14.2 alkenes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
State the ways in which alkenes can be produced
Elimination of HX from halogenoalkane
Dehydration of alcohol
Cracking of longer chain alkane
Élimination of HX
Elimination of halogenoalkane by heating with ethanolic NaOH to form alkene salt and water

Dehydration of alcohol
Alcohol vapour is passed over a hot catalyst of aluminium oxide powder (Al2O3) to produce alkene and water
Cracking of longer chain alkanes
An aluminium oxide catalyst and 600’C are used to speed up this reaction.
State the ways in which alkenes can react via electrophilic addition
Electrophilic addition of:
Hydrogen
Steam
Hydrogen halides
Halogen
Hydrogenation
Reaction alkene with hydrogen to form alkane
Heat and Ni catalyst
Hydration
React alkene with steam to form alcohol
Use H3PO4 catalyst and heat
Add HX
React alkene with HX to form halogenoalkane
RTP
Halogenation
React alkene with halogen to form dihalogenoalkane
Oxidation of alkenes
By cold dilute KMnO4
Forms diol
Pale purple to colourless
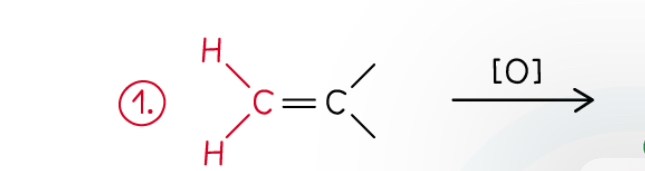
How do alkenes with C atom attached to 2 hydrogens react when oxidised by hot concentrated KMnO4.
Oxidised to CO2
Each carbon treated separately
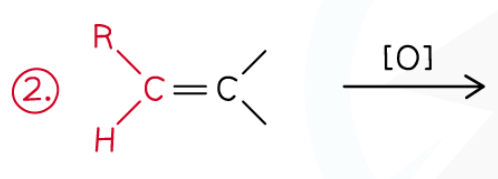
How do alkenes with C atom attached to 1 hydrogen and an R group react when oxidised by hot concentrated KMnO4.
Oxidised to aldehydes then carboxylic acid
How do alkenes with C atom attached to 2 R groups react when oxidised by hot concentrated KMnO4.
Oxidised to ketone
How to test for unsaturated compounds
unknown compound is shaken with the bromine water
If the compound is unsaturated, an addition reaction will take place and the coloured solution will decolourise
Draw the mechanism for electrophilic addition
What is the major carbocation intermediate
The most stable intermediate
Define positive inductive effect
The alkyl groups attached to the positively charged carbon atoms are ‘electron donating groups’
Which carbocation intermediate is most stable and thus the major intermediate?