BIO 5, CH.14 - Nervous Tissue / Axon Regeneration
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Central Nervous System (CNS)
includes the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
includes the cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and ganglia
Brain (CNS)
receives & processes sensory information, initiates responses, stores, memories, generates thoughts & emotions
Spinal Cord (CNS)
conducts signals & from the brain, controls reflex activities
Sensory Neurons (PNS)
sensory organs to CNS
Motor Neurons (PNS)
CNS to muscles & glands
Somatic Nervous System
controls voluntary movements
Autonomic Nervous System
controls involuntary responses
Sympathetic Division (ANS)
“fight or flight”
Parasympathetic Division (ANS)
“rest or digest”

COLLECT Information
receptors in PNS detect changes in environment, pass information on to CNS
PROCESS AND EVALUATE Information
CNS determines required response
INITIATE Response
CNS initiates impulses that PNS carries to effectors (muscles or glands) to react to changes in environment
COLLECT
information
PROCESS & EVALUATE
information
INITIATE
response
Sensory Nervous System
detects stimuli & transmits information from receptors to the CNS
Sensory Nervous System: Somatic Sensory
sensory input that is consciously perceived from receptor (e.g., eyes, ears, & skin)

Sensory Nervous System: Visceral Sensory
sensory input that is not consciously perceived from receptors of blood vessles & internal organs (e.g., heart)
Motor Nervous System
imitates & transmits information from the CNS to effectors
Motor Nervous System: Somatic Motor
motor output that is consciously or voluntarily controlled; effector is skeletal muscle
Motor Nervous System: Automatic Motor
motor output that is consciously or is involuntarily controlled; effectors are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, & glands
NEURONS (NERVE CELLS)
electrically excitable cells that initiate, transmit, and receive nerve impulses
GLIAL CELLS
NON-excitable cells that support
NEURON: characteristics
- High metabolic rate
- Excitable
- Extreme longevity
- Conductive (propagate electrical signal)
- Nonmitotic
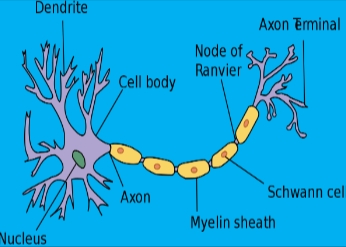
Neuron Structure
• Neurons vary in shape, but most have:
• cell body
• dendrites
• axon
CELL BODY (soma)
center part
- nucleus & surrounding cytoplasm of a neuron (excluding its dendrites & axon)
– contains several organelles:
• nucleus with nucleolus
• mitochondria
• free ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum (Nissl bodies)
AXON
away from the cell body
- transmits nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body and to other cells (OUTPUT)
• Neurons have either 1 axon or no axon (anaxonic)
– The region where the axon connects to the cell body is the axon hillock
DENDRITES
towards the cell body
- are short processes (INPUT), neuron process that conducts information to the cell body (input)
• Transfer signals TOWARD the cell body
Glial Cells
• Neuroglia (glial cells) protect and nourish neurons
• Found in both CNS and PNS
• Smaller and more numerous than neurons
• Capable of mitosis
• Brain tumors are more likely to be derived from glial cells than neuron
CNS (Central Nervous System) Glial Cells
four types of glial cells in CNS
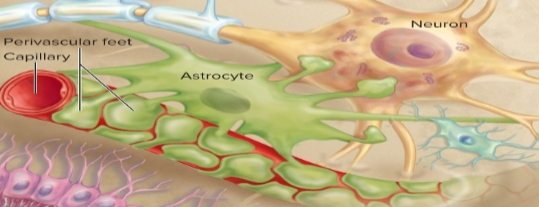
Astrocytes (CNS)
helps form the blood-brain barrier (BBB), regulates tissue fluid composition, provides structural support & organization to CNS, replaces damaged neurons, assists with neuronal development, helps regulate synaptic transmission
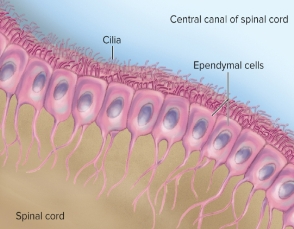
Ependymal Cells (CNS)
lines ventricles of brain & central canal of spinal cord, assist in production & circulation of CSF
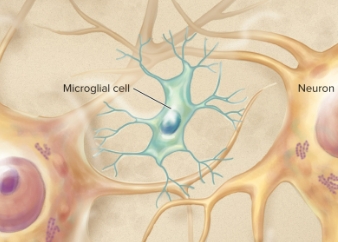
Microglial Cells (CNS)
defends against pathogens, removes debris, phagocytosis wastes
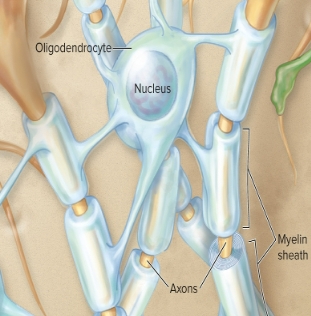
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
myelinates & insulates CNS axons, allows faster nerve impulse conduction through the axon, wrap themselves around the axons like electrical tape wrapped around a wire
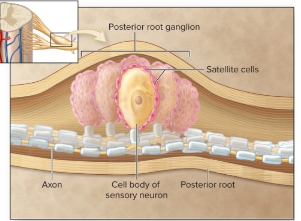
Satellite Cells
arranged around the neuron’s, regulate fluid composition around neuron cell bodies
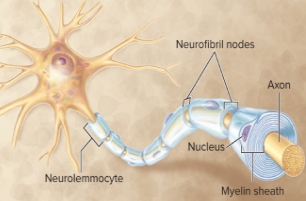
Neurolemmocytes/Schwann Cells
wrap neuron’s axon, associated with PNS axons only, wrap an axon like electrical tape wraps a metal wire, produces myelin an insulator of electrical activity, similar in structure & function to oligodendrocytes
Myelination of Axons
• Myelin affects the ability of neurons to conduct nerve impulses (action potentials)
• Myelination is the process of wrapping the axon with a myelin sheath to electrically insulate it
• The glial cells involved are neurolemmocytes in the PNS and oligodendrocytes in the CNS
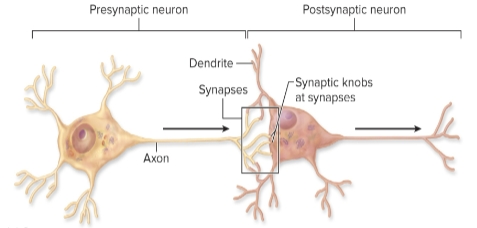
Synapses
specialized junctions between two neurons
– Some synapses are connections between a neuron and a muscle cell or a gland cell
Presynaptic Neuron
has synaptic knobs at axon endings for sending signal
Synaptic Cleft
narrow space between cells
Postsynaptic Neuron
receives signal