AS103 Astronomy Final Exam
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
how does the use of the word “theory” differ from its everyday use?
science: theory is tested and reliable set of ideas. Everyday: a guess
what does it mean to say that a theory should be “falsifiable” as opposed to being “proveable”
a theory must make testable predictions, which may be wrong. But it cannot “prove” unless all possible solutions have been tested
why do we see things in the night sky as they were in the past, instead of right now and why doesn’t this matter in daily life?
things are light years away and takes a long time for their light to reach us. It doesn’t matter in daily life because the amount of time that has passed is not very significant
how many total constellations are there
88
what do we call the 12 constellations the sun travels through
zodiac constellations
an astronomer thinks of a constellation not as a stick figure but as what?
an area of the sky
what point on the meridian do the constellations rotate around
NCP for us (or Polaris)
which way is the moon’s orbital motion
it orbits in the same sense as the Earth’s rotation
what naked eye observation led to the development of solar system models in the first place
the retrograde motion (or any motion), “wanderers”
Early (Ptolemaic) models put what object at the center
Earth at the center
Later (Copernican) models put what object at the center
Sun at the center
is the celestial sphere we used in lab Ptolemaic or Copernican model?
Ptolemaic (geocentric) model
the same force applied to both the Earth and the Moon produces very different accelerations. What is the reason for this difference?
larger mass = smaller acceleration. (F = ma)
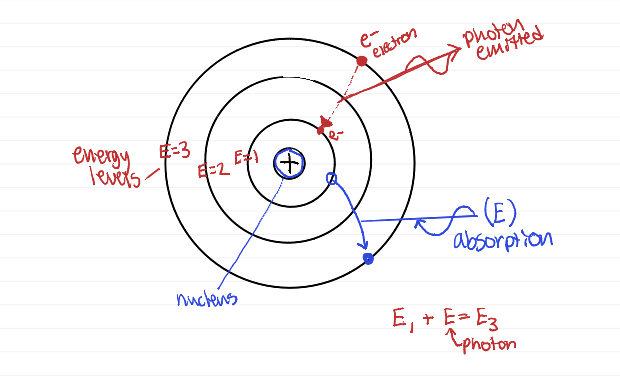
equation that relates the initial and final energies of the system (photon emission)
conservation of energy: E initial = E final (example: E3 = E + E2)
description of an equatorial mount
declination can be fixed, telescope turns to follow objects in the sky.
Advantages of equatorial mount
easier to take pictures and easier to follow objects in the sky
advantages of alt az mount
strong
description of alt az mount
axes parallel/perpendicular and zenith aligne
what is the universality of physical law
physics laws observed on Earth are assumed to be the same everywhere
Why do you see stars in the past
very far distance, light years away.
distance angle formula
D = 2πd(α/360)
time for light to reach somewhere formula
T = d/c
What causes the diurnal motion of the stars and constellations across the night sky?
Earth’s daily rotation
What causes different constellations to appear at night in different seasons?
orbit (revolution) of Earth around the Sun
What causes seasons?
inclination of Earth’s spin (rotation) axis from direction perpendicular to the plane of the orbit (23.5)
why are you more likely to see a lunar eclipse than a solar?
Solar is along a narrow path and lasts a few mins. Lunar is visible for hours from entire night side of the Earth
Why don’t we get an eclipse every new/full moon?
Earth, Moon, Sun must align both in the plane of Earth’s orbit and perpendicular to the plane. (line of nodes) Also: shape, tilt, and orbit are not perfect.
what does it mean to say the moon orbits synchronously with respect to Earth?
The orbital and rotational periods are the same
What is one piece of evidence that ancient astronomers had that the Earth is a sphere?
gradual disappearance of ships hull with distance. Varying height of pole star with geographic location. shadow edge on Moon during lunar eclipse
Solar eclipse diagram
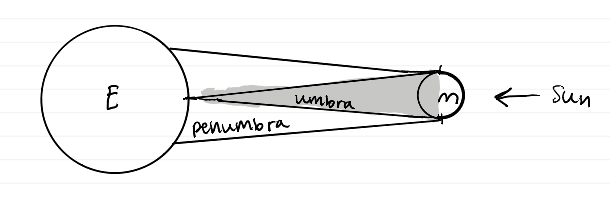
lunar eclipse diagram
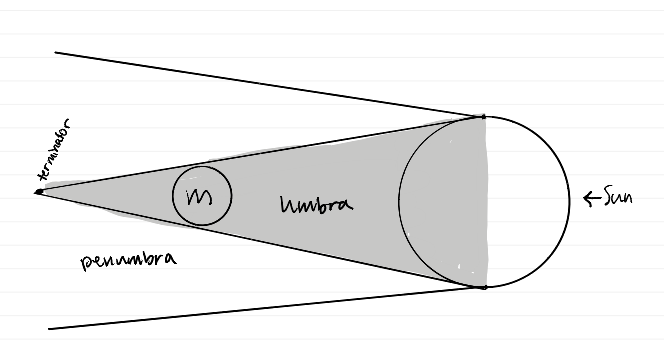
why don’t we have eclipses all the time (diagram)
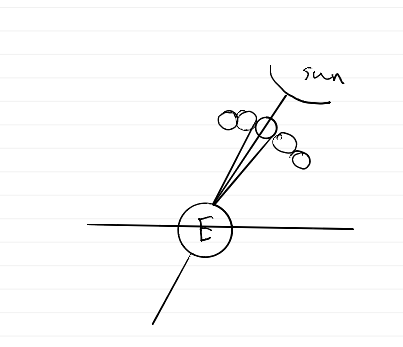
diagram showing synchronously orbits
horizon label diagram
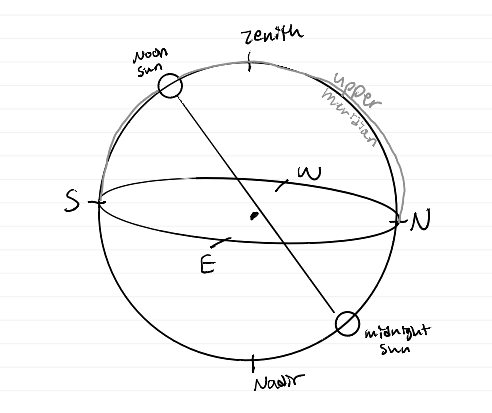
diagram showing solstices and equinoxes
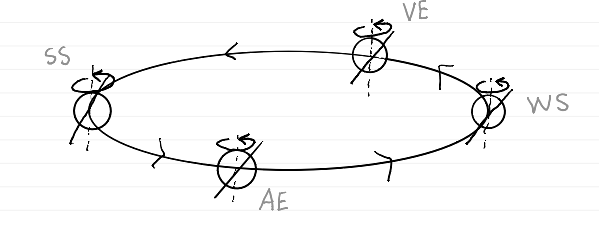
moon phases diagram

Why do we say that astronomy often deals in extremes?
the universe has extreme temps, distances, energy
Why is it so important to understand the properties of light?
to be able to calculate distances
What force is most important on astronomical scales?
gravity
why the moon always shows the same face to Earth.
synchronous rotation. moon rotates once each time it orbits the Earth
celestial sphere diagram
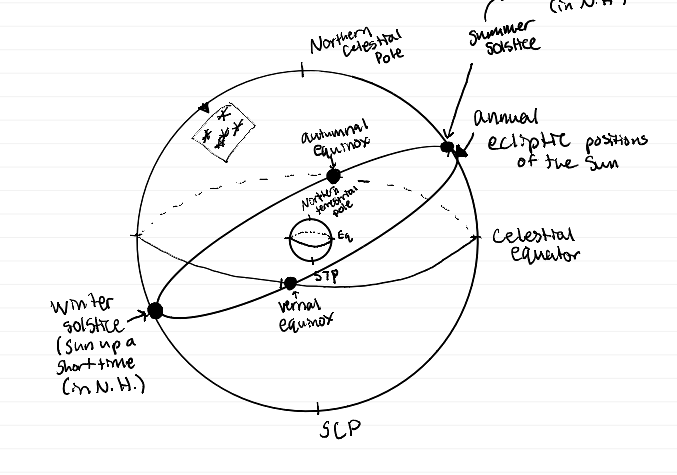
what does right ascension correlate with
longitude
what does declination correlate with
latitude
difference between solar and sidereal day
solar is 4 minutes longer. solar based on sun getting from high to high point in day. sidereal based on certain star crossing meridian.
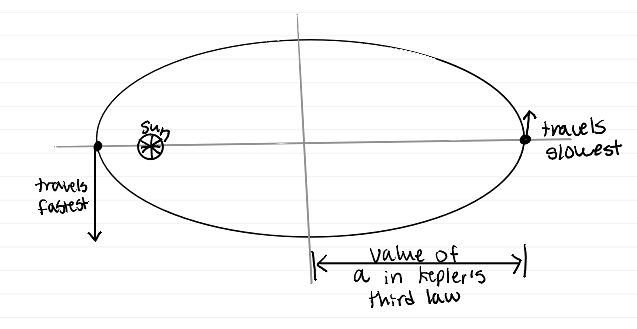
Planets’ orbits are
elliptical with the sun at a focus
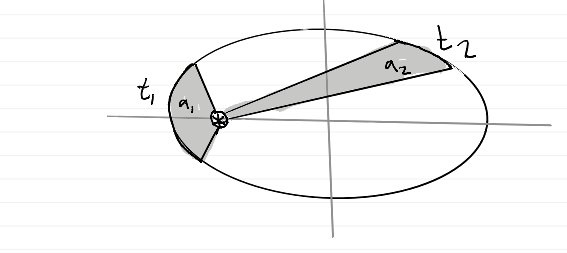
The line between a planet and the sun sweeps out
equal areas in equal times
A complete orbit has P^2 = a^3, where P and a represent
sidereal orbital motion (yr) and semi major axis (Au) (conservation of angular momentum)
Newton’s first law
an object’s velocity will remain constant if there is no net external force acting on it
Newton’s second law: the acceleration of, mass of, and net force on an object are related as (equation)
acceleration = net force / mass (F = ma)
Newton’s third law
the action and reaction forces between two bodies are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ΣF12 = -F21
Why do we say that an object traveling at constant speed on a circle is accelerated, even though its speed is not changing?
its direction of motion is changing. acceleration is a change in velocity and velocity is speed and direction
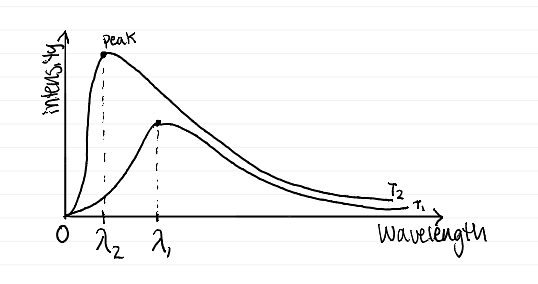
SB law says
total emission is proportional to T^4
Wien’s law says
different temperatures peaks at a wavelength is inversely proportional to the temperature
What is special about the Kelvin/absolute scale?
kelvin has zero temperature at minimum molecular kinetic energy. As cold as you can get. Energy is proportional to temperature. (more convenient)
What is conservation of energy
initial energy = final energy
Equation that relates initial and final energy of system (e- jumps from level 3 to level 1)
E1 + E = E3
Why is it possible to use the emission/absorption spectra of atoms to identify what element the atoms are?
the spectra (the photons) are unique to each element or chemical compound
What is the biggest obstacle to Earth-bound viewing in astronomy?
the atmosphere
Why are telescopes placed in high locations?
to get above some of the atmosphere. (less absorption)
Why are telescopes placed in remote locations?
darker, less light pollution (reflection)
What are two main types of telescope mounts
Altitude-azimuth, equatorial
How is alt-az aligned
zenith aligned
How is equatorial mount aligned
polar aligned
Which mount can carry the most weight
altitude-azimuth
Which mount is easier to use for taking pictures
equatorial
Rank eye, photo film, CCD based on sensitivity, linearity, data analysis
poor: eye, good: film, excellent: CCD
If you increase the diameter of telescope 3 times, by what factor does the image brightness change
B α D^2 … B’/B = (3D)^2 / (D)^2 = 9
If you increase the diameter of telescope 3 times, by what factor does the image resolution change
R α D … R’/R = 3D/D = 3
Rank the importance of magnification, brightness, and resolution
brightness=1, resolution=2, magnification=3
Is magnification improved by a larger diameter?
no
Is brightness improved by a larger diameter?
yes
Is resolution improved by a larger diameter?
yes
Mathematical relation to diameter (magnification)
none (D^0)
Mathematical relation to diameter (brightness)
D^2
Mathematical relation to diameter (resolution)
D^1
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with construction
reflector
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with spherical aberration
they perform the same
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with chromatic aberration
reflector
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with atmospheric transmission
they perform the same (relates to location)
Which telescope (reflector or refractor) performs better with light pollution
they perform the same (relates to location)
Why do we sometimes speak of light as rays and sometimes as "electromagnetic waves"?
they can behave as particle and have magnetic field. Light travels in a straight line
Why do we have to use the absolute temp scale in describing blackbody radiation
because this scale is based on thermal energy
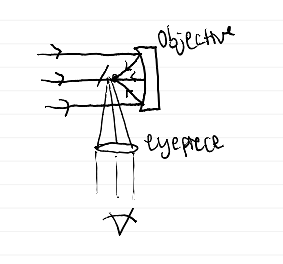
What are the two processes used by lenses and mirrors to focus light and create an image?
reflect and refract
What countermeasures can we employ against things that make for poor viewing
high, dry, and dark places
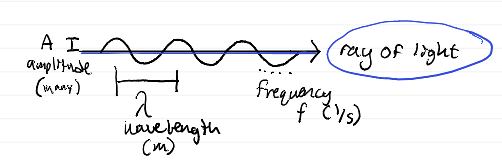
parts of a wave diagram
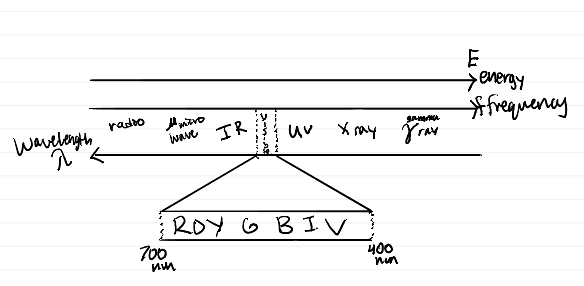
Electromagnetic spectrum diagram
blackbody diagram
photon emission/absorption diagram
equal areas equal times diagram
object traveling around sun diagram
object traveling in a circle diagram
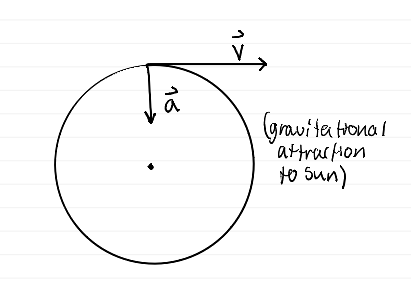
diagram of refractor
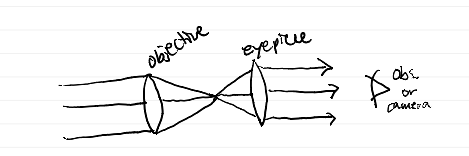
diagram of reflector
equation relating wave speed (v), frequency (f), and wavelength (lambda)?
v = f * λ
Terrestrial planets location (inner/outer)
inner
Terrestrial planets density (high/low)
high
Terrestrial planets mass (high/low)
low
Terrestrial planets overall composition (light/heavy)
heavy
Terrestrial planets moons (many/few)
few
jovian planets location (inner/outer)
outer