Physics Definitions
1/79
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Physical Quanity
A quantity that can be measured. Consists of a numerical magnitude and unit.
Period (of a pendulum)
Time taken for one complete oscillation.
Scalar Quantity
Physical quanities with only magnitude.
Vector Quantities
Physical quantities that have both magnitude and direction.
Velocity
The rate of change of displacement.
Speed
Distance moved per unit time.
Instananeous speed
The speed of an object at a particular moment in time; how fast it is moving at that instant.
Uniform Speed
When the change in distance travelled by an object for every unit of time is the same.
Distance
The total length traveled by an object, regardless of direction of motion.
Magnitude only
Displacement
The shortest distance from the initial to the final position of an object, including direction.
Magnitude and direction
Acceleration
Rate of change of velocity.
Speed/Direction changes
Vector qty
Uniform Acceleration
Change of velocity for every unit of time is the same. (constant rate of change of velocity)
Non-uniform Acceleration
Change of velocity for every unit of time is not the same.
Types of contact forces
Friction, Air resistance, Normal force, Tension
Normal force
Push exerted by surface on an object pressing on it
Always perpendicular to surface
Types of non-contact forces
Magnetic force, Electrostatic force, Gravitational force
Mass
Measure of amount of matter in a body.
Cannot be changed by location, shape, speed.
Scalar qty
(kg)
Beam balance/Electronic balance
Weight
Gravitational force acting on an object that has mass.
Vector qty
(N)
Sprint balance
Gravitational field
Region which mass experience a force due to gravitational attraction.
Gravitational Field Strength
Gravitational force per unit mass placed at that point.
Relation between Mass and Weight
Weight directly proportional to mass.
If W x2, M x2.
Density
Mass per unit volume.
Pressure
Force acting per unit area
(Pa, N/m2)
Effects of Force on a moving object
Body at rest moves.
Moving body increases/decreases in speed.
Moving body changes direction.
Resultant Force
When forces are balanced.
F = 0N, A = 0, Constant speed, At rest
Vector qty
(N)
Newton’s first law of motion
Every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a FR acts on it.
Newton’s second law of motion
When a resultant force acts on an object of constant mass, the object will accelerate in the direction of the FR.
F = ma
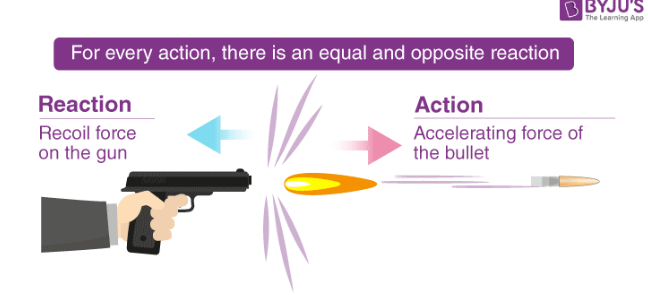
Newton’s third law of motion
If a body A exerts force on another body, body B will exert an equal and opposite force on body A.
Friction
Opposes motion between surface in contact.
Negative & Positive effects of friction
Walk without slipping
Cars less effecient by 20% (suffer wear and tear)
How to reduce negative effects of frictions?
Ball bearings (machines)
Lubricants
Polishing surface (surface irregularities)
Torque
Moment of a force
The turning effect of a force about a pivot. Product of F x Perpendicular D from pivot to line of action of force.
(Nm)
Principles of Moment
When a body is in equilibrum, sum of CW moments = sum of ACW moments about the same pivot.
Conditions for equilibrum
Stationary, resultant M = 0, resultant F = 0
Centre of Gravity
Imaginary point where entire weight of object acts on. (Below pivot)
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed. Energy can be transferred from one store to another. Total energy in an isolated system is constant.
Work done
The amount of energy transferred when a force applied to an object causes it to move in the direction of the force.
1 J is work done by 1 N force.
(J)
Power
Work done/energy transferred per unit time.
(W)
How can energy be transferred?
Mechanically
Electrically (current)
Heating (temp diff)
Propagation of waves (electromagnetic & mechanical sound waves)
Internal Energy
Energy store made up of total KE from random motion of particles & total PE between particles.
Temperature (and energy)
Increases with avg KE of particles.
Conduction
Energy transfer where energy is transferred from passing on of vibrational motion from one particle to another.
Convection
Energy transfer by means of convection currents of liquid/gas due to a diff in density.
Radiation
Process of energy transfer by electromagnetic waves. Does not require a medium.
A wave
Disturbance that propagates through space, transferring energy with it.
Transverse wave
Direction of vibration/motion is perpendicular to direction of wave travel.
Longitudinal wave
Direction of vibration/motion is parallel to direction of wave travel.
Displacement of a wave
From rest position to the point on the wave.
Amplitude
Maximum magnitude of displacement from its rest position.
Loudness
In phase (wave)
Two points on a wave that always have the same direction of motion/oscillation. All crests & troughs are in phase.
Wavelength
Shortest distance between 2 sucessive crests/troughs.
Period (of a wave)
Time taken by each point on the wave to complete one oscillation.
Frequency (of a wave)
Number of oscillations each point on the wave completes per second.
Pitch
Wave Speed
Distance travelled by the wave per unit time.
Determined by medium
Speed of sound in diff media
Solid < Liquid < Gas
Higher frequency ≠ Travel faster
What is a human’s audible range?
20 Hz to 20 000 Hz
Use of Radio waves
f = 108
Communication, Radio/TV broadcasting
Use of Microwaves
f = 1010
Cooking, GPS
Use of Infrared waves
f = 1012
Cooking, keeping warm
Use of visible light
f = 5 × 1014
Photography
Use of Ultraviolet light
f = 3 × 1016
Disninfection
Use of X-Rays
f = 3 × 1018
X-ray imaging
Use of Gamma rays
f = 3 × 1020
Kill cancer cells in radiotherapy
Law of reflection
Angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Incident ray, reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence all lie on the same plane.
Refraction
Bending of light as it passes from one optical medium to another.
Refractive index
Ratio of speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
Electric current
Rate of flow of electric charge
Electromotive force
Work done by electrical source in driving a unit charge around a complete circuit.
E = W/Q
Potential Difference (p.d)
Work done per unit charge in driving charges through the component.
V = W/Q
Resistance
V = IR
Scalar qty.
Resistor
A conductor/insulator that has high resistance.
Fixed & Variable resistor.
Closed circuit
When there is closed loop path connecting the components together.
Open circuit
Large or infinite resistance in the path (air gap).
Short circuit (path)
A low resistance path.
Live wire
Brown. High voltage & current.
Earth wire
Yellow and green. Safety wire, earth appliances with a metal case.
Neutral wire
Blue.
0V (connection to earth).
Completes path for current to flow through appliances.
Nuclear decay
Random process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses its energy by emission of electromagnetic radiation/particles.
Ionising radiation
Radiation with high energies that can knock off electrons from atoms to form ions.
Background radiation
Nuclear radiation in an environment where no radioactive source is deliberate;y introduced.
Rocks, Medical X-rays, Waste product from nuclear power stations.