Immunization – basic concepts, passive immunization.
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Immunization
The process of inducing immunity against a disease
Types of Immune System
Innate
Acquired
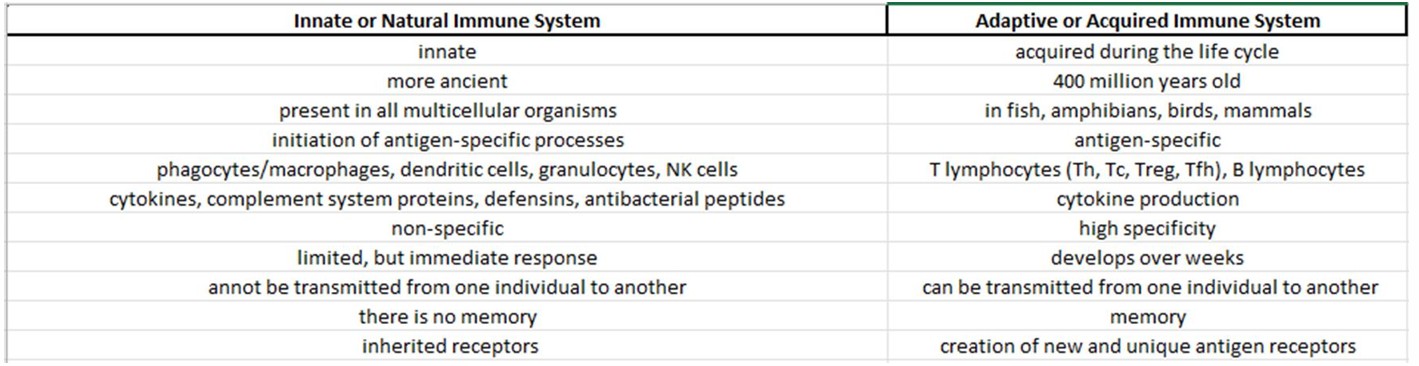
The natural or innate immune system
Recognition, mobilization, destruction– Against any molecule identified as foreign!
Cells (+ cell membrane receptors):
Interstitial space: phagocytes/monocytes- macrophages, dendritic cells;
In circulation: monocytes, neutrophil granulocytes, NK (natural killer) cells
Cytokine production (IFN, IL, TNF), Chemokine production
Humoral components: In circulation: antimicrobial enzymes, proteins, and peptides (e.g., defensins) – complement system proteins!
No antigen specificity, barriers
Adaptive or acquired immunity
Components: Cells (Th; Tc; Treg; B lymphocytes) – signaling molecules, receptors
Cytokine production, Chemokine production
Site of production is the bone marrow -> migration to lymphoid organs
Antigen specificity!
Passive immunisation
Natural passive: Maternal antibodies crossing the placenta (IgG), breast milk (IgA)
Artificial passive: Specific antibodies (immune serum, immunoglobulin) → immediate but short-term protection (a few days to 3–4 weeks)
Passive immunisation characteristics
Contains antibody
Immediate effect
Short-term immunity
No memory
Ability to mount an immune response is not required
Only helps humoral defense
Rapid but short-lived immunity