Data Collection Periodontics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Pain, Detnal Emergencies, path conditions
Start
Diagnosis, prognosis, therapuetical options
Planning
Antiinfectous therapy, extractions, occlusion, orthodontics
Phase 1
Periodontal surgery, implant insertion
Phase 2
Prosthodontics
Phase 3
Maintenance therarpy
Phase 4
What N is probing force?
0.2-0.5 N
Deepening of the gingival sulcus as a result of an increase in the size of the gingiva with no apical migration of the junctional epithelium or loss of alveolar bone.
Gingival pocket (pseudo pocket)
Deepening of the gingival sulcus with destruction of the adjacent gingival fibers, periodontal ligament, and crestal alveolar bone with apical migration of the junctional epithelium.
Suprabony pocket
Deepening of the gingival sulcus to a level at which the bottom of the pocket and the junctional epithelium are apical to the crest of the alveolar bone
Infrabony pocket
Increase probing depth of greater than 1mm had a positive predictive value of what?
68% at 42 months
An increase probing depth of 1mm and bleeding on probing had a positive predicitve value of what?
75% at 42 months
Furcation Glickman Grade system:
1?
2?
3?
4?
Pocket formation into the flute but intact interradicular bone
Loss of interradicular bone and pocket formation of varying depths into the furcation but no completely through to the opposite side
Complete loss of interradicular bone with pocket formation that is completely probable to the opposide side of the tooth
Loss of attachment and recession, rendering the furca completely visible to the eye
The shorter the root trunk, the less _______needs to be lost before the furcation is involved.
attachment
Furcation Entrances:
Maxillary molars?
Mesial?
Buccal?
Distal?
Manibular Molars?
Buccal?
Lingual?
3mm
4mm
5mm
3mm
4mm
Many times the furcation entrance is smaller than the instrument making ________ impossible. 81% of furcations are less than ___mm.
scaling
1mm
What probe is used for furcation involvement
Nabers probe
Miller Index Classification:
Class 1?
Class 2?
Class 3?
Mobility greater than normal
Up to 1mm in any direction (
More than 1mm in any direction ± vertical depression
how much can a normal tooth move?
0.2mm any direction
Varies tooth by tooth and day by day
What are the 3 reasons for increased mobility?
Alveolar bone loss (periodontitis)
Occlusal trauma (Widening of the PDL space)
Endodontic lesion (periapical lesion)
Random facts:
Teeth that are mobile have deeper ________
Mobile teeth don’t respond well to ________ tx
________ adjustment may enhance perio tx
pockets
perio
occlusal
What does BOP tell us?
Inflammation is present, it does not mean the site willl loose attachment but its chances increase and if it doesnt bleed rarely will there be attachment loose
Suppuration is found 3-5% of _________ _________sites
perio disease
Can be stabilized with comprehensive periodontal treatment maintenance, and with less chance of future breakdown
Favorable
Influenced by local and or systemic factors that may or may not be controlled; periodontium can be maintained with proper care
Questionable
Influenced by local and or systemic factors that cannot be controlled
Unfavorable
Must be extracted
Hopeless
If prosthetic treatment needed:
Favorable and questionable?
Unfavorable and Hopeless?
Periodontal stability
Extraction
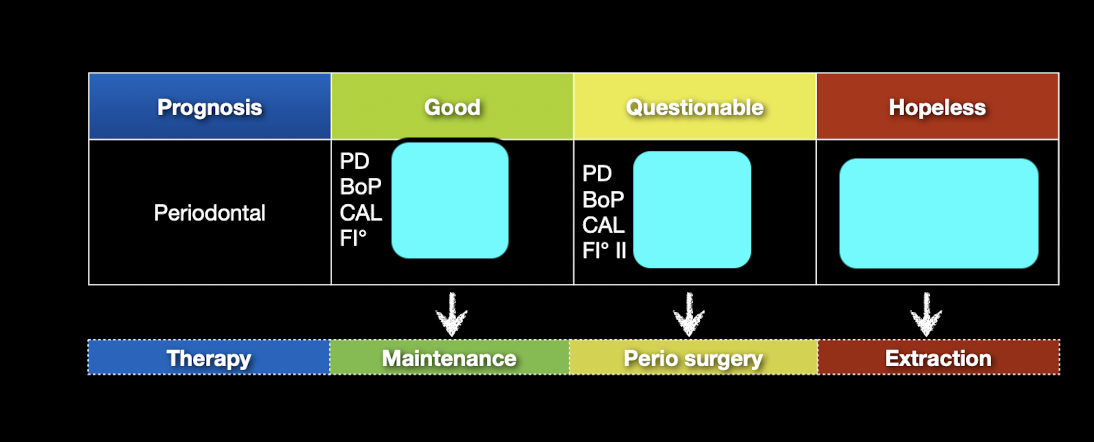
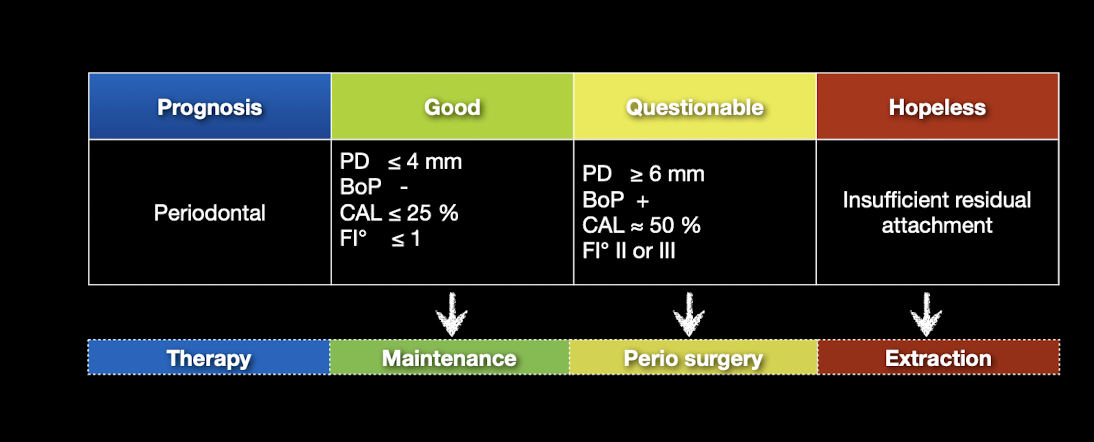
When a tooth with RCT shows a single deep pocket be warned of what?
Root fracture
The prevelance of overhanging margins is in a range from ________ of restored surfaces in _________ of the patients
25%-76%
32%-90%
________ _______ are correlated with food impaction, and food impaction is correlated to deeper probing depths
open contacts
The smaller the interraciduclar distance the higher risk for what?
Alveolar bone disease
Where are Cervical enamel projetions mosst common?
Buccal surfaces of molars in mandible #1
Buccal surface of molar in maxilla #2
What is biological width?
2.04mm and composed of the junctional epithelium and Connective tissue attachmet
Peri implant esthetic outcome is ___________
predictable