QA and QC
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MLT 114
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What stage of QA may have the most errors?
Pre-analytical phase
What is QA?
Quality assurance that ensures reliability of results
What is accuracy?
Reliability, the closeness of values being the actual/true value
What is precision?
Reproducibility, if a test was repeated, how close to the same value would it be?
What is inherent variability?
The expectation that no method would give the exact same result each time. These errors are not significant in reporting results
What is normal distribution?
The distribution of values that fall within normal references based on the mean, median, and mode
What is a Gaussian curve?
A bell-shaped graph displaying the normal distribution with 68% of expected results in the middle of the curve and 99.7% of expected results to fill the length of the curve
What is the mean/average?
The sum of all values divided by number of values
What is the median?
The middle value of all values organized numerically. If two values are central, take the average of the two values.
What is mode?
The most occurring value
What is the range?
Highest value minus lowest value, or displayed as a low to high range
What is standard deviation?
Defines the degree of imprecision, the higher SD = the lower precision of a method
What is the SD formula?
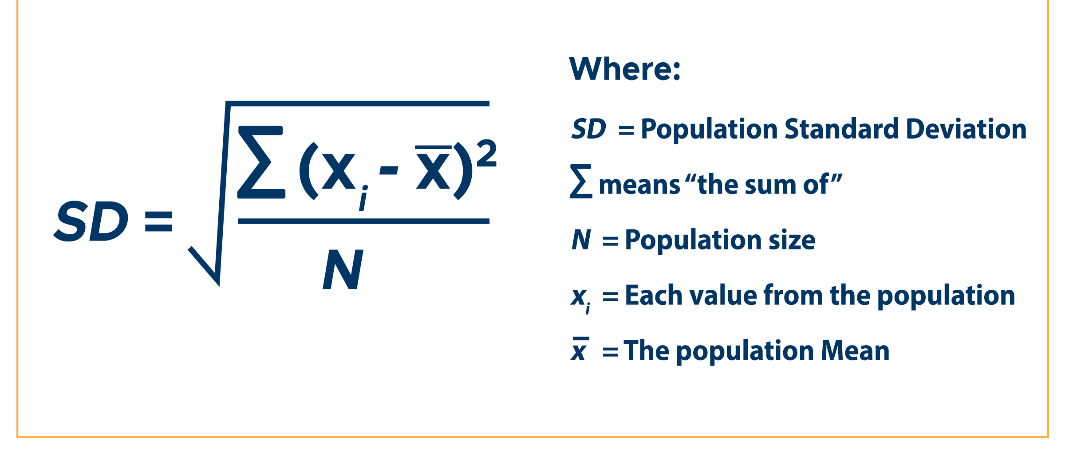
How do you calculate ±1SD, ±2SD, and ±3SD?
±1SD: Mean + and - 1(SD)
±2SD: Mean + and - 2(SD)
±3SD: Mean + and - 3(SD)
What does ±1SD represent?
68% of results fall within ±1SD
What does ±2SD represent?
95% of results fall within ±2SD
What does ±3SD represent?
99.7% of results fall within ±3SD
How is a reference range established?
Take the range of values that fall within ±2SD (95% of results)
What are the confidence limits?
68%, 95%, and 99.7% as calculated by SD
What is the coefficient of variation (CV)?
Expresses SD as a percentage and is used to compare SD values to find the most accurate method
Method 1 has an SD of 5
Method 2 has an SD of 4
Which method is most precise?
Method 2
Method 1 has a mean of 100mg/dL and an SD of 2.5mg/dL
Method 2 has a mean of 5.0mg/dL and an SD of 0.5mg/dL
Which method is more precise?
Method 1
How is the CV calculated?
(SD/mean) x 100
What is inherent change?
A minor change in reproducibility that could indicate either an inherent error, or that a method/treatment isn’t effective
What is a real change?
A significant change in reproduced results that could indicate a treatment is working
What does “QC is in” mean?
When QC results fall within acceptable limits
What does “QC is out” mean?
When QC results fall out of the acceptable QC range, and results cannot be reported.
Improper pipetting, improper sample mixing, and fluctuations in temperature are examples of what kind of error?
Random error
What sort of variance in results derive from a systematic error?
Trends and shifts
Accumulation of debris in tubing, aging reagents, deterioration of controls, deterioration of light source, are examples of what kind of error?
Systematic trend error
A change of reagent or lot, instrument maintenance, change in room temperature, inaccurate calibration, are examples of what kind of error?
Systematic shift error