TCI Government Alive! Chapter 14
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Fiscal Year
The 12-month accounting period an organization uses for budgeting, record keeping, and financial reporting. (Runs October 1st to September 30th)

Balanced Budget
A spending plan in which the revenues coming into an organization equals its expenditures.
Budget Surplus
The amount by which an organization's revenues exceed it expenditures.

Federal Deficit
The amount by which the national government's annual expenditures exceed its revenues.

National Debt
The amount of money a country owes to lenders.

Deficit Spending
Government expenditures financed by borrowing rather than by tax revenues.

Impoundment
The refusal by a chief executive to spend funds that have been appropriated by the legislature.

Budget Resolution
An official statement outlining Congress's spending priorities for the annual budget.
Budget Cycle
The various steps of the government process, from planning to implementation.
Continuing Resolution
A joint resolution, passed by Congress and signed by the president, that allows the government to operate at current funding levels for fixed period; required when Congress and the president cannot reach agreement on a new budget.

Budget Crisis
A situation caused by the failure of Congress and the president to reach agreement on a new budget and that may result in the shout down of government programs.

Tax Freedom Day
The date, calculated each year, when the country has earned enough income to pay its annual tax burden; rising budgets have published this date back over time.

Individual Income Tax
A tax levied on the annual income of an individual or a married couple.

Social Insurance Tax
A tax used to fund government assistance to the elderly and to unemployed or disabled workers.

Corporate Income Tax
A tax paid by businesses on their profits each year.

Excise Tax
A tax levied on the sale of certain goods and services.

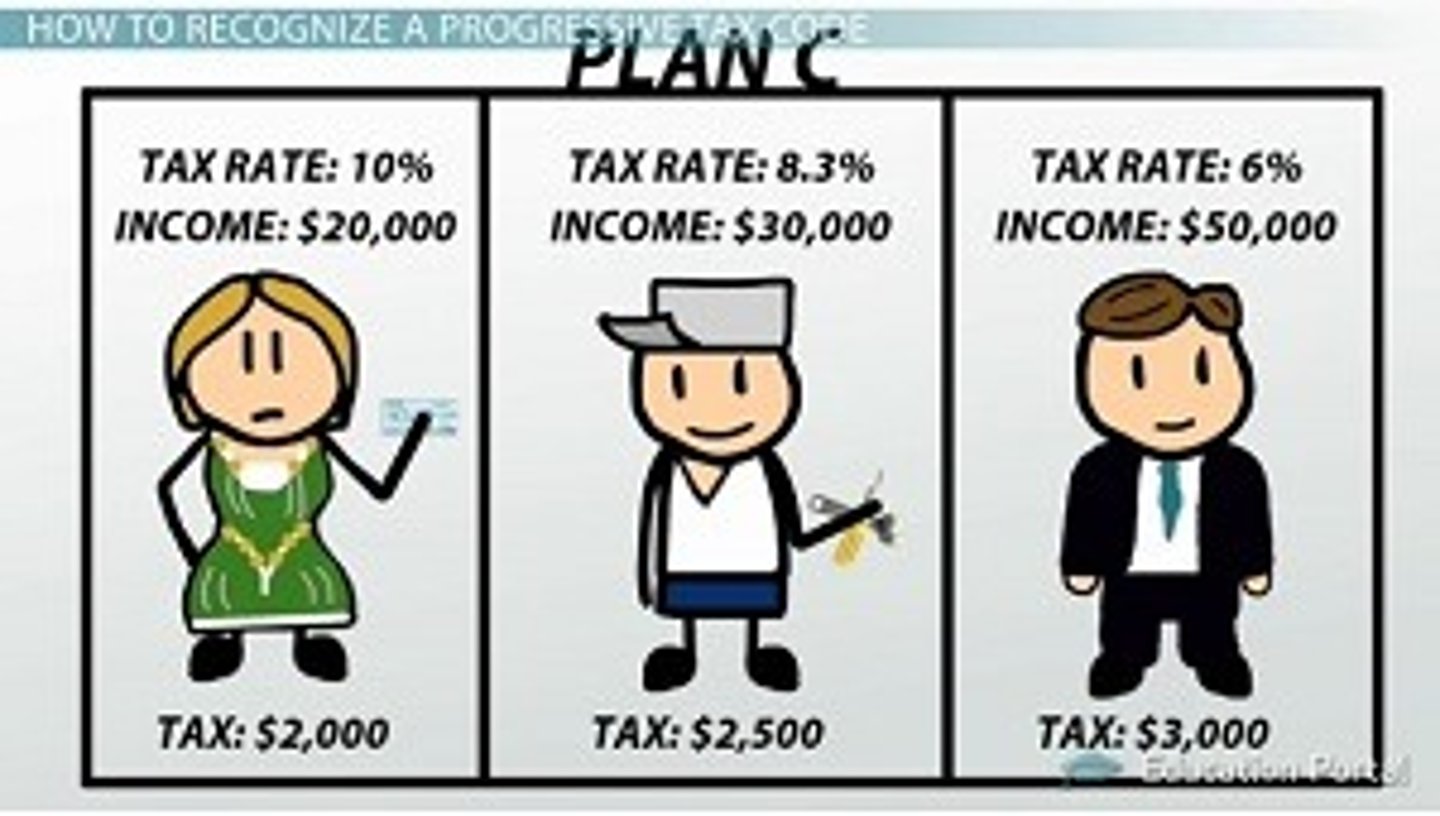
Progressive Tax
Any tax in which the burdens falls more heavily on the rich than the poor.

Regressive Tax
Any tax in which the burden falls heavily on the poor than the rich, at least as a percentage of their income.
Mandatory Spending
Government expenditures required by law to be allocated in specific ways.
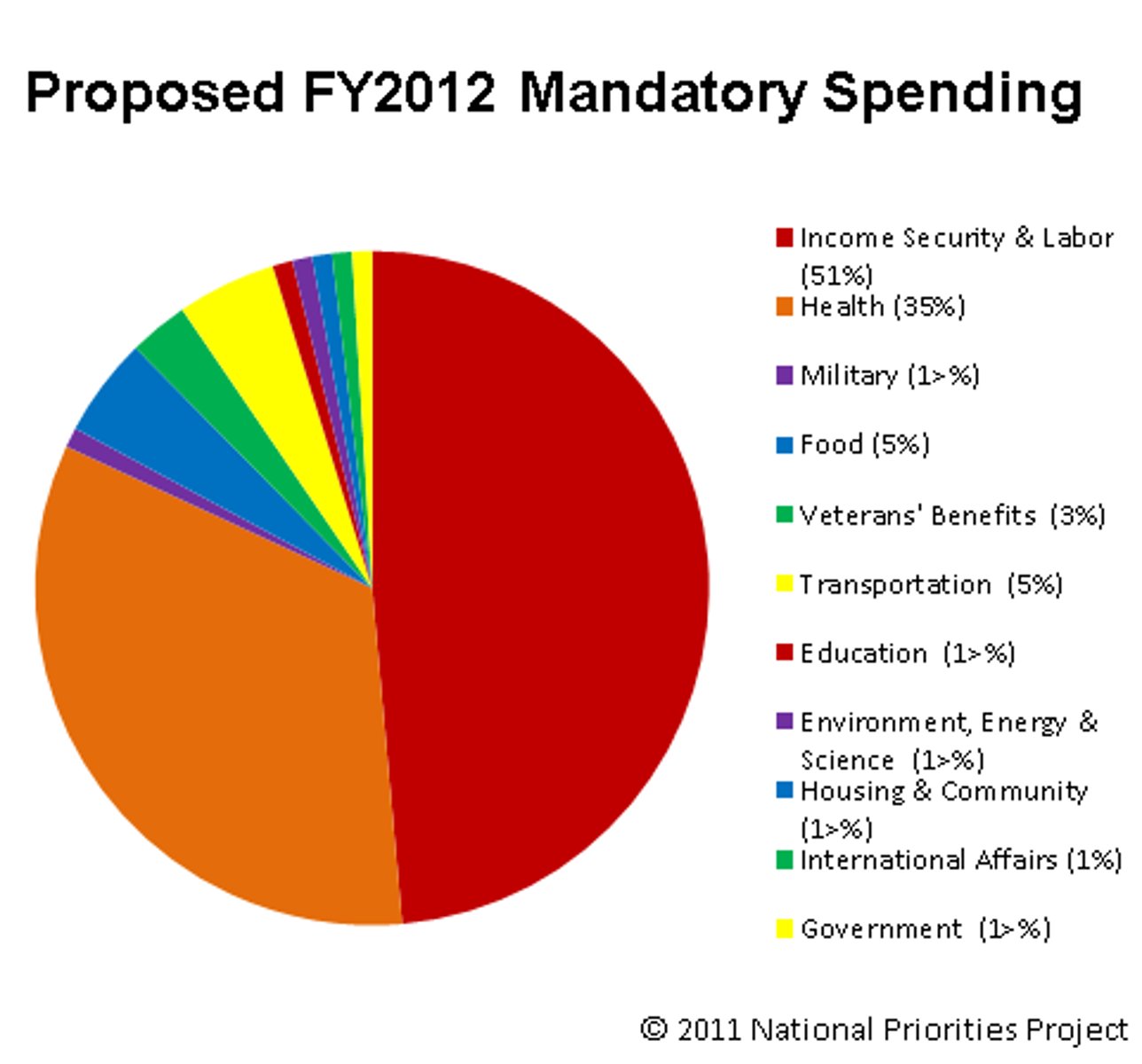
Entilements
Benefits that must be provided to all eligible people who seek them; examples include Social Security and Medicare.

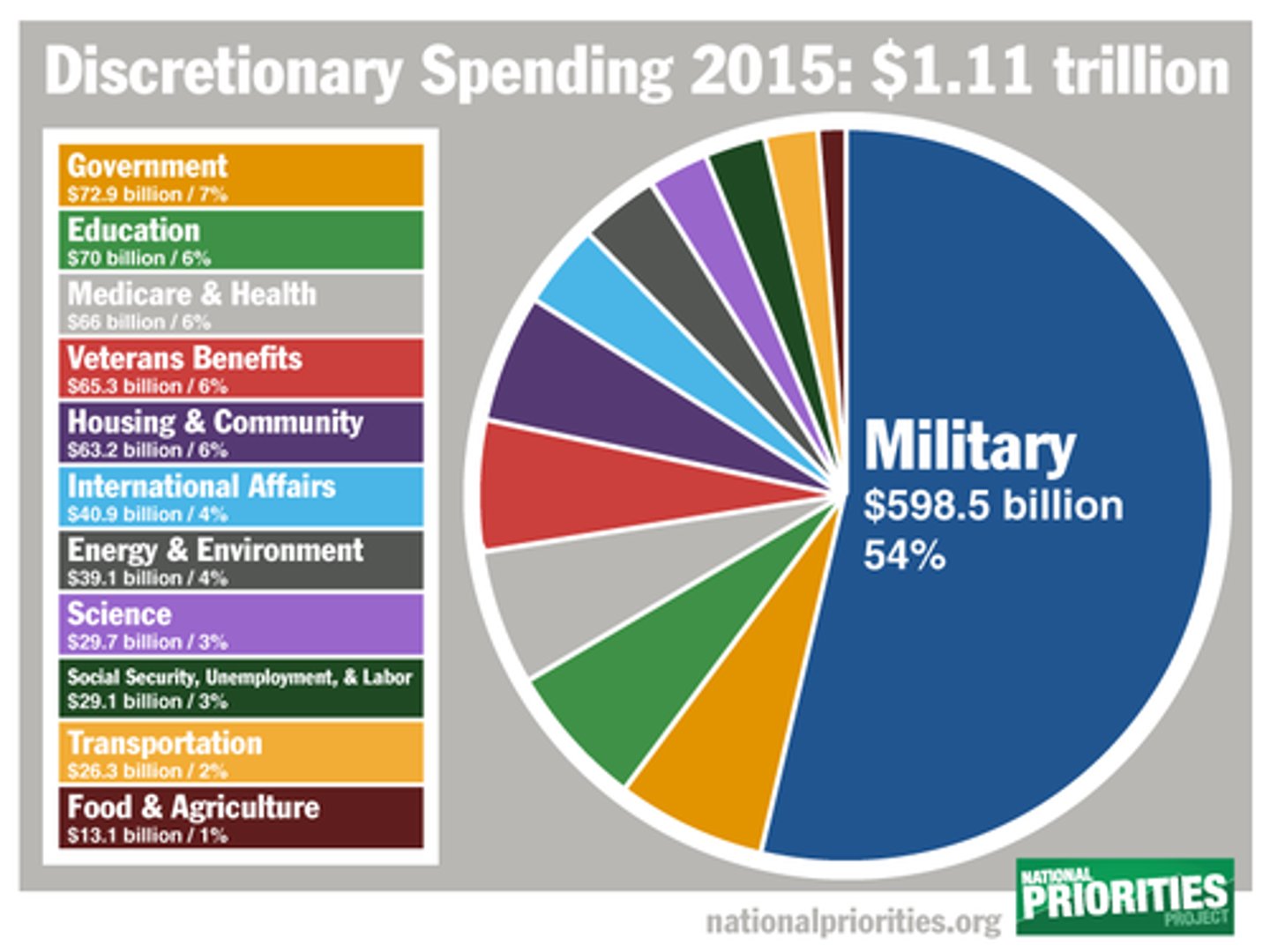
Discretionary Spending
Government expenditures that can be raised or lowered as determined by Congress.
Earmarks
Specific spending proposals that members of Congress attach to legislation, usually to benefit their home districts or states.

Classical Economics
an economic philosophy, originating with Adam Smith, that focused on how free markets and market economies work; this philosophy, which dominated economic thinking until the Great Depression of the 1930s, held that capitalism was self-regulating and required few government controls
Keynesian economics
a school of thought, pioneered by John Maynard Keynes, holding that government intervention in the economy is necessary to ensure economic stability; Keynesians support demand-side policies to revive economic growth
monetarism
a school of thought, based on the ideas of Milton Friedman, holding that changes in the money supply are the main cause of inflation and of economic expansions or contractions
stagflation
a combination of economic stagnation—or slowdown—and high inflation; features of stagflation include slow or zero economic growth, high unemployment, and rising prices
misery index
the sum of the inflation rate and the unemployment rate
expansionary fiscal policy
a policy designed to promote economic activity by increasing government spending, cutting taxes, or both
contractionary fiscal policy
a policy designed to lower inflation and cool an overheated economy by cutting government spending, increasing taxes, or both
demand-side economics
the theory that the best way to ensure economic growth is to stimulate demand by putting more money in the hands of consumers, either by increasing government spending or cutting taxes on lower-income earners, or both; this theory, which is associated with Keynesian economics, assumes that consumers will spend this additional money on goods and services, thus stimulating the economy
supply-side economics
the theory that the best way to ensure economic growth is to stimulate overall supply by cutting taxes on businesses and high-income taxpayers; this theory assumes that producers and investors will use their tax savings to expand production, thereby stimulating the economy
easy-money policy
a monetary policy designed to accelerate the rate of growth of the money supply in order to stimulate economic growth
tight-money policy
tight-money policy: a monetary policy designed to slow the rate of growth of the money supply in order to reduce inflation
reserve requirement
the regulation that requires banks to keep a certain percentage of deposits on hand at all times to repay their depositors
open-market operations
the purchase and sale of government bonds by the Federal Reserve for the purpose of regulating the money supply and controlling interest rates
fiscal policy
government policy regarding taxing and spending
monetary policy
central bank policy aimed at regulating the amount of money in circulation