Beloved: AO3 (historical & social)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Margaret Garner
the story for Sethe came from the story of a real woman (Margaret Garner)
the factual source of her story comes from Reminiscences of Levi Coffin (a man who helped people to freedom on the Underground Railroad)
Margaret Garner “appeared to be 21 or 23y.o”
“the undying love of freedom that is planted in every breast, the resolve to die rather than submit to a life of degradation and bondage'.”
she was returned to slavery, however en route she and the child fell into the river; she survived but was overjoyed to hear that her child had drowned and clearly wanted to perish with her
Morrison wanted to ‘translate historical data into a personal tragedy’
setting
set 1872-3
has flashbacks to 1850s
Civil War - split North (pay for labour) and South (free labour - slaves)
lynching
a method of social and emotional control meant to terrorise African Americans into submission
widely practised in the South of the US
‘started’ in 1877-1950 but would have began much longer ago when slaves were still viewed as property (so it wasn’t documented)
vigilante justice: lynch mobs - hundreds of people, children, were brought. a social event, entertainment of sorts.
the Underground Railroad
a network of secret routes and safe houses used be enslaved people in the US to escape to freedom in the North/Canada
a form of civil disobedience and resistance to slavery, operating primarily from the late 18th century until the Civil War
conductors: individuals, often free Black people, who guided freedom seekers along the routes e.g. Stamp Paid
the Middle Passage
the forced journey of millions of enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to the Americas (a key part of the transatlantic slave trade)
a brutal and inhumane experience with high mortality rates
Enslaved Africans were packed tightly onto ships with little room or ventilation, enduring harsh conditions
15-16% of enslaved people died during the voyage (disease, malnutrition, harsh conditions)
could take 2-3 months
identity and race
identities were based on race - seen in language such as mulatto, quadroon, octoroon, chattel
motherhood
themes of motherhood - kindness, selflessness, unconditional love, goodness
slavery denies the slave the agency of the mother; subverting the working definition of motherhood constructed
The Moynihan Report
a report by government official/sociologist Daniel Moynihan that suggested the breakdown of the Black Family unit was causing poverty & structural inequality on race; criticising families that had a dominant matriarchal figure
36% of black children were living in broken homes
26% of black husbands were absent/divorced
blamed black cultural patterns rather than systematic racism and historical oppression for inequality
‘Beloved’ critiques this in how the matriarch is empowered and dignified; her suffering is caused by slavery not cultural disfunction
also removes(?) the blame from black men who were crushed and dehumanised of their masculinity through slavery
survival itself is heroic
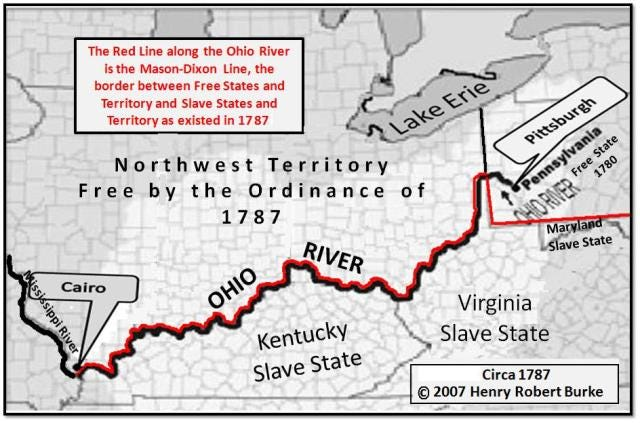
the Ohio River
served as a natural border between slave states and free states
for those escaping slavery, crossing the river offered a chance to escape the brutal realities of bondage and seek a life of freedom
in Sethe’s journey across the river she gives birth to Denver → new beginnings, chance to be free + raise her children
a major route for the Underground Railroad
Beloved comes out of the river, from “the other side”; the Ohio River also coming to symbolise the border between this world and the next (for free ex-slaves, crossing back into slave territory would be a kind of death)
Stamp Paid’s occupation as a ferryman on the river furthers this association; resembling Charon from Greek mythology (who ferried souls across the river Styx into the underworld)
Fugitive Slave Act 1850
passed in 1850
enabled slaveowners to recover escaped slaves more easily with federal help (how Margaret Garner was taken back into slavery)
meant that escaped enslaved people could be captured and returned to their enslavers even if they had passed into ‘free states’ like Ohio
further marginalised enslaved people as legal judges who ruled in favour of enslavers were paid 2x as much and prevented enslaved people from speaking in their own defence
Social Darwinism
misapplied Darwin’s theory of ‘Survival of the Fittest’ to illustrate wealthy white people as superior due to the power they already held and poor/working class people as inferior; that certain people become powerful in society because they are innately better
the theory that individuals, groups, and peoples are subject to the same Darwinian laws of natural selection as plants and animals
this theory was used to justify colonialism/slavery and encouraged people to view poor/African American people as less than human
Black Church
refers to the collection of Christian denominations/congregations in the US that predominantly sever as are led by African American
emerged from the experiences of enslaved African Americans and has been a centre for resistance, community building and the preservation of African culture
also serves as a community hub, offering social services, educational programs and cultural activities
historically served as a space for healing, hope and community
interwhile ‘Beloved’ explores the haunting legacies of slavery and the struggle for healing and reconciliation
Intersectionality
introduced by Kimberlé Crenshaw, highlights how various social categories like race, class, gender, and sexuality intersect to create unique experiences of discrimination and oppression
highlights the interconnectedness of different forms of discrimination and how they compound to create distinct experiences
e.g. a Black woman experiences racism and sexism simultaneously
‘Beloved’ presents the unique challenges faced by Black mothers and how the intersection between race and gender creates a complex and often oppressive reality for Black women particularly in the context of slavery and its lasting effects