Classical Greece
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
what was culture heavily influenced by in the Orientalizing period
Eastern Mediterranean and Near Eastern ideas, myths, and decorative styles
when was the Greek colonization into Western Mediterranean
Orientalizing period
what were two changes seen in the Orientalizing period
Mould Making
Papyrus importation
order the different Greek periods
Classical
Dark Ages
Geometric Period
Orientalizing Period
Archaic Period
High Classical
when does the Archaic period end
with the defeat of Persians
what did the classical period of the archaic see
more documentary and textural evidence
what period was the basis for democracy established in Athens
Archaic period
what were Solon’s reforms
abolished debt slavery
laws to protect the poor
bolster commerce in Athens by allowing skilled foreigners to settle in the city
what was the archaic period a mix of in turns of ruling
a mix of tyranny and factional strife
how did the polis change in the archaic period
became fully developed with defined body and a constitution
describe the constitution of the polis
it was independent of outside authority
what were some characteristics of the polis
self governance
autonomy
independence
citadel, temples, altars
urban planning
gymnasia
theatres
coins
political life (laws, criminal trials)
social classes
what are the order of column parts
base → shaft → capitol → entablature
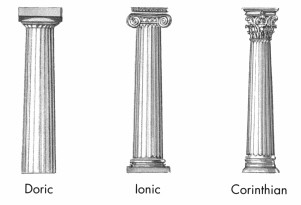
what are the three types of columns
doric
ionic
corinthian
contrast the three types of columns
doric
oldest, shortest and simplest
sturdy, unadorned columns
no base
Ionic
stand taller and are more slender than Doric
capital is characterized by two large, volute-shaped scrolls
Corinthian
most elaborate and ornate
similar to Ionic columns in their slender proportions and the number of flutes
capital is adorned with leaves, entwined with tendrils and flowers
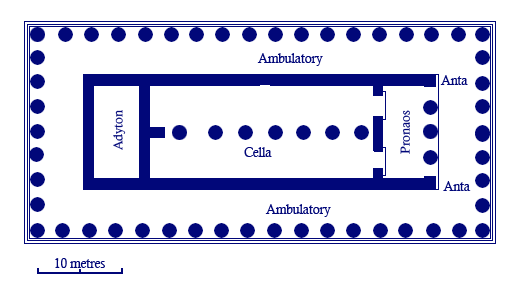
what is the standardized temple plan
external colonnade wraps around all sides
central Cella
False porch at one end (for symmetry)
Porch at the other end
what two things is the temple of Hera associated with
Disc of Iphitos
table of Kolotes
Disc of Iphitos
contained the treaty that established the Sacred Truce for the duration of the ancient Olympic Games
table of Kolotes
displays the wreaths of wild olive for crowning olympic victors
contrast the temple of zeus and great altar of zeus
Temple of Zeus
enclosed house for the god's image
one of the 7 Wonders of the World
Altar of Zeus
open platform for the act of sacrifice
place lightening strike hit the ground
who was the sculptor of the temple of zeus
Pheidias
where were the olympics first held
Olympia
what marked the beginning of the self conscious greek identify
Olympics
what was the oldest panhellenic game
Olympic Games
what was the main sport of the Olympics for the first 13 years
foot race
what art style emerges during the archaic period
foundation for what we now call Classical Greek art
major artistic style that emerges of the archaic period
naturalism
what was the experimental period of art
period mixing the geometric styles with Orientalizing styles
what were large scale standing marble statues used for
dedications in temples, tombs and public spaces
kouros vs kore
kouros - nude male statue
kore - draped female statue
what country had major influences on kore and kouros
Egypt
what do kore and kouros statues demonstrate a movement towards
realism
what are pediments
triangular space above the horizontal structure of a building's façade holding carvings
black vs red figure painting
black
FIRST developed at Athens
figures: Black silhouettes.
background: red-orange color of the fired clay
details: scratched through the black slip to reveal the red clay beneath.
Red
figures: natural red-orange color of the clay
background: glossy black covering
details: Painted directly onto the red clay with thin lines of black

black and red figure painting are essentially what of each other Black silhouettes.
reverse techniques of one another
which columns first saw black figure paintings
Corinthian
what was the high classical characterized by
idealized human form, balance, and democracy
describe the Athenian Society
patriarchy: men held all rights and advantages, such as access to education and power. Athenian women were dedicated to the care and upkeep of the family home
which society saw the aristocratic government slowly become democratic
Athenian
what was the basis of Athenian society
oikos (household)
what governments were the spartan society a mix of
monarchies
oligarchic
democratic
what were the different classes in the spartan society
Spartiates
Spartan citizens, who enjoyed full rights
Mothakes
non-Spartan, free men raised as Spartans
Perioikoi
free, but non-citizen inhabitants
Helots
state-owned serfs, part of the enslaved
how many kings did the spartan society have and why
two hereditary kings equal in authority
to have checks and balances
ensure 1 ruling lives if one dies at war
what was the spartan society oriented towards
warfare
what were some rights women had in Spartan society
property owning
equal rights in divorce
marriages were later
lighter clothing
when did state education of spartan boys start
7 years old
Importance of Olynthos
best archaeological source for the study of Classical Greek households
what kind of plan did the Olynthos have
Hippodamian
what was significant of the Villa of Good Fortune
largest of the houses discovered at Olynthos
mosaic floors
what is an andron
part of a Greek house that is reserved for men
what is important to remember about the Acropolis
was completely destroyed by persians = totally rebuilt later
who spearheaded the rebuilding of the Acropolis
Pericles
what were some buildings rebuilt at the Acropolis
Parthenon
Propylaea
Temple of Athena Polias
Temple of Athena-Nike
what was the high point of architecture under Pericles
Parthenon
describe the format of the Parthenon
8 columns across front and double row on sides
no false porch
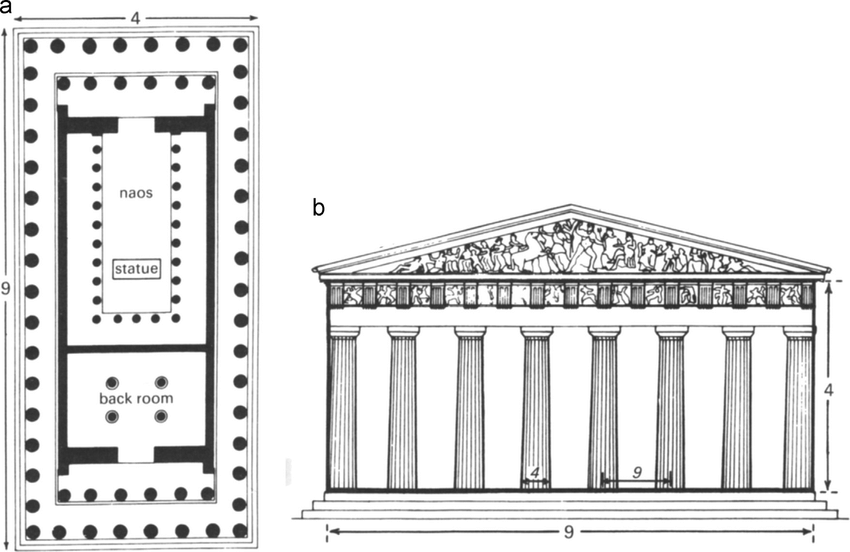
what did refinements see
deviations from Greek norm and mathematic regularity in favour of overcoming optical illusions of straight lines
what were noteworthy features of 5th century art
simplification of forms
return to plain Doric garments
interest in motion/emotion
contrast the start and end of 5th century art
start
lingering archaic style (forced smile)
severe style
tight hold on Phidian style
end
loosening of Phidian style
more elaboration of details
what changes were seen in 4th century art compared to 5th century
better execution
more complicated
posture (knee bent(
Numismatics
coins
how was one drachma
from six rod shaped obeloi
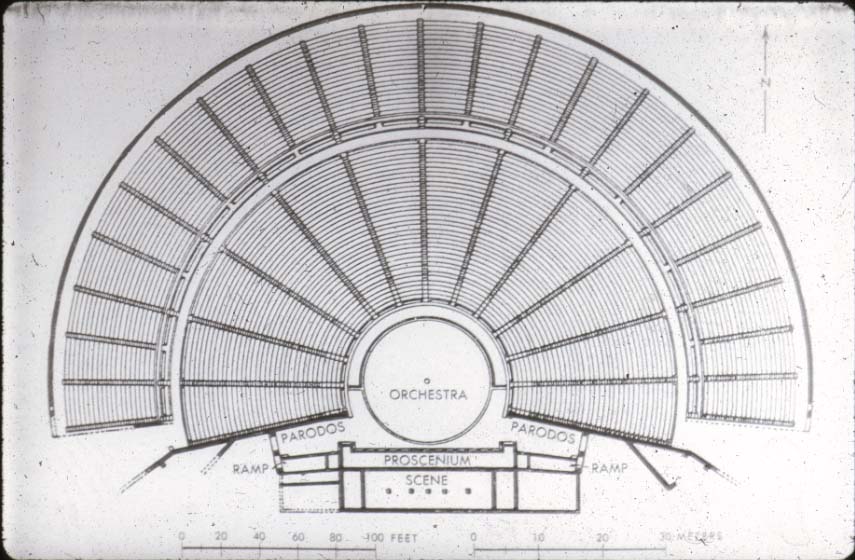
what was the theatre at Epidaurus set into
slope of a hill which was easier to build the arc
which god had a statue in the orchestra at the Theater at Epidaurus
Dionysus
three parts of a theatre
Theatron - seating area
Orchestra - where actors or chorus preformed
skene - backdrop or scene wall
summarize what happened to King Philip II of Macedon
he was very expansionist
getting ready to punish the Persians
he was murdered
who reigned after King Philip II of Macedon
Alexander the Great
what kind of cities did Alexander the Great erect
Greek or Greek-like cities
what is the key aesthetic of the Hellenistic era
realism
what art styles are foundational for Roman styles
Hellenistic
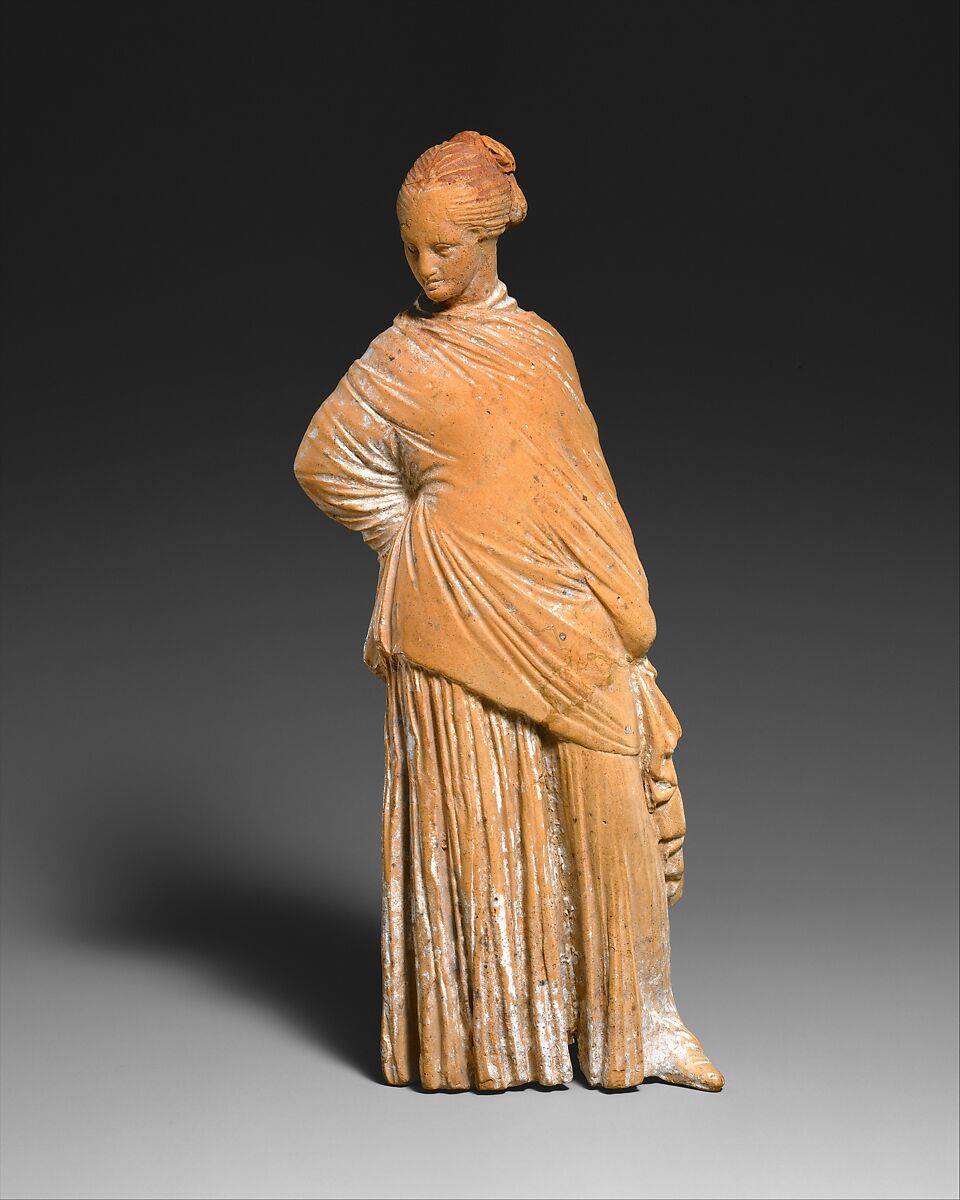
what are Tanagra Figurines
they were mold made figurines of mostly women and likely souvenirs from the theatre
