Water
1/20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Uses of water?
makes up the fluid in cytoplasm in all cells, which aids metabolic reactions
Found as interstitial fluid between cells of multicellular organisms
Good solvent: allows transport of substances in cell
What cause polarity in water molecules?
the unequal sharing of electrons caused by the attractive oxygen nuclei
this causes a partial positive change in the hydrogen atoms as its electrons try to move closer to the oxygen nuclei
And a partial negative charge in the oxygen atom
Hydrogen bond
A weak intermolecular bond between the hydrogen of a water molecule and the oxygen of another water molecule
Cohesion
Water molecules sticking together due to hydrogen bonds forming a tetrahedral
This creates surface tension droplets on the surface form hydrogen bonds (2) with water molecules adjacent to them as they are nearest
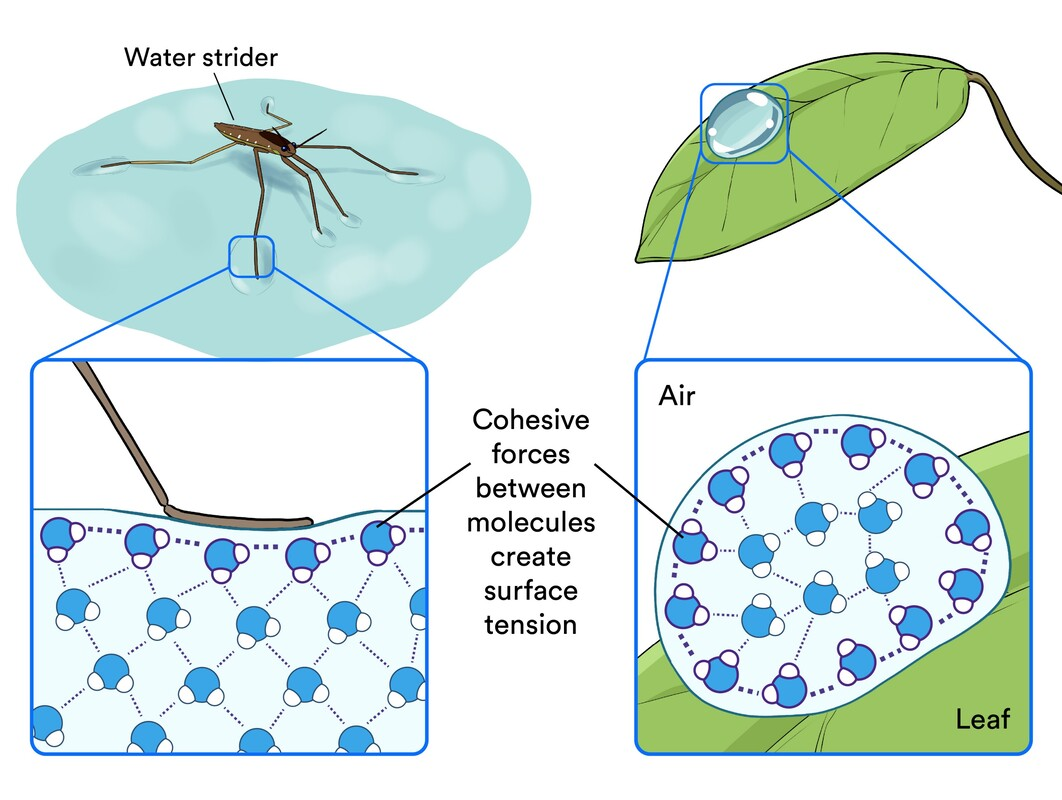

What is the use of cohesion?
Cohesion allows the transport of water under tension in plants
the molecules are linked via hydrogen bonds, and the pulling forces caused by the evaporation of water from the leaves make water move upwards against gravity (capillary action)
Adhesion
Attraction between water and a different polar surface
What is the use of adhesion?
helps with capillary action in roots as adhesion to the cells walls of xylem helps resist the downward pull of gravity
Solvency and why it’s useful?
Water is a universal solvent as anything w a charge will dissolve due to its polarity
Use: medium for metabolic and enzyme catalysed reactions as reactants need to be dissolved in water in cytoplasm + ions need to be dissolved in plasm (90% water)
Polarity of Fats + Fatty acids
fat molecules are entirely non polar and insoluble in water
They are carried in blood inside lipoprotein complexes to prevent bulky droplets from forming
polarity of steroid hormones?
Estrogen, testosterone, progesterone and cortisol are non-polar and hydrophobic thus do not dissolve in water
Polarity of glucose?
Polar and soluble due to OH groups which create hydrogen bonds with water
Polarity of amino acids?
Some polar, some non-polar, some hydrophilic, depends on R-Group
Polarity of Sodium chloride?
Polar molecules as Na cations and Cl anions, held together by an ionic bond.
Hydrophilic:
polar molecules that’s dissolve in water: cellulose, glucose, polar amino acid chains
Hydrophobic:
Non-polar (non charged) substances that’s dissolve well in water: oil, fatty acids, wax
these dissolve well in non-polar substances such as acetone, chloroform
Specific heat capacity and its uses:
lots of hydrogen bonds so takes more energy to break them and change the temperature
This is beneficial for aquatic habitats ( ringed seals) as slow change in temperature
Constant temperature is ideal for enzyme activity
Thermal conductivity and its uses?
the rate at which heat passes through a substances
Water has high conductivity so it is colder for aquatic animals this harder to survive in winter
Black-loom: oil from glands and plumage + have feather (insulating layer) as it catches prey underwater
Ringed seal: fat layer blubber
Buoyancy and its affects:
The ability of something to float
black throated loon: have solid bones so they don’t float as they’ll be heavier
Ringed seal: have blubber so it can float
Viscosity and its affects:
How resistant a fluid is to flowing, which water isn’t
Black throated loons use their webbed feet and hydrodynamic torpedo like body shape to reduce drag as it moves through water
Ringed seals have flippers to propel themselves and a streamlined shape to reduce drag
Explain the origin of water?
Water has an extra planetary origin as it was found on an asteroid during collision
Earths atmosphere and gravity prevented it from leaving
Goldilocks zone:
The perfect distance from the sun that’s is not hot nor too cold to sustain life