AP - Tissues Overview - Chapter 4
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Tissues
Tissues are groups of specialized cells and cell products that work together to perform specific functions
Histology
study of microscopic structure of tissues and cells; microanatomy
What are the 4 tissue types?
Epithelial tissue
Connective tissue (CT)
Muscle tissue
Nervous tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Function, Location, Distinguishing Characteristics
Function: protection, secretion absorption, excretion
Location: Cover body surfaces, cover and line internal organs, make up glands
Distinguishing: Lack blood vessels, cells divide, cells are tightly packed
Connective Tissue: Function, location, distinguishing characteristics
Function: bind, support, fill spaces, store fat, produce blood cells
Location: distributed through body
DC: are vascularized, cells are farther apart vs epithelial, have extracellular matrix
Muscle Tissue: Function, location, DC
Function: movement
Location: attached to bones, in internal organ walls, heat
DC: able to contract to stimuli
Nervous Tissue: Function, location, DC
Function: conduct impulses for coordination, integration, sensory reception
Location: brain, spinal cord, nerves
DC: cells communicate with each other and other body parts
Epithelia cover every _____ surface of your body.
exposed
What are the 4 main functions of epithelial tissue?
Physical protection (combat abrasion, dehydration, etc)
Control permeability
Sensation (large sensory nerve supply; seen in neuroepithelia in smelling, vision, balance, etc)
Secretions (through gland cells)
Epithelia Cellularity
epithelia are comprised majority of cells
minimal extracellular material
Epithelia Polarity
apical and basal surfaces show polarity
apical is top layer to open space
basal layer is attached to basement membrane and is closer to CT
Epithelium Avascularity
tissue lack blood vessels
receive nutrients by diffusion/absorption
Epithelia Basement Membrane
base of tissue is bound to basement membrane (BM)
BM is made of successive layers
Epithelia Regeneration
cells are continuously replaces through cell division
happens at high rates
Epithelial sheets are supported by __________ _______.
connective tissue
What 3 factors maintain the integrity of epithelium barriers?
Intercellular connections (aka cell junctions)
Basement membrane attachment
Maintenance/repair
Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
transmembrane proteins that bind to each other and help epithelial cells attach
Proteoglycans
polysaccharide derivatives (GAGs/hyaluronic acid) that act as an intercellular cement
What are cell junctions?
Specialized areas of plasma membrane that attach cells to each other/ or extracellular stuff
What are the 3 types of cell junction?
Gap junctions
Tight/occluding junctions
Anchoring junctions
Gap Junctions are made of two interlocking _______ proteins. Each _______ is made of 6 ________ that make a cylinder channel. This channel exchanges ions, second messengers, etc. These junctions are important for cell _________ and cell growth.
connexon
connexins
synchronization (muscle contractions)
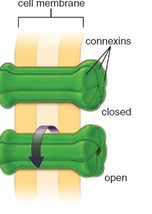
connexon proteins
Tight/Occluding Junctions are formed by two membrane proteins, __________&________. They prevent water and ________ from passing between cells. This is a physiochemical separation. Can be found at the _______/
claudins & occludins
solute
blood brain barrier
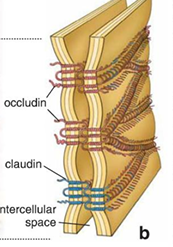
tight/occluding junction
Adhering Junctions are characterized by a continuous belt called the _______________ that circles and binds them to other cells _______. This makes _______ adhesion.
zonula adherins
cadherins
lateral
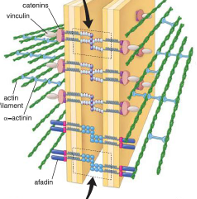
adherins junction
Desmosomes are specially resistant to __________ stress. This includes stretching and twisting. Each of the two cells has a ________ area that is connected to the __________. The membranes are linked by __________.
mechanical
dense
cytoskeleton
desmoglein (cadherin protein)
desmosome
Hemidesmosomes/Anchoring Junctions connect filaments of the _________ into the basement membrane. They help increase adhesion to the _(2 words)__________.
cytoskeleton
basal lamina
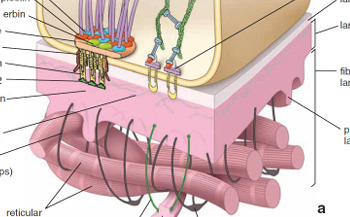
hemidesmosome (anchoring junction)
What makes the basement membrane?
Basal lamina
Reticular lamina (dense layer)
Basal lamina is _______ to the epithelium and is clear. It contains _______ and functions to restrict ____________ movement to underlying CT.
closer
glycoproteins
large molecule
The Dense Reticular layer contains coarse ______ fibers that give the basement membrane its strength. Dense layer acts as a _________________ between adjacent tissue and epithelium.
protein
diffusion filter
Epithelial cells continuously __________ through stem cells to combat chemical and physical disruption. The stem cells are located near the _________ for protection.
divide
basement membrane