calcium channel blockers
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
T/F: Ca+ leads to smooth muscle dilation resulting in vasodilation and increase in BP
false
causes smooth muscle contraction → vasoconstriction
what are the different types of calcium channels throughout the biological system?
L
N
R
S
which channel does calcium enter through in the cardiovascular system?
a) L
b) N
c) R
d) S
a) L
what are the 3 major CV Conditions that CCBs are used for? Specifically, what muscle/part is targeted?
HTN (Arteries)
arrhythmia (cardiac muscle)
angina (BV in heart)
T/F: Ca+ Is ubiquitous
true
it is everywhere
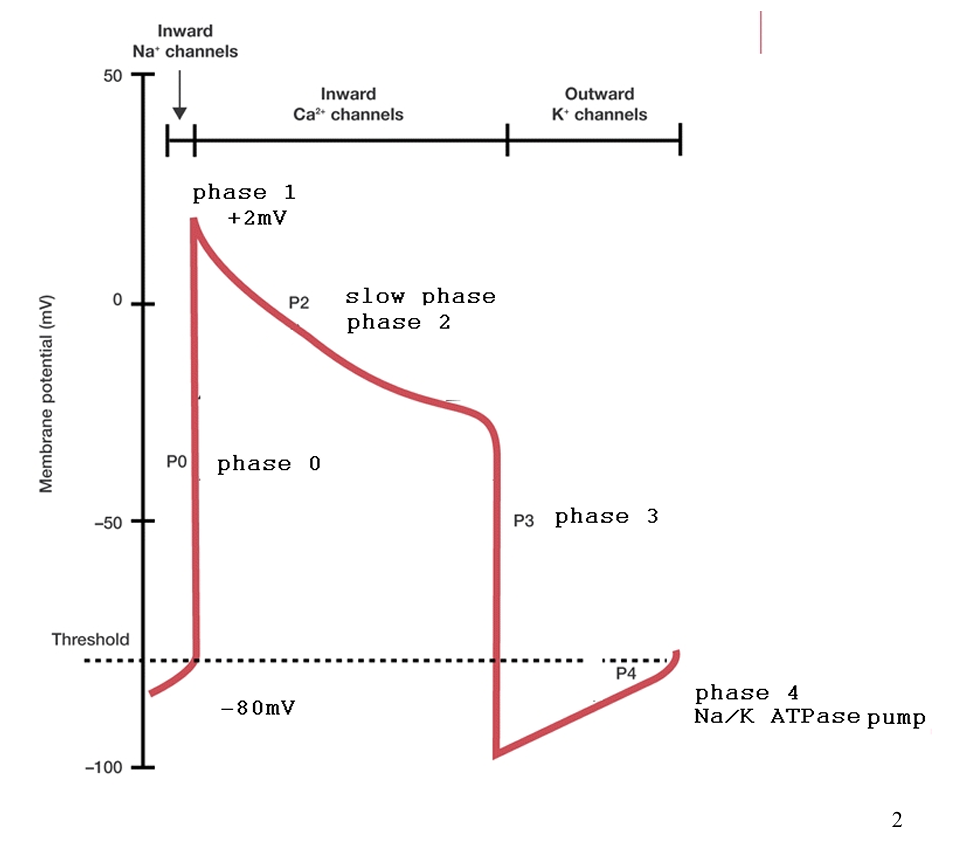
T/F: this action potential diagram represents the stepwise events of calcium entry into a single cell of the cardiac system
true
a diagram showing the action potential of a single cardiac cell is
a) electrocardiogram
b) action potential diagram
b) action potential diagram
SATA: what 2 ions contribute to the electrical system completion by calcium
a) potassium
b) magnesium
c) sodium
d) nitrates
a) potassium
c) sodium
what is the resting membrane potential of a cardiac cell?
-80 mV
during resting membrane potential, the outside is (positive/negative) because of the (K+/Na+/Ca+) inside while the inside is (positive/negative) because of the (K+/Na+/Ca+) outside
outside = positive
because of only K+ inside cell
inside = negative
because both Ca+ and Na+ are outside
what happens during phase 0
Na+ Influx
Na+ enters cell (outside → inside)
increases positive membrane potential
caused by stimulation of membrane ( ex. NT)
T/F: K+ hates Na+ and Ca+
true
what happens during phase I?
K+ starts to leave in small amounts
what happens during phase 2?
slow Ca+ Influx by channels
the slow phase or the plateau phase refers to…
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 1
c) Phase 2
d) Phase 3
c) Phase 2
what happens during phase 3?
Potassium starts to leave the cell
in response to more Ca+ Influx
Na+ Still inside
sodium influx into the cell refers to
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 1
c) Phase 2
d) Phase 3
a) Phase 0
when potassium starts to exit the cell, that refers to
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 1
c) Phase 2
d) Phase 3
b) Phase 1
when Ca+ starts to slowly enter the cell, that refers to
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 1
c) Phase 2
d) Phase 3
c) Phase 2
when K+ starts to leave the cell very quickly, that refers to
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 1
c) Phase 2
d) Phase 3
d) Phase 3
what does calcium do once inside the cardiac cells?
reacts with 3 proteins (myosin, actin, troponin)
Ca+ takes myosin OUT →
troponin + actin snap together →
causes conduction or contraction
when the action potential is restored By Na/K ATPase, that refers to
a) Phase 0
b) Phase 3
c) Phase 4
d) Phase 1
c) Phase 4
what happens during phase 4?
action potential is restored
Na+ and Ca+ exit cell
K+ influx
caused by K/Na ATPase
how does the calcium enter into blood vessel epithelium occur?
through L-type cells
less dependence on Na+ & K+
diagram = more bell shaped
what are the 3 chemical nuclei that have properties to block CC?
dihydropyridines
arylalkylamines
benzothiazepines
what are DHP used for?
a) angina only
b) HTN and arrhythmia
c) HTN only
d) angina and HTN
d) angina and HTN
T/F: DHP can cause an indirect negative chronotropic effect
false
indirect positive chronotropic effect from baroreceptor reflex
what are benzothiazepines an arylalkylamines useful for?
a) HTN
b) angina
c) arrhythmia
d) All of the above
d) All of the above
CCB are more selective to (veins/arteries), which causes (veinous/arterial) vasodilation and decrease (preload/afterload) In angina.
arteries
arterial
decrease afterload
what is the parent nucleus of dihydropyridines?
pyridine nucleus with one of the 3 double bonds = hydrogenated
1 double bond = saturated
2 hydrogens = positions 1 + 4
which of the following is a correct description of the dihydropyridines?
a) pyridine nucleus with 2 double bonds are saturated/hydrogenated
b) pyridine nucleus with 1 double bond saturated/hydrogenated
c) aliphatic tertiary nitrogen surrounded by carbon chains
d) 1,4-thiazepine with various functional groups
b) pyridine nucleus with 1 double bond saturated/hydrogenated
what type of CCB class is nifedipine?
1,4- dihydropyridines
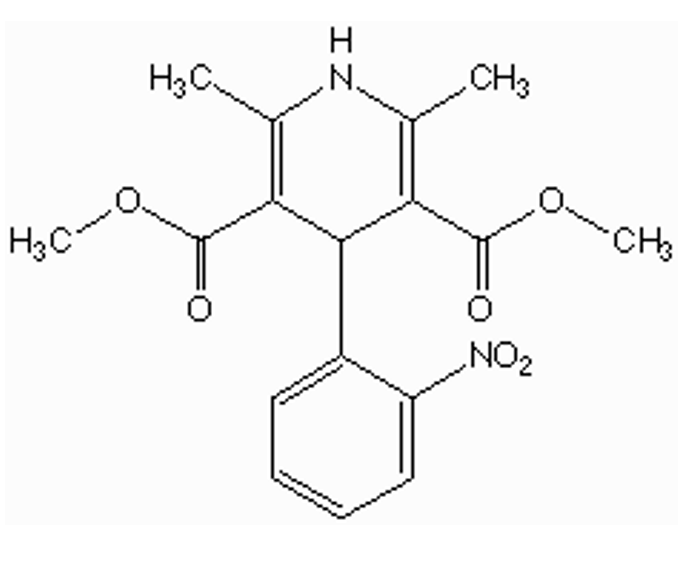
what type of CCB is this?
1,4-dihydropyridine
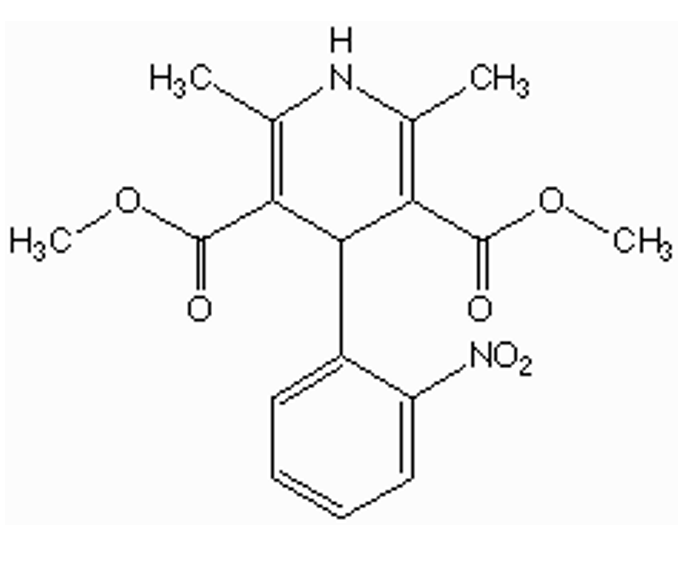
is the nitrogen in nifedipine basic? can it be a salt?
not basic
lone pair = conjugate with double bonds and ester carbonyl
can not be salt
nitrogen needs to be able to donate a proton
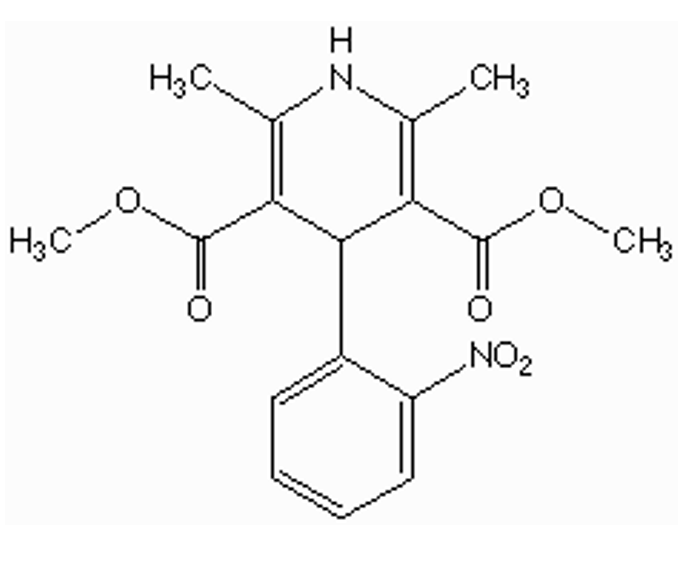
is nifedipine hydrophilic or lipophilic? why?
lipophilic
phneyl ring + 2 esters
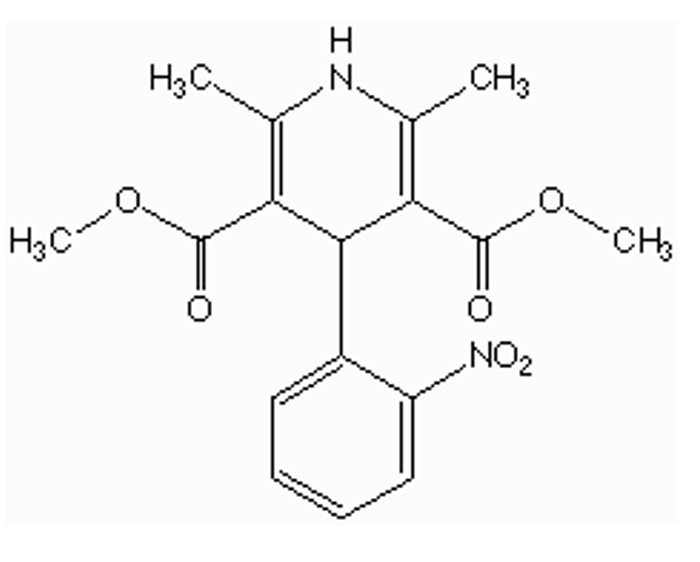
how is nifedipine administered? how is it absorbed?
given only ORALLY (very lipophilic)
extensive FPM
low bioavailability because of esterases in GIT, liver, plasma
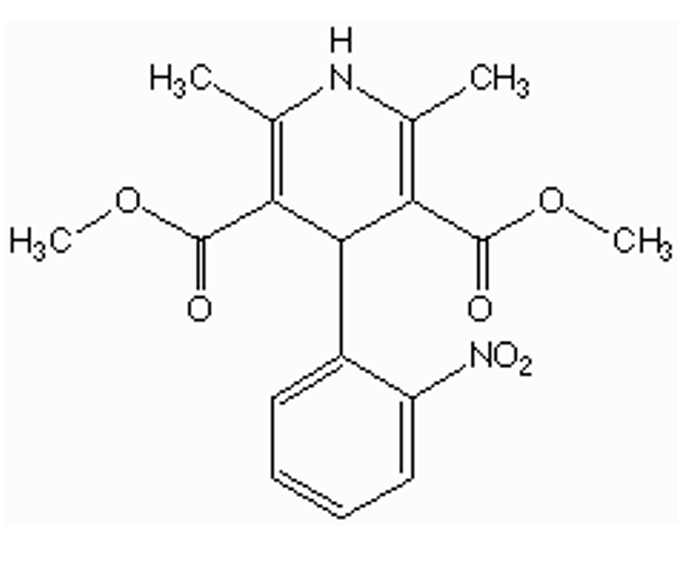
how is nifedipine metabolized?
esterases in GIT, liver, plasma
what is nifedipine used for?
HTN + angina
T/F: DHP are very effective in the treatment for arrhythmias
false
do NOT use DHPS for arrhythmias
why does nifedipine have low bioavailability?
a) Extremely lipophilic nature
b) esterase metabolism
c) o-demethylation metabolism
d) dependent on pt being slow/fast acetylators
b) esterase metabolism
esters at positions 3 + 5
DHP
a) dilate peripheral veins
b) dilate peripheral arteries
c) dilate both peripheral veins and arteries
b) dilate peripheral arteries
SATA: which of the following DHP have basic nitrogen atoms in the side chain?
a) nifedipine
b) nicardipine
c) amlodipine
d) felodipine
b) nicardipine
c) amlodipine
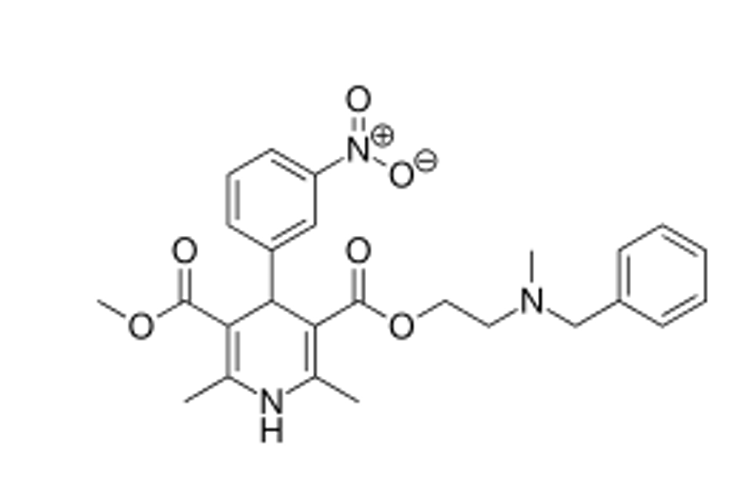
what type of CCB is this?
DHP (Nicardipine)
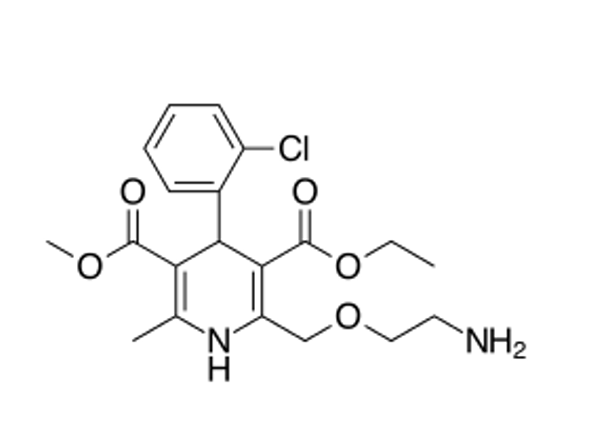
what type of CCB is this?
DHP (amlodipine)
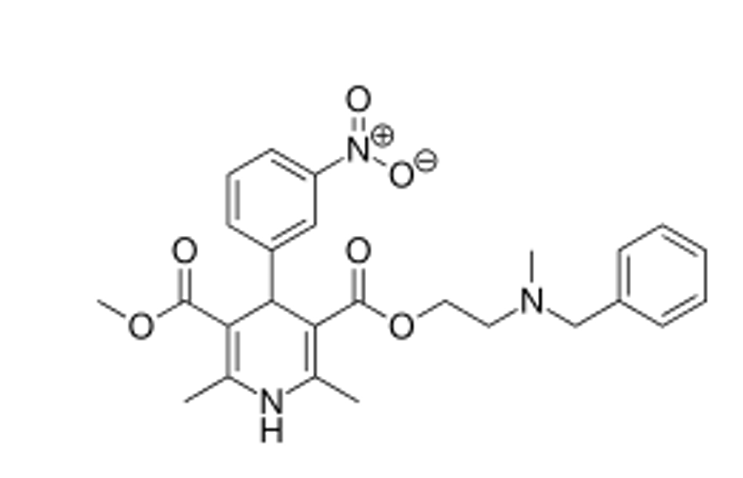
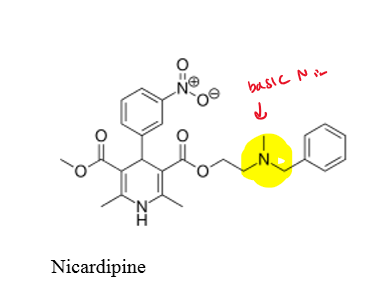
where does nicardipine have a basic nitrogen?
basic nitrogen on ester alkyl position 3
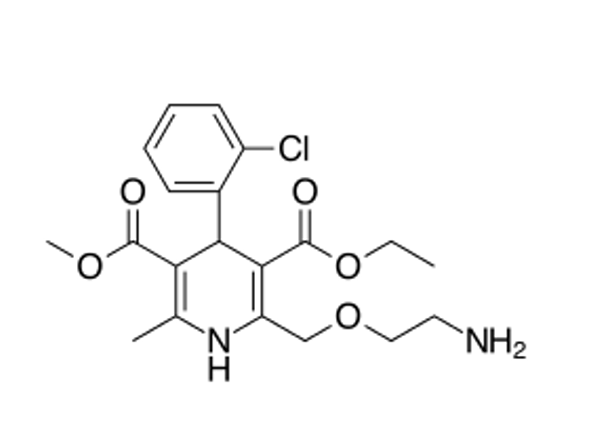
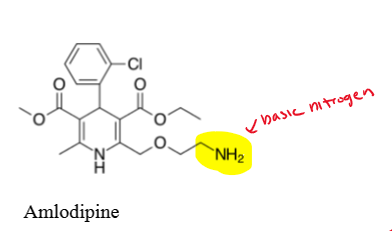
where does amlodipine have a basic nitrogen?
basic nitrogen in the side chain at position 2
what type of salt is nicardipine given as? How is it administered?
given as a HCl salt by injection
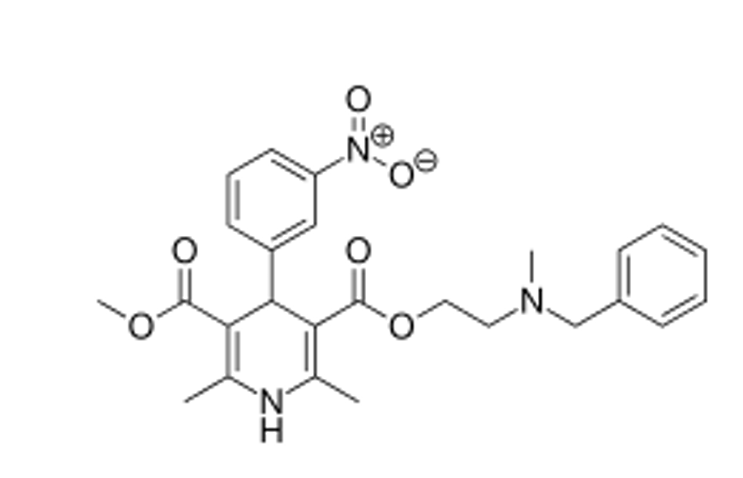
can nicardipine be used orally?
no, only use by injection
ester hydrolysis can occur orally → decreases bioavailability
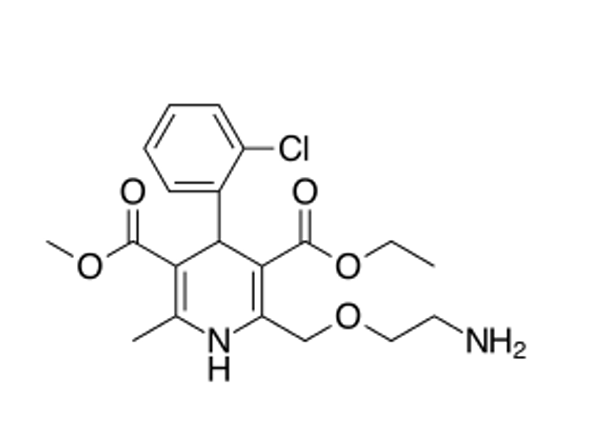
can amlodipine made into a salt? how is it administered?
make salt with weak organic acid (Besylate)
slowly released in oral dosage form (Long-acting, use once per day)
T/F: amlodipine is made into a salt with HCl
false
uses besylate
HCl = hygroscopic = absorbs moisture = bad
what drug is the prime example of aryl-alkyl amines
verapamil
what is verapamil used for?
HTN
angina
arrhythmia
how is verapamil administered?
-orally and by injection as a hydrochloride salt
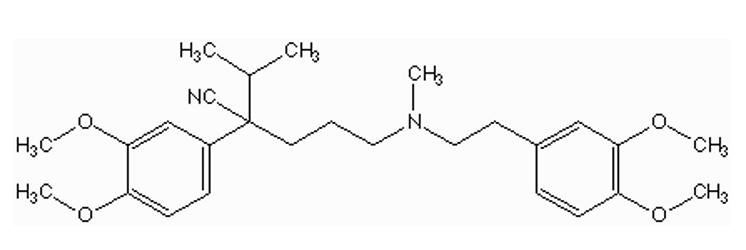
what type of CCB is this?
aryl-alkyl amine (verapamil)
how well is verapamil absorbed? how is it metabolized?
verapamil = very lipophilic = well absorbed
no strong polar groups
liver metabolizes drug very fast = low bioavailability
high FPM
O-demethylation or N-demethylation
what is the common structure of aryl-alkyl amine?
aliphatic tertiary nitrogen surrounded by carbon chains attached to aromatic rings
nifedipine dose vs verapamil dose
nifedipine = lower doses (5,10,20 mg)
most active class
verapamil = higher doses (200, 400 mg)
least active class
T/F: verapamil has a high bioavailability and low FPM
false
very low bioavailability because of high FPM (lipophilic, O-demethylation/N-demethylation
SATA: which of the following CCBs work on both the blood vessels and cardiac muscle?
a) nicardipine
b) verapamil
c) amlodipine
d) diltiazem
b) verapamil
d) diltiazem
(aryl-alkyl amines and benzothiazepines )
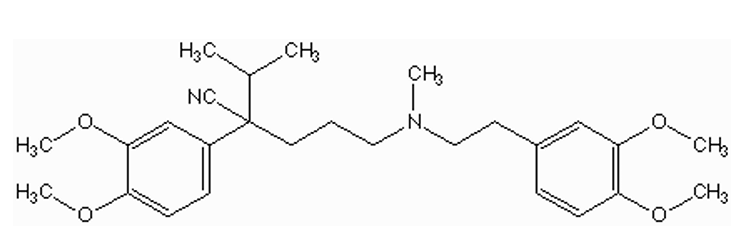
what are some functional groups in verapamil?
ethers (o-demethylation)
tertiary amine (N-demethylation)
cyano or nitrile
isopropyl
what type of drug is diltiazem?
benzothiazepine CCB
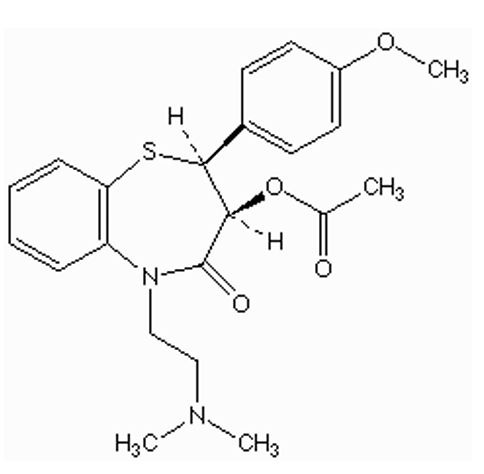
what type of CCB is this?
benzothiazepine (diltiazem)
what is the common structure of benzothiazepines?
1,4-thiazepine fused with a benzene
how is diltiazem administered?
orally or by injection (hydrochloride salt)
rank the CCB (nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem) by dose strengths
verapamil (highest, hundreds) > diltiazem (50) > nifedipine (5-20)
what is diltiazem used for?
HTN
angina
arrhythmia
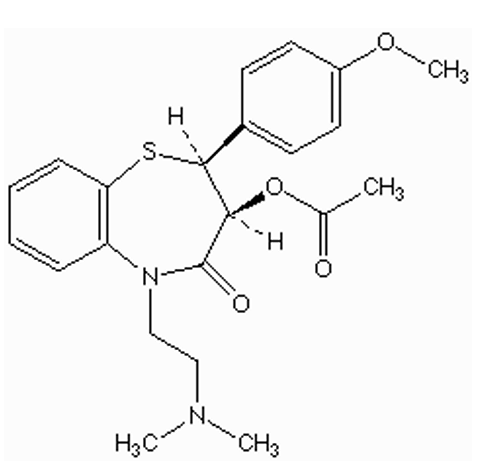
how is diltiazem absorbed?
well-absorbed
diltiazem = very lipophilic
low bioavailability (FPM) because of esters
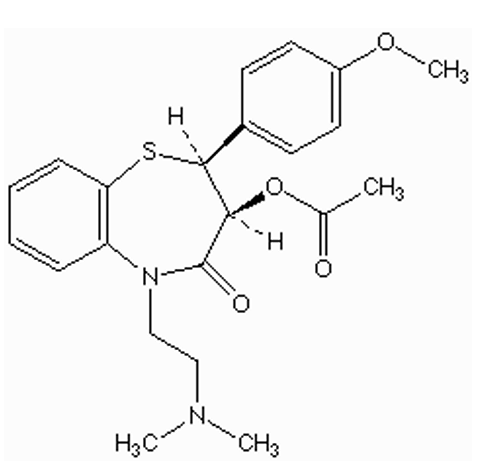
what are some functional groups in diltiazem? how might they affect metabolism?
ether (o-demethylation)
ester (esterases in GIT)
amide (amidases)
tertiary amine (N-demethylation)
benzene ring (possible aromatic hydroxylation)
how are verapamil and diltiazem similar and different?
both can be HCl salt or orally
both affect cardiac and vascular tissues
diltiazem does not have as low bioavailability as verapamil