Earth Science (EARTH-1141) - Structure/Earthquakes Vocab
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
1
New cards
earthquake
vibration of the earth produced by the rapid release of energy. radiates in all directions as waves and dissipates rapidly with distance. caused by the build up of pressure at faults
2
New cards
stick slip motion
3
New cards
tectonic creep
4
New cards
fault
a break in a rock mass along which movement has occured
5
New cards
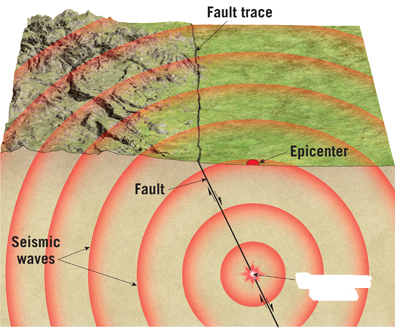
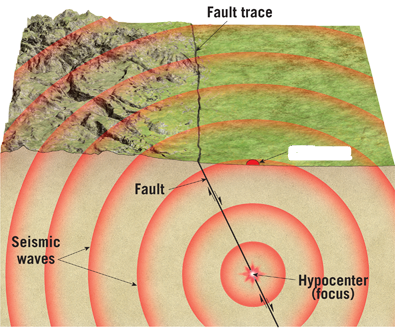
focus
in an earthquake, the location within earth where slippage begins - location of break
6
New cards
epicenter
surface of the earth above where the focus is, where the earthquake actually takes place
7
New cards
seismic waves
8
New cards
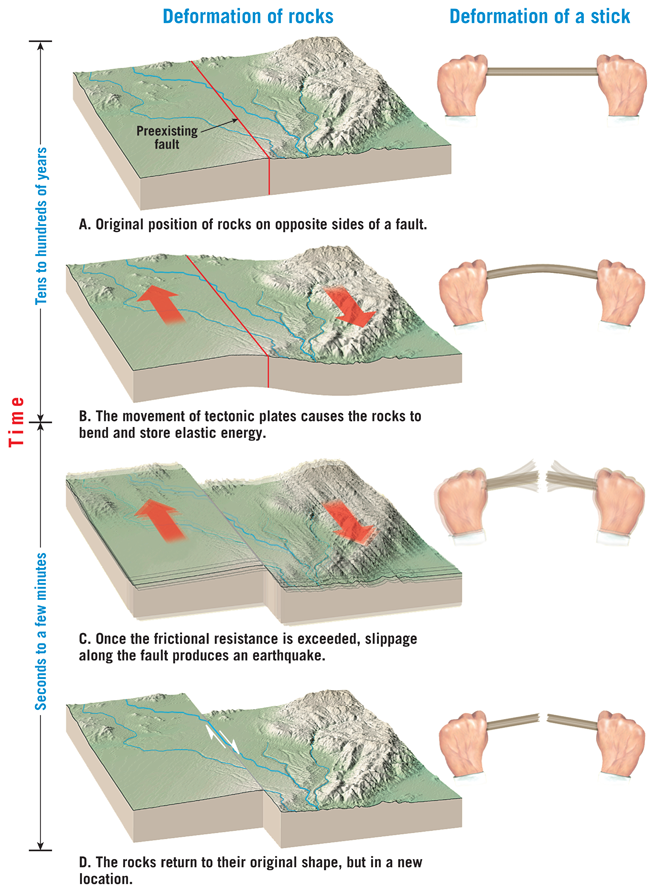
elastic rebound
9
New cards
aftershocks
Strong earthquakes are followed by numerous earthquakes of lesser magnitude
10
New cards
foreshocks
ften, but not always, precede major earthquakes by days or, in some cases, several years.
11
New cards
megathrust fault
When convergence entails the subduction of oceanic lithosphere under another plate, the area of contact between the two plates forms an extensive fault zone
12
New cards
fault creep
slow, gradual displacement produce little seismic shaking
13
New cards
seismagraph
14
New cards
seismogram
record made by seismograph
15
New cards
body waves
travel through Earth’s interior P and S waves
16
New cards
surface waves
travel through Earth’s interior
17
New cards
P waves
“push/pull” waves; they momentarily push (compress) and pull (stretch) rocks in the direction the waves are traveling
18
New cards
s waves
“shake” the particles at right angles to their direction of travel.
19
New cards