Imagery -1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Mental Imagery
creating a perception of smth in your mind, in absence of that actual input to the senses
Imageless thought debate happened in
1800s (before behaviorism and modern cognitive psychology )
Imageless thought debate question:
Does all thought require mental imagery? is it necessary
Francis Galton was known for
his ‘breakfast table experiment‘
breakfast table experiment
Asked his friends to picture items on their breakfast table in their mind’s eye and describe the scene to him
breakfast table experiment results:
some had the imagery ability, some had no such ability but still can recalled what was on the table (can think of the items but don’t actually see it in their mind)
Galton concluded that: Thought doesn’t
necessarily involve mental imagery
imageless thought is
possible
Modern Cog psychologists supported
Galton’s observation
The psychologists had participants do
Vividness of mental imagery questionnaire to quantify the ability to perform imagery
The questionnaire has
rating scale (1-5) and questions are about “can you imagine…. (specific scenario/scene)”
The psychologists also found the same results as Galton
have imagery
doesn’t have imagery
The psychologists termed this condition
Aphantasia
Aphantasia
inability to form mental images, but can still think
The questionnaire and Galton’s experiment made many psychologists want to prove further that
Even tho you can think of things without imagery, it is still important for some mental function
A classical experiment to prove that you still need imagery for cognitive tasks is
Mental Rotation
Mental Rotation experiment is by
Shepard and Metzler (psychologist)
Task in mental rotation
say whether the 2 pictures are the same in different orientation, or different objects
Mental rotation relies on
reaction time
If people use mental imagery to rotate one of the objects in their mind’s eye to see if it fits, they should take longer
if there is a long distance to rotate
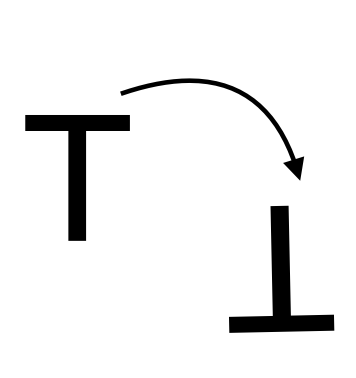
If people use mental imagery to rotate one of the objects in their mind’s eye to see if it fits, they should take shorter
if there is a short distance to rotate
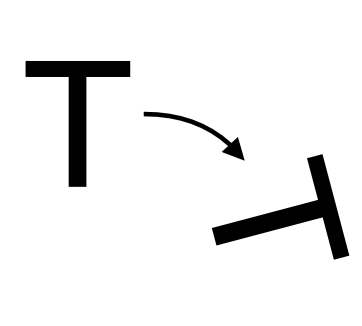
Main finding:
The farther the object has to be rotated, the longer your reaction time (linear + according to their thinking)
The reaction time is indicate that participants form
a mental image of the objects, that they rotate in their mind
So imagery does play a role in
cognitive functioning, for instance in solving this task
It is possible for thought to form without imagery, but imagery does play
a role in some forms of thinking, for instance solving mental rotation