6- Equilibria
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is meant by dynamic equilibrium?
Forward and backward reactions occur at the same rate so the concentrations of the reactants and products are the same
What is meant by a closed system?
Reactants ,products and energy cannot escape, be added or removed
What are the features of a dynamic equilibrium?
-F + R reactions occurring at the same rate
-R + P have unchanging concentration
-Occurs in a closed system
Sulfur trioxide is made by the following reaction
2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3
The forward reaction is exothermic
This reaction reaches a state of dynamic equilibrium in a closed system
a) If the temperature of this reaction was increased, what would happen to the yield of sulfur trioxide
b) If the pressure of this equilibrium was increased, what would happen to the yield of sulfur trioxide
c) If more oxygen was added to the mixture, what would happen to the yield of sulfur trioxide?
a) The yield would decrease, LCP states how the equilibrium shifts to the left to counteract the increase in temperature
b) The yield would increase, LCP says the system will shift to the right to counteract the increase in pressure
c) The yield would increase, LCP shifts to the right to counteract the increase in the reactant O2
When bismuth chloride is added to water, a reaction occurs and a white precipitate is formed. The following equilibrium is set up, what would the effect on the amount of precipitate if sodium hydroxide solution is added to the mixture?
BiCL2 + H2O ⇌ BiOCl + 2HCl
LCP says the system will shift to the right to counteract the increase in hydroxide ions
Meaning of
a) Kc value of 1
b) Kc value larger than 1
c) Kc value smaller than 1
a) similar/exact same concentrations of reactants and products
b) product dominate, equilibrium lies to the right
c) reactants dominate, equilibrium lies to the left
Kc expression format
A + 2B ⇌ 3C + D

What is meant by a homogenous equilibrium?
Equilibrium with all chemicals in the same state/phase
What are the units for Kc if the equilibrium moles on both hand side of the equation are the same
No units
Units for Kc
a) A + B ⇌ C + 2D
b) P + 2Q ⇌ 3R + 2S
(more product than reactant moles)
a) Total moles has increase by 1, moldm-3
b) Total moles increased by 3 to 5 (+2)
so mol2dm-6
count number of "mol" to get 2 add powers of -3 to get -6
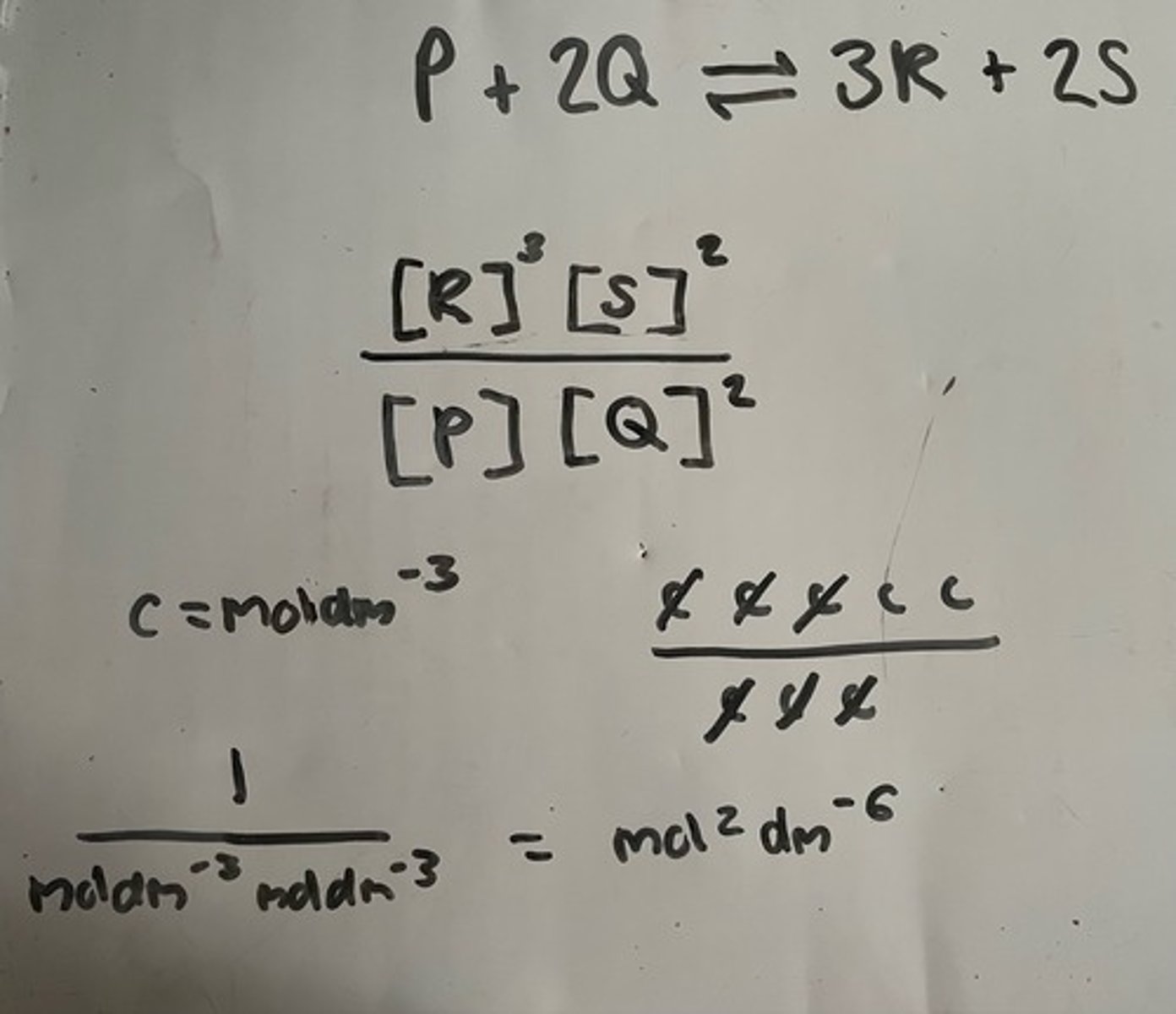
Units for Kc
a) 2A ⇌ B
b) 4E ⇌ F + G
(more reactant than product moles)
The signs are the opposite to an increase in moles when there is a decrease
a) Total moles decreased by 1, mol-1dm3
b) Total moles decreased by 2, mol-2dm6
Data needed to calculate Kc
Equilibrium moles, hence equilibrium concentrations
Factor that affects Kc
Temperature only
2.00 moles of PCl5 vapour are heated to temperature T in a vessel of volume 2×10¹ dm³. The equilibrium mixture contains 1.20 moles of chlorine. Calculate Kc for the equilibrium temperature at T.
Here is the equation: PCl5(g) ⇌ PCl3(g) + Cl2 (g)
0.09moldm-3
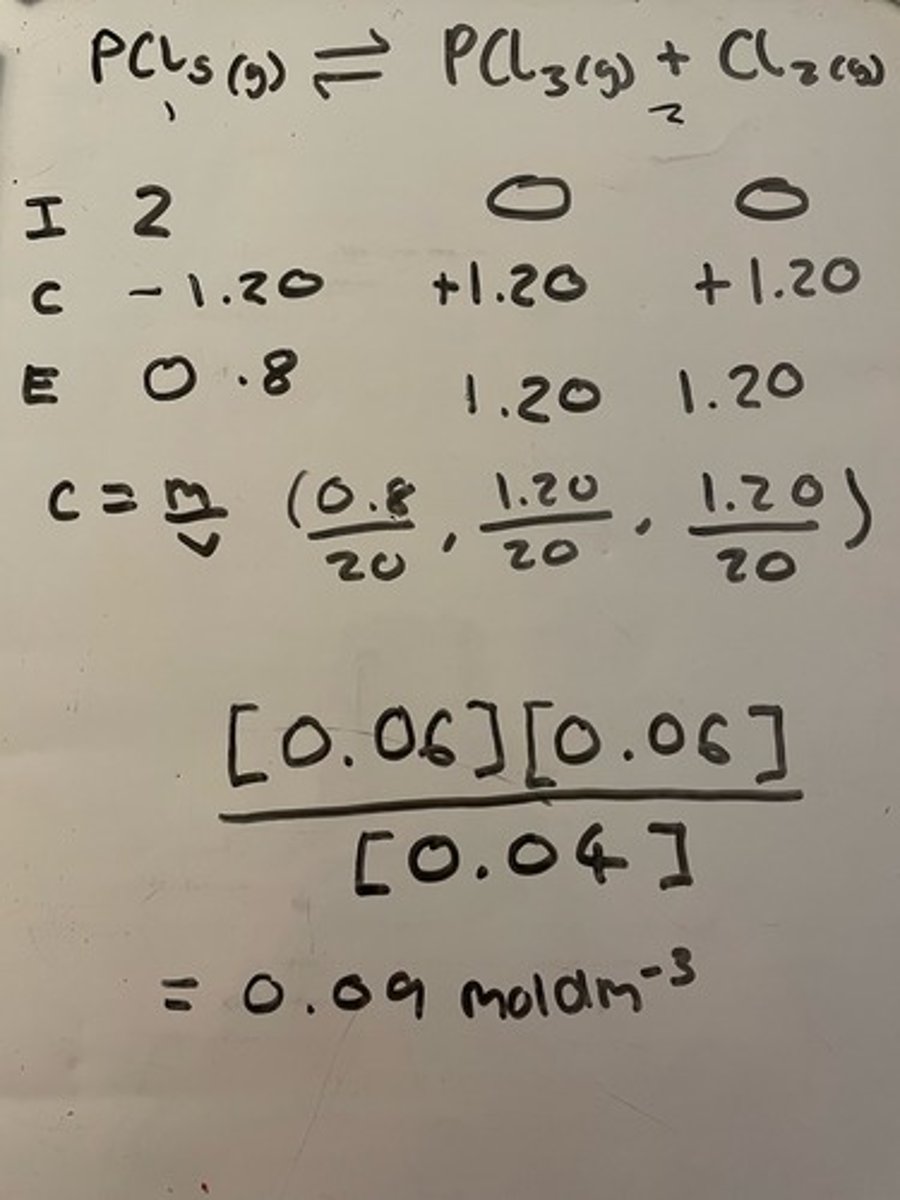
When 5.0 moles of A is mixed with 5.0 moles of B in a container of volume 12dm3, an equilibrium is established which contains 3.0 moles of C. Find Kc at this temperature. Here is the equation: A + 2B ⇌ 2C
7.685mol-1dm3

200.0g of ethyl ethanoate and 7.00g of water were refluxed together. At equilibrium, the mixture contained 0.250mol of ethnic acid. Calculate Kc for the hydrolysis of ethyl ethanoate
CH3COOCH2CH3 + H2O ⇌ CH3COOH + CH3CH2OH
0.224mol-1dm3

Explain why using a catalyst has no effect on the percentage yield
Catalyses both the forward and reverse reaction equally