BMS 503- Immunization
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the definition of immunization
the process by which a person or animal becomes protected against a disease
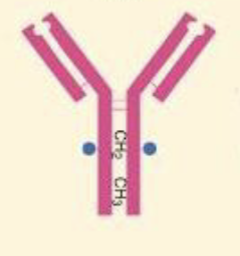
What Ig is a monomer, has 2 antigen binding sites, with the function of long-term immunity; memory antibodies; neutralizes toxins, opsonizes, fixes complement
IgG
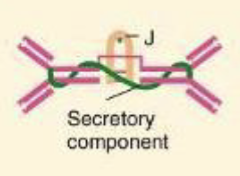
What Ig is a dimer or monomer, has 4 or 2 antigen binding sites, is a secretory antibody; on mucous membranes
IgA
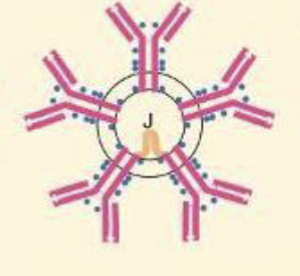
what Ig is a pentamer, has 10 antigen binding sites, and is produced at first response to antigen; can serve as B-cell receptor
IgM
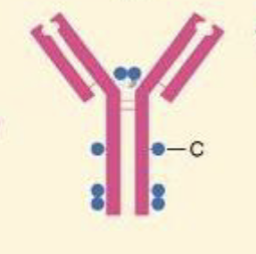
What Ig is a monomer, has 2 antigen binding sites, and is a receptor on B cells
IgD
What Ig is a monomer, has 2 antigen binding sites, and is the antibody of allergy; worm infections
IgE
what’s a hapten
molecules too small to illicit an immune response
what antibody mechanisms enhance phagocytosis
neutralization, agglutination of microbes, precipitation of dissolved antigens
what antibody mechanism leads to cell lysis
activation of complement system
what is the injection of a killed or weakened infectious microorganism or piece of infectious microorganism in order to prevent the disease
vaccination/inolculation
what was the first human vaccine
small pox
what immunization is the injection of purified or antibody-containing- serum to provide rapid, temporary protection or treatment
passive
what immunization is an immune response triggered because of challenge with an immunogen (i.e. exposure to infectious agent or its antigens, vaccine, is long lasting)
active
in herd immunity, what does reducing the # of infectious hosts prevent
spread of an infectious agent and new genetic variants of the agent
what vaccine type is regarded as the most successful vaccine
live attenuated
what vaccine type contains only the antigenic parts of the pathogen
subunit
what’s an example of a subunit vx
Tdap