Earth and Space Year 9 Real
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Life cycle of a star
a star's life cycle depends on its size
as stars age, they change in size, colour, and energy, ultimately reaching one of several possible endings
First step in the star life cycle
Nebula/e
stars are formed from massive clouds of dust and gas in space called nebulae which are mostly composed of hydrogen
as gravity pulls the cloud closer together, it heats up and begins to glow
eventually, it becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion to begin
A large collection of gas and dust
The second step of the star life cycle
Proto star
the larger the star, the shorter the protostar stage
A young, forming star that's still gathering mass
Third step in cycle
Main sequence star
nuclear fusion takes place deep in the cores of main-sequence stars, fusing hydrogen into helium
this releases massive amounts of energy as heat and light
A star in the most stable and longest phase of its life; nuclear reactions inside the star produce light and heat
life cycle of a star order
Star nebula → proto star
average star/ main sequence star
Red giant
plantery nebula
white dwarf
Massive star
red supergiant
supernova
neutron star/black hole
Next step for average star
red giant
hydrogen in the star’s core runs out so it begins to use hydrogen further out from its core
it grows 400 times its original size
as the star expands it also cools, causing the star to glow red
nuclear fusion in the core now fuses helium into heavier elements like iron
Forms after a star has run out of hydrogen fuel for nuclear fusion and has begun the process of dying
An aging giant star that has used up all its core's supply of hydrogen fuel
Second step in the average star life cycle
Planetary nebula
when the red giant runs out of fuel for nuclear fusion, it becomes unstable and explodes
the outer layers of dust and gas are shedded, forming a planetary nebula
A ring-shaped nebula formed by an expanding shell of gas round an ageing star
Final step in average star life cycle
White dwarf
the hot, dense solid core that remains after a red giant has shed its outer layers of dust and gas
very dense
emit large amounts of heat and light energy
eventually the amount of energy emitted becomes so low that the star becomes a black dwarf and can no longer be seen
A stellar core remnant, formed after a star exhausts its nuclear fuel and sheds its outer layers
Next step for a massive star
Red supergiant
forms when massive stars run out of hydrogen
helium fuses into heavier and heavier elements until the core consists of iron
Second step massive star cycle
Supernova
an enormous explosion that forms when a supergiant collapses under its own gravity
huge amounts of energy are released - bright
new elements form in the process, like gold, silver, uranium and copper
some material is expelled outwards, leaving behind a very dense core
The colossal explosion of a star
Whats one of the things after supernova
Neutron Star
the collapsed core left behind after a supernova explosion
very small and dense
some have been found to rotate several hundred times a second - called pulsars
A dense, collapsed remnant of a massive star after a supernova explosion
Second thing that could happen after a a super nova
Black Hole
extremely dense
gravitational forces are so strong, that nothing, not even light, can escape once it crosses the boundary known as the event horizon
A region of spacetime with such strong gravity that nothing, not even light, can escape its pull
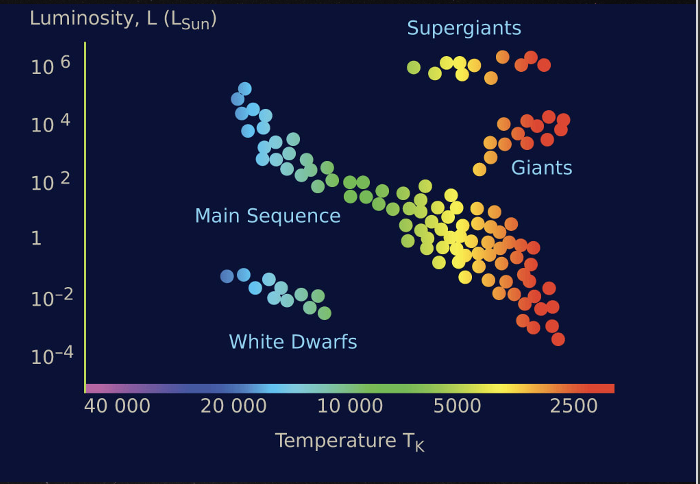
What is the Hertz-spring russel diagram
a diagram that helps scientists classify stars based on their physical properties and evolutionary stages
What does the H-R diagram do
plots a star’s luminosity (often compared to the Sun) against its surface temperature
stars at different stages in their life cycle are located in different regions of the graph
A scientific diagram that can be used to find the temperature, luminosity, spectral class and absolute magnitude of any star
What is the Big Bang Theory
the most widely accepted explanation for the origin of the Universe
according to this theory, the Universe expanded from an extremely small, extremely hot, and extremely dense state around 13.7 billion years ago
evidence for the origin and evolution of the universe
What happened to the universe after the big bang
the Universe has expanded and become less dense and cooler
Edwin Hubble’s theroy
red shift, blue shift
what is edwins hubbles theory
galaxies that are far away have greater red shifts
he realised this by analysing the redshift of light from distance galaxies
this provides evidence the universe is expanding
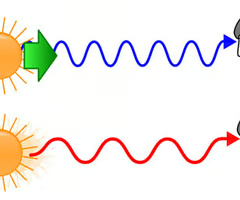
What is hubbles law
the farther away a galaxy is from Earth, the greater its velocity
what is red shift
when light from an object in space moving away from Earth is stretched to longer wavelengths
this causes spectral lines to shift towards the red end of the electromagnetic spectrum
provides evidence for the origin and evolution of the universe
Evidence for the big bang
Cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation
light from the beginning of the Universe released about 380,000 years after the Big Bang
at first, CMB was very energetic X-ray light but, over time, it has lost energy and become lower-energy microwaves
accidentally discovered by Robert Wilson & Arno Penzias, while using a microwave telescope
scientists consider this 'fossil' radiation to be a 'shockwave' of the Big Bang
How is the universe changing
the Universe is continuing to expand, with galaxies moving farther apart over time
star formation and stellar evolution are ongoing, with new stars forming while others age, explode as supernovae, or collapse into neutron stars or black holes
galaxies are changing shape and size through collisions and mergers
the Universe is cooling overall as it expands
What is the nebular theory?
The scientific explanation that the Sun and planets formed from a rotating cloud of gas and dust called a nebula.
What is a nebula?
A large cloud of gas and dust in space that can form stars and planetary systems
Why does nebular theory apply beyond Earth?
It explains the formation of the entire solar system and can be applied to other star systems
What force first causes dust particles to stick together?
Electrostatic attraction (“static cling”).
How old is the solar system according to the nebular theory
About 4.6 billion years
How quickly did the solar system form after the supernova?
Within 2–5 million years.
What existed before the solar system?
A massive star that exploded as a supernova.
white dwarf cooling
phase in between white dwarf and black dwarf
What is the final final step in the stars life cycle
A white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently to no longer emit significant heat or light
cosmic microwave background radiation
the faint, nearly uniform, remnant glow or "afterglow" of the Big Bang, representing the earliest light in the universe, released roughly 380,000 years after its origin
provides evidence for the origin and evolution of the universe
Luminosity
The total amount of energy it radiates per second of time. Hotter stars produce more energy per unit area making them more luminous than cooler stars of the same size. Larger stars have a greater surface area than smalll stars, allowing them to radiate more energy.
Absolute Magnitude
How bright a star would appear if it were located at a standard distance of 10 parsecs (32.6 light years) from Earth. Also the lower the magnitude the brighter the star is
Spectral Class
What category a star is in
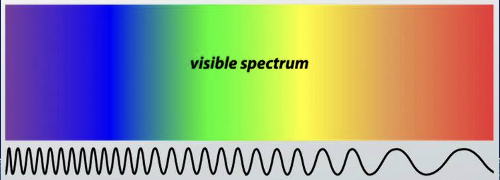
Electromagnetic spectrum
Encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation
Types of electromagnetic radiation (in order of shortest wavelength to longest)
Gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet, visible light, infared, microwaves, radio waves