Condensation Polymers
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
"Addition Polymerization of Alkenes"
Under certain conditions, alkenes undergo polymerisation to form additional polymers. Each alkene loses a double bond and forms 2 single bonds with neighbouring carbons. Additional polymers are very large so we represent them as repeat units.
"What is the general notation for representing a polymer's repeating unit?"
We draw the shortest section of the polymer that is repeated (needs to be at least 2 carbons long). Then we draw square brackets around this and write a n.
"What are polyesters and what type of bond do they contain?"
Polyesters are polymers that contain ester links (O=C-O)
"How are polyesters formed?"
Polyesters (a type of polymer) can be produced from the reaction between dicarboxylic acids and diols.
"What is the word equation for polyester formation?"
A dicarboxylic acid (monomer 1) + A diol (monomer 2) _------------- 2 monomer Polyester (type of polymer) + lots of H2O
"How are 2-monomer polyesters formed?"
2 monomer polyesters can be formed form a reaction between nay dicarboxylic acid and diol
"What do you need to remember for polyesters in the exam?"
In the exam:
you need to be able to identify the monomers given a polyester
Or identify the polyester formed given the monomers
Drawing repeat units for a polyester
The repeat unit for a polyester made from a dicarboxylic acid and diol contains
2 carbonyl groups. (C=O)
2 oxygen groups. (--O--)
The atoms between 2 oxygens.
The atoms between 2 carbonyl groups.
We often represent the repat unit like above starting from oxygen
How can polyesters be made from a single monomer?
Polyesters can be made from a single monomer containing
An alcohol group
Carboxylic acid group
The repeat unit for a single monomer polyester contains.
a single carbonyl group.
a single oxygen atom.
the atoms between oxygen and the carbonyl group.
We often represent the repat unit like above starting from oxygen
What do a carboxylic acid and an amine produce when they react?
A carboxylic acid and an amine react to produce an Amide and water. In the exam you will need to know the products of thai reaction ( O=C-N-H)
"What is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an amine?"
A carboxylic acid and an amine react to produce an Amide and water
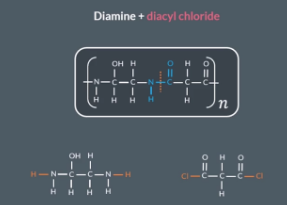
What do diamines and dicarboxylic acids react to form?
Diamines (2 NH2 groups) and dicarboxylic acids (2 COOH groups) react to form a polyamide and water
What are polyamides, and what functional group do they contain?
Polyamides are polymers that contain amide links (O=C-N-H).
The repeat unit for a two monomer polyamide contains...
Two NH groups
Two carbonyl groups.
The atoms between two NH groups.
The atoms between two carbonyl groups.
We often represent the repat unit like above starting from a N-H group
Polyamides can be made from a single monomer containing…
An amine group (NH2)
A carboxylic acid group (COOH)
The repeat unit for a single monomer polyamide contains...
A single carbonyl group.
A single NH group.
The atoms between NH group and the carbonyl group
What are polyesters and polyamides examples of?
Polyesters and polyamides are examples of condensation polymers.
What is a condensation reaction, and what does it produce?#
Condensation reaction produce a polymer and small molecule (trypically water/HCl)

identifying monomers: two monomer polyesters
Step 1 - identify the ester link
Step 2 - break ester link and seperate atoms
Step 3 - Add H to O and OH to C-O
Step 3 - Add H to O and OH to C-O
Another example
identifying monomers: two monomer polyamides
Step 1 - identify the amide link
Step 2 - Break amide link and separate atoms
Step 3 : Add O-H to C=O and H to NH
Step 3 : Add O-H to C=O and H to NH
Another example
Identifying monomers: single monomer polymers method
Single monomer polyesters
Single monomer polyamides
Harder monomers
"How do you identify monomers from a given polymer?"
If we’re given a section of the polymer and asked to identify the monomers, we first need to identify the repeat unit (starts from N or O)
Then we look at what the monomer contains. IF it contains OH, COOH its a polyester. If it contains NH2 and COOH is a polyamide
Count the number of oxygen atoms/carbonyl atoms/NH groups. If there are two of each in the repeating unit it has two monomers. If there only 1 set of each it has one monomer
Once we have identified whether it is a two monomer polyester, two monomer polyamide, single monomer polyester or single polyamide we follow the procedures outlined above e.g identify and break ester link etc…
Identify the monomers on this section of polymers
Find the repeating unit and identify what the monomer is
Follow the correct procedure for this monomer
IF you are told in the exam that one of the moomers involves a acyl chloride (e.g this monomer involves a diacyl chloride)
"How do we identify a monomer if an acyl chloride is involved?"
If we’re told one of the monomers involves an acyl chloride, we replace OH with Cl on each carbonyl group
You need to be able to recognise and name these specific polymers from drawings and know if its a polyester or polyamide
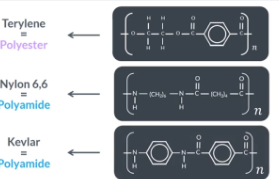
Specific examples of condensation polymers
Terylene is polyester. Nylon 66 and Kevlar are examples of polyamides
TIPS:
for recognising and naming these specific polymers from drawings and know if its a polyester or polyamide
If you are given a repeat unit of a drawn polyester and asked to give its common name it can only by terylene
If you are given a repeat unit of a polyamide and asked to give its common name it can be either nylon 66 or kevlar. Just remember Kevlar has benzene rings (Kekule provided a model for benzene which sound a lot like Kevlar)
"What type of intermolecular forces do addition polymers have?"
Addition polymers only experience permanent van der waals forces (only contains C-H bond)
"What intermolecular forces do polyesters experience?"
Polyesters experience van der waals forces and permanent dipole dipole forces (they contain polar C=O bond)
"What intermolecular forces do polyamides experience?"
Polyamides experience van der waals forces, Permanent dipole-dipole forces (polar C=O bond) and hydrogen bonding (because they contain a N-H bond)
intermolecular forces in polyesters and polyamides
3 ways to dispose of plastics
Bury plastic waste in a landfill by creating a hole, filling it with plastic and covering it with soil. Eventually plants can grow on this area
Burn plastics in a incinerator. This produce steam to power turbines which can generate energy for electricity
Recycle plastics. Sort the plastic according to the polymers they are made of.Some plastics are melted and remolded. Others plastics are broken down into their monomers to make new plastics
summary of ways to dispose of plastics
advantages of recycling plastics
disadvantages of recycling plastics
Definition of Biodegradable plastics…
Biodegradable plastics are broken down by living things into naturally occurring molecules within six months.
Which type of polymers are biodegradable, and which are not
Additional polymers are not biodegradable. COndensation polymers (e.g polyesters and polyamides) are biodegradable.
Why are condensation polymers biodegradable?
If you get a question like this this is what your write
Why aren't additional polymers biodegradable
If you get a question like this this is what your write