CHEM 120A Terms + Conversions
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all terms from lecture slides + metric conversions !!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
atom
the smallest particle of an element that cannot be chemically or mechanically divided into smaller particles
element
a pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances
compounds
a pure substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically bonded in fixed proportion
law of definite proportions
a compound always contains the same proportion of its component elements
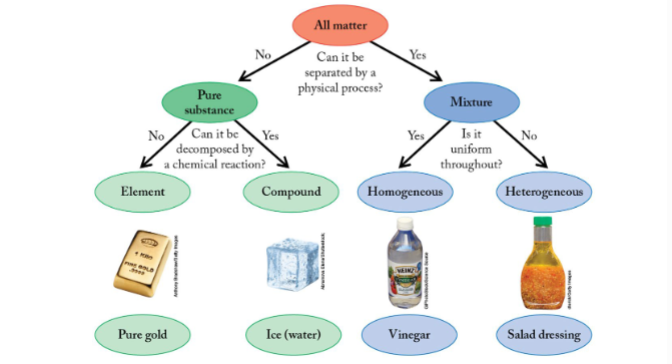
classification of matter
law of multiple proportions
when it is possible to have two different masses of one element react with a given mass of another element, the two masses of the first element must be a small, whole-number ratio
pure substances
a form of matter that contains only one type of particle, meaning it's either a single element or a single chemical compound
intensive properties
property that is independent of the amount of substance
extensive properties
property that is dependent on the amount of a substance
physical properties
properties that can be measured without changing the substance into another substance
chemical properties
properties that can be observed only by reacting the substance with something else to form another substance
density
the ratio of the mass (m) of any substance or object to its volume (V)
d=m/v
homogeneous mixture
mixture that has substances distributed uniformly, and the composition and appearance of the mixture are uniform
heterogeneous mixture
mixture that has substances that are not distributed uniformly and contain distinct regions of different composition
distillation
a process of purifying a liquid compound (separation) by heating it into a vapor that is then condensed back into a liquid
filtration
process that separates solids from liquids or gases using a filter medium that allows the fluid to pass through but not solid particles (think: pasta)
chromatography
technique for separating the components, or solutes, of a. i tire on the basis of the relative amounts of each solute distributed between a moving fluid stream, called the mobile phase, and a contiguous stationary phase; the mobile phase may be either a liquid or gas, while the stationary phase is either a solid or a liquid
solid
has a definite shape and volume
liquid
occupies a definite volume but takes the shape of its container
gas
has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape
sublimation
solid → gas
melting
solid → liquid
vaporization
liquid → gas
condensation
gas → liquid
freezing
liquid → solid
deposition
gas → solid
energy
capacity to do work
work
the exertion of a force (F) through a distance (d) → w = f x d
law of conservation of energy
states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another
potential energy
the energy stored in an object because of its position or composition
kinetic energy
energy of motion → KE = 1/2mu²
ionic compounds
compound that contains ions (charged particles) held together by attraction of opposite charges
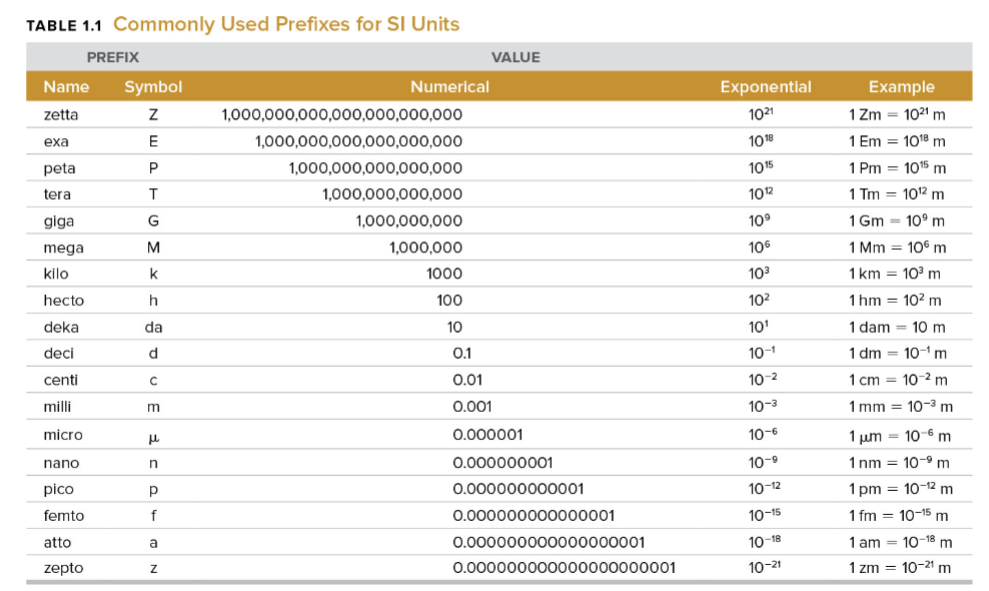
metric system prefixes (separate set for these!)
equation for celsius/fahrenheit
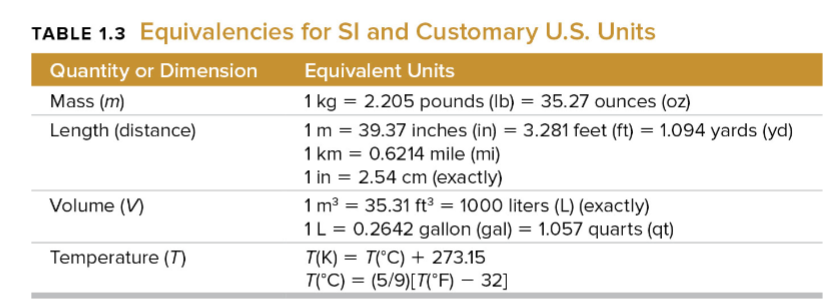
T(C) = (5/9)[T(F) - 32]
equation for kelvin
T(K)= T(C) + 273.15
precision
based upon the reproducibility of a measurement or the agreement between values
accuracy
refers to how close a measured value is to the true value
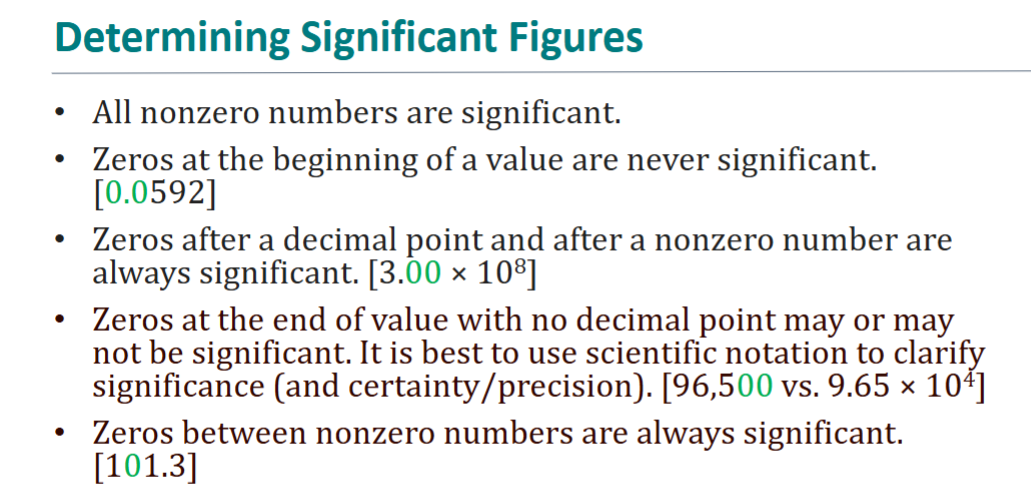
sig fig rules !!
unit conversions (separate deck made for these!!)
standard deviation
a measure of the amount of variation, or dispersion, in a series of related values
confidence interval
a range of values that has a specified probability of containing the true value