7.2 Eukaryotic Cell Structures and Their Functions
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Eukaryotic cells have a what kind of surface to-to- volume ratio
large
large surface-to-volume ratio makes it Difficult for
molecules to diffuse across the entire cell
what do Organelles do in Eukaryotic cells
break up the large cell volume into smaller membrane-bound organelles
compartmentalization offers two advantages (Eukaryotic cell)
Separation of incompatible and increased efficiency of chemical reactions
The Nucleus has a ? envelope
Double-membrane
the nuclues has ? openings
pore
where are Ribosomal RNA synthesized
Nucleolus
the Nucleolus is where ? subunits are assembled
Ribosome
where is the Center for Information Storage and Processing
nucleus
where are chromosomes contained
nucleus
what occupies a distinct area in the nucleus
chromosome
where is DNA densely packed
periphery of the nucleus
where is DNA loosely packed
where is DNA densely packed of the nucleis
how long would the DNA molecules in a single human cell were unwound from their histones and placed end-to-end,
6 feet
Complex Molecular Machines that Manufacture Proteins
ribosomes
what do ribosomes lack
membrane
what is not considered an organelle
ribosomes
where are ribosomes free
in the cytosol
what do ribosomes do that remain in the cytosol
Manufacture proteins
what are some ribosomes attached to
endoplasmic reticulum
what is do ribosomes Manufacture
proteins
endoplasmic reticulum
organelle that is an extension of the nuclear envelope
what are the two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum
rough and smooth
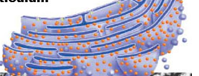
what does the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum house
ribosomes

what does the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum do
Synthesizes Lipids
Proteins move to the
lumen of the rough ER
Lumen
inside of any sac-like structure
proteins in the lumen are
folded and processed
Proteins made on the RER may
Carry messages to other cells, Carry messages to other cells, and Catalyze reactions
what does the smooth ER lack
ribosomes
the smooth ER contains
enzymes
what does the enzymes in the smooth ER do
catalyze reactions involving lipids
what is needed by the organism from the smooth ER
Synthesize lipids
what does in the smooth ER do
Break down lipids and other molecules that are poisonous
the smooth ER is a reservoir for
Ca2+
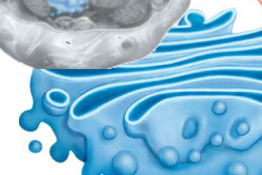
Golgi Apparatus
Two Sided (Cis & Trans)
cisternae
series of stacked, flat, membranous sacs
where is cisternae located
Golgi Apparatus
The cis (“on this side”) Golgi Apparatus
surface is closest to the nucleus
The trans (“across”) Golgi Apparatus
surface is oriented toward the plasma membrane

what is at the back of the arrow and what is at the front side called
cis; trans
what Receives Products from RER & Ships Them Out
Golgi Apparatus
the Golgi Apparatus does what from the stuff from the rough ER
Processes, sorts, and ships proteins
what does the cis side of a Golgi apparatus do
receives products from the rough ER
what does the trans side of the Golgi apparatus do
ships them out to other organelles or the cell surface

what do Membranous vesicles do
carry materials to and from the organelle

Lysosomes
Recycling Centers Found Only in Animal Cells
how many different enzymes do Lysosomes contain
40
what do the Enzymes in Lysosomes do
hydrolyze macromolecules and export monomers
what pH does lysosomes work best at
5
pH of Proton pumps in membrane
maintain low internal pH
what acid is Lysosomes
Acid hydrolases
what is part of the Endomembrane System
Lysosomes
Endomembrane System consist of
ER + Golgi + Lysosomes
lysosomes function in the Endomembrane System
Produces, processes, and transports proteins and lipids
what is first in the Endomembrane System for Lysosomes
Synthesized in the ER
what is second in the Endomembrane System for Lysosomes
Processed in the Golgi apparatus
what is third in the Endomembrane System for Lysosomes
Shipped to lysosomes

Vacuoles
Large, Membrane-bound Structures in Plants & Fungi
what are functions of vacuoles
digestion, store water, and ions to help the cell maintain its normal volume
In seeds what is the vacuole filled with
proteins
in flower petals or fruits what do vacuoles contain
pigments
for protection vacuoles might contain
pigments
everything a vacuole contains
noxious compounds, proteins, and pigments
Distinct to Cell Type
Peroxisomes
where do Peroxisomes Originate from
ER
what reactions do Peroxisomes do
Redox reactions
Redox reactions
e- transfers
what cells contain enzymes that oxidize ethanol (Peroxisomes)
Liver cells
Oxidation often produces in Peroxisomes
hydrogen peroxide
what does the enzyme catalase in peroxisomes
detoxifies
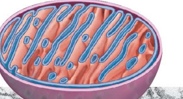
Mitochondria
Supplies ATP to Cells
how many membranes does the Mitochondria contain
2
Inner Mitochondria membranes
folded into a series of sac-like cristae
Solution inside =
the mitochondrial matrix
what does Mitochondria have their own of
mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
what does the Mitochondria their own of
ribosomes
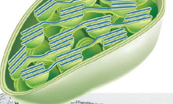
Chloroplast
Where photosynthesis takes place
Most Plant & Algae Cells have
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts have their own
DNA
Chloroplasts can manufacture
ribosomes
how many membranes do Chloroplast have
3
Innermost membrane of Chloroplast contains
flattened sacs called thylakoids
Thylakoids
arranged in stacks called grana
what does the innermost membrane of Chloroplast surround
thylakoids is the stroma
Endosymbiotic Theory or Symbiogenesis
Bacteria were engulfed and a mutually beneficial relationship evolved
what could have been free living bacteria
Chloroplasts and mitochondria
Evidence for endosymbiosis
Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain their own DNA, Grow and divide independently of cell division, Synthesize their own small ribosomes
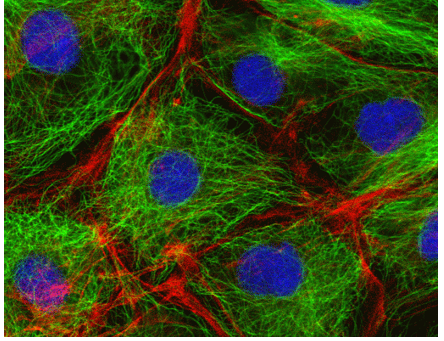
Cytoskeleton
Comprises Protein Fibers
what Gives cells shape and structural stability
Cytoskeleton
Cytoskeleton aids in
cell movement
what does the Cytoskeleton Organize
organelles and other cellular structures into a cohesive whole
Cytoskeleton Transports …
materials within the cell
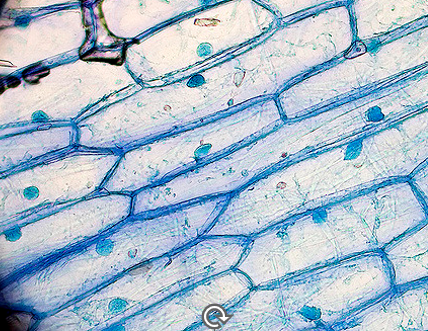
The Eukaryotic Cell Wall
Structural Support
what has a stiff outer cell wall
Fungi, algae, and plants