3.1.1.2 Drainage basins
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Outline how the drainage basin is described as a natural system [4 marks]
A drainage basin is an area of land drained by a river and its tributaries (river system). There is an imaginary line separating drainage basins called a watershed. As an open system, drainage basins have inputs, outputs, stores and flows. Inputs are the addition of water to a drainage basin through precipitation. Inputs vary throughout the year (rain, sleet, snow, location etc) and intensities (flood, drought, temperature etc) and frequency (seasonal, monsoon etc)
A drainage basin is an open system and is an area (of land) which is drained by a river and its triubtaries. There is an imaginary line seperating drainage basins called a watershed. As an open system, drainage basins have inputs, outputs, stores and flows. Inputs are the matter or energy added to drainage basins e.g. precipitation. Inputs vary throughout the year (rain,snow,sleet,hail and drizzle) and intensities (flood,drought, temperature) and frequency (seasonal, monsoon etc)
Explain precipitation as an input to drainage basins
Precipitation is the main input into the drainage basin system. Precipitation, which includes rain, drizzle, sleet, snow, and hail, results from the condensation of atmospheric water vapor falling due to gravity.
Explain evapotranspiration as an output to drainage basins
Evapotranspiration is the sum of all processes by which water moves from the land surface to the atmosphere via evaporation and transpiration
Explain runoff as an output to drainage basins
Overland flow/surface runoff occurs when precipitation runs directly over the ground. It occurs when the amount of precipitation exceeds the soil's capacity to absorb it or when the ground is saturated.
Explain interception as a store to drainage basins
Interception – this is when precipitation lands on buildings, vegetation and concrete before it reaches the soil. Interception storage is only temporary as it is often quickly evaporated.
Explain surface water as a store to drainage basins
The total volume of water held on the Earth’s surface in lakes, ponds and puddles.
Explain soil water as a store to drainage basins
Water stored within the soil profile, available for plant uptake or infiltration.
Explain groundwater as a store to drainage basins
Water stored beneath the ground surface within aquifers or porous rock layers.
Explain channel storage as a store to drainage basins
This is all of the water held in the river channel.
Explain stemflow as a flow to drainage basins
Water flow down the stems or trunks of plants after rainfall or condensation.
Explain overland flow as a flow to drainage basins
OVERLAND FLOW: (Also known as surface runoff)
Overland flow/surface runoff occurs when precipitation runs directly over the ground. It occurs when the amount of precipitation exceeds the soil's capacity to absorb it or when the ground is saturated.
Explain channel flow as a flow to drainage basins
The movement of water within the river channel. This is also called a river’s discharge.
Explain how water flows through drainage basin [4 marks]
Water can flow through stemflow which is water flowing down the stems or trunks of plants after rainfall or condensation.
Water can flow through channel flow which is the movement of water within the river channel. This is also called a river’s discharge.
Water can flow through OVERLAND FLOW: (Also known as surface runoff)
Overland flow/surface runoff occurs when precipitation runs directly over the ground. It occurs when the amount of precipitation exceeds the soil's capacity to absorb it or when the ground is saturated.
Explain how water is stored in a drainage basin [4 marks]
Water can be stored in surface water which is The total volume of water held on the Earth’s surface in lakes, ponds and puddles.
Water can also be stored through interception – this is when precipitation lands on buildings, vegetation and concrete before it reaches the soil. Interception storage is only temporary as it is often quickly evaporated.
Explain inputs and outputs in a drainage basin [4 marks]
Precipitation is the main input into the drainage basin system. Precipitation, which includes rain, drizzle, sleet, snow, and hail, results from the condensation of atmospheric water vapor falling due to gravity.
In terms out outputs, evapotranspiration is the sum of all processes by which water moves from the land surface to the atmosphere via evaporation and transpiration
Outline flows within the water cycle operating on a hill slope [4 marks]
Overland flow/surface runoff occurs when water runs directly over the ground. It occurs when the amount of precipitation exceeds the soil's capacity to absorb it or when the ground is saturated.
Groundwater flow is the movement of water through permeable rock under the force of gravity. This is the slowest flow of water on a hillslope
What is the water balance?
The water balance (water budget) is the balance between inputs and outputs. The water balance can be shown using the formula:
precipitation (P) = streamflow (Q) + evapotranspiration (E) +/- changes in storage (S)
P=Q+E +/- S
To rearrange the formula to find storage (S)
S = P - Q - E
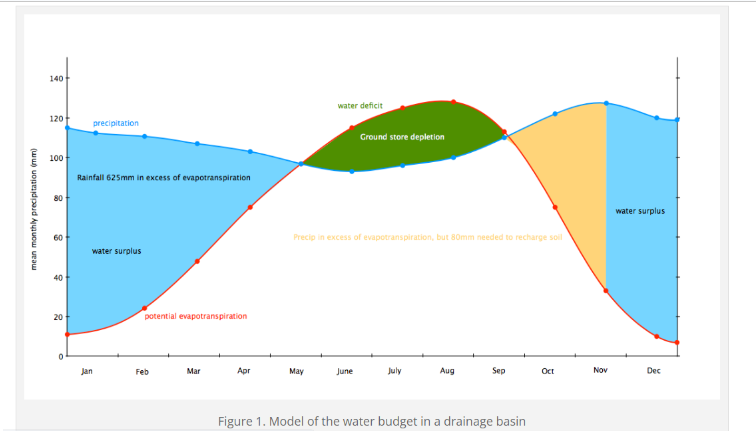
Explain this diagram in terms of the water balance
The water balance affects how much water is stored in a system. The general water balance in the UK shows seasonal patterns. In wet seasons precipitation is greater than evapotranspiration which creates a water surplus. Ground stores fill with water which results in increased surface runoff, higher discharge and higher river levels. This means there is a positive water balance. In drier seasons evapotranspiration exceeds precipitation. As plants absorb water, ground stores are depleted. The is a water deficit at the end of a dry season.
In which season is the water balance negative, and in which season is the water balance positive?
Winter - water balance - negative
Summer - water balance - positive
