved first
* final e acceptor is pyruvate
Oxidati ve
* mass amounts of ATP
* Needs O2
* Evolved after fermentation
* Final E accepter O2
\
fermentation
* produces little ATP
* Does not need O2 l ‘‘
* Evolved first
* final e acceptor is pyruvate
Oxidati ve
* mass amounts of ATP
* Needs O2
* Evolved after fermentation
* Final E accepter O2
\
45
New cards
Glucogenesis
Produces glucose
* occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasma
* Anabolic
* Endorgenic
* occurs in mitochondria and cytoplasma
* Anabolic
* Endorgenic
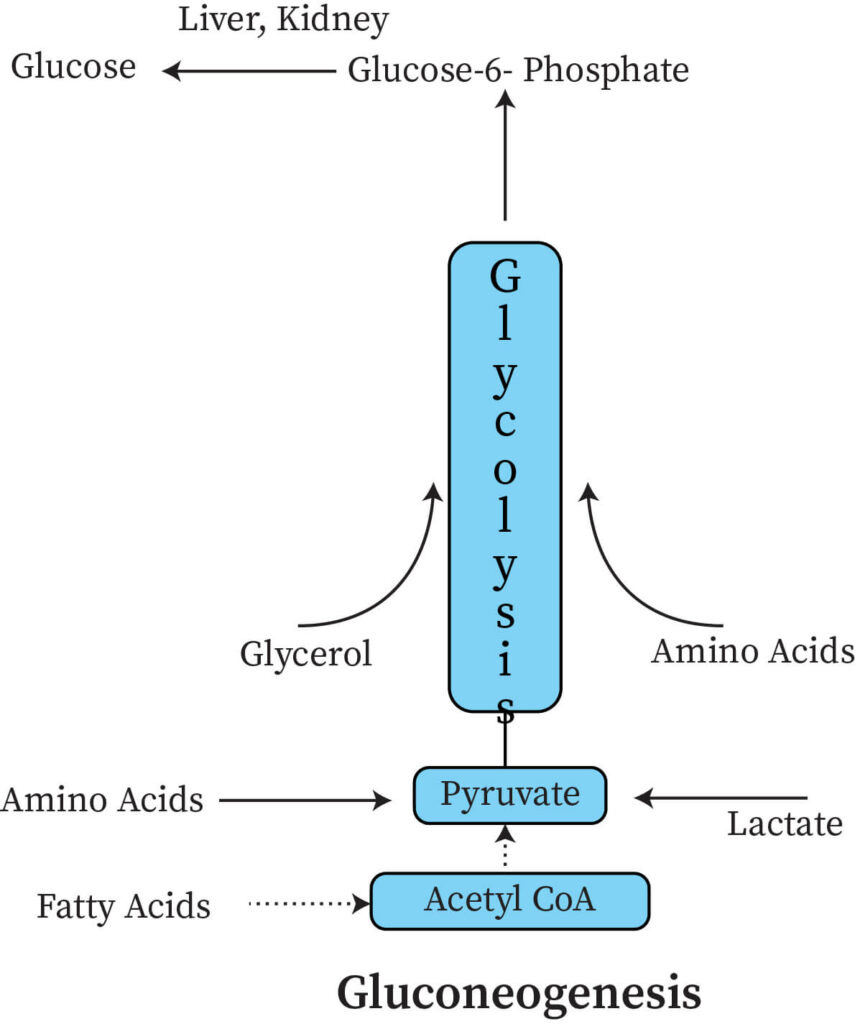
46
New cards
Pentose phosphate pathucy
* glucose 6 phosphate denhydrogenesis
* ATP synthesis and NADPH
* CO2 releases during oxidation
* ATP synthesis and NADPH
* CO2 releases during oxidation
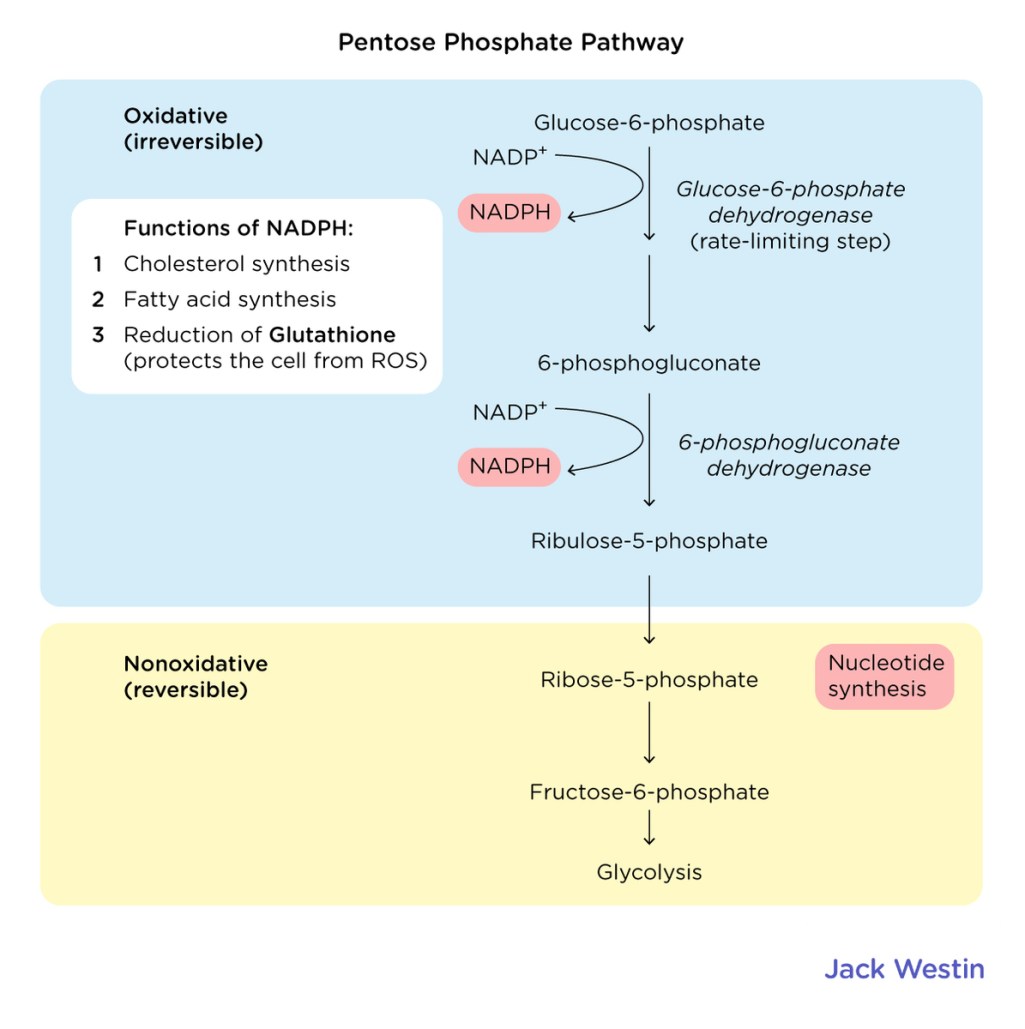
47
New cards
Calvin Cycle
* enzyme is rubisco
* CO2 fixation
* Produce NADPH
* CO2 is fixed in the environment
* Use products of Light dependent reactions
* CO2 fixation
* Produce NADPH
* CO2 is fixed in the environment
* Use products of Light dependent reactions
48
New cards
Ether functional group
* central oxygen bonded to two Carbons
49
New cards
Esterbonds
* Central carbon bonded to oxygen
50
New cards
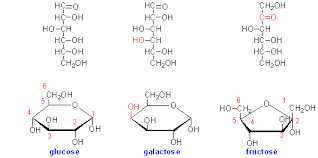
Glucose vs galactose
\-Direr at position c4
\-aldose
\-aldose
51
New cards
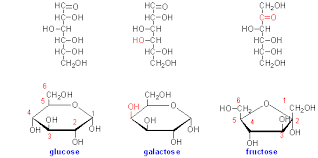
Fructose
* divers at C 1 and C2
* Ketone
* Ketone
52
New cards
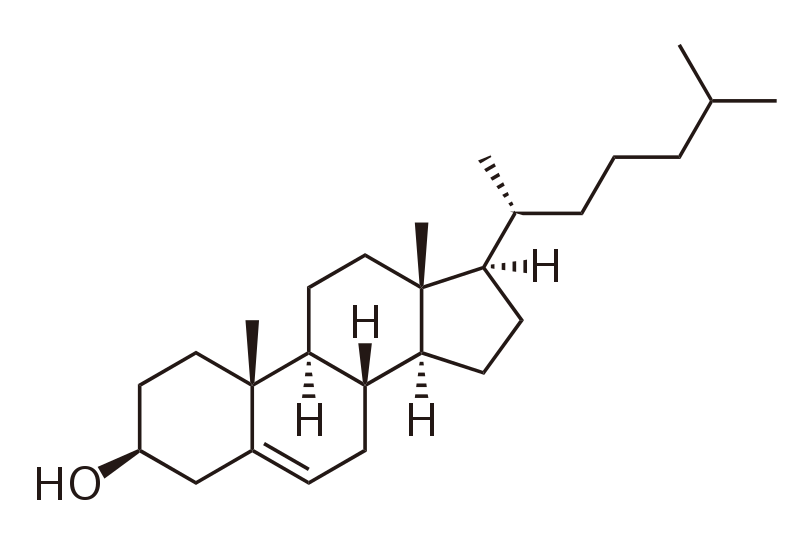
Nome of biomolecule
Chosteral
* lipid molecule
* \
* lipid molecule
* \
53
New cards
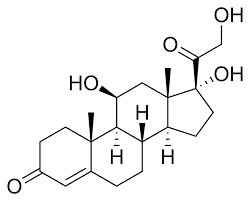
Name molecule
Cortisol
54
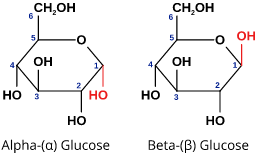
New cards
A vs B glucose
* differ at C1
* H top = A
* \
* H top = A
* \
55
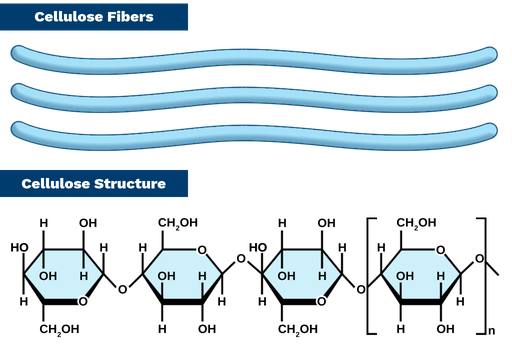
New cards
Cellulose structure
1-4 b linkages glucose
56
New cards
Components of membrane
_Proteins
* lipids
* Carbonyardes
* lipids
* Carbonyardes
57
New cards
Integral membrane proteins
* integrates completely into membrane structure
* Can stretch from one side to another
* Can stretch from one side to another
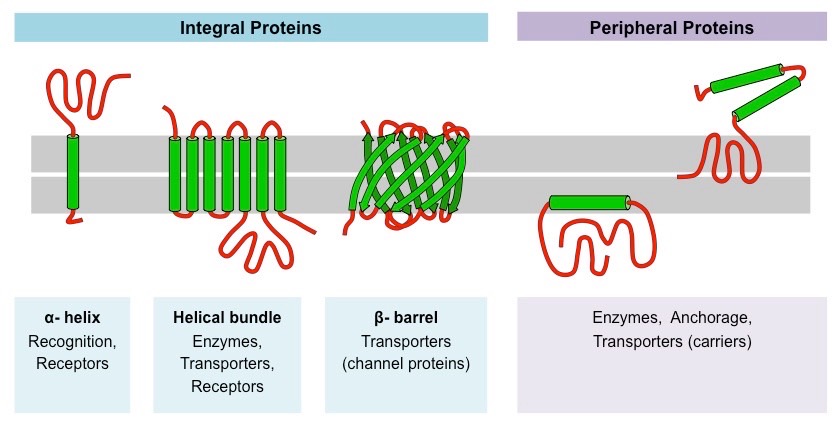
58
New cards
Photo phosphorylation
* transfer of energy from eight
* Creat PMF
* Nadph
* ATP
* Creat PMF
* Nadph
* ATP
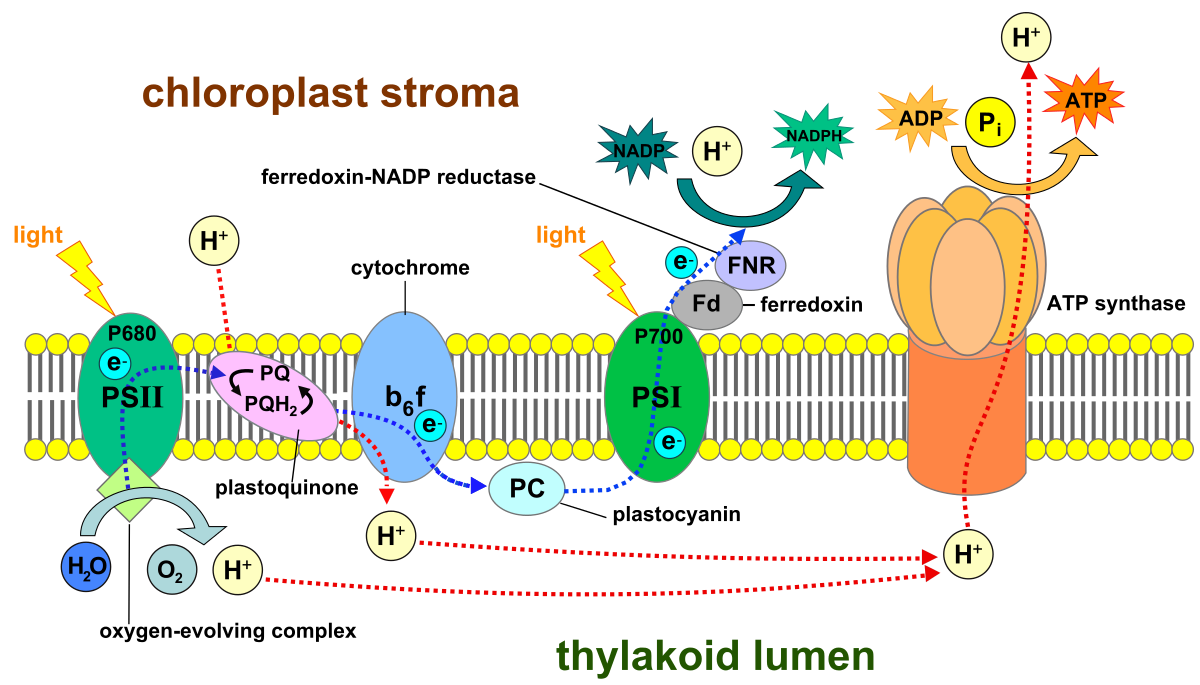
59
New cards
DNA helices
* couples ex hydrolysis of ATP to unwind DNA
60
New cards
Telomerase
* fixes overhang of RNA using DNA
* RNA dependent polymerase
* Contains RNA primer
* RNA dependent polymerase
* Contains RNA primer
61
New cards
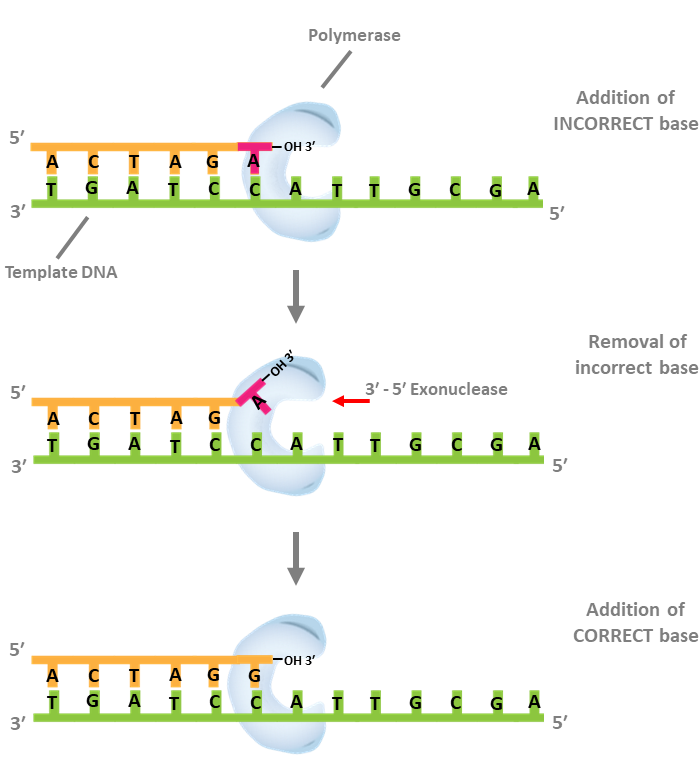
DNA polymerase 1
\-Proofreads DNA
* removes incorrect sequence
* Adds correct base
* removes incorrect sequence
* Adds correct base
62
New cards
Direct chemical reversal
* No excision of backbone
* Removes mismatched pair
* Removes mismatched pair
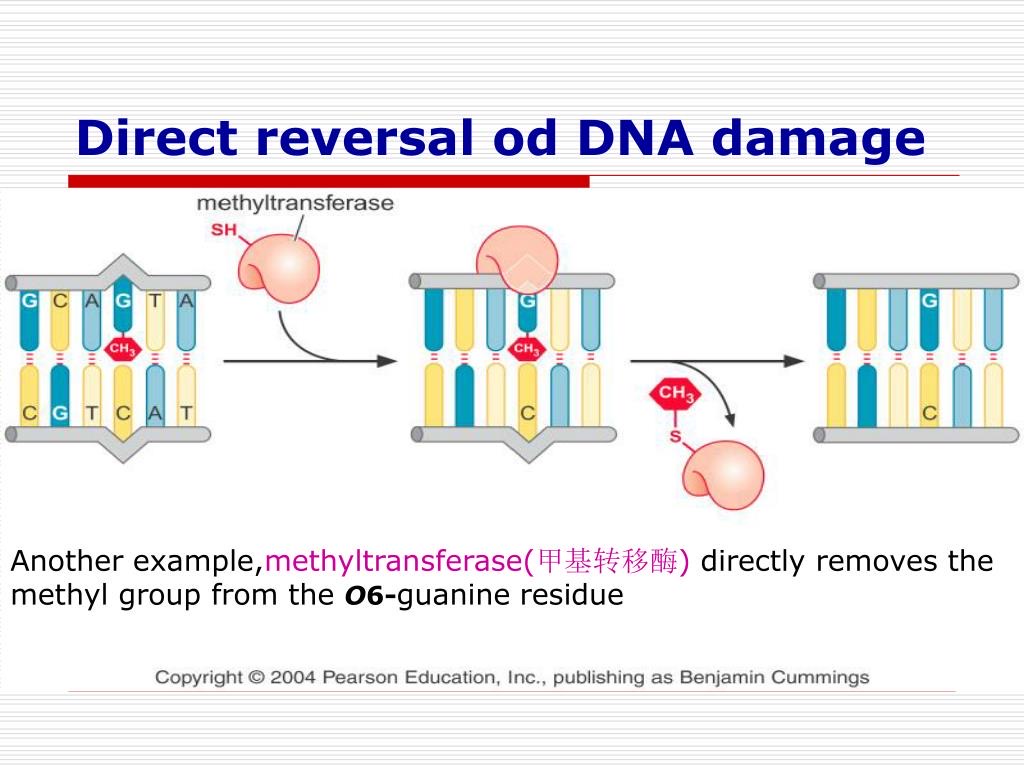
63
New cards
Base excision repair
\-Excision of DNA backbone
* damage ATP
* Glycolsylase detects and removes it
* End nuclease removes site
* Poly/ligase fill gap
* damage ATP
* Glycolsylase detects and removes it
* End nuclease removes site
* Poly/ligase fill gap
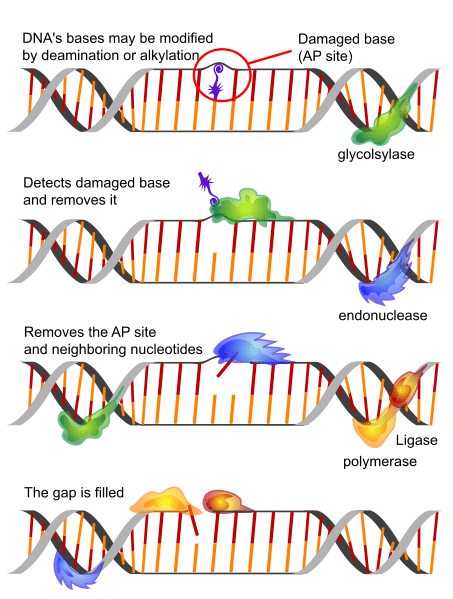
64
New cards
Nucleotide excision repair
* involves THYMINE DIMER
* Damaged region cut cut
* Gap filled in
* Damaged region cut cut
* Gap filled in
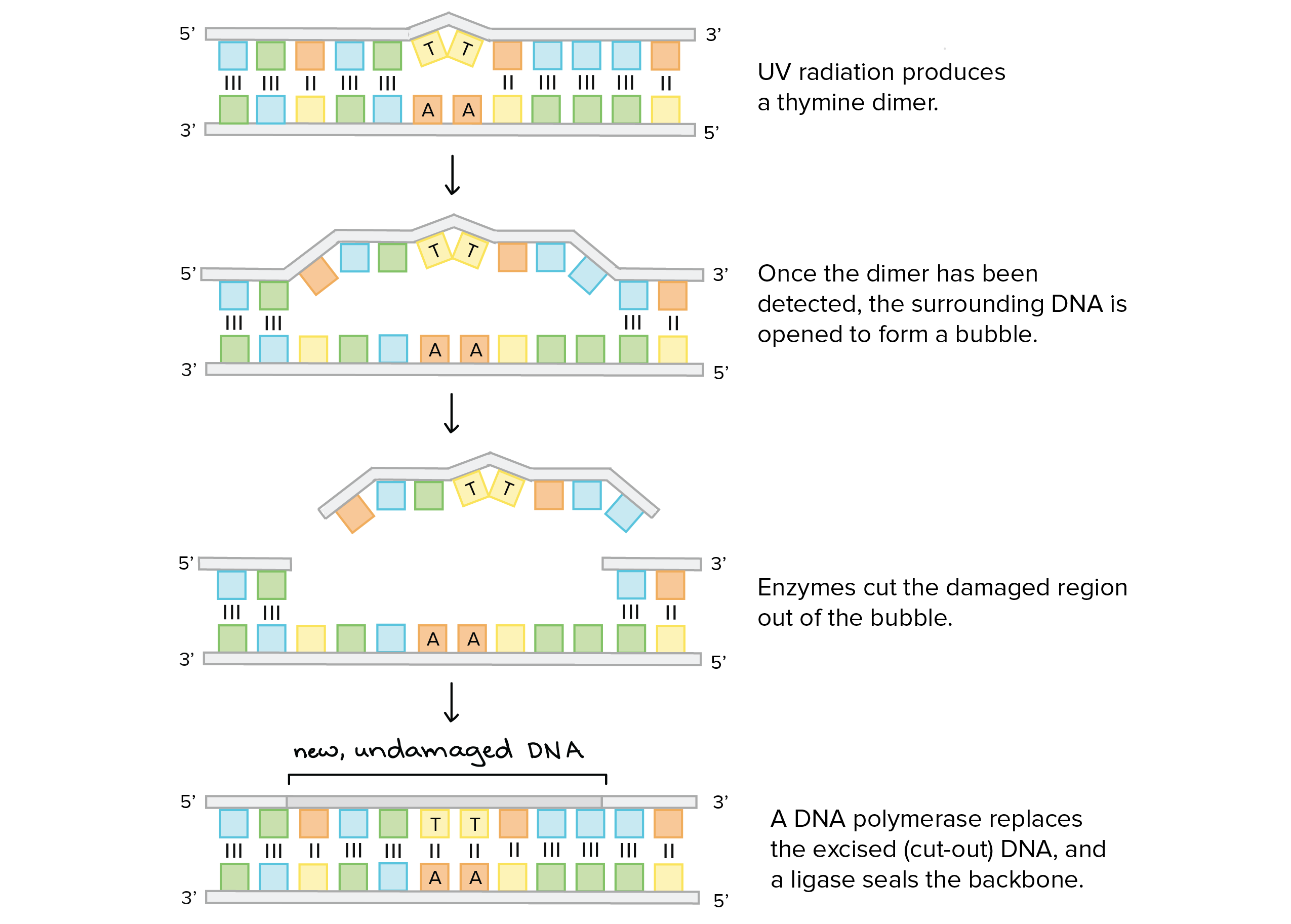
65
New cards
What are the challenges of replicating the ends of linear chromosome and how telomerase solved this?
The DNA in end can not be fully replicated. Resulting in shorter chromosome which telomerase helps
66
New cards
What is the central dogma?
DNA to RNA to protein
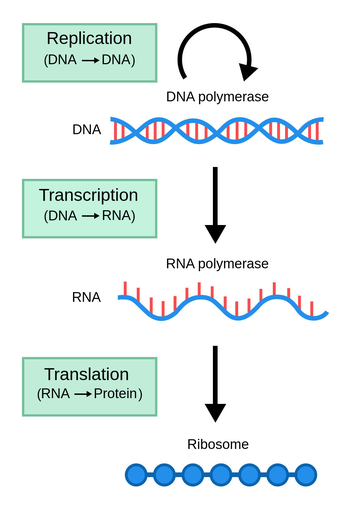
67
New cards
RNA polymerase
5 to 3’
\-Unwinds DNA (transcription
* does not proofread and correct mistakes
\-Unwinds DNA (transcription
* does not proofread and correct mistakes
68
New cards
Eukaryotic mRNA
* splicing and capping occur in nucleus
* Introns degraded in nucleus into nueleuides
* Leaves to cytoplasma
* Introns degraded in nucleus into nueleuides
* Leaves to cytoplasma
69
New cards
Gram negative
* ping (spaced)
* Outer membrane and space
* Outer membrane and space
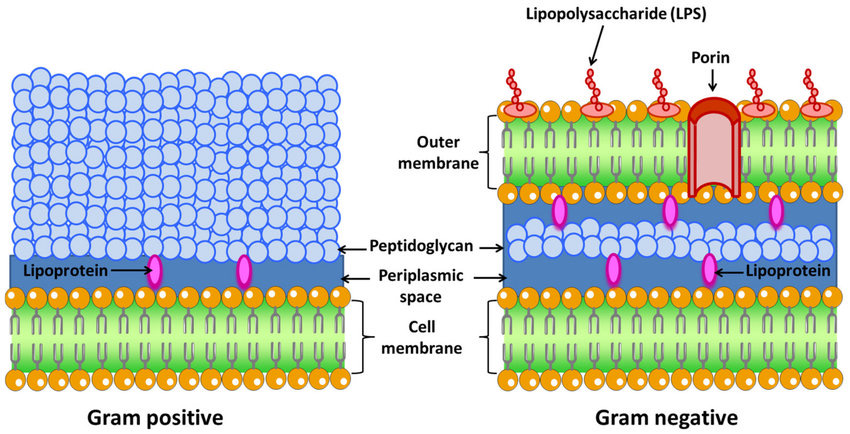
70
New cards
Gram positive
\-Purple
\- pep layer
* plasma membrane
\- pep layer
* plasma membrane
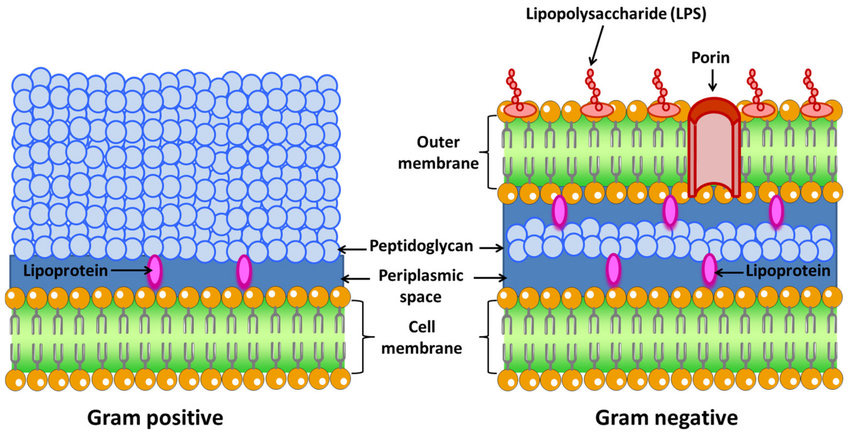
71
New cards
Endoplasmic reticulum
* Folding protein
* Transport proteins to Golgi apparatus
* Transport proteins to Golgi apparatus
72
New cards
Lysosomes
* contain digestive enzyme
* Digest excess
* Engulf
* Digest excess
* Engulf
73
New cards
Vacuole
* maintains pressure
* Provide structure
* Provide structure
74
New cards
Peroxisome
* breaks down toxic materials
* Metabolic activity
* Metabolic activity
75
New cards
How can surface area be increased?
* Can increase protein receptors
* Increase membrane
* \
* Increase membrane
* \
76
New cards
Microfilements
* composed of actin
* Bound to ATP
* Thicken cortex
* \
* Bound to ATP
* Thicken cortex
* \
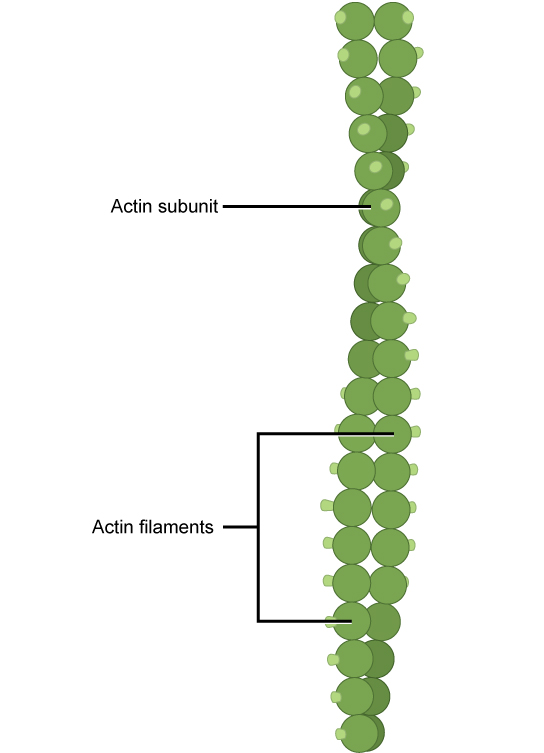
77
New cards
Microtubules
* maintain cell shape
* GTP BOND
* Creates GDP
* GTP BOND
* Creates GDP
78
New cards
Intermediate filaments
\-Holds organelles in place
\
\
79
New cards
Moter proteins
* converts energy from ATP hydrolysis to walk along microtubule
80
New cards
Dynein
Moves from (+ to-)
81
New cards
kinesins
Moves from ( - to+ )
82
New cards
What is the consequences of not having nad+?
Glycolysis would not continue
No ATP formed
No ATP formed
83
New cards
\#Of hyorgenbonds stun adenine and thymine
2
84
New cards
. in DNA
Ump
85
New cards
Reverse transpitase
DNA copy from RNA
86
New cards
Promoter
DNA element
* instructs RNA polymerase where to bird
* instructs RNA polymerase where to bird
87
New cards
When does saturation Occur
When a group of carrier proteins is operating at max
88
New cards
Silent mutation
Negligible reject
89
New cards
of ligase
Joins 3 hydroxyl and 5 phosphate
90
New cards
Overview of transcription
Intiation
Elongation
\
Termination
Elongation
\
Termination
91
New cards
Sites on DNA required for transcription
Promoter
* transcription start
* Termination site
* transcription start
* Termination site
92
New cards
Sigma factor
RNA polymerase
_Recognizes promoter
\-Tatta box
_Recognizes promoter
\-Tatta box
93
New cards
Transcription
5 to 3
\-RNA polymerase (unwinds DNA)
’
\-RNA polymerase (unwinds DNA)
’
94
New cards
Eukaryotic transcription
5 cap modified
Poly A tail added
’
Poly A tail added
’
95
New cards
Translation initiation and stop codons
Start: Aug
_Ribosome chooses start
Stop: USA, UAG,UGA
_Ribosome chooses start
Stop: USA, UAG,UGA
96
New cards
tRNA
Translates code
97
New cards
Aminoacyl tRNA
Charges TRNA with correct amino acid
ATP required
ATP required
98
New cards
Overview of translation initiation
* ribosome around mRNA
* TRNA with codon
* 5cap mRNA REQ
* TRNA with codon
* 5cap mRNA REQ
99
New cards
Translation elongation
TRNA transfers amino acid to the next trna
100
New cards
Translation translocation
Ribosome moves to the next mRNA codoln