Rumen & Abomasal Dz
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Primary rumen contractions
-mixing of ingesta
-dense particles settles via strafiting
-cyclical contact of feed and microflora
Primary rumen contractions stimulated by
-feeding/chewing
-distention receptors
-abomasal acidity
-environmental cold to help stay warm
Primary rumen contractions inhibited by
-high VFAs
-wall too tight
-pain
-fever
Secondary rumen contractions
-move gas to cardia and clears cardiac
-requires esophagus relaxation and glottis closure for negative pressure
How are VFAs buffered?
Bicarbonate rich saliva & villi exchange VFA with electolytes
Causes of pear shape
-pregnant
-hydrops
-urinary bladder rupture
-distended SI
Causes of papple shape
Vagal indigestion
Cause of apple shape
-gas bloat
-eructation failure
Left sided ping differentials
-LDA
-pneumoperitoneum
-physometra
-pneumorectum
Right sided ping differentials
-RDA
-RVA
-cecal dilation/volvulus
-ascending colon gas
-pneumoperitoneum
-pneumorectum
-rectal palpation can help to distinguish between cecum, colon, and abomasum
When to measure rumen pH?
2-4 hours after grain and 4-8 hours after TMR
High chloride =
Abomasul reflux/outflow issues
No sedimentation
Frothy bloat or vagal indigestion
Rapid sedimentation
Poor microflora activity
New methylene blue test
All blue should be ate up by anaerobic bacteria in about 3 min
Causes of bloat
-esophageal obstruction
-partial esophageal obstruction
-frothy gas
-failure to clear cardiac
Partial esophageal obstruction
-compression from masses
-tetanus
-LDA
-usually chronic, rarely life threatening
Failure to clear cardiac
-rumen weakness from hypocalcemia
-lateral recumbency
-rumen overfill
-vagus n damage
What can cause frothy bloat?
-lush alfalfa
-alfalfa cubes
-high grain leading to s. Bovis proliferation
-high legumes
Treatment for frothy bloat
Do not tube or trochar! Go ahead and use surfactant (proloxalene) or veggie/mineral oil in non-emergencies. In emergency setting, do a rumenotomy
Prevention of frothy bloat
-more fiber
-ionophores
-lick block with surgactant
Free gas bloat - is it an emergency?
Not usually presented as an emergency but chronic
Causes of free gas bloat
-hypocalcemia weakening contractions
-lateral recumbency
-acidosis/hardware dz
-overfilled
Clinical signs of acute traumatic reticuloperitonitis
-fever
-pain/arched back/extended neck
-rumen stasis from reflex inhibition due to pain/inflammation
-anorexia
-scant, dry feces
Clinical signs of chronic traumatic reticuloperitonitis
-no fever
-wt loss
-poor production
-prolonged stasis, mat sinks = PING
-decreased rumen size
-bacterial fermentation almost abselt
Sequela of chronic traumatic reticuloperitonitis
-pleuritis/pericarditis
-reticular wall abscessation leading to vagal indigestion
Traumatic reticulopericarditis
Restrictive right sided heart failure causes jugular pulse/distention, brisket edema, washing machine murmur. If you were to do a pericardiocentesis, you would get purulent fluid with fibrin.
4 key signs of obstructive indigestion
-chronic, progressive abdominal distention
-gradual wt loss/body condition loss
-decrease in fecal volume
-papple shape
Omasal transport outflow failure causes
-abscess of reticular wall
-ostruction of omasal orifice
Pyloric outflow failure causes
-DA/RVA causing vagal n injury or significant damage to wall to lose function
-abomasal impaction
What can you expect to see on rumen fluid analysis?
Elevated chloride because the acid from the stomach passes back into the rumen
Abomasal emptying defect in suffolk sheep
Chronic weight loss, increased rumen chloride, etiology unclear and is not common anymore
Pathogenesis of rumen acidosis
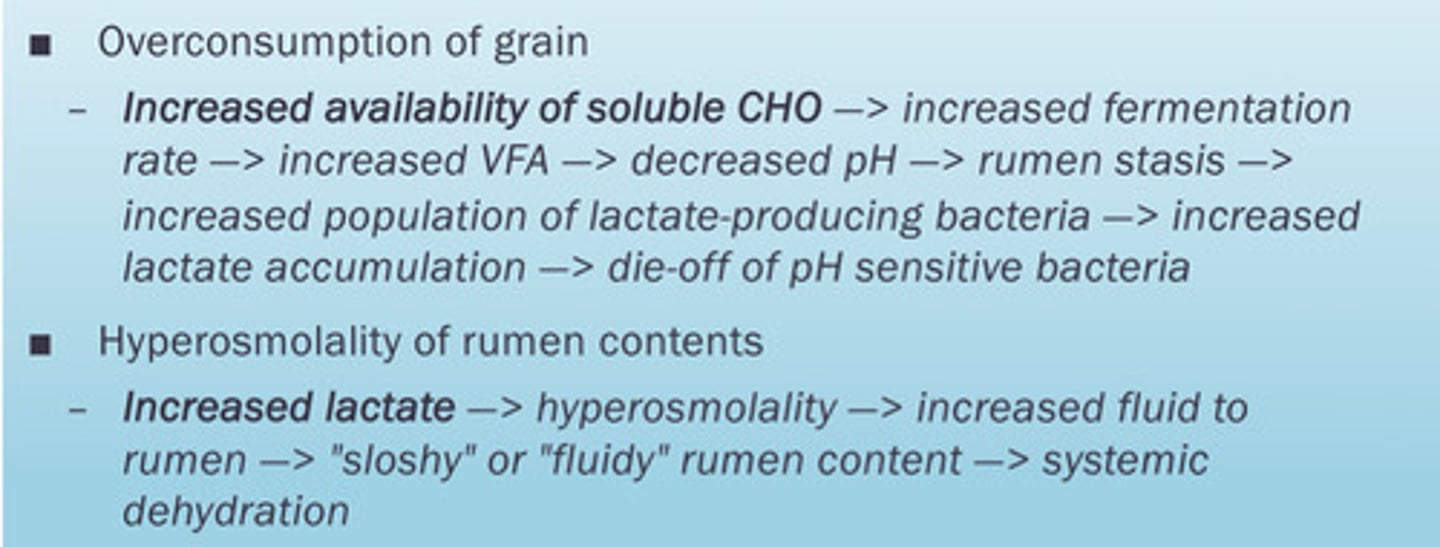
Blood work of rumen acidosis patient
-hemoconcentration
-hyperphosphatemia
-hypocalcemia
-hyperlactemia
Severe vs mild rumen acidosis clincial signs

Sequela of rumen acidosis
-PEM
-laminitis
-liver abscess
-caudal vena cava syndrome
-pneumonia
-pulmonary arterial abscess
-poor weight gain (rumen wall fibrosis)
What type of vomiting is common in ruminants
Abomasal reflux = internal vomiting
Causes of vomiting

Abomasal ulcers are common in
Dairy calves/adults and beef calves
Etiologies of ulcers
-BVDV/MCF
-C perf type A in calves
-stress
-reduced perfusion
-lymphoma
-abrasive roughage
Common spot for ulcer in adult
Fundic region
Risk factors for adults for ulcers
-high energy, freshly ground diets
-fresh cows 30-40 DIM (neg energy)
-LDA
-cows in peak milk
-close-up dry cows
(Above two have to deal with perfusion)
-NSAID use
Risk factors for calves for ulcers
-mineral deficincies (copper)
-trichobezoars
-consuming sand, bedding
-feed large volume of milk in 2 feedings/day
Lymphosarcome
-common near pylorus
-can be BLV associated or not
-ulver development from disruption of mucosal integrity
Clostridial abomasitis
-c perf type A
-2-6 week old calves and lamps
-acute bilateral bloat/shock, dehydration, succusible fluid and pings
Do LDA or RSA usually present in worst condition?
RDA
Biochem abomasul reflex
Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, azotemia, hyponatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperproteinemia, hyperlactatemia, hyperketonemia
Abomasal reflux sequela
-metabolic alkalosis leads to decreased bone resorption
-hypocalcemia in fresh cows
Aciduria in abomasul reflux
