Chapter 8: Descriptive and Predictive Research Designs: Understanding Conditions and Making Clinical Predictions
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Descriptive Studies
explain health conditions and provide information about the incidence and prevalence of certain conditions within a diagnostic group
Predictive Studies
provide information about factors that are related to a particular outcome
Epidemiology
the study of health conditions in populations
Incidence
The frequency of new occurrences of a condition during a specific time period.
- Calculated as the number of new cases during a time period, divided by the total population at risk
Prevalence
The number of individuals in a population who have a specific condition at a given point in time, regardless of onset
- Calculated as the number of cases at a given time point, divided by the total population at risk
Incidence and Prevalence Studies
Help practitioners know how widespread a particular condition is and how likely someone is to develop it
Not possible to make conclusions regarding causation
Large samples needed in epidemiological studies result in the use of efficient data collection methods such as surveys
Ex Post Facto Comparisons
cross-sectional designs that compare two or more groups, often those with and without a certain condition, at one point in time
Developmental Research
longitudinal design used to compare groups
Group Comparison Studies
Lack of random assignment and manipulation of the independent variable present potential threats to validity.
Survey Research
Questionnaire is administered via mail, electronic media, telephone, or face-to-face contact
Advantages = ease with which large amounts of data can be collected, particularly when surveys are administered electronically; opportunity to use random sampling methods, as it is possible to reach individuals in different geographic locations
Response Rate
percentage of individuals who return a survey based on the total numbers of surveys administered
Response Bias
measurement error that creates inaccuracy in the survey results
Self-Reporting Issues
desire to present self in a favorable light
Cross-Sectional
Most surveys used in research are _____________ in nature (i.e., gather data at a single point in time).
Longitudinal
However, some surveys are _____________ and collect data over periods of years or decades.
Study Designs to Predict an Outcome
Two major categories:
1)Studies that use correlational methods
2)Studies using group comparison methods
Purpose = identify factors that are most predictive of an outcome
Correlational Studies
Examine the relationships between variables
In a simple correlation, the association between two variables is determined.
____________ ____________ are cross-sectional, with data collected at a single point in time.
May administer multiple measures and explore the relationships using a correlation matrix.
Complex Correlational Designs
Look at multiple predictors for a single outcome
Regression analysis used.
- To trust results, need large sample
These studies have the advantage of examining the total amount of variance accounted for by multiple predictors and the relative importance of each individual variable as a predictor.
Shared Variance
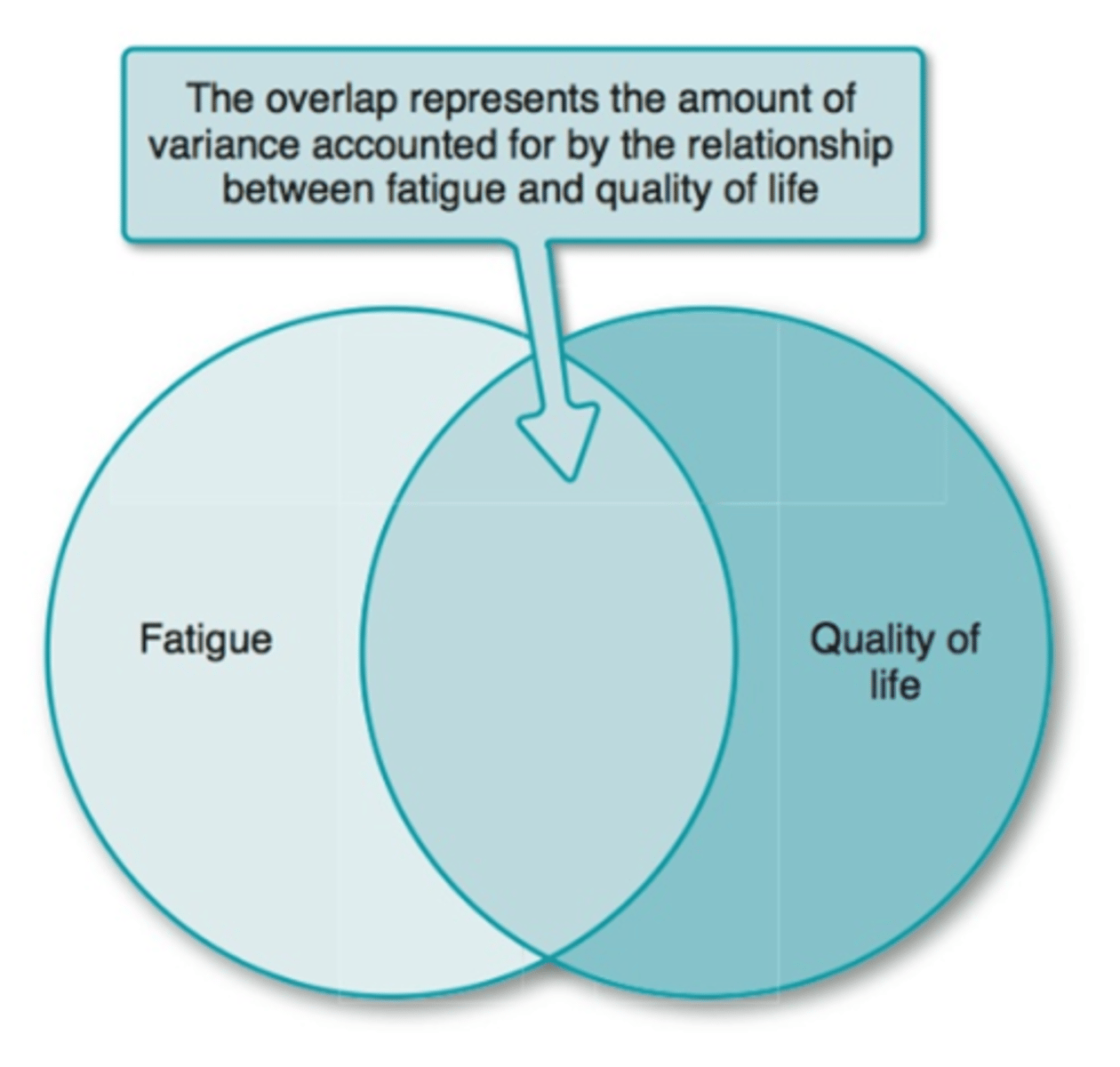
Multicollinearity
Circumstance in which variables are correlated with one another
To determine the unique variance of a predictor, it is entered last into the regression equation.
Two primary types of regression analyses that examine multiple predictors:
1)Multiple linear regression
2)Multiple logistic regression
Multiple Predictors
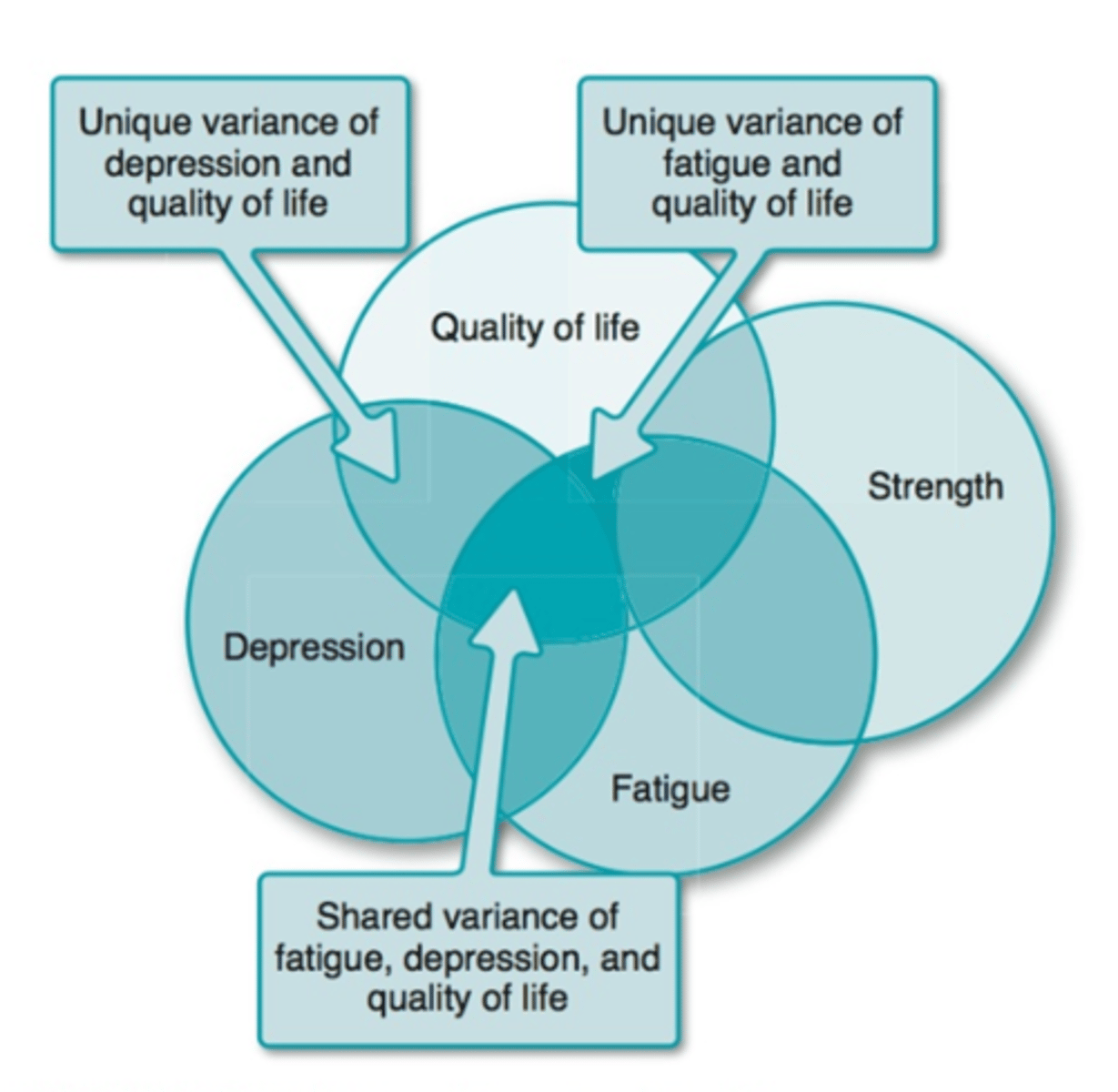
Multiple Linear Regression
Used when the outcome is a continuous variable
Multiple Logistic Regression
Used when the outcome and predictors are categorical variable
- Odds Ratio
Odds Ratio
Probability statistic that determines the likelihood that, if one condition occurs, a specific outcome will also occur
An ___________ ___________ of 1.0 means there is no difference between the groups. When the _____________ _____________ is greater than 1.0, there is a greater chance of experiencing the outcome; when the _____________ ______________ is less than 1.0, there is a lower chance of experiencing the outcome.
Case-Control Design
Observational, retrospective, cross-sectional study that can be used to answer prognostic research questions concerning which risk factors predict a condition
Landmark Example
Compared individuals with lung cancer with individuals without lung cancer and identified smoking as a predictor
Cohort Study
Observational, but differs from a case-control design in that participants are followed over time, making this design longitudinal
Hypothesized risk factor is identified and individuals with and without risk factor are followed to determine the impact that the risk factor has on the outcome.
Prospective Cohort Study
Research question identified before the study begins, and individuals are followed over time to determine who did and who did not develop the condition
Retrospective Cohort Study
Existing records or the client's report on past behavior is used to determine if changes occurred over time
Evaluating Descriptive and Predictive Studies
Cannot be analyzed using the levels-of-evidence hierarchy
When evaluating should consider:
- Control over outside variables
- Matching
- Use of statistical procedures to control for factors that might influence outcome
- Prospective studies are stronger than retrospective analyses
- Sample size
- Sampling bias
- Measurement methods
Level I
Systematic reviews of prospective cohort studies
Level II
Individual prospective cohort study
Level III
Retrospective cohort study
Level IV
Case-control design
Level V
Expert opinion, case study