PCS 3 Exam 2
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
At a well visit, you would measure length and height and weight how often?
every visit
When do you start measuring length and height of a child standing ?
at 2 years old
For what aged patients do you measure head circumference?
birth to 36 months old
How to measure length/hieght of a child under 2
-Measure the crown-heel length using a recumbent stadiometer.(shown below) Ask a parent or assistant to hold the baby's head stilland stretch out the legs until the baby is fully extended.
-Most places wont have this though, so just lay them on the exam table and mark it off on the paper
A patient's height is related to
average of their parents' height centile ± 2 standard deviations
How to weigh an infant
fully undressed on an electronic scale accurate to 5g
how to measure head circumference
Measure at greatest circumference -> place tape measure slightly above points just above the eyebrows and the pinna and around the occipital prominence.
To nearest millimeter, measure 3 times and take largest .
Plot on appropriate growth chart.

failure to thrive
a condition in which the baby does not grow and develop properly
learn to use a growth chart
fine
preterm infants
Those born before the completion of 37 weeks of gestation (the time between fertilization and birth).
premmie growth chart rules
use preterm growth charts
can use regular chart once they hit 40 weeks
for first 2 years of life, adjust age to expected date of delivery instead of DOB
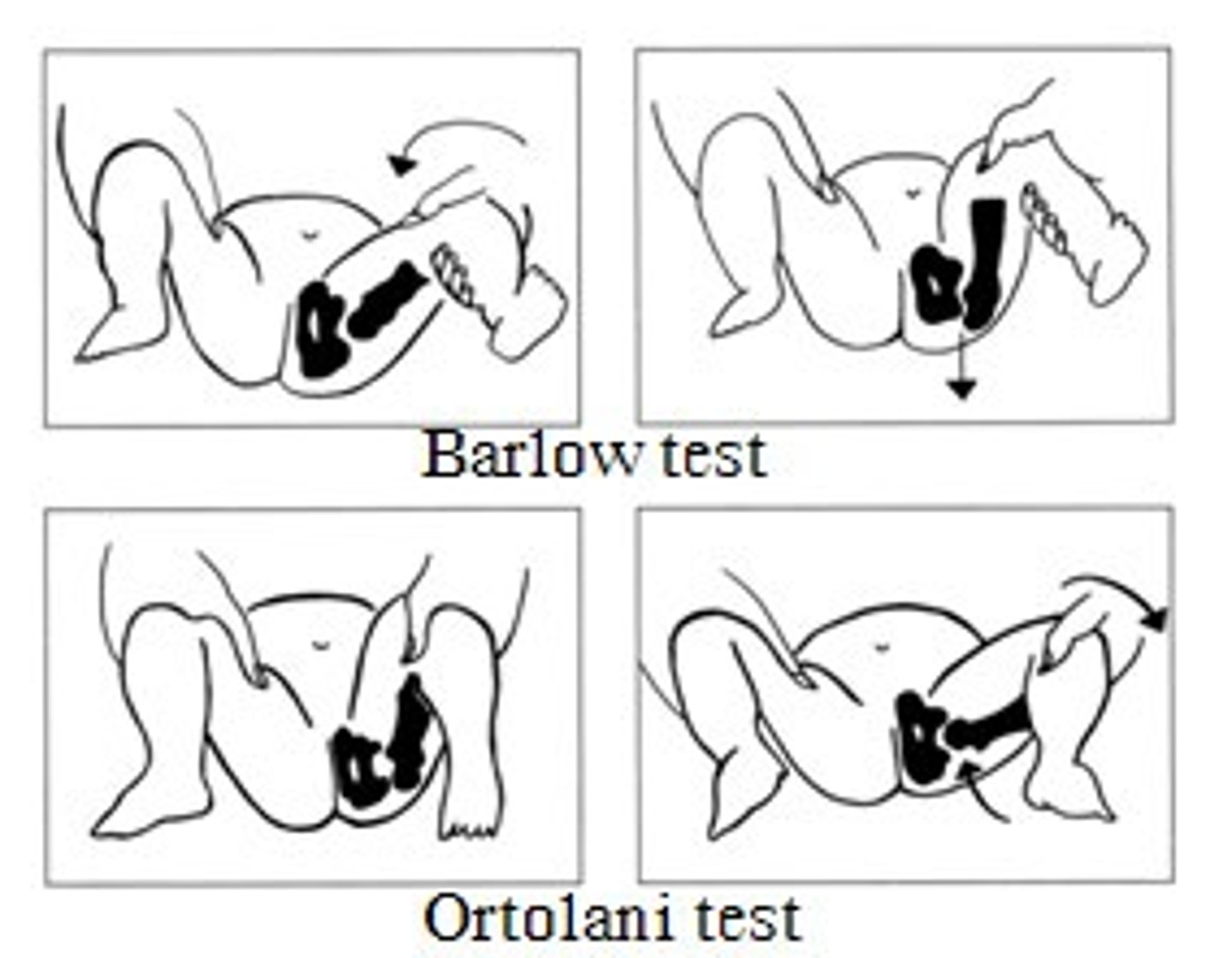
Ortolani maneuver
the hip is abducted and gentle pressure isapplied to the proximal thigh from behind. Here, the examiner attemptsto relocate an already dislocated femoral head back into theacetabulum. If the joint is dislocated, a palpable "clunk" is noticed asthe head slides back into place.
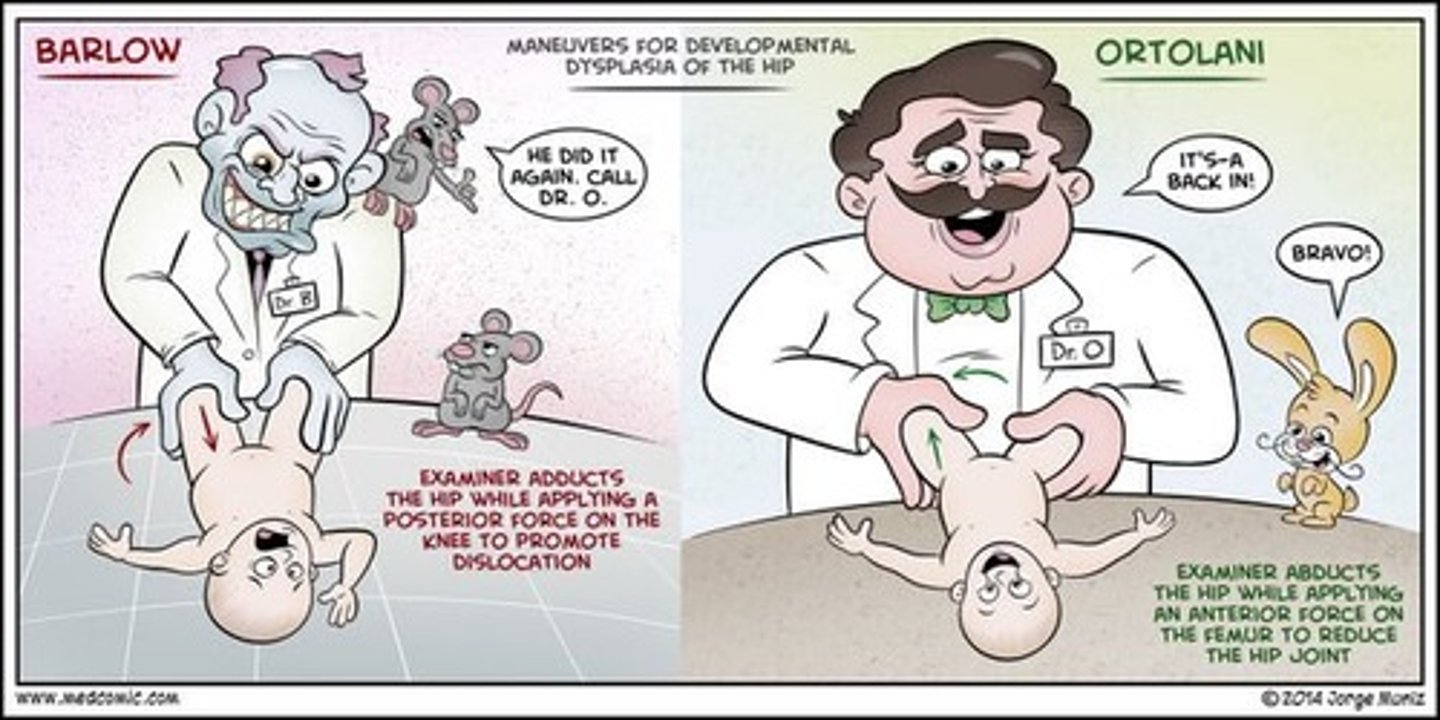

Barlow maneuver
The examiner grasps the infant's thigh near the hip and with gentleposterior/lateral pressure, attempts to dislocate the femoral head fromthe acetabulum. Normally, there is no motion in this direction. If the hipis dislocatable, a distinct "clunk" may be felt as the femoral heads popsout of joint.
between length/weight/height, what is least reproducible
length
6 most significant behaviors affecting adolescents
• Inadequate physical activity
• Poor nutrition
• Sexuality-related behaviors•
Substance use and abuse (including tobacco products)
• Unintentional injury
• Intentional injury
Acronym for Adolescent Social Hx taking
S Strengths*
S School
H Home
A Activities
D Drugs
E Emotions
S Sexuality
S Safety
Failing grades can indicate
an underlying learning or attention disorder and also correlates withpsychosocial issues.
Home questions can help identify
protective and risk factors in their home environment
working more than 20 hours a week while in school associated with
-lower grades, less investment in education
-substance use:alcohol and drug use
-delinquency and distress
7 Ps Framework of Sexuality
• Partners
• Practices
• Protection from STIs
• Past History of STIs
• Prevention of pregnancy
• Permission
• Personal gender identify
Being bullied is associated with
-negative coping and significant more medical problems or complaints
-Also associated with poorer quality relationships and loneliness
two potential harms to performing a psychosocial screening
• It can contextualize a person's life through a lens of brokenness or risk. By starting with the highlighted strengths, the SSHADESS screening is designed to address this.
• It holds potential of retraumatizing a young person by triggering memories.
It is important to be what in an adolescent interview
nonjudgemental and flexible
Clear mucois sputum associated with
COPD/bronchiectasis without current infection/rhinitis.
Yellow (mucopurulent) sputum associated with
acute lower respiratory tract infection/asthma
Green (purulent) sputum associated with
current infection - acute disease or exacerbation of chronicdisease, such as COPD
Red/brown (rusty) sputum associated with
pneumonccocal pneumoniae
Foul-smelling sputum is present in
anaerobic lung abscess, thick tenacious sputum in cystic fibrosis.
Large volumes of sputum are present in
bronchiectasis and lung absecces
hemoptysis
the coughing up of blood from the lower respiratory tract
For patients reporting hemoptysis:
o Quantify the volume of blood produced
o The setting and activity
o Any associated symptoms.
causes of hemoptysis include
severe, forceful cough, infections, pulmonary embolism, cancer,vasculitis
Massive hemoptysis (>200 cm3) may be life-threatening
How to determine severity of SOB
based on a patient's daily activity
a family history of atopy is relevant in
rhinitis
In patients with epistaxis, it is important to
establish a family history of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia or inherited bleeding disorders. Heavy alcohol intake is also relevant to this
history of COPD at a young age indicative of
Alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency
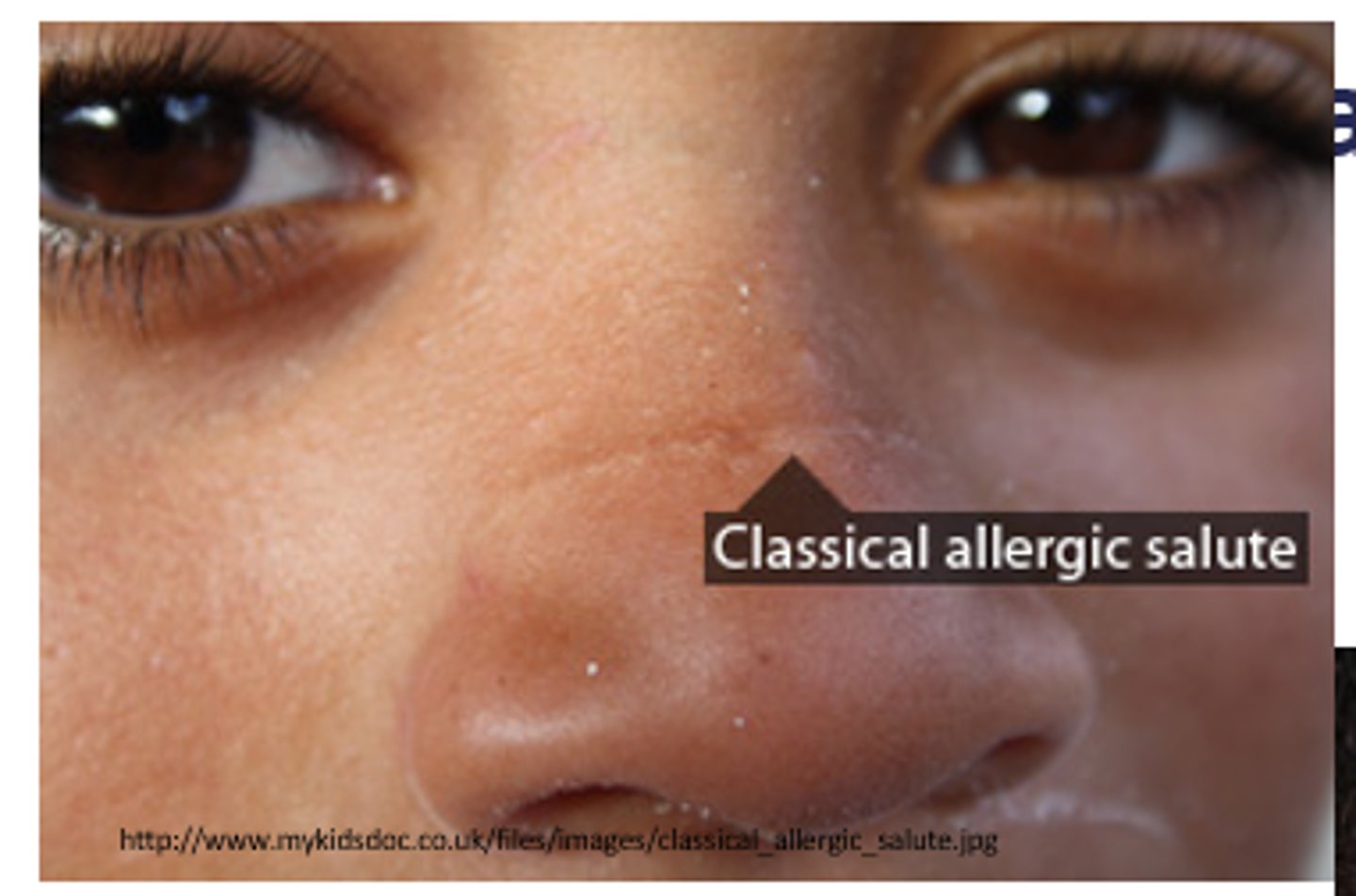
classic allergic salute
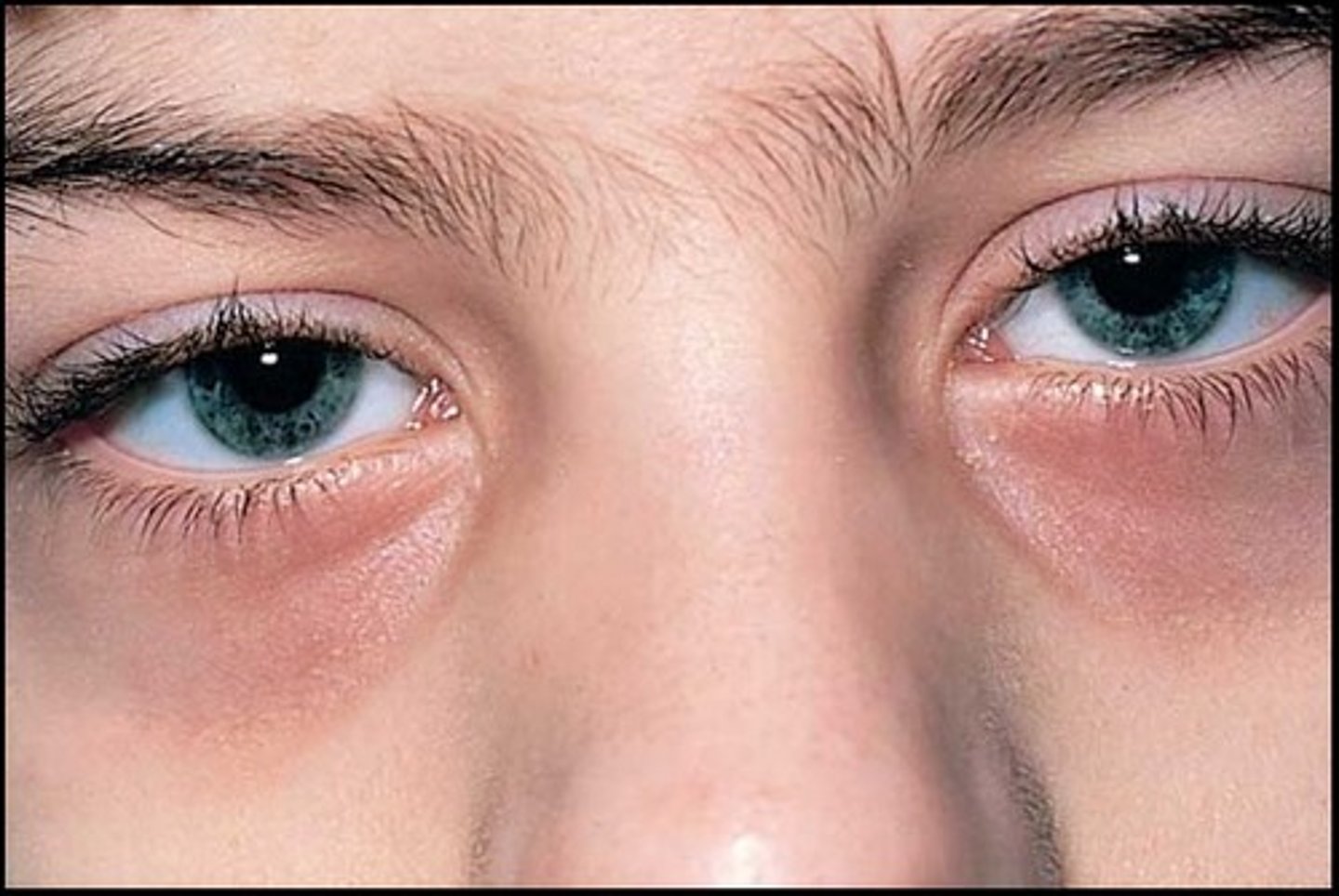
allergic shiners
dark circles under eyes
aka me constantly
Pale, boggy turbinates
allergic rhinitis
Jugular venous pressure is raised in patients with
pulmonary hypertension and maybe acutely raised in those with tension pneumothorax or large pulmonary embolism
Tracheal deviation away from the affected side is seen acutely in
tension pneumothorax
Chronic tracheal deviation towards the affected side occurs with
loss of lung volume in upper lobe fibrosis or collapse and following lobectomy or pneumonectomy.
Surgical emphysema
palpation of the chest wall can indicate this, air trapped in the subcutaneous tissue
crepitus commonly complicates
pneumothorax with chest drainage or rib fracture and feels like a palpable crackling under the skin of the upper thorax and neck
Consolidation indicates
filling of the alveoli and bronchioles with pus(pneumonia), fluid (pulmonary edema), blood, or neoplastic cells.
A solitary wheeze that is present consistently with each breath and does not clear with coughing suggests
a possible fixed bronchial obstruction and can be an important sign of underlying cancer
Crackles that persist after several breaths and do not clear with a deliberate cough are
pathological
fine crackles
fine crackles during inspiration, resembling the sound made by peeling a Velcro fastener, are characteristic of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, and are most commonly heard atthe lung bases posteriorly and laterally.
coarse crackles
generally heard in patients with significant purulent airway secretionssuch as those with bronchopneumonia or bronchiectasis. (Rhonchi)
bronchophony
• Have the patient repeat "99" as you auscultate
• An area of increased sound transmission suggests consolidation
Egophony
• Ask the patient to say "Eeeee" as you auscultate
• If consolidation is present the "E" will be heard as "A"
whispered pectoriloquy
• Ask your patient to whisper "1, 2, 3"
• Normally whispering produces a muffled sound
.• In an area of consolidation, the words will be louder.
Tactile Fremitus
• Place the ulnar surface of your hands against the chest wall and ask the patient to repeat "99" as you move your hands down the chest wall. (You can also use the palmar surface of your hand.)
• Tactile fremitus (vibrations) o Increased in consolidation o Decreased in conditions that decrease transmission of sound such as increased fat, an air-fluid level, or over expansion from emphysema. (seevideo!)
#1 preventable cause of mortality in the US
smoking
The use of appropriate skills to address smoking is not associated with longer visits.
nice
how quick does nicotine reach the brain
less than 10 seconds after inhalation, and achieves max concentrations within 1 minute
Fagerstrom Tolerance questionnaire
meausres dependence
Heaviness of Smoking Index
-How soon after you wake up do you smoke your first cigarette?
-On average how many cigarettes do you smoke per day?
5 A's of tobacco counseling
- Advise: importance of quitting
- Assess: level of readiness to quit
-Agree: on goals and methods , based on willingness
- Assist: let me know when ready to quit
- Arrange: follow up
Stages of Change Model
The Stages of Change Model:
1. Precontemplation- Patient has no interest in quitting in the foreseeable future.
2. Contemplation- Patient is ambivalent about quitting and not willing to make a commitment to change.
3. Preparation- Patient intends to quit within the next month, or has made recent changes in smoking behavior,
4. In action- Patient has recently quit and is using strategies to remain abstinent.
5. Maintenance- Patient has quit for at least 6 months
Relapse
occurs frequently in smokers trying to quit, almost 80 % sometimes
importance
what patients believe about the importance of giving up smoking
confidence
how patients feel about their ability to quit despite obstacles
even brief advice increases quit rates!
true
dancing with discord can elicit
patient "change talk" that reflects movement towards considering quitting
The outcome goal patients agree to choose is rarely
abstinence now and forever
Assure that you and patients agree on goals that are based on
patient's past experience
other pearls to consider
Agreeing on an achievable goal is far better than persuading patients to assent to an "optimal" goal which they neither want nor are capable of reaching.
• A sensible goal encourages small successes instead of big failures and enhances the likelihood of successful change
• For patients with high levels of nicotine dependence suggest
nicotine replacement therapy
The combination of counseling and pharmacotherapy is more effective than ether modality alone
okie
essential aspect of the smoking intervention
patient follow up
Effective telephone counseling or texting can be conducted by
clinical staff or a community resource,including the national quit line and texting programs available at https://smokefree.gov/
quitting is not an event, it is a
stepwise process
tobacco dependence is a
chronic and relapsing disorder
Successful clinical intervention depends on
appropriate assessment, a trusting relationship, and skillful informing and advising of patients
myth or fact? smokers do not want to quit
MYTH
About 70% of smokers want to quit smoking, and almost half make a serious attempt to quiteach year
Why is nicotine optimal for development of physical dependence
instantly enters the neurons, and impacts brain function
what percent of smokers trying to quit experience significant withdrawal sx?
50 %
what are some smoking withdrawal symptoms and concerns ?
craving, increased hunger, dreaming about smoking, concern of weight gain, (more in women)
What smokers may have a higher level of nicotine dependence
smoking withing 30 minutes of arising, or 25 or more a day
what is associated with higher prevalence of smoking and harder to quit
psychiatric comorobidity like anxiety or mood disorders
how to address confidentiality to parents and pateint in adolescent interview
-Will need to explain the transition to allow more autonomy and privacy for the adolescent, may invovle asking the parent to leave
-give a confidentiality statement
-explain confidentiality with the goal of promoting open communication with the family
-reassure parent that they will be brought back in
vague answers in a teen like "just hanging out" may need to be probed at further because...
could be a sign of engaging in risky behavior and activities the adolescent is reluctant to discuss
how to ask adolescents about suidical idealations
-dont use vague terms like "harming yourself"
-open with a statement that normalizes thoughts of suicide to help them open up
-use clear language
if an adolescent expresses suicidal idealations...
-determine if there is a specific plan
-determine if they have the ability to carry it out
**ONE OF THE EXCEPTIONS TO CONfIDENTIALITY
where else can hemoptysis come from thats not lungs?
nose bleeds, vomitus
Anxious patients may have episodic dyspnea both during exercise and at rest, as well as ____, or rapid, shallow breathing.
hyperventilation
family hx of clots may indicate risk for
PE
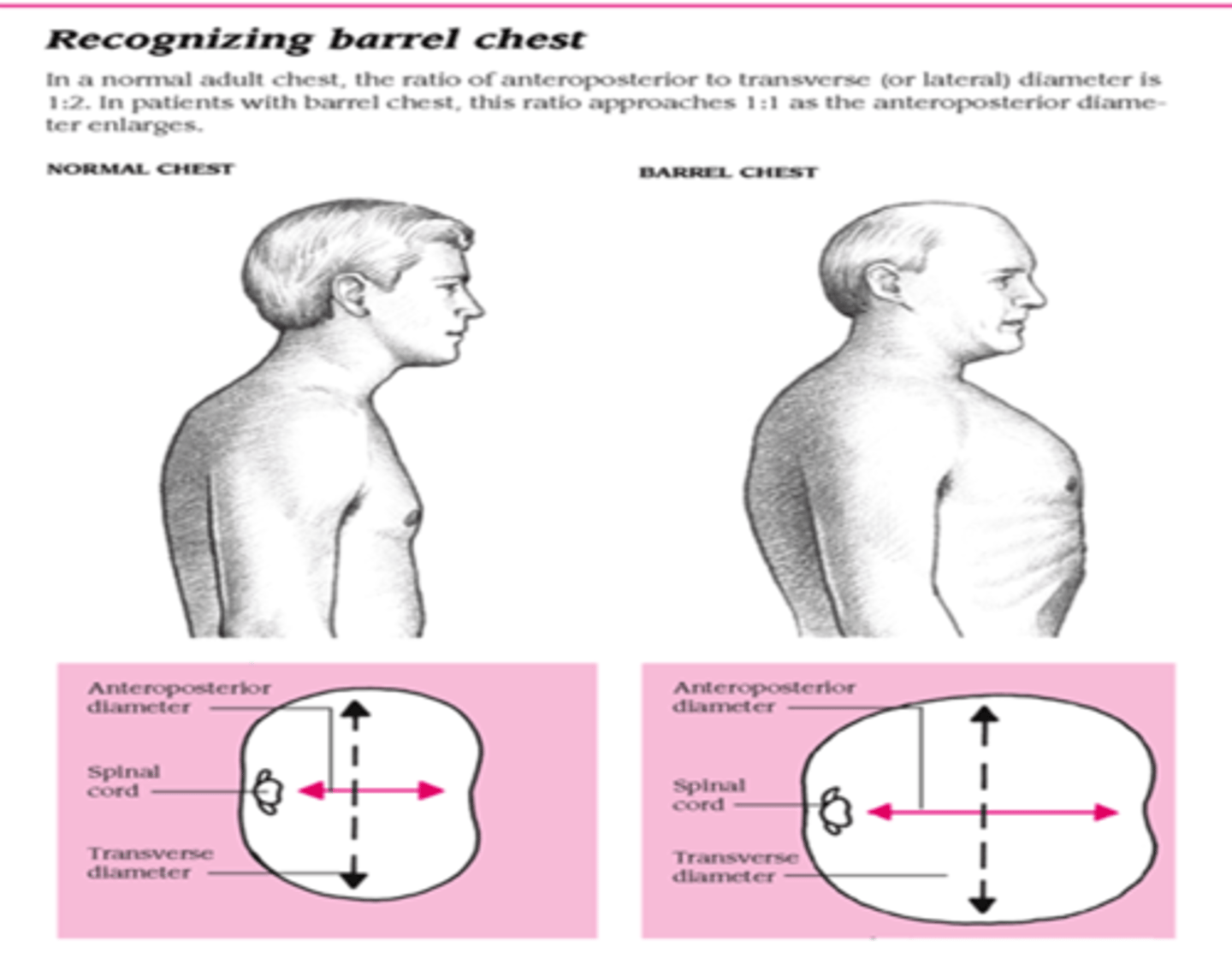
barrel chest
a condition characterized by increased anterior-posterior chest diameter caused by increased functional residual capacity due to air trapping from small airway collapse. A barrel chest is frequently seen in patients with chronic obstructive diseases, such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
wheeze
high-pitched, musical, squeaking adventitious lung sound, usually expiratory and of smaller airways
polyphonic wheeze is common in
asthma, bronchitis, COPD exacerbation
indications for pulmonary function tests
- pt with dyspnea duh
-evaluating disease severity and monitoring tx response
-determing if fit for surgery (thoracic/lung resection)
Tidal Volume (TV)
amount of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions
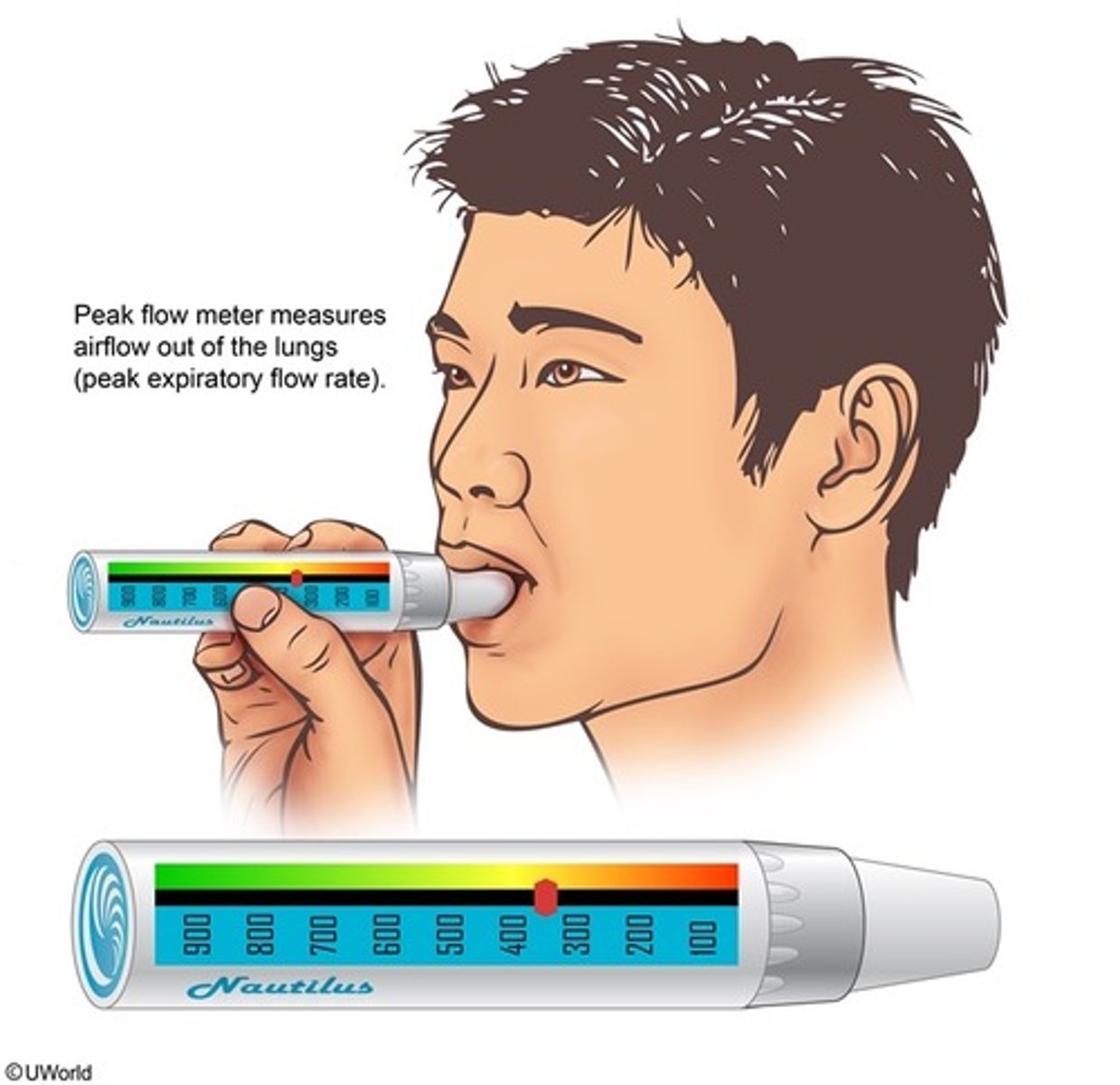
peak flow meter measures
peak expiratory flow
nasal cannula
A device that delivers low concentrations of oxygen through two prongs that rest in the patient's nostrils.
24-40% oxygen, delivery rate is 1-6 L/min
Simple face mask flow rate
6-10L/min
40-60% oxygen
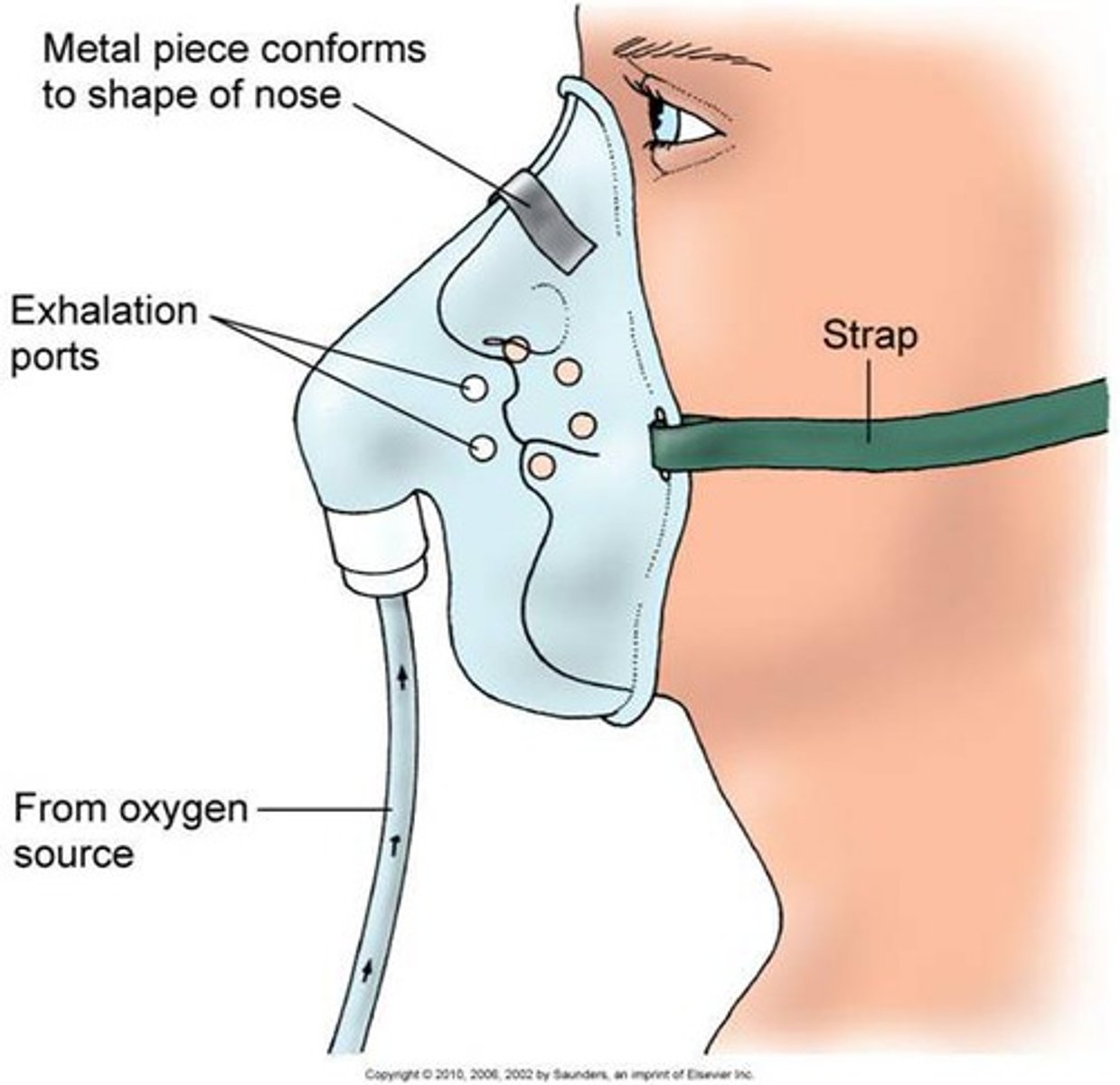
Non-rebreather mask
allows higher levels of oxygen to be added to the air taken in by the patient
60-80% oxygen
10-15 L/min
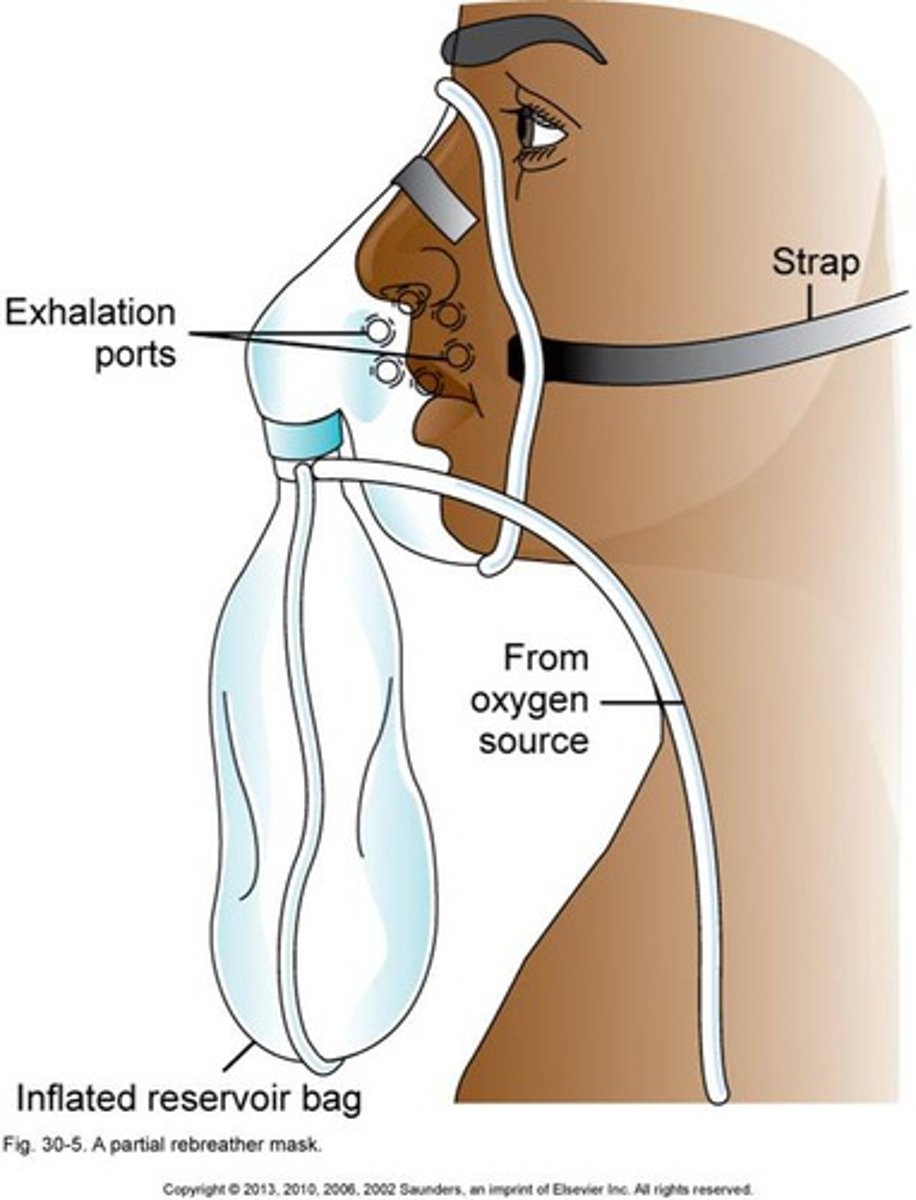
non rebreather risks
-Risk of suffocation if the gas flow is interrupted. The bag should never totally deflate
• Risk of hyper-oxygenation
• Difficult to eat with mask on. Mask may beconfining for some patients, who may feel claustrophobic with the mask on.
Venturi mask flow rate
24-60% O2 at 4-12 L/min

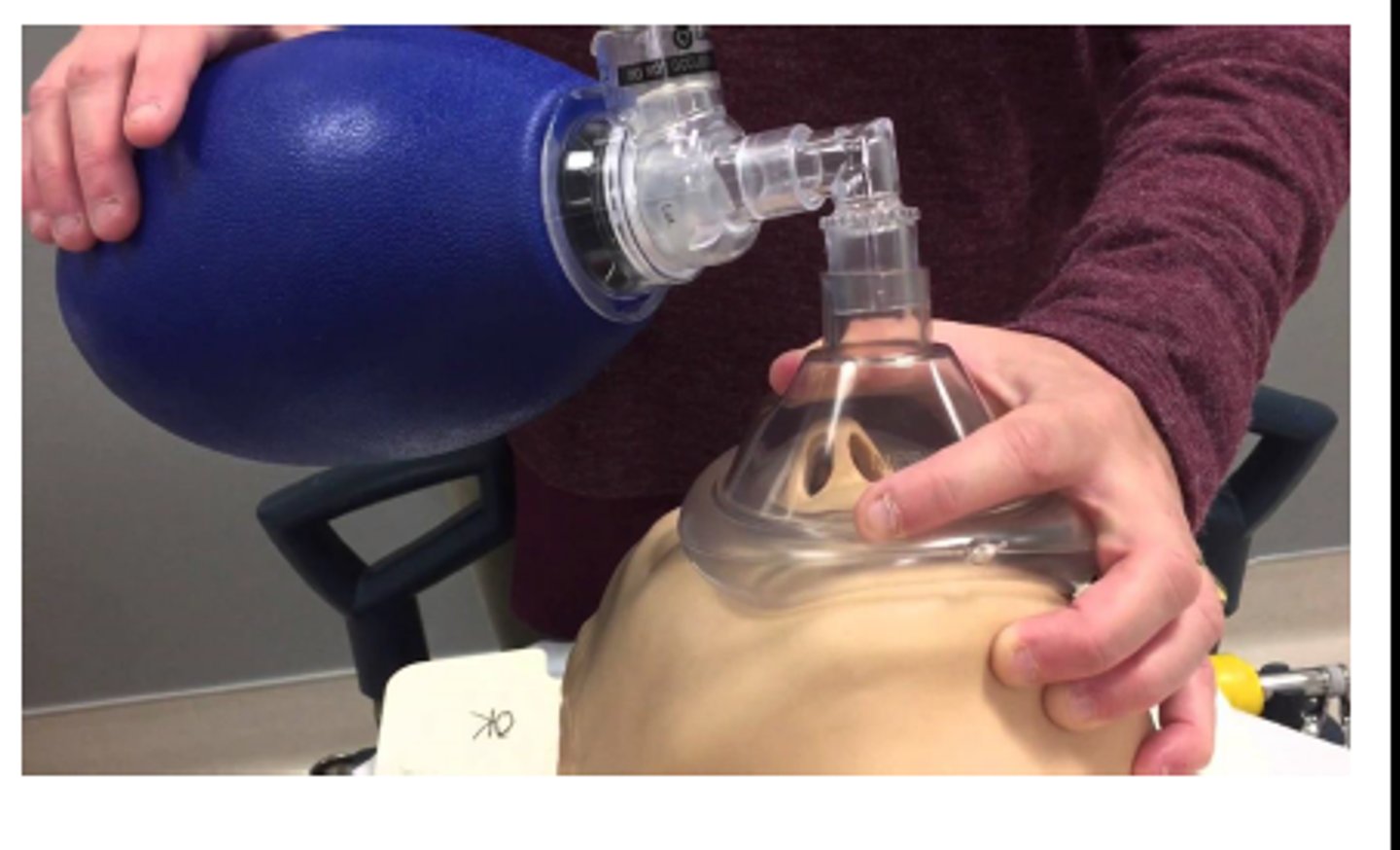
bag-valve mask (BVM)
A device with a one-way valve and a face mask attached to a ventilation bag; when attached to a reservoir and connected to oxygen, it delivers more than 90% supplemental oxygen.
dont use if patient is conscious duh