Cognitive Psychology Assessment 2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Dichotic Listening Task
2 different channels to each ear in headset and repeat was is hear from each ear
Selective Attention
Cognitive process of directing awareness to relevant stimuli while ignoring irrelevant stimuli in the environment
Cocktail Party Effect
When you hear your name your attention switches to unattended message
Dopamine
Motivational component of rewards-motivated behavior
Acetylcholine
CNS, plays role in arousal, memory, and learning
Endogenous Attention
Top down/goal oriented, dopamine driven, visual cortex —> prefrontal cortex
Exogenous Attention
Bottom up/stimulus oriented, acetylcholine driven, prefrontal cortex —> visual cortex
Incentive Sensitization Theory
Appetitive cues trigger desire for dopamine release
Spatial Covert Attention
Selection of information based on spatial location in the absence of eye movements
Sustained Attention
Perform a task continuously over a prolonged duration without significant loss in performance on the task
Dot Probe Task
Determine stimuli fixations with dots on L or R of screen
Rapid Serial Visual Presentation Paradigm
Single task (click when you see x), and dual task (x and o)
Attentional Blink
If you are finding specific shape after series of shapes are presented, you will miss the specific shape because of how fast the shapes are being presented
Affects of ADHD on Attentional Blink
Children with ADHD will have a greater attention deficit that will lead to a larger blink
Kahneman Capacity Model of Attention
Humans posses only a limited amount of processing capacity and the extent to which tasks can be performed successfully depends on how much demand those tasks place on the limited capacity processor
Focused Attention
Auditory and visual processing can be the only input for full processing
Divided Attention
Task similarity, task difficulty, and practice help us process multiple inputs
Stroop Effect
Naming printed color of colored words ahs two conflicting tasks (Ian failed at this)
Automatic Process
Fast, effortless, unconscious, heuristic (no interference on other tasks)
Controlled Process
Slow, effortful, conscious, strategic (interference). Can become automatic process with practice.
STM
Set of processes used to hold onto and rehearse information in awareness. Depends on capacity and duration
STM Simple Span Capacity
7 ± 2 chunks of information
STM Digital Span Capacity
4 ± 1 chunks of information
STM Duration
Unless information is kept active, people will forget within 15 - 30 seconds
Decay Theory
Information is forgotten because it becomes weaker or less activated over time
Interference Theory
Information is forgotten because of competition, or interference, from other items, which compromises learning
Waugh and Norman Study
Paper that found that with a 16 digit list when people were asked to retrieve first instance after probe digit strength of recall decayed over time and more digits lead to more interference and therefore more forgetting.
Working Memory Capacity
Information storage in the short term that occurs in the context of other processing
Complex Span Tasks
Involve both storage and processing components
Baddeley’s Working Memory Model
2 slave systems and central executive coordinate mental activities using the slave systems to carry out processing tasks
Phonological Loop
Baddeley slave system that handles processing of verbal info
Visuo-Spatial Sketchpad
Baddeley slave system that handles processing of visual and spatial info
Central Executive
Baddeley’s attentional controller of the system
Episodic Buffer
Baddeley addition that states how episodic information from long-term episodic memory may be stored temporarily in the slave systems and manipulated in working memory
Selective Interference
Similar activities using the same slave system will interfere with each other
Problems with Tripartite Model
Slave systems over look touch and smell
Atkinson and Shiffrin Model
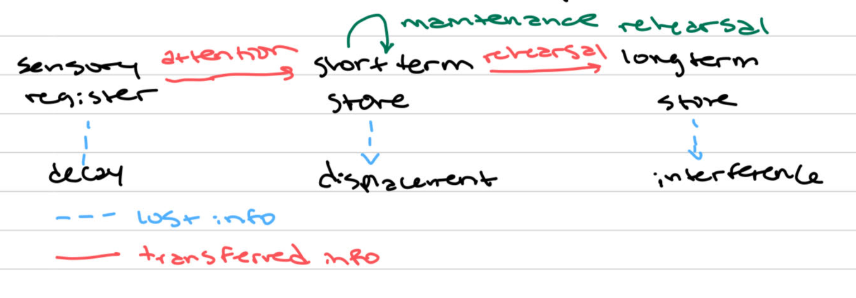
Word Length Effect
Shorter words are recalled faster than longer words
Canberra
Capital of Australia
Availability
Info being stored in the “box”
Accessibility
Info that is able to be taken out of the “box”
Cue Overload Principle
Competition from similar target creates interference (ex: forgetting where you parked your car)
Proactive Interference
Old memories interfere with new memories (PORN)
Retroactive Interference
New memories interfere with old memories (PORN)
Two-List Interference Paradigm
Research method used to study interference in memory, specifically proactive interference and retroactive interference. It involves participants learning two lists of items, with the second list often overlapping with the first, to assess how the learning of one list impacts the recall of the other.
Retrograde Amnesia
Deficit in learning/remembering events that occurred prior to some event or brain trauma
Anterograde Amnesia
Deficit in learning/remembering events that occurred subsequent to some event or brain trauma
Graded Amnesia
Memory loss is not uniform, but varies depending on the age or recency of the memory
Retrieval as a Reconstructive Process
Using a verbal label to reconstruct a visual memory can lead to distortion
Loftus and Palmer
Participants recalled traffic accidents and were asked questions with different words to prompt a certain kind of answer that didn’t happen (ex: How fast did the cars bump? Was there broken glass? How fast did the cars collide?)
Tulving’s Encoding Specificity
Retrieval success depends on how info is encoded and how the reconstruction process maps onto the encoding process (environment, mental states, processing)
Context Dependency
Memory improves because the retrieval environment recapitulates the encoding environment (ex: scuba divers recall better underwater than on land)
Transfer-Appropriate Processing
Focuses on how well cognitive operations used to encode overlap/match the cognitive operations used to retrieve (semantic and phonemic of same word have different processing that encode differently)
Mood-Dependent Memory
Inducing a happy or sad mood in participants during recall leads to better memory if the same mood was induced during encoding
Simcock and Hayne
Paper that described how encoding specificity for preverbal memory doesn’t allow for language activation. Details described by language required to form memory for language description. Kids didn’t have the vocab to describe the event as kids and were unable to describe the event when they developed language (ex: bilingual kids forgetting memories in one language)
Episodic Memory
Memory for experienced events
Semantic Memory
Memory for general knowledge and facts
Implicit Memory
Unconscious retrieval of skills/procedures like riding a bike
Explicit Memory
Conscious retrieval of info from experiences
Lexical Decision Task
Participants determine whether items are part of one’s mental lexicon (dictionary)
Priming
Procedure to measure implicit influence via response time of activation
Repetition Priming
Faster reaction time to stimulus after seeing it a second time
Semantic Priming
Faster reaction time for stimulus with directly related associations (car/garage)
Positive/Negative Constructs
Faster reaction times for inherent biases and stereotypes (love/friendly, hate/anger)
Roediger and Mcdermont Paper
In word recall test, participants were trying to recall or recognize the the critical lure (sleep) and a false memory was observed
Serial Position Effect
Performance is best for words at beginning and end of list
Primacy Effect
Remembering the beginning of list (LTM)
Recency Effect
Remembering the end of list without retention interval since words are in STM
Associations
Links connecting nodes
Nodes
Idea or representation (conceptual or physical, think of them as lightbulbs)
Active Node
Activation or accumulated inputs is above threshold
Semantic Network
Nodes can receive activation from one or more neighboring nodes
Spreading Activation
Response times depend on association strength and stronger associations have faster responses
Fan Effect
Activation spreads across nodes in fan like manner. Bigger fans mean there is less activation energy available to overcome threshold value
Forward Association
Main node branches to other node
Backward Association
Other nodes branch to main node
Familiarity and Recognition
Bread analogy: Fresh bread are the strong studied words and stale bread is the not studied weak words
False Fame Effect
Individuals mistakenly identify non-famous names as famous due to a familiarity based judgement error
Misinformation Paradigm
Tendency for info you learned after an event to interfere with your original memory of what happened