Botany Exam 3
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
According to the description of "true leaves", a feature seen in true leaves but not in microphylls is;
the presence of branched veins
In the evolutionary history of land plants, which of these is a landmark evolutionary feature appeared in Lycophytes?
they evolved the dominant diploid sporophyte generation
Which sequence represents the correct order in which land plants became more advanced in structure and function during their evolution?
Bryophytes, Lycophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms, Angiosperms
Among all land plants, which phylum carries the smallest and least advanced sporophyte generation?
Phylum Hepatophyta
True stems with vascular tissues can be seen among:
Phylum Lycopodiophyta
Phylum Pteridophyta
Phylum Equisetophyta
Which statement is true about a difference between fern allies and true ferns?
True leaves are present in true ferns but not in fern allies
Why are gymnosperm seeds said to be naked?
They are not enclosed within a fruit.
Which two phyla are considered as the most primitive among Gymnosperms, and why?
Cycadophyta and Ginkgophyta because they have swimming sperm
The microgametophyte of a Gymnosperm should produce;
sperm
Your friend brags to you about his fearless adventures in the Alaskan wilderness where he was once lost for several weeks and survived by eating fruits of giant conifers that were the only available food in that area. You laugh and tell him, "that can't be true". Why?
Because conifers do not produce fruits
Ginkgo biloba is the only species in the phylum Ginkgophyta. Why have scientists given this one species its own phylum?
It is the only remaining species of a previously larger group
Gnetophytes have some advanced characteristics in common with angiosperms. Why are they classified as gymnosperms?
Their seeds are naked
In seed plants, which of the following would be dispersed away from the parent plant?
microgametophytes and seeds
Why do Bryophytes, Lycophytes and Peridophytes prefer to grow in moist habitats closer to water?
Because they have swimming sperm that need a film of water
What is always true about heterosporous plants?
they produce small male microspores and large female megaspores
Where do you find integument? What does integument become at later stages?
Around the megasporangium in the ovule of all seed plants, later becomes the seed coat
In Gymnosperms as well as in Angiosperms, the female gametophyte is very small. How does it feed the developing embryo?
It draws nutrients from the parent sporophyte tissues.
What characteristics among these are typical to both gymnosperms and angiosperms? Choose all that apply. Penalty for wrong answers. (Hint: 4 correct answers)
They are vascular plants with true stems and leaves
Their female gametophyte is contained within the
sporophyte
Their pollen represent the male gametophyte
Their male gametophyte travels to the female gametophyte
What is a correct statement describing a relationship between ovules and seeds in "both gymnosperms and angiosperms"?
the unfertilized egg cell inside the ovule becomes the embryo inside the developing seed after fertilization
Dicots and monocots differ from each other in several ways. Select all answer choices that describe differences between them. Penalty for wrong answers. (Hint: 3 correct answers)
Venation pattern in the leaves of dicots and monocots differ
Dicots produce two cotyledons, monocots produce only one
The arrangement of vascular bundles in dicot and monocot stems differ
Which of the following statements most accurately explain what recent molecular evidence shows about monocots and dicots?
dicots were the first to emerge, and monocots separated later from a dicot ancestor
Here is something to think about. Read patiently! You treated a developing flower of a self-pollinating diploid angiosperm with a chemical that disrupts sister chromatid separation in the anaphase II of meiosis during both microspore and megaspore formation, producing spores that have double the number of chromosomes. If the plant pollinates itself, what would you expect as the ploidy of the integument, zygote and endosperm?
integument 2N, zygote 4N, endosperm 6N
The double fertilization is seen;
in all angiosperms and some gymnosperms
What is carried inside the seed of a gymnosperm?
embryo of the future sporophyte
During the event known as double fertilization, which of these is/are fertilized by a sperm nucleus to generate the 3N endosperm?
Two polar nuclei
What is the function of the pollen tube in an Angiosperm?
delivering two sperm into the ovule
The zygote of an angiosperm undergoes _______________ to produce the embryo, that develops into the __________________ .
mitosis, future sporophyte
The fruit is;
a mature ovary
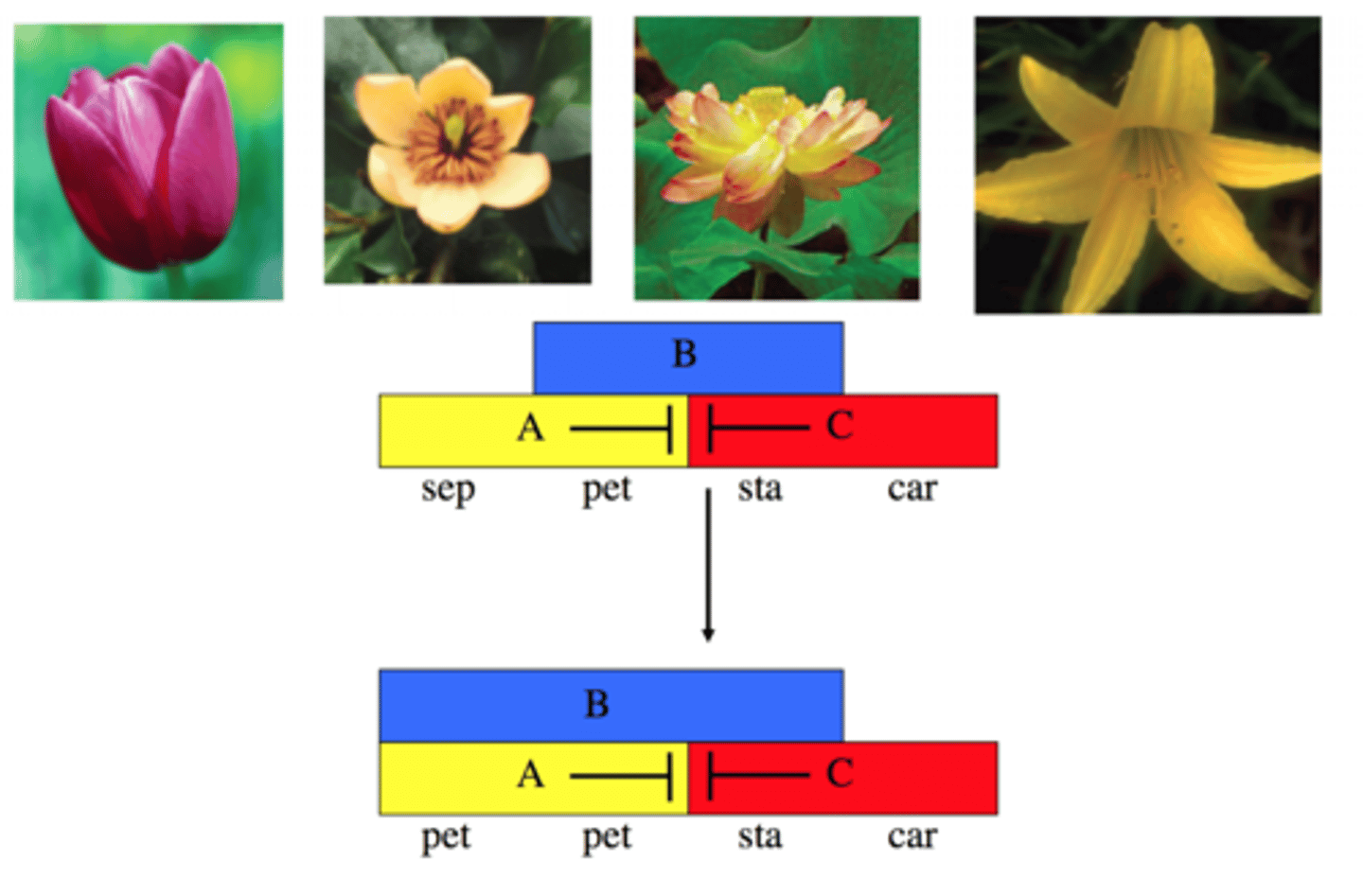
Refer to the ABC model of floral organ development. Gene A is expressed in whorls 1 & 2, gene B is expressed in whorls 2 and 3, gene C is expressed in whorls 3 & 4 (whorl 4 is the innermost). A scientist used genetic engineering techniques to express gene B in all whorls. What would the pattern of floral organs in the resulting transgenic plant be?
petals, petals, stamens, stamens
How do you tell if a symbiotic relationship is a mutualism or commensalism?
mutualism benefits both, commensalism benefits one without harming the other.
What words should go in the blanks? In the life cycle of a land plant, diploid sporophyte produces spores using cell division by ____, and haploid gametophyte produces gametes using cell division by ____ .
meiosis, mitosis
Heterospory is a feature that is invariably found in;
all seed plants
Which of these are true about heterospory? Choose all that apply. Penalty for wrong choices. (Hint: 3 correct answers)
There are megaspores and microspores
Heterospory first appeared in Lycophytes
Heterospory paved the way for plants to evolve seeds
Which of these is NOT a part of a gametic life cycle?
Alternation of generations
What happened to the gametophyte stage during the course of evolution of land plants?
became smaller and more dependent on sporophyte
The ABC model explains;
how different whorls of flower parts are determined
Coevolution can be defined as;
An alliance between species that influence the evolution of each other.
Your friend says; A symbiotic relationship between two organisms is beneficial to both organisms involved. You say:
False, these relationships may benefit both or only one partner.
A farmer owns a successful organic apple orchard. For many years he has had excellent yield from his trees. This year his orchard yielded very poorly even though he had not changed his farming strategies, and weather was very consistent. Which of the following reasons might best explain the drop in fruit production?
only answers A and C could be possible explanations
When flowers are self pollinated, they get their own pollen onto the stigma of a flower, therefore, it can be considered as a form of asexual reproduction.
False, because pollen and eggs are not identical due to meiosis in sporangia
A plant lives in a remote valley, with only a few other flowering plant species nearby. It reproduces only sexually by being pollinated only by one specific butterfly species, which pollinates most of the plant species in the valley. Also living in the valley is a bird that eats only the fruit of the plant and preys on the butterfly. Extinction of which of these three species would cause the extinction of the other two?
the butterfly
Why have some plants coevolved with animals for pollination, rather than depending on physical forces like wind and water for pollination?
because coevolved animals are more reliable in carrying pollen between flowers
Your aunt who is highly allergic to bee stings, loves flowers but would like to keep bees away. What would be your best advice to her about the types of flowers she should have in her garden?
plant mostly bright red, long tubular flowers without landing platforms
What is the advantage to a tomato plant in having green unripe fruit and red ripe fruit?
this lowers the chance that immature seeds are dispersed by animals
Early plants
-small
-no roots, stems, flowers, or seeds
-evolved from green algae (chlorophyta)
Order of seedless plant evolution
-Chlorophyta (green algae)
-Bryophytes
-Lycophytes (fern allies)
-Pteridophytes (true ferns)
Bryopyhtes
-Phylums Hepatophyta and Bryophyta
-next step from algae, need close water
-moist environments
-flagellated sperm need water
-no vascular tissue
-no true organs (stems, leaves, roots)
Bryophyte Life Cycle
-dominant gametophyte (haploid)
-diploid sporophyte grows and depends on dominant gametophyte
Where is the sporophyte the smallest?
In Phylum Hepatophyta (Bryophytes)
Phylum Hepatophyta (liverworts)
-simple body form
-rhizoids to anchor
-gametophyte forms archegoniophores and antheridiophores to produce gametes
-sperm fertilizes egg to form diploid zygote in archegonia
-sporophyte grows from zygote, still in archegoniophore
-sporophyte, thru meiosis, produces haploid spores
-haploid spores germinate to form haploid gametes
Commensalism
Benefit one, harm to other
antheridiophore
-male, in bryophytes
-disc shaped
-produce flagellated sperm
Phylum Bryophyta (mosses)
-erect body form
-no vascular system (no stems/leaves/roots)
-rhizoids to anchor
-archegonia and antheridia form at gametophyte tips
-sperm spreads by wind and water and swims to fertilize egg
-diploid zygote forms
-produces diploid sporophyte at female plant tip
Rhizoids
anchors, but does NOT absorb anything
Gemmae cups in Bryophytes
-for asexual reproduction
-gametes produced by MITOSIS
Importance of Bryophytes
-common starter species for poor soils
-common foundation for food chains
-wide distribution
Leaves come from
modified stems and branches
Cycad corraloid roots in symbiosis with cyanobacteria
Plants will provide nutrients/protection to the cyanobacterium
(ANABAEN, NOSTOC) which will provide fixe nitrogen and toxins to the plant
Example: Azolla is symbiotic with Anabaena
Plant Diseases Caused By Bacteria
Internal Defenses to recognize pathogen
Ex: Hypersensitive response and SAR
Plants Interaction with Fungi
Good: Mycorrhizal fungi. Decomposers that recycle nutrients from dead plant matter back to soil
Bad: Pathogens that cause diseases
What is a Fungi?
-Some Unicellular
-Most are multicellular and filamentous
Mycelium
Filaments aka HYPHAE make the body of the fungus (mycelium)
Mushrooms Eaten Are
Reproductive Organs of the fungus
Mycorrizhal
90% of plants benefit from it. Increases surface area for absorption. Plant will provide carbs to the fungus.
Fungal Mycelia
Help absorb phosphorus and nitrogen from soil
Ectomycorrhizae
have hyphae that do not enter into root cells
Endomycorrhizae
produce structures that enter root cells
Mycorrhizae inside plant roots come in two forms
Ectomycorrhizae
Endomycorrhizae
Pathogenic fungi
plant diseases are caused by fungi
Ex; mildews, rots, rusts, smuts, anthracnose
Plants have also developed mechanisms to resist
infections (coevolution for defense)
Monotropa
Completely heterotrophic
angiosperm that draws
nutrients from soil fungi.
Plants can be parasitic in fungi
Mutualistic Coevolution Between Plants and Animals
- pollination
- seed dispersal
- protection
Plant-animal coevolution strategies are important
to humans too
An apple orchard needs pollinating agents
for better yield
A squash garden needs pollinators to carry
pollen from male to female flowers
Self pollinating flowers
- Must be perfect flowers
- Anthers and stigma mature
at the same time
- Anthers can touch stigma
or placed above stigma
- Usually less colorful
Cross pollinating flowers
Show mechanisms that prevent self pollination and promote cross pollination
Mechanisms to promote cross pollination
- Stamens below stigma
- Imperfect flowers
-
- Self-incompatibility if
perfect flowers
- Male and female plants
Ex: Squash
Where does meiosis occur in the plant life cycle?
-diploid sporophyte produces haploid spores by MEIOSIS
-haploid spores develop into gametophytes
-gametophytes produce gametes by MITOSIS
-haploid gametes (female+male) come together to form genetically unique sporophyte zygote
How does meiosis increase genetic variation in plants?
Meiosis is a reduction division
-shuffles alleles in homologous chromosomes
-separates homologous chromosomes
-endless new allele combinations
-results in unique new cells
-produces cells with half the number of chromosomes
Result of Meiosis in Plants?
4 genetically different haploid spores
Meiosis events
-Meiosis I (PMAT I) Homologs seperate
-Cytokinesis I
-Meiosis II (PMAT II) Sister Chromatids seperate
-Cytokinesis II
3 Stages of Development in Flowering Plants
-Vegetative Stage
-Reproductive Stage
-Senescence
Vegetative Stage
-first stage of flowering plant development
-increase size
-produce more roots, leaves, and branches
Reproductive Stage
-second stage of flowering plant development
-produce flowers, fruits, and seeds for sexual reproduction
Senescence
-third stage of flowering plant development
-individual organs or whole plant wither and die
:(
What is the sexual organ in Angiosperms?
the flower
Flower Reproductive Organs
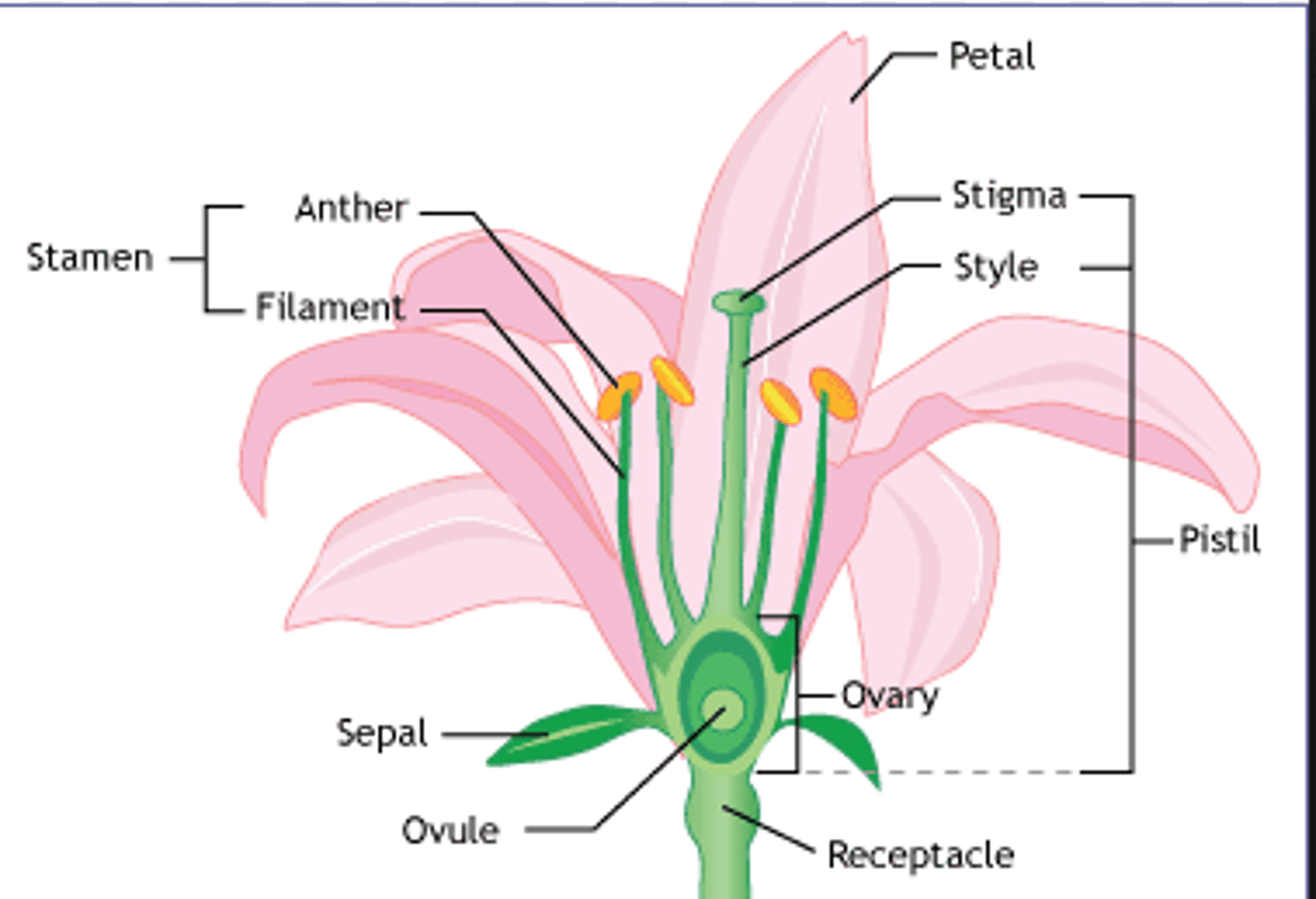
Pistil
-female part
-ovary and bottom
-stigma at top
-style connects ovary to stigma
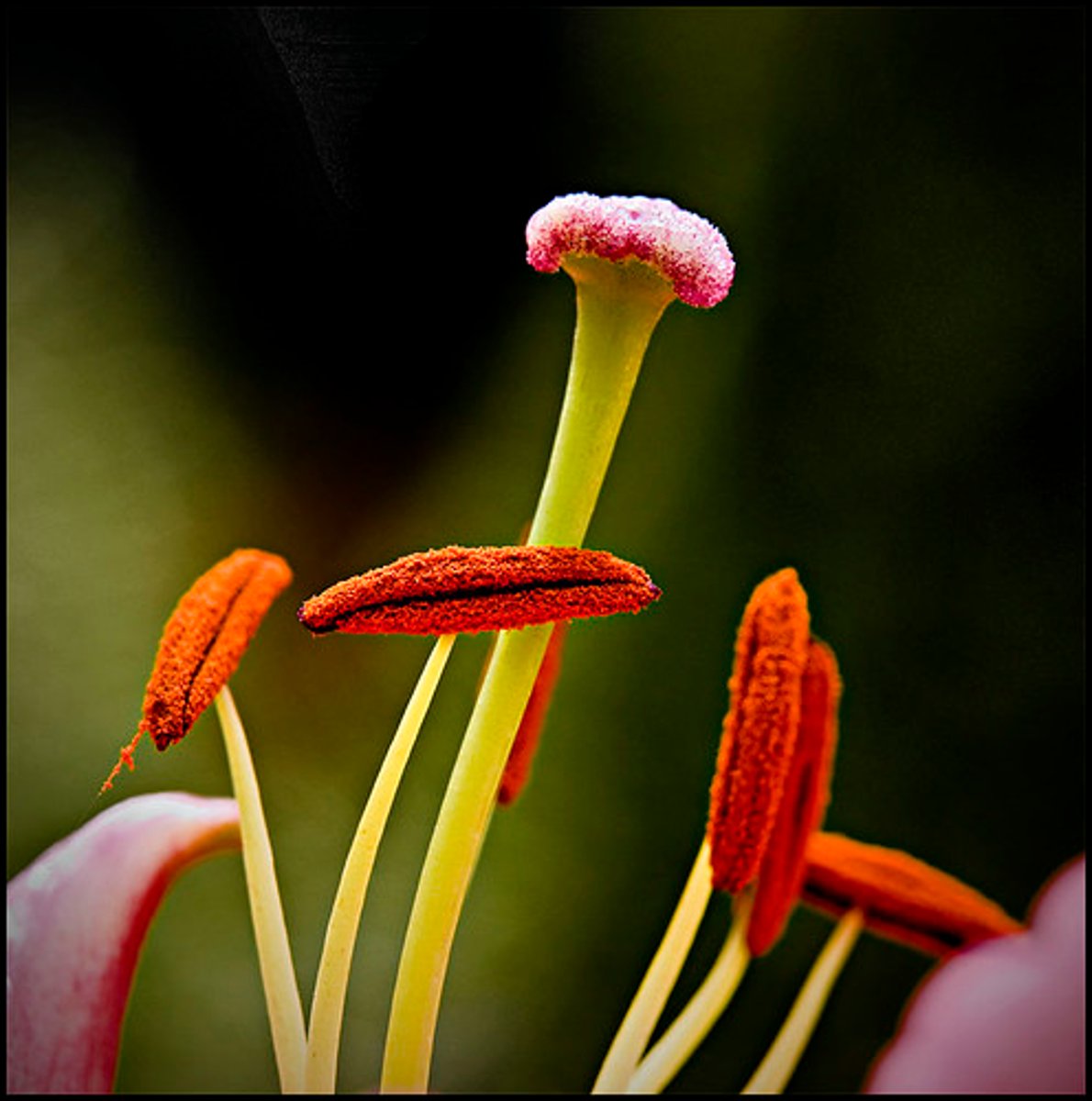
Stamen
-male part
-anther at top
-filament raises it to stigma

Perianth
petals and sepals
Receptacle
The base of a flower

What causes vegetative meristem to become floral meristems?
-Internal signals (hormomes/metabolites_
-Environmental cues (temp, day length, stress factors)
How is pollen formed?
-meiosis inside of MICROsporangia in anthers prodice microspores that become pollen
Pollen grains contain
-tube cell
-tube cell nucleus
-generative cell
How is pollen dispersed?
-by anther dehisence
-pollen grains land on stigma
-pollen tube grows inside the style to reach ovary
-after pollenation, g cell nucleus divides by MITOSIS to produce 2 sperm nuclei
-tube nucleus controls the pollen tube growth into an ovule
ABC Floral Development
-A only = sepals
-A and B = petals
-B and C = stamens
-C only = carpels
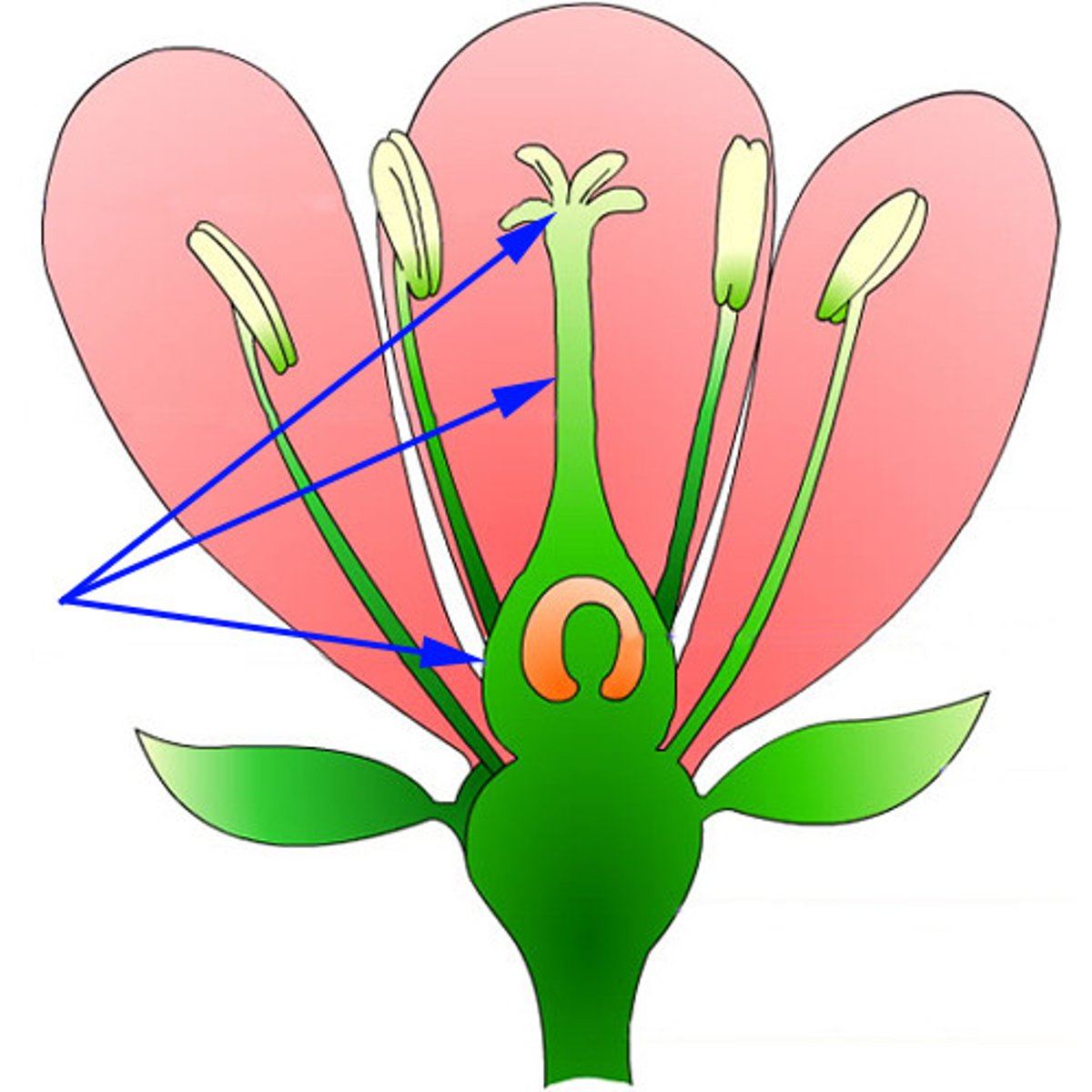
What happens in the ovule during sexual reproduction?
-meiosis inside ovule produces megaspore that develops into a female (mega) gametophyte
-pollen tube grows into ovule
-one sperm nucleus fertilizes the egg cell nucleus
Microgametophyte
-male
-2 cells inside pollen
-dispersed from sporophyte
Megagametophyte
-female
-few cells inside ovule
-contained and nourished within sporophyte
After fertilization in plants
-zygote is the fertilized egg
-embryo inside seed
-becomes future sporophyte
Zygotic Life Cycle
-in protists (algae)
-DOMINANT HAPLOID
-produce spores through MEIOSIS
-zygote is the only diploid stage
Gametic Life Cycle
-animals, some algae
-produce gametes directly through meiosis
-gamete only haploid stage
-DOMINANT DIPLOID