Art Movements, Literary Devices, and Historical Contexts in 20th Century Culture
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
Picasso's Guernica
A significant artwork representing the horrors of war.
Dada
An art movement characterized by absurdity and anti-art sentiments.

Surrealism
An art movement aimed at revealing hidden truths of the human psyche.

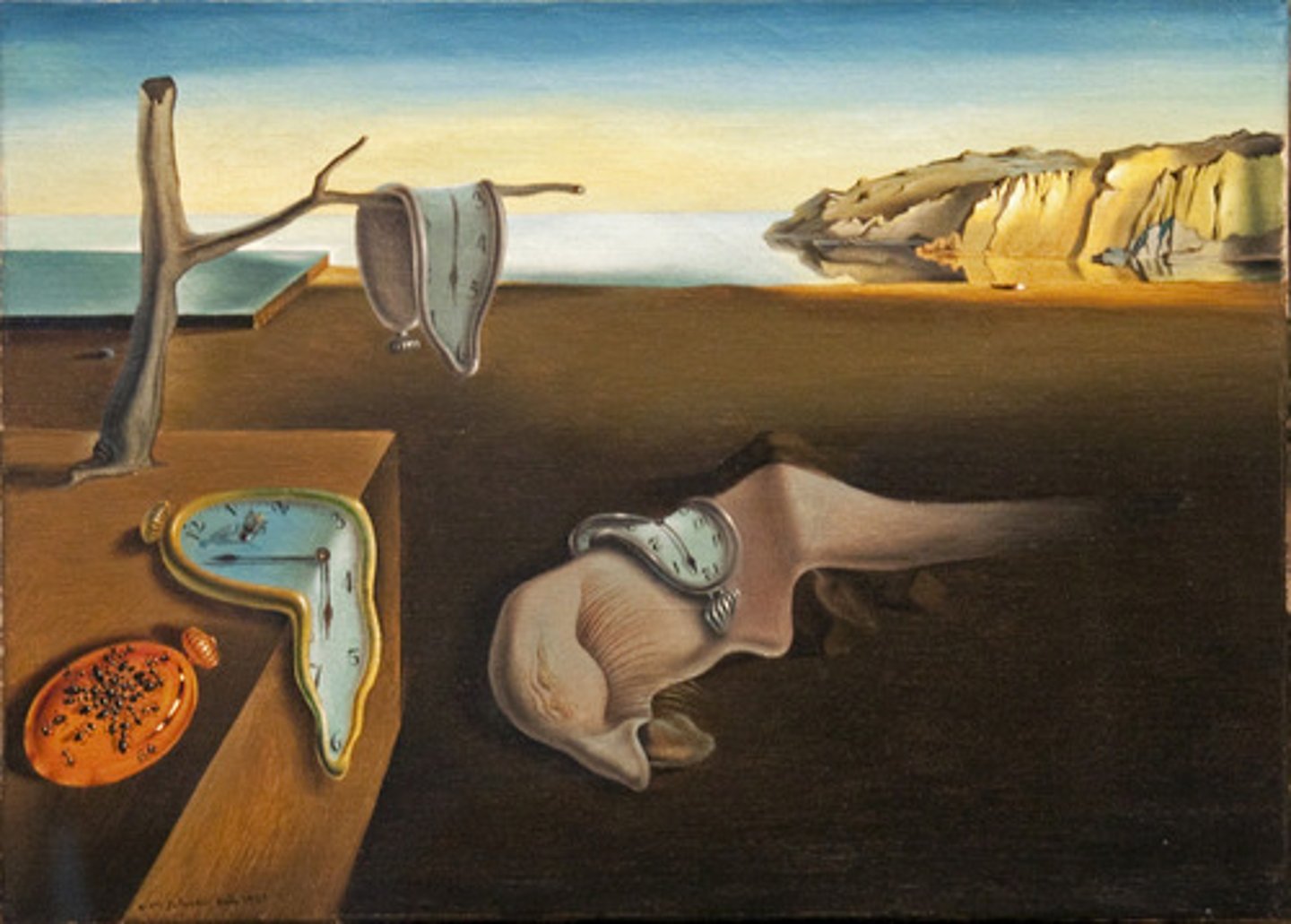
The Persistence of Memory
A famous painting by Salvador Dalí representing time and memory.

De Stijl
An art movement seeking harmony and order in response to chaos.

Harlem Renaissance
A cultural movement celebrating African American art and literature.

Abstract Expressionism
An art movement valuing process over product in artistic creation.

Shell-shock
A psychological condition experienced by soldiers in World War I.
Kafkaesque
Describes situations that are nightmarishly complex or illogical.

Simile
A figure of speech comparing two unlike things using 'like' or 'as.'

Metaphor
A figure of speech that equates one thing with another.

Alliteration
The repetition of initial consonant sounds in closely placed words.

Anaphora
The deliberate repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of clauses.

Assonance
The repetition of vowel sounds within nearby words.

Stream of Consciousness
A narrative technique presenting a character's continuous flow of thoughts.

Women's Suffrage (1918-1920)
The movement securing women's right to vote in many nations.
World War I (1914-1918)
A global conflict introducing modern warfare and massive casualties.
The Lost Generation
A group of disillusioned writers and artists post-World War I.
World War II (1939-1945)
A global conflict marked by significant historical events and changes.
Minimalism
An art movement emphasizing simplicity and minimal elements.
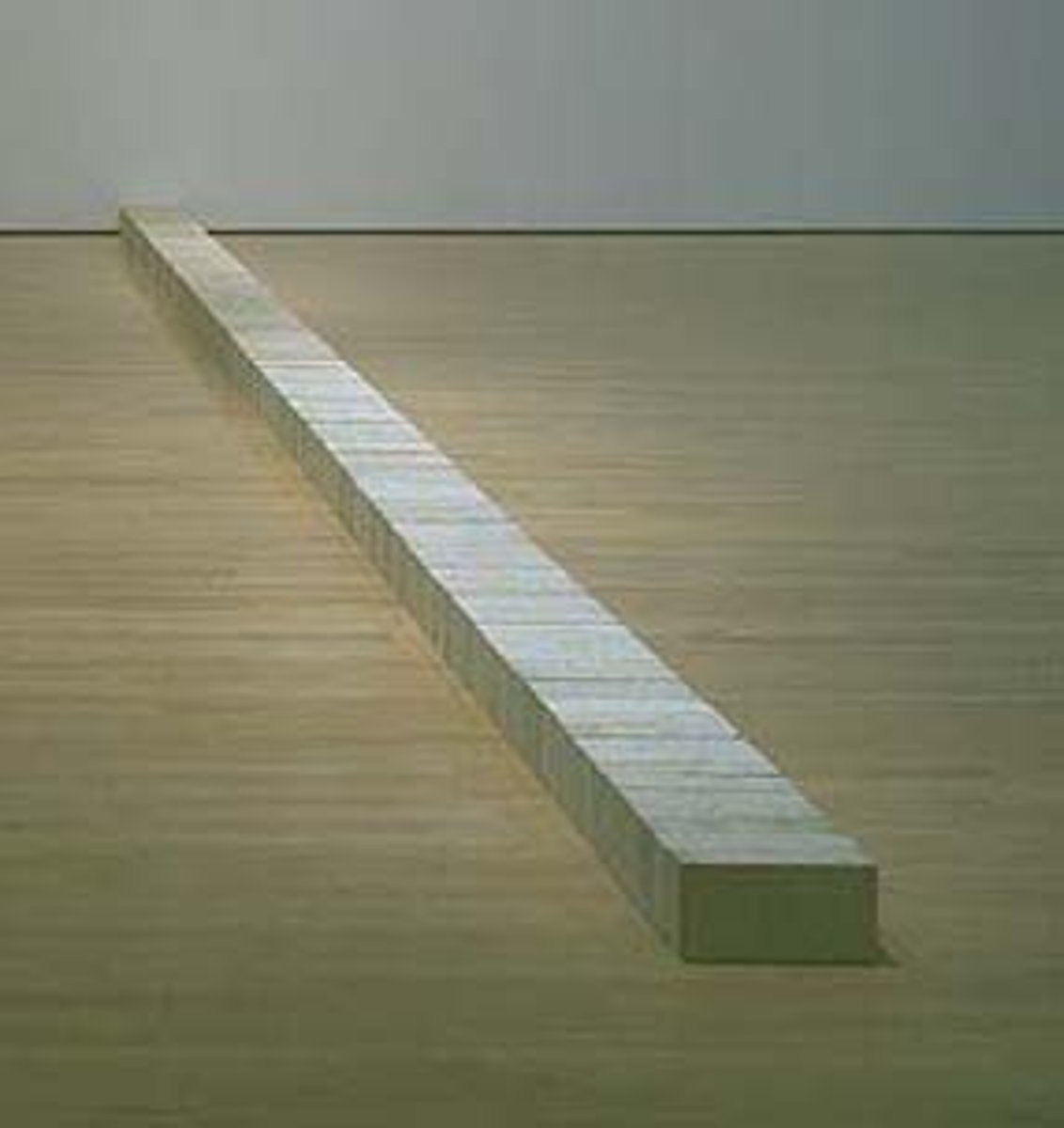

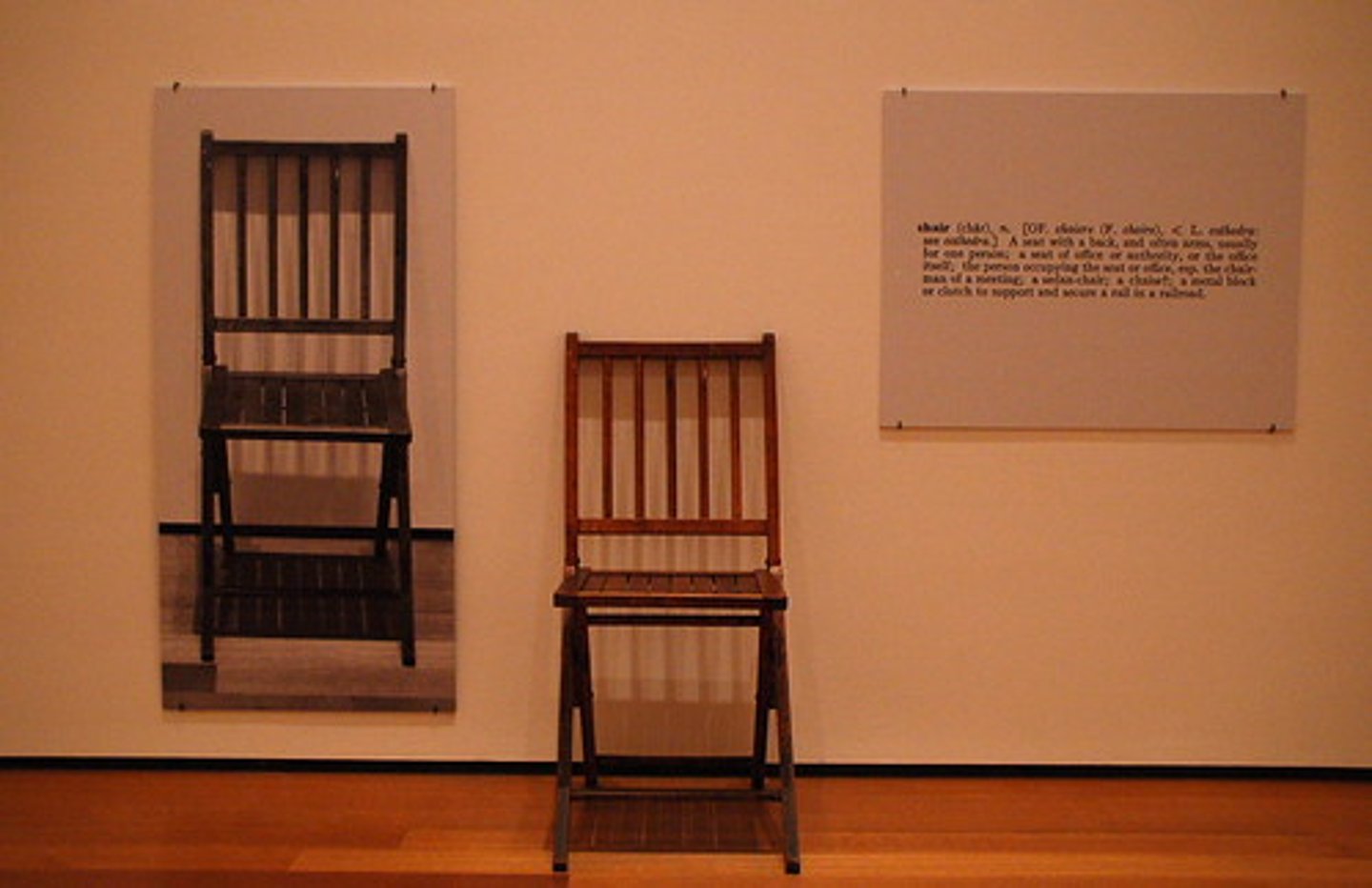
Conceptual Art
Art where the concept or idea is more important than the finished product.

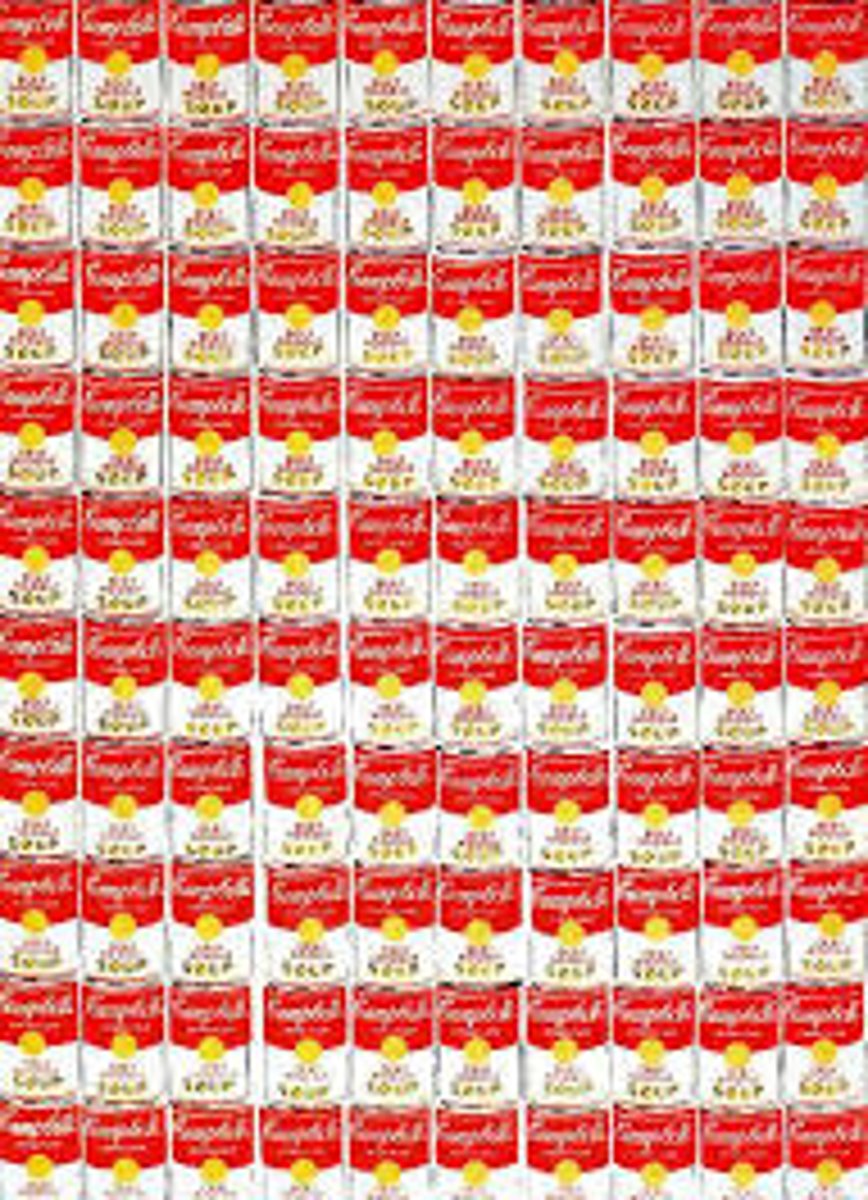
Pop Art
An art movement celebrating everyday objects and commercial aesthetics.

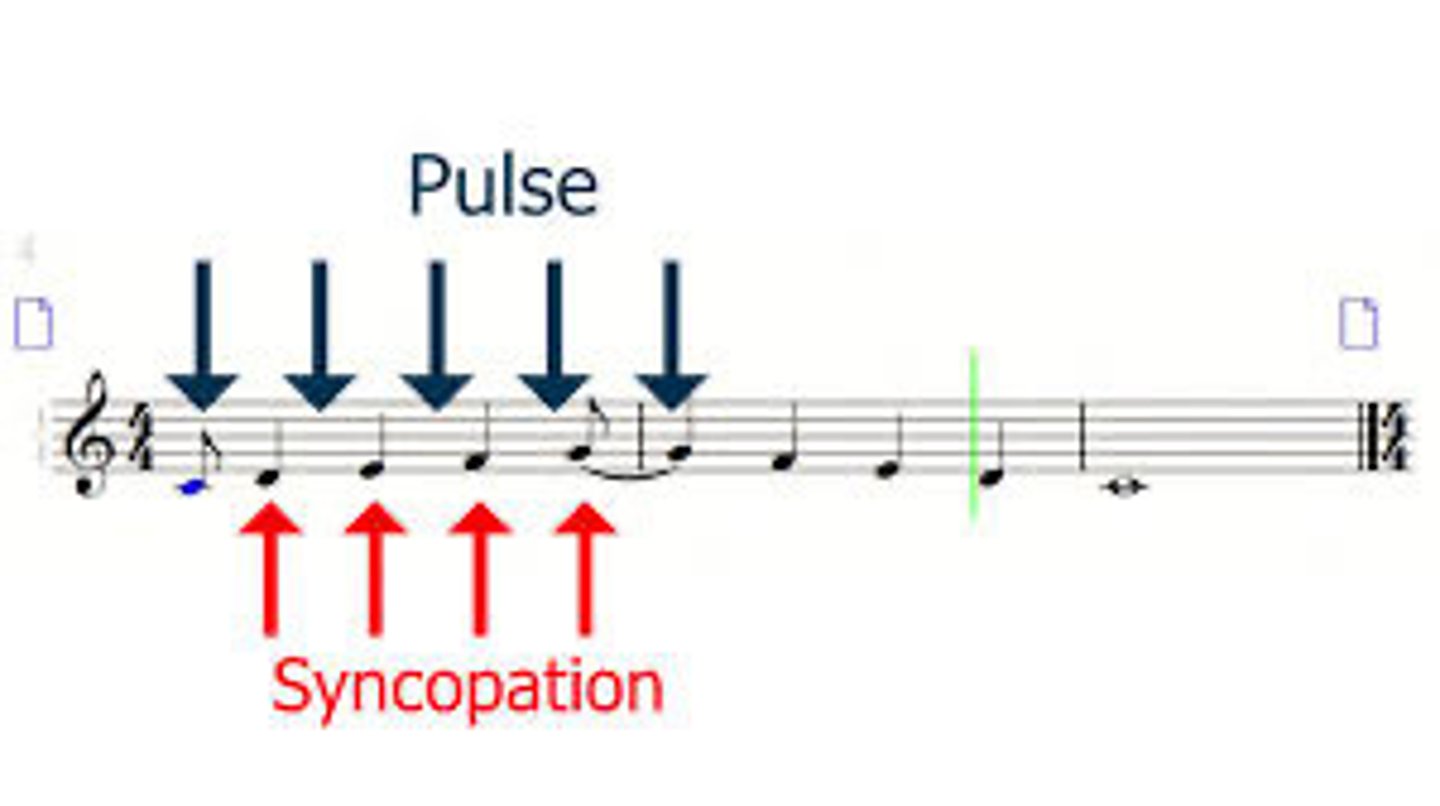
Syncopation
A musical technique disrupting normal beat patterns for rhythmic surprise.
Jazz
A genre of music characterized by syncopation and improvisation.

Improvisation
The spontaneous creation of musical ideas during performance.

Scatting
A vocal jazz technique using nonsensical syllables instead of words.

Studio System
The system of film production in Hollywood characterized by a few major studios controlling the production and distribution of films.

Production Code
A set of industry guidelines for the self-censorship of content in films.

Depicting Decency
The portrayal of moral and ethical standards in film.
Dangerous getaway to bad behaviour
A narrative theme that explores the consequences of immoral actions.
French New Wave
A film movement in the late 1950s and 1960s that challenged traditional filmmaking conventions.

Auteur
A filmmaker whose personal influence and artistic control over a movie are so significant that they are regarded as the 'author' of the film.
New Hollywood
A period in the late 1960s and 1970s when a new generation of filmmakers emerged.

Jaws
The first blockbuster film that set the standard for summer blockbusters.
Mesh of thesis and antithesis
A concept in dialectical reasoning where opposing ideas are reconciled.
Theory of Evolution
The scientific theory that species develop over time through natural selection.
Social Darwinism
A misapplication of Darwin's theories to justify social inequality.

Communism
A political and economic ideology advocating for a classless society and the abolition of private property.
Proletariat
The working class who do not control the means of production.
Bourgeois
The wealthy class who own the means of production.
Capital
The excess value gained from selling produced goods.
Alienation of Labor
Marx's concept that workers become estranged from their work and the products they create.
Hegel's Dialectic
A method of argument involving contradiction and its reconciliation.
Thesis
An initial idea or proposition in dialectical reasoning.
Antithesis
The opposite or contradiction of the thesis.
Synthesis
A higher-level resolution that reconciles the tension between thesis and antithesis.
Romanticism
An artistic movement emphasizing emotion, nature, and individualism.
Realism
An artistic movement depicting everyday life and ordinary people with unidealized accuracy.
Lyric Poetry
A type of poetry expressing personal feelings, often in a musical style.
Narrative Poetry
Poetry that tells a story and includes a narrator.
Irony
A literary device where the intended meaning is different from the actual meaning.
Transcendentalism
A philosophical movement emphasizing intuition and the inherent goodness of people and nature.
Hudson River School
An American art movement focused on landscape painting, particularly of the Hudson River Valley.

Photography, daguerreotype
The first widely used photographic process capturing images on light-sensitive surfaces.

War photography
The practice of documenting armed conflict through images, shaping public perception of war's realities.
Royal Art Academies
State‑sponsored institutions in Europe that set official standards for artistic training, style, and exhibition.
Salon de Refusés
The 1863 Paris exhibition showcasing works rejected by the official Salon, marking a turning point toward modern art.
Modernity (modernité)
A cultural condition of rapid change, urbanization, and innovation, often explored in 19th‑century art and literature.
Übermensch
Nietzsche's concept of the 'Overman,' an individual who creates new values beyond conventional morality.
Will to power
Nietzsche's idea that the fundamental human drive is not survival but the pursuit of growth, strength, and self‑overcoming.
Plein Air
Painting outdoors to capture natural light, atmosphere, and immediate impressions of a scene.
Color Theory
The study of how colors interact, combine, and affect perception, emotion, and artistic composition.
Pointillism
A painting technique developed by Georges Seurat using tiny dots of pure color that blend visually from a distance.
Synthetism
A Post‑Impressionist style (associated with Gauguin) combining simplified forms, bold colors, and symbolic meaning rather than direct representation.
Impasto
A technique of applying thick layers of paint so brushstrokes or palette knife marks create visible texture.
Impressionism
A late 19th‑century French art movement that captured fleeting effects of light, color, and atmosphere through loose brushwork and outdoor scenes.
Post‑Impressionism
A diverse movement that followed Impressionism, where artists like Van Gogh, Gauguin, and Cézanne emphasized emotional expression, symbolic meaning, and structural form beyond mere visual impression.
Futurism Manifesto
A 1909 declaration celebrating speed, technology, violence, and modernity, rejecting tradition in favor of radical innovation.
Remembrance of Things Past
A multi‑volume novel exploring memory, time, and identity through richly detailed reflections on French society.
Au Bonheur des Dames (The Ladies' Delight)
A realist novel depicting the rise of the department store in 19th‑century Paris and its impact on women and commerce.
The Importance of Being Earnest
A satirical comedy of manners that critiques Victorian social conventions through witty dialogue and mistaken identities.
A Doll's House
A groundbreaking realist play exposing gender roles and marital inequality, culminating in Nora's decision to leave her husband and children.
Bronze Casting
A sculptural process of pouring molten bronze into molds to create durable artworks.
Abstraction
An artistic approach that emphasizes shapes, colors, and forms rather than realistic representation.
Free Association
A psychoanalytic technique where patients say whatever comes to mind to reveal unconscious thoughts.
Blue Period (Picasso)
Picasso's phase (1901-1904) marked by somber, melancholic paintings dominated by blue tones.
Rose Period (Picasso)
Picasso's phase (1904-1906) featuring warmer colors and more optimistic, often circus‑themed subjects.
Monochromatic
A work of art created using variations of a single color.
Collage
An art technique combining different materials (paper, fabric, photographs) into a unified composition.
Dynamism
A Futurist concept emphasizing movement, energy, and the vitality of modern life in art.
Light Opera
A genre of opera with lighter themes, accessible music, and often comedic elements.
Opera Buffa
Italian comic opera of the 18th century, featuring everyday characters and humorous plots.
Impressionistic Music (Claude Debussy)
A style emphasizing atmosphere, tone color, and suggestion rather than strict form, paralleling Impressionist painting.
Psychoanalysis (Sigmund Freud)
A theory and therapeutic method exploring the unconscious mind, dreams, and repressed desires.
Id
Freud's concept of primal instincts and desires seeking immediate gratification.
Ego
The rational mediator balancing the id's impulses with reality.
Superego
The internalized moral conscience guiding behavior according to societal values.
Aestheticism (art for art's sake, Oscar Wilde)
A movement asserting that art's value lies in beauty itself, independent of moral or utilitarian purpose.
Modernism
Broad term to encompass the art of the late 19th century to mid 20th century.
WWI
First mechanized war, 15-22 million people died between 1914-1918, 1918-1920 was the flu pandemic-50 million people died, disillusionment.
What is Humanism?
A movement that emphasizes the study of art, literature, music, and history to understand human experiences and perspectives.
What does 'Renaissance' mean?
It means 'rebirth' and refers to the revival of classical Greek and Roman learning.
What was the influence of Humanism on Reformation thought?
It emphasized human potential, individualism, civic responsibility, and the importance of education.
What is Christian humanism?
A belief that humans can improve morally and spiritually through education, while still acknowledging the need for divine grace.
What were the causes of Luther's reforms?
The sale of indulgences, church corruption, focus on ritual over faith, and the printing press spreading reform ideas.
What were the effects of Luther's reforms?
Formation of Protestant denominations, weakening of papal authority, wars of religion, and rise of individual interpretation of scripture.
What is Anabaptism?
A Protestant tradition that advocates for adult baptism, separation of church and state, and pacifism.
What is Calvinism?
A Protestant tradition that emphasizes predestination, moral discipline, and simplicity in worship.
What is Anglicanism?
A branch of Protestantism started by Henry VIII, where the monarch became the head of the Church of England.
What was the Free Will Debate between Erasmus and Luther?
Erasmus believed in human free will guided by God's grace, while Luther believed in the bondage of the will and that salvation is only by God's grace.