.1) General principles of cell communication AND membrane receptors
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
paracrine signalling
secreting cell secretes to nearby cells
Autocrine signalling
Secreting cell is same as target cell
Hormone exits cell then enters cell
Endocrine signalling
Secrete into circulation to target cell e.g. pancreas beta cells secreting insulin
Juxtacrine signalling
Secreting cell targets adjacent cell
Intracrine signalling
Hormone targets secreting cell and stays within cell
Milestones in receptor biology

Otto Loewi experiment
Evidence for receptors
Isolated two frog hearts and placed each of them in a chamber filled with saline
Connect them with a tube
Measure heart rate
Stimulate vagus nerve of one heart to slow down
After a delay the second heart gets stimulated
Hypothesis: electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve released a chemical into the fluid of chamber 1 that flowed into chamber 2. He called the chemical “Vagustoff” which we now know is the neurotransmitter ACh
Henry dale
Isolated ACh from ergot (fungus)
Isolated ACh from human body
Proved with Loewi that ACh is a neurotransmitter
ACh receptors
ACh receptors can have different effects
Can become ion channels
Agonist - compounds that produce the same effects as the neurotransmitter
Antagonist - blocks active site but has no response
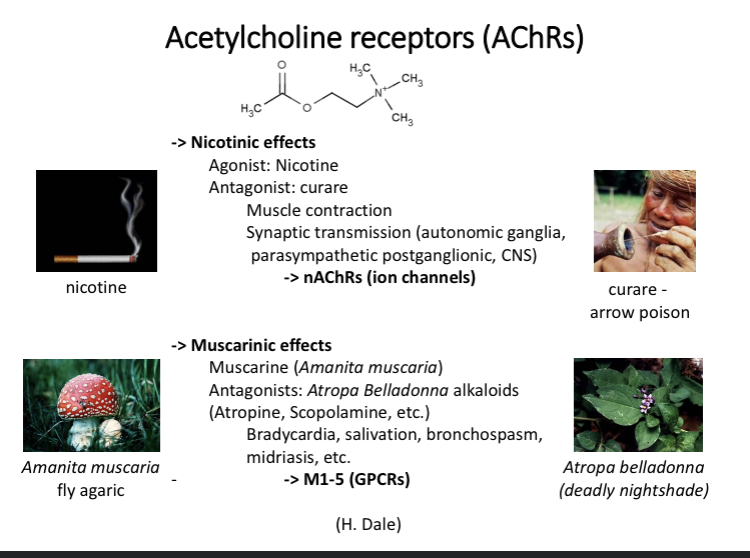
Nicotinic AChR
Nicotinic AChR - two extracellular domains (binding sites) for ACh
Pentametric ion channel - 5 different subunits
transmembrane portion - alpha helices and intracellular domain
muscle stripe
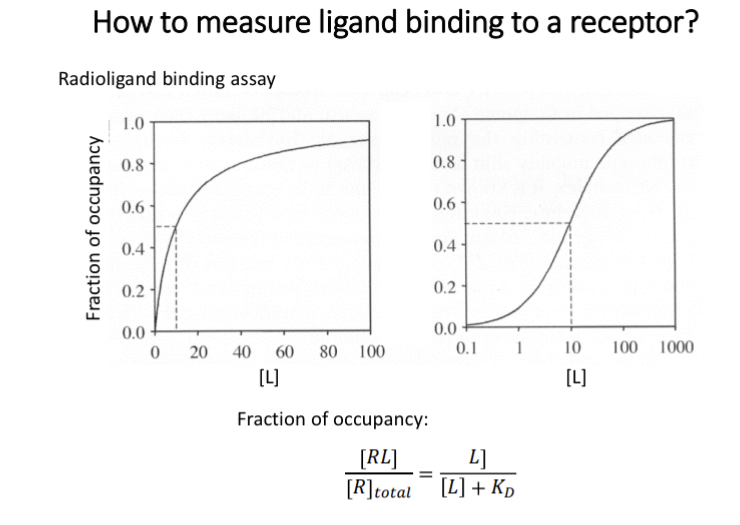
Radioligand binding assay
incubate to allow binding
wash excess ligands
radioactivity proportional to number of receptors that have ligands bound
can measure affinity at a concentration of ligand

Affinity
How strongly a certain compound binds to a receptor
Affinity = 1 / KD
KD (equilibrium dissociation constant) - 50% of receptors occupied by ligand
Lower KD has a greater affinity
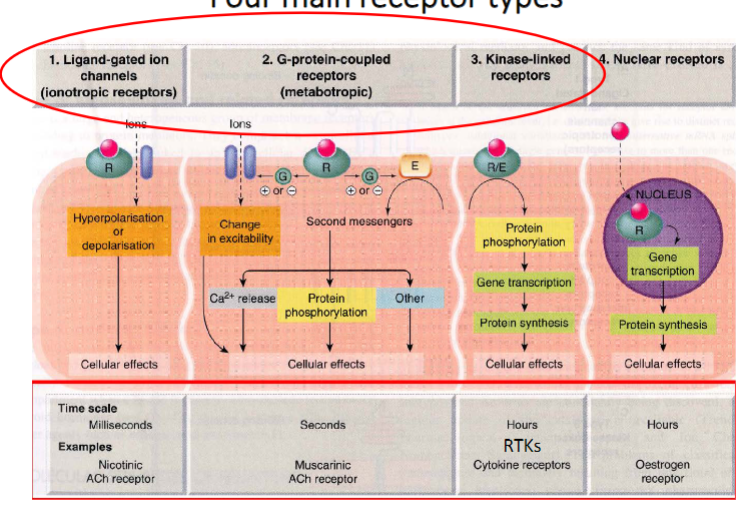
Types of receptors
Ligand gated ion channels (ionotropic)
milliseconds
Nicotinic ACh Receptors
G coupled protein receptors (metabotropic)
seconds
Muscarinic ACh receptors
largest family of membrane receptors
Kinase linked receptors
hours
Cytokine receptors
Nuclear receptors
hours
Oestrogen receptor
Kinase linked receptors
Summary:
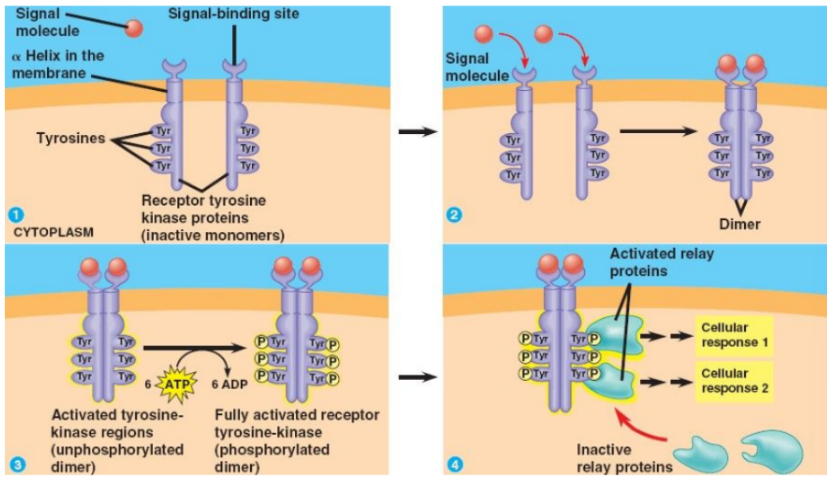
GF (1st messenger) binds to receptor
Causes dimerisation of receptor
Tyrosine kinase regions are activated and become phosphorylated (6 x ATP)
(Receptor tyrosine kinase) RTK is now fully activated
Cellular proteins become activated which causes a cascade which initiates a cellular response
Speed: Slow
Example: Tyrosine kinase receptor
If these receptors are mutated, they cause cell proliferation and so are often implicated in various form of cancer.
kinase
Phosphatase
Kinase - adds phosphate
Phosphatase - removes phosphate
GPCRs
Mediate effects of many hormones and neurotransmitters
When G proteins are inactive they contain a nucleotide GDP
Alpha subunit contains enzymes which hydrolyse GTP to GDP to stop the reaction
GPCR typically have 7 alpha helixes and spans the plasma membrane 7 times
have alpha, beta and gamma subunits
Types of G proteins
G alpha s - activates adenylyl cyclase (AC)
- opens calcium ion channels in some tissues
ATP —AC→ cAMP—cAMP phosphodiesterase → AMP
G alpha q - activates phospholipase C
G alpha i- inhibits AC
G alpha 12/13 - regulates small g proteins for cytoskeleton contraction
G beta gamma - regulate ion channels and enzymes like PLCb
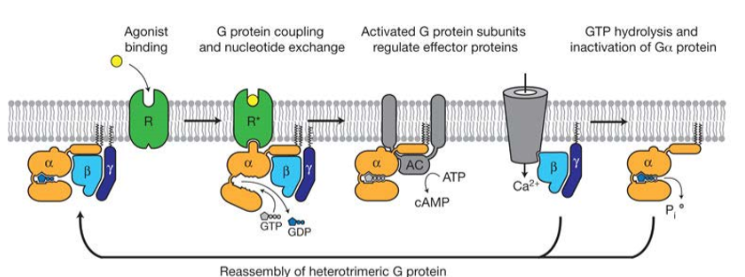
GPCR mechanism
agonist binds to receptors causing a conformational change allowing it to bind with the heterotrimetric G proteins
causes G protein to open and GTP binds to alpha subunit displacing GDP
G protein dissociated with receptor and alpha subunit separates from beta and gamma
subunits interact with other effectors initiating a biological response
alpha subunit hydrolyses GTP to GDP……
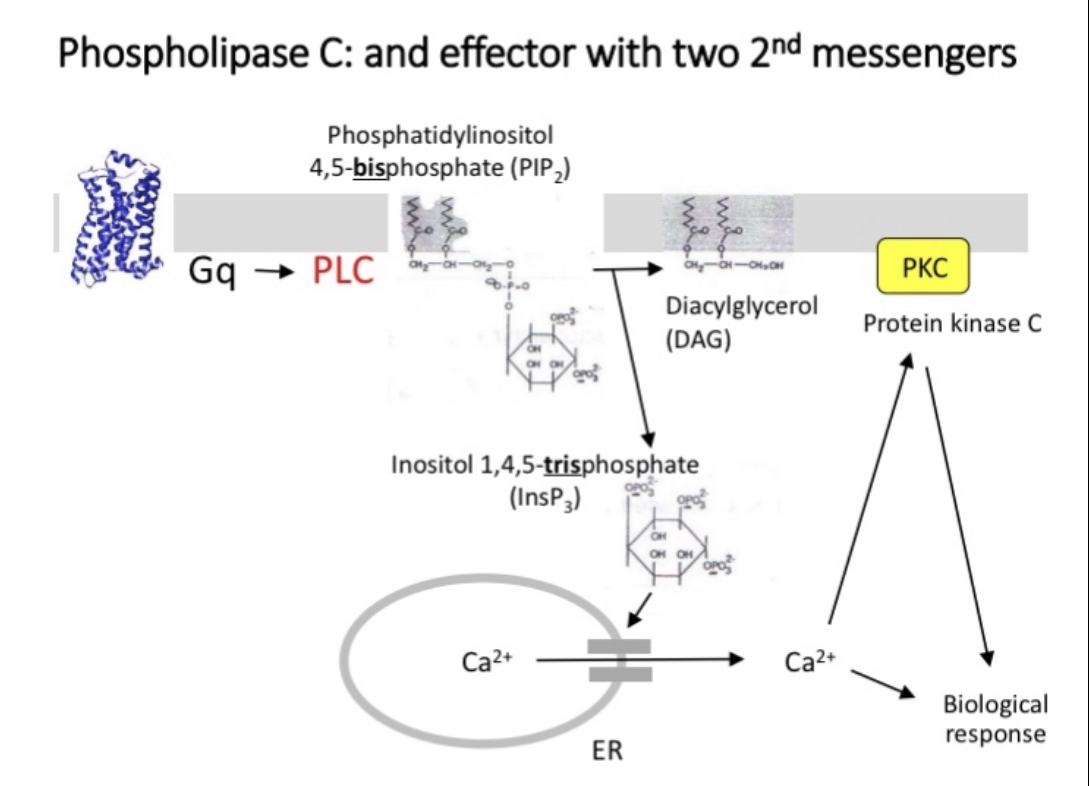
Phospholipase C (PLC)
PLC cleaves a membrane phospholipid, PIP2, to give two secondary messengers (IP3 and DAG)
DAG remains in cell membrane and attracts and activates protein kinase C
Calcium signalling
G protein dependent opening of ligand gated ion channels
Release of intracellular stores of calcium in ER mediated by release of IP3
Calcium acts as a secondary messenger activating calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase
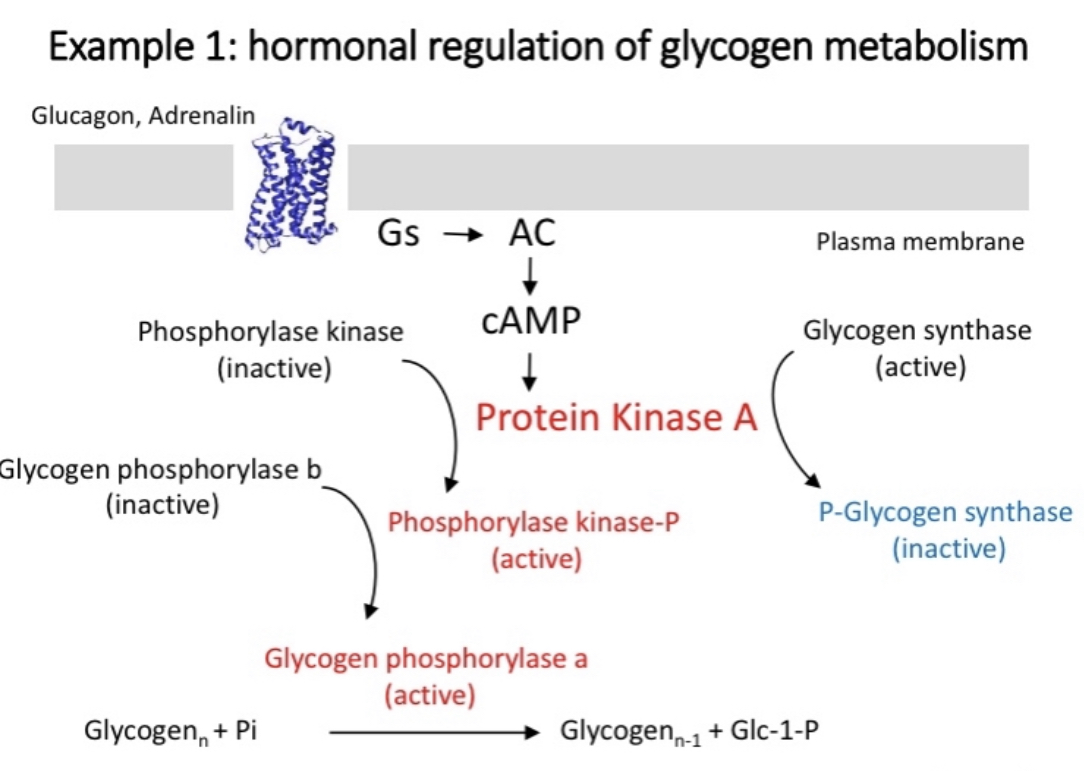
Example 1
Hormonal regulation of glycogen metabolism
Glucagon or Adrenaline binds to G alpha s
Activates AC
converts ATP to cAMP
Causes release of protein kinase A
Cascade of reactions converts glycogen to glucose
Same process inactivates glycogen synthase
cAMP phosphodiesterase keeps the reaction controlled by degrading cAMP to prevent the reaction from reoccurring, cAMP to AMP
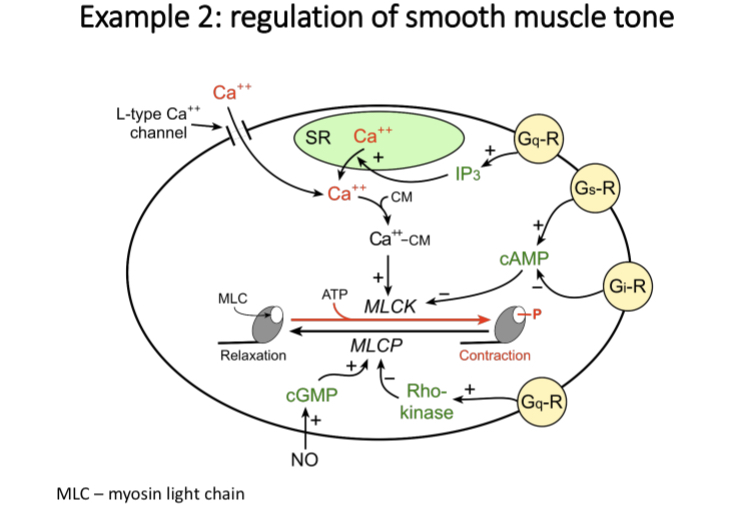
Example 2
Regulation of smooth muscle tone
Calcium bind with calmodulin and the complex stimulates myosin light chain kinase (MLCK)
Phosphorylates myosin light chain
Myosin light chain Phosphatase (MLCP) removes phosphate group
G alpha s induces muscle relaxation
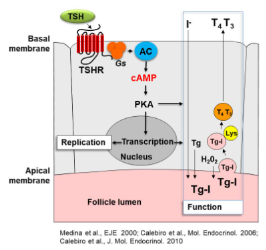
Example 3 - real life
TSH receptor signalling in the thyroid - Gαs
1) TSH (released via pituitary gland) binds to Gs-protein coupled receptors on the surface of thyroid cells leading to the production of cAMP which activates PKA 🡪 CREB activation (TF)
2) This leads to an increased replication of thyroid cells and it also induces the synthesis and release of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream.
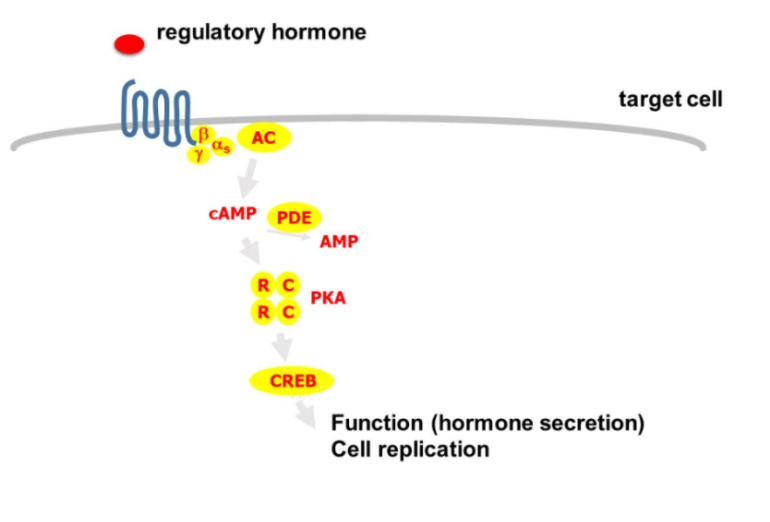
cAMP/PKA pathway
alpha subunit interacts with AC.
AC converts ATP into cyclic AMP which binds to protein kinase activating Protein kinase A (PKA)
The activated PKA enters into the nucleus and helps activate CREB (transcription factor)
This induces a response which results in the secretion of hormones or cell replication.
PDE also degrades cAMP converting it into AMP to shut off signalling cascade.
Effects of cAMP/PKA pathway in endocrine cells
Increase hormone secretion
Under prolonged stimulation - increased cell proliferation
TSH receptor
Autonomous thyroid adenoma (ATA)
TSH is secreted by anterior pituitary
ATA - cause hyperthyroidism
- benign tumours caused by activating mutations in TSHR gene (somatic mutation)
TSH resistance - inactivating TSHR mutations
complete (very rare) - homozygous, severe congenital hypothyroidism
Partial (common) - heterozygous, mild hypothyroidism
Cushing syndrome
Mutation in PKA C subunit
Adrenal tumour
GPCR animation