Labour markets
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is the labour market diagram and what does it show?
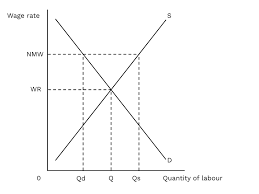
The labour market diagram shows the equilibrium for the quantity of labour and wage rate. If wages are too high, there will be excess supply (unemployment). If wages are too low, there will be excess demand for labour.
What affects the wages that people receive?
Elasticity of labour demand - Impacted by number of substitutes, % of total cost and time
Elasticity of labour supply - Impacted by skills and qualifications, unemployment level and time
What are the diagrams for elasticity of supply and demand of labour?
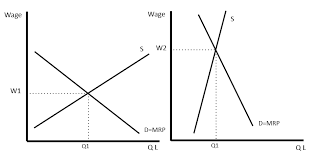
The left graph shows elastic supply and demand of labour, while the left shows inelastic. For inelastic, wages are higher.
What affects the elasticity of labour demand?
1) How easy it is to substitute a worker. If a worker if easy to replace, their demand will be elastic. This means that employers can switch to alternate workers or invest in capital if wages rise. However, if demand is inelastic, there aren’t many substitutes and there is no other choice but to pay.
2) If wages make up a small % of a firms cost, an increase in wage will have a small impact on the firm, meaning they will be more wage inelastic
3) In the short run, firms won’t have enough time to respond to changes in wages, so demand will be inelastic. In the long run, firms will have more time to look for substitutes, so wages will be elastic.
What affects the elasticity of labour supply?
1) In markets where workers require few skills, wage will be elastic. This means that an increase in wage will lead to a big increase in supply, as many workers can do the job. When there are lots of skills required, less workers can do that, so it is inelastic
2) When unemployment is high, there will be many people looking for a job, so workers will be very responsive to a change in the wages. Therefore, supply will be elastic.
3) In the short run, workers won’t have enough time to apply or train for jobs, so supply will be inelastic. In the long run, workers will be able to respond and prepare, so supply will be elastic
What factors cause a shift in labour supply and demand? (1)
1) Derived demand - How demand for labour is derived from demand for a good/service (Builders for houses, chefs for restaurants). Demand of that good/service will shift the curve.
2) Productivity - If something, such as improved capital, could improve productivity, firms may demand more workers to increase profits. However, to evaluate, firms may want to meet a quota, so by improving efficiency they may actually decrease demand.
3) Capital costs- Capital and labour are substitutes. If capital costs increase, demand for labour increases.
4) Migration - If workers migrate from a country, supply of labour will decrease.
What factors cause a shift in labour supply and demand? (2)
5) Income tax and benefits - If benefits increase, there is a decrease in the supply of labour. If income tax decreases, there may be increased incentive to work, increasing labour supply.
However, to evaluate, some people may only need to make a certain amount of money, and some may work less leading to a decrease in supply
6) Non-pecuniary benefits - Anything other than the wage an employee is payed. If benefits are higher, the job is more appealing, increasing supply.
7) Education and training - If more people can be educated, for example through apprenticeships, then the supply of labour will increase.
What is a monopsony and how does it impact suppliers?
A pure monopsony is when there is only 1 buyer in a market. When a firm has monopsony power, it means that it is able to control the price/wage it pays. Firms in an oligopoly may also collude together to act as a monopoly for lower AC.
This can lead to very low wages for suppliers (Workers, suppliers of goods) as they have no other choice but to supply to that firm.
How does the minimum wage counter labour market failure?
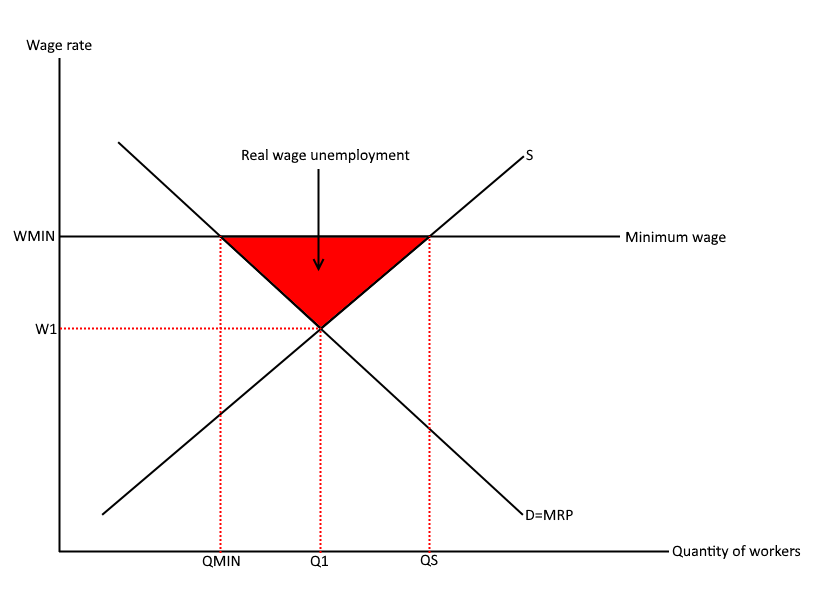
A minimum wage, such as the national mimimum wage, ensures that workers earn sufficient wages. However, it is always set above the equilibrium, increasing unemployment.
How do trade unions counter labour market failure?
A trade union is a group of workers who collectively bargain to improve employee welfare. This can include wage, working hours etc. If these requests aren’t met, it could lead to workers going on strike.
How do maximum wages counter labour market failure?
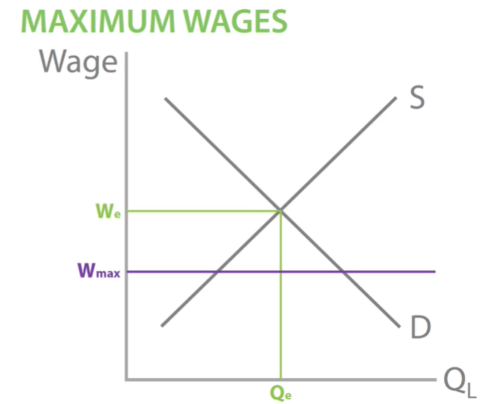
A maximum wage is to prevent some individuals in a firm, such as managers and directors, from earning too much money. This is done to reduce inequality. However, as it is set below the equilibrium, it leads to excess demand, so the market is stuck in a disequilibrium.
However, to evaluate, it could lead to talented workers leaving the UK to find higher wages elsewhere. This may reduce the quality of businesses in the UK and reduce competitiveness.
How do occupational mobility improvements counter market failure?
Occupational immobility is when workers can’t move between different jobs because they lack the skills required. If the government doesn’t intervene, this could lead to structural unemployment. Therefore, to counter this, the government intervenes with education, training and apprenticeships.
How do geographical mobility improvements counter market failure?
Geographical immobility is when workers struggle to move between different areas. This could lead to unemployment. To counter this, the government intervenes with improved transport and relocation subsidies to aid with moving to a different area.