Esters
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are derivatives of carboxylic acids?
A compound that can be hydrolysed to form the parent carboxylic acid and all contain the acyl group - RCO
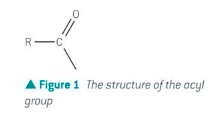
Name the 4 types of carboxylic acid derivatives
Esters
Acyl chloride
Acid anhydride
Amide
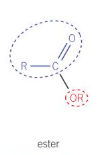
For esters, give:
The general displayed formula
The way of naming
Remove ‘oic acid’ and replace with ‘oate’
First word is alkyl chain attached to O on COO
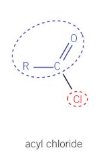
For acyl chlorides, give:
The general displayed formula
The way of naming
Remove ‘oic acid’ from carboxylic acid and replace with ‘oyl chloride’
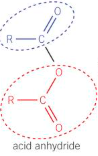
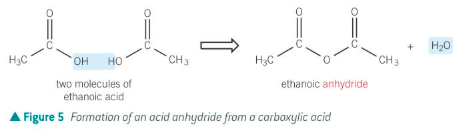
For acid anhydride, give:
The general displayed formula
The way they are formed
Removal of water from two carboxylic acids
Give 2 ways of making an ester - which produces a better yield?
Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water
Acid anhydride (meaning no water) + alcohol → ester + carboxylic acid (produces a better yield)
Give the equation for esterificaion and the conditions needed
Alcohol + carboxylic acid → ester + water
Conditions: reflux, concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst
Why is reflux used?
To ensure reaction occurs without the reaction flask boiling dry
Give the 2 ways of making methyl ethanoate ( equations )
Methanol + ethanoic acid → methyl ethanoate
Methanol + ethanoic anhydride → methyl ethanoate + ethanoic acid
How is an acid anhydride formed?
By the removal of water from two carboxylic acid molecules
Define hydrolysis
The chemical breakdown of a compound into 2 compounds in the presence of water or aqueous solution of hydroxide ions
Give the 2 ways esters can be hydrolysed and their products
In hot aqueous acid to form carboxylic acids and alcohols
In hot aqueous alkali to form carboxylate salts and alcohols
Summarise acid hydrolysis
The reverse of esterification
Give the equation for acid hydrolysis of esters
Ester + water → alcohol + carboxylic acid
Describe the process of acid hydrolysis and conditions needed
The ester is heated under reflux with dilute sulfuric or hydrochloric acid, where water is present
The ester is broken down by the water, with the acid acting as a catalyst
Carboxylic acid and alcohol is formed
What can be said about the amount of reactants vs products in acid hydrolysis?
The reaction is at equilibrium
There are always molecules of reactant and product present
Carboxylic acid will be present in the equilibrium mixture
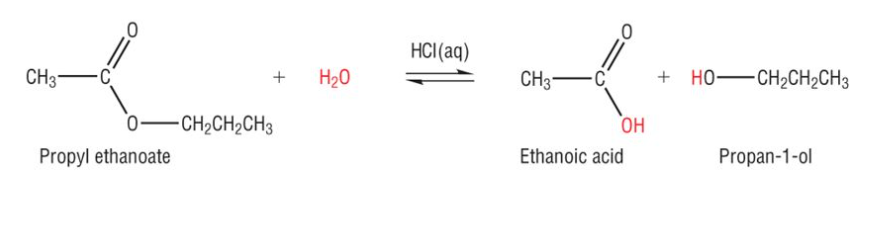
Show the acid hydrolysis of propyl ethanoate
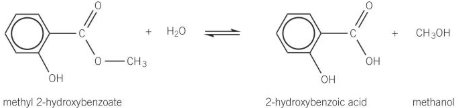
Show the acid hydrolysis of methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate
Summarise alkaline hydrolysis
Alkaline hydrolysis is also known as saponifacation (process of making soaps)
It is irreversible
Describe the process of alkaline hydrolysis and the conditions needed
The ester is heated under reflux with aqueous hydroxide ions ( sodium or potassium hydroxide)
This non-reversible reaction leads to the formation of a (sodium or potassium) carboxylate salt of the carboxylic acid and alcohol
Give the equation for alkaline hydrolysis
Ester + alkali (aq) → carboxylate salt + alcohol
Show the alkaline hydrolysis of ethyl propanoate in sodium hydroxide

Give a brief method of making esters
Add alcohol and carboxylic acid into a boiling tube
Add concentrated sulfuric acid
Place the boiling tube in a hot water bath of 80 degrees
Leave for 5 minutes
Pour into a beaker of aqueous sodium carbonate to neutralise acids and remove the smell